
An Exploratory Study of the ODL Course in Structural Engineering
Stella M. Mlasi
1
and R. Naidoo
2
1
Department of Civil & Chemical Engineering, University of South Africa, c/o Christiaan de Wet & Pioneer Avenue,
Florida, Johannesburg, South Africa
2
Institute for Open & Distance Learning, University of South Africa, 1 Preller Street, Muckleneuk, Pretoria, South Africa
Keywords: Module, Structural Steel, Open Distance Learning, Pass Rates, Interventions.
Abstract: The study was conducted on a structural steel design module taught via distance learning mode at the
University of South Africa, UNISA. Structural steel design is part of structural engineering under the broad
field of civil engineering. It is very challenging for students to learn or study structural steel design in an open
distance learning (ODL) environment; because students struggle to put concepts in the correct perspective
without any assistance. This lead to few but major challenges such as poor pass rates, graduates with low
confidence and lack of quality skills and decision-making. In addressing these challenges, few interventions
were introduced including improving communication and teaching methods, redesigning study materials and
prescribing up to date books. The interventions were implemented progressively from the year 2013 up to
date, and the outcomes measure was the examinations. The examination results showed that the pass rates has
been improving annually after 2013, with the overall pass percentages increasing and the number of
distinctions increasing from 0 to 6. This implies that the intervention that were implemented are effective but
needs to be applied strategically.
1 INTRODUCTION
Engineers think from the abstract to the concrete and
vice versa. The learning of concepts and strategies are
essential in engineering teaching, learning and
assessments. Engineering students frequently use
strategies influenced by the instructional method and
assessment procedures (Heywood, 2000).
Engineering knowledge is changing hence lecturers
should establish new approaches to engineering
education. The approaches must encourage deep or
surface approaches to learning. Assessments used can
have a harmful or less than positive effect on learning
because they cause surface learning. Engineers
require a variety of learning styles when they are
engaged in projects due to both convergent and
divergent thinkers. Spatial ability is important in
engineering design. Engineers need to be able to
visualize. Learning style may be in conflict with the
style of teaching to which we are exposed.
Consequently teaching and learning styles should be
matched. The nature of engineering learning suggest
variety of styles. Consequently teachers may have to
change their teaching styles.
In the United Kingdom another type of student
approach to learning was identified (Entwishle,
1979). The strategic approach described the class of
student who tried to manipulate the assessment
procedures to her/his own advantage by combining
her/his efforts to the reward system as they see it. It is
extrinsic and achievement motivation. Kneale (1997)
believed that there was an increase in strategically
motivated students in British universities. Strategies
adopted are indicative of the different perceptions of
what students believe is wanted from them by their
teachers in order to measure their performance.
(Wilson, 1981). The preknowledge concept is
important in students learning orientation. Teaching
and assessment strategies used can influence the
orientation that students take to deep and surface
learning. Clearly, if students are to overcome the
misconceptions they have about concepts, then a deep
learning approach will have to be encouraged. In this
situation a traditional lecture approach, however good
the lecturer, may not be adequate.
Engineering is particularly suited to holistic
assessment because of its desire to simulate the real
world that students will meet when they exit from
their courses. Project work has been introduced,
246
Mlasi, S. and Naidoo, R.
An Exploratory Study of the ODL Course in Structural Engineering.
DOI: 10.5220/0006751302460251
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2018), pages 246-251
ISBN: 978-989-758-291-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

laboratory methods have changed and continue to
change because of technological advances. These
caused changes in curriculum content. The normal
traditional tests does not connect to the real world.
This review article is written in order to present
feedback from the interventions that were
implemented in a module that was not yielding good
results. The module is called Structural steel and
timber design, facilitated both online and on print by
the Civil Engineering Department at the University of
South Africa, UNISA, which is an open distance
learning institution. The module contents cover the
application of all the concepts and theories learned in
the earlier days of ones career in civil engineering. In
South Africa, the design decisions are guided by the
South African National Standards (SANS) published
codes and the engineering and environmental
sciences and as well as social needs. This full year
module is on the exit level of a three year Civil
Engineering Diploma and it is actually a two in one
module, which comprise two components: Structural
steel design & Structural Timber design.
The basic knowledge for structural steel and
timber design is defined by:
Memorizing and understanding definitions,
equations, etc.
Applying equations and procedures;
An understanding of the concepts and
procedures involved;
A more complete understanding of the
phenomena involved.
Vuc, Baloi and Litcanu (2015), Olds, Moskal and
Miller (2005) explain two assessment methods in
engineering education as 1) descriptive studies and 2)
experimental studies. The assessment or examination
results used in this paper can be classified as
experimental data and the techniques were
quantitative.
In 2001, the authors Anderson & Krathwohl
(2001) published a revised Bloom’s taxonomy that
covers six levels of educational objectives. The
module structural steel and timber design educational
objectives are covered by two of the six, that is
analysing and applying. For the module under
consideration, analysing involves examining the
structure (of steel or timber) or its components to
determine their capacity and then organising the
design steps logically. On the other hand, applying
involves using the acquired knowledge from other
modules such as theory of structures and structural
analysis.
1.1 Theoretical Framework
1.1.1 Connectivism
Connectivism is a learning theory that describes
complex learning in a complex changing social digital
world. Learning occurs through connections within
networks. The theory uses the concept of a network
with nodes and connections to define learning.
Learners recognize and interpret patterns. Learners
are integrated by the diversity of networks, strength
of ties and their context. Learning is a process that
occurs within wide environments of shifting core
elements – not entirely under the control of the
individual. Learning is focused on connecting
specialized knowledge states and creates a
community of practice. Connectivism is driven by the
cognition that decisions are based on rapidly altering
foundations. New information is frequently being
acquired. Discrimination between important and
unimportant information is vital. The ability to
recognize when new information alters the cognition
based on decisions made yesterday is also critical.
Siemen's Principles of connectivism: (Siemens,
2015)
• Learning and knowledge rests in diversity of
opinions.
• Learning is a process of connecting
specialized nodes or information sources.
• Learning may reside in non-human
appliances.
• Capacity to know more is more critical than
what is currently known.
• Nurturing and maintaining connections is
needed to facilitate continual learning.
• Ability to see connections between fields,
ideas, and concepts is a core skill.
• Currency (accurate, up-to-date knowledge)
is the intent of all connectivist learning
activities.
Decision-making is itself a learning process.
Choosing what to learn and the meaning of incoming
information is seen through the lens of a shifting
reality. While there is a right answer now, it may be
wrong tomorrow due to alterations in the information
climate affecting the decision.
An Exploratory Study of the ODL Course in Structural Engineering
247

1.2 Syllabus
The syllabus comprises structural loading (load
patterns, load factors, limit state designs and
analysis), design of structural elements such as
beams, compression and tension members,
connections and base plates.
The assessment comprises of one multiple choice
questions assignment, one or two written assignments
in the same format as the examination; and this is
done in order to give the students a fair opportunity to
show how much they know the subject.
This paper focuses only on the results from the
examination and not the assignments. The
examinations are venue based and students adhere to
the set rules. However, the assignments are conducted
at a distance and at the convenience of the students;
therefore the results will not necessarily indicate that
the students showed their sole potential without any
help from other people or resources. Although the
module has been facilitated over the previous years,
the results presented in this paper date back from the
year 2013 to 2016; because this is the period during
which different interventions were introduced. The
interventions were introduced in order to improve the
quality of knowledge and skills students acquire, the
confidence of graduates thereafter, pass rates, design
concepts based on what the industry needs as well as
promoting the course itself to make it interesting and
fulfilling to the students. The interventions were
teaching and communications in which concepts were
introduced and explained one at a time, summarized
teaching notes and introducing new up to date
textbooks:
The nature of the structural steel and timber
design module is that, the science is derived from
structural analysis, theory of structures and materials;
and then followed by uncountable complex design
steps. The theory of structures and materials covers
topics such as the sectional properties, stress and
strain calculation, computing reaction forces and
member forces in pin-jointed trusses. The structural
analysis involves analysing determinate and
indeterminate structures with regard to the applied
bending, axial and shear forces, which cause the
structure to deform within the limits or fail by yield
or collapse. Structural steel and timber design module
involves the design of flexural or bending members
likes beams, slabs and beam-columns, compression
members such as columns and struts, trusses and
connections; and all these can be made from either
steel or timber.
In the ODL environment for almost all the
modules, there could be or not at all the learning and
teaching arrangement. Felder and Silverman (1988)
describe learning as a two-step process that involves
the reception of information and processing of
information. This is true, and for engineering students
it might be a prolonged process especially in the ODL
environment; because most of the concepts in
engineering are hard to conceive and interpret. ODL
students are self-taught and follow different styles or
methods within the time constraints that they choose
themselves. It is therefore easier for the lecturer,
assessor or the module coordinator to interpret the
effectiveness of the learning styles and methods from
the results of the assessments, in this case
examination results.
2 METHODOLOGY
The module outcomes are: that the students should
have a thorough understanding of structural loading,
be able to design structural steel and timber elements
such as beam, columns, connections and trusses and
tension members at the end of the academic year.
The sketch in Figure 1 summarises the stages that
students go through when studying the structural steel
and timber design. All the three stages are equally
important and lead to the outcomes of the module.
The assignments results contribute towards the
students’ final mark in the range of 20 to 30% and the
examination covers 70 to 80%; and this is done to
encourage them to keep up with the studies through
to the examination stage. The students who failed to
pass are given the opportunity to write supplementary
examination, provided they satisfy the given criteria.
The graphs plotted under the results and discussion
sections below include both actual and supplementary
examinations.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
248

Figure 1: Learning stages.
3 RESULTS
Figure 2: Annual pass rate.
Figure 3: Annual intakes and pass rates.
44
38
34
64
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
2013 2014 2015 2016
% Passed
Years
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
Number of students
Time (Years)
Written exams Passed
Module Outcomes
An Exploratory Study of the ODL Course in Structural Engineering
249
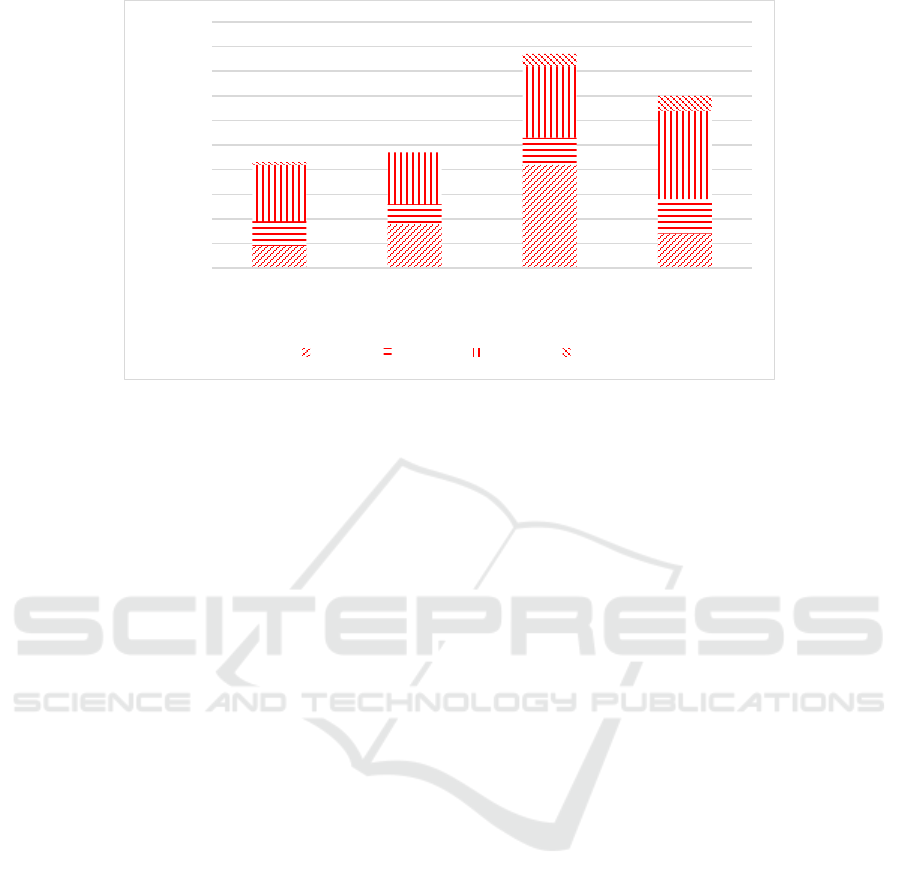
Figure 4: Breakdown of pass percentages.
3.1 Admission, Dropout and Success
Rate
During the year 2013, there were 48 admitted
students, and the number went up to 55 in 2014, a 100
in 2015 and dropped back to 91 in 2016. Two students
dropped out in 2013, none in 2014, two in 2015 and
only one in 2016. So generally, the module has a very
low dropout rate, which is not often the case for
difficult subjects such as this at many universities.
The success rates of the modules will be presented
and discussed under the results and discussion later in
this paper.
4 DISCUSSION
Figure 2 shows a graph of an annual pass rate for the
module structural steel and timber design. The
percentage incorporate the number of students who
wrote the examination and passed, those who failed
and were granted supplementary examination and
passed. The 2013 average results resemble more or
less the results from the previous years, before the
above mentioned interventions were introduced. The
written lecture notes were introduced first in the year
2013, and the prescribed books of the previous years
were changed to be a recommended (which means
any student was not forced to possess them). Since the
prescribed books have been for longer, students still
adhered to it when preparing for the 2014 and 2015
examinations, which were rather based on the written
notes. The contents and the standard were still the
same as the book, but the approach and style of asking
questions were improved. Hence, it took about two to
three years to get students used to the style and
approach in the notes. The average results for the
years 2014 and 2015 were therefore not impressive.
Presented in Figure 3 is the number of students
admitted annually for and passed the examination. In
2013, there were 48 students and 21 of them passed;
the number increased to 55 in 2014 and 21 of them
passed; a 100 students in 2015 and 34 of them passed
and of 91 students in 2016 about 58 passed. The
lower numbers in 2013 and 2014 led to the
accumulation of students as most of those who did not
pass will re-register for the following year.
However, it can been seen from Figure 3 that the
number of students passing the examination is
increasing annually but not with the same percentage.
The gap or difference between the number of students
who got admitted and those who passed the
examination is those who failed or chose not to write.
The number of students who passed the examination
was further broken in four groups in order to see the
actuality and worth of the results. The groups were 0
– 39%, 40 – 48%, 49 – 69% and 70% or above. From
Figure 4, it is particularly encouraging that in 2016
the 0 – 39% group was the least compared to the
previous years. In the same year, the both the 40 –
48% and 49 – 69% groups has increased in numbers;
and that shows that the understanding of course
material has improved, quality of ideas and decision
making when writing the examination has increased.
The number of distinctions has been increasing yearly
from 0 to 6 in 2016.
Due to the complexity of the module, the students
need to be aware of certain things that are not
included in the syllabus (such as analysing the
structure and deducing necessary information to help
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
2013 2014 2015 2016
Pass rate (%)
Time (years)
0 - 39 % 40 - 48 % 49 - 69 % 70%
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
250

in the design process, calculating forces and stresses,
as well as having a substantial knowledge of steel
properties). The results presented in Figure 4 was
therefore not taken for granted as they prove that the
effort was extraordinary.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The intervention that were introduced made the
module delivery to be effective and efficient. The
average results improved annually and it was also
found that the number of average performing students
whose results falls in the 49 to 69% increased by 15%.
The number of distinctions increased from 0 to 6 in a
space of four years. In conclusion, it is convincing
that the interventions must be kept and improved for
the better, as the next goal is to reduce the number of
students whose results falls between 0 and 39%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the University of
South Africa for the data used in this paper and
funding they have provided for the work to proceed.
REFERENCES
Anderson, L.W. & Krathwohl, D.R., 2001. A taxonomy for
learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of
Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives,
Longman. New York
Entwistle, N. J., Hanley, M., and G. Ratcliffe (1979).
Approaches to learning and levels of understanding.
British Educational Research Journal, 5,99-114.
Felder, R.M. & Silverman, L.K., 1988. Learning
and teaching styles in engineering education,
Engineering Education, 78 (7), pg 674 – 681
Howell, D.C., 2004. Fundamental statistics for the
behavioural sciences, Brooks/Cole – Thomson
Learning Inc. Belmont, USA, 5
th
edition
Heywood, J (2000). Assessment in Higher Education
Student Learning, Teaching, Programmes and
Institutions. Jessica Kingsley, London
Kneale, P (1997). The rise of the ‘strategic student’. How
can we adapt to cope? In S. Armstrong, G. Thompson
and S. Brown (eds.). Facing Up to Radical Change in
Universities and Colleges. Kogan Page, London.
Olds, B.M, Moskal, B.M & Miller, R.L., 2005. Assessment
in engineering education: Evolution, approaches and
future collaborations, Journal of Engineering education,
Vol (11) pg 13 – 25
Siemens, G. (2015). Connectivism: A learning theory for
the digital age, Https://members.educause.edu
(Accessed: October 2017)
University of South Africa (UNISA), 2015. My Modules @
Unisa: Information, codes and purposes, University of
South Africa, Pretoria
Vuc, G, Baloi, F, Litcanu, M, (2015) Adapting Methods of
Student Evaluation and Grading in Electrical Power
Engineering. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
191, 147 – 151.
Wilson,(1981). Wilson, J. D (1981). Student Learning in
Higher Education. Croom Helm, Beckenham
An Exploratory Study of the ODL Course in Structural Engineering
251
