Who Learns Better
Achieving Long-term Knowledge Retention by Programming-based Learning
Stefano Federici, Claudia Medas and Elisabetta Gola
Dept. of Education, Psychology and Philosophy, University of Cagliari, Italy
Keywords: Knowledge Retention, Active Learning, Programming-based Learning, Exponentiation, Block Languages,
Scratch, Computational Thinking.
Abstract: In this paper we describe the experience of a year-long experiment devoted to understanding if retention of
knowledge acquired by students while learning a specific subject can be improved by letting them build by
themselves interactive models of that knowledge by means of a visual programming language based on the
block metaphor. What we propose is along the lines of active learning and learning-by-teaching. Students
build an interactive model that tests the knowledge of a specific topic and it is assumed that the topic will be
better memorized and understood than using standard learning strategies. To test this hypothesis, we run an
experiment on the students of two 5th grade classes, split in three groups. One group learned the topic by
both following standard explanations and by creating by themselves multimedia interactive projects by
means of a block language. A second group learned by following standard explanations and by playing with
multimedia interactive projects created by their peers in the first group. A third group learned by only
following standard explanations. The experiment outcome shows that there is a significant improvement in
the retention rate after several months for those students that build their digital tools by themselves with
respect to both students that use digital tools built by others and students that do not use digital tools at all. It
is our opinion that this strategy can be applied to topics of all disciplines, providing the bases of what we
can define as programming-based learning, a general learning methodology based on computer
programming.
1 INTRODUCTION
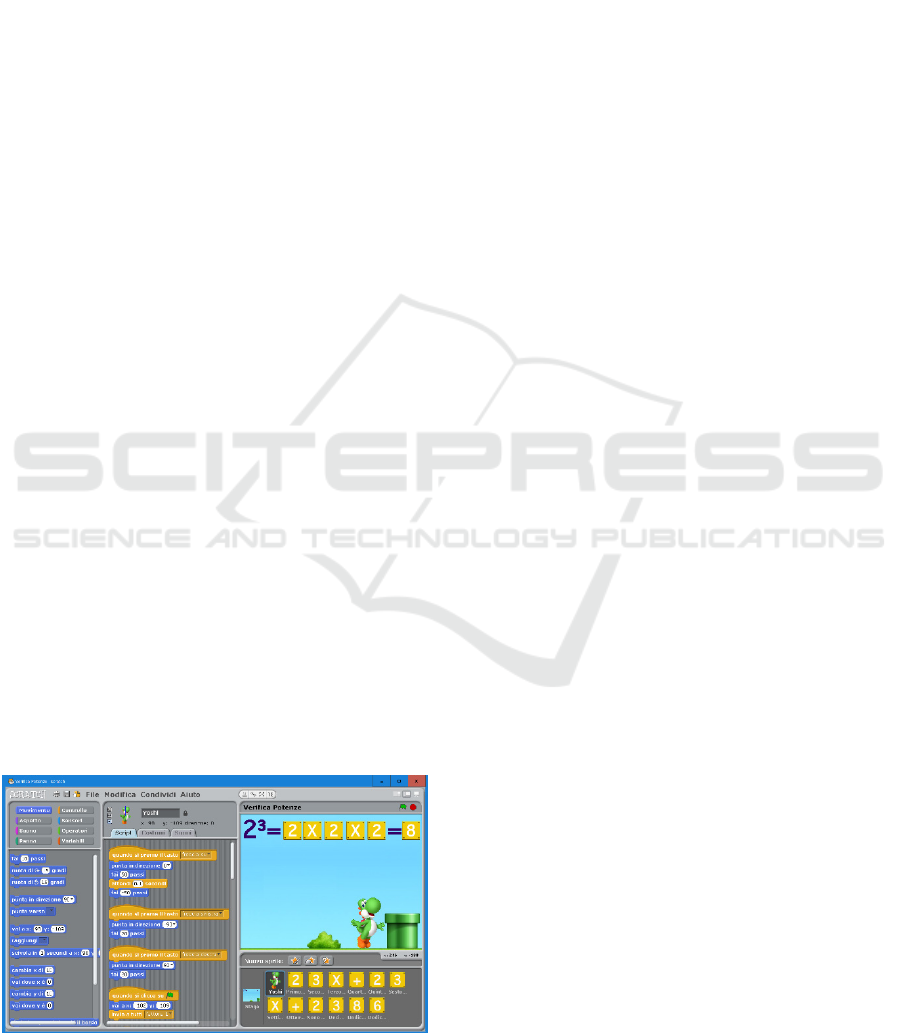
Can the usage of a block programming language, for
example a tool such as Scratch (scratch.mit.edu,
figure 1), help students to better remember topics
that are usually felt as particularly difficult to recall
after a long time?
Figure 1: Interactive explanation with Scratch.
The study of long-term retention of knowledge and
how this retention can be improved, is something
that has been analysed many times (Bridge and
Porteus, 1965; Fogel and Drew, 2008; Palha et al,
2015). Specific studies concentrated on knowledge
acquired at school (Semb and Ellis, 1994; Bethune,
2011; Boulton, 2013; Kirby, 2013) and especially
scientific knowledge (Engelbrecht et al, 2007;
Custer, 2008; Upadhyay and DeFranco, 2008;
Darland and Carmichael, 2012; Chin et al, 2013;
Deng and Gluckstein, 2014).
We often forget what we have learnt when we
have to remember it after a long time so that just
looking at the problem does not turn on anymore in
out mind the path from problem to solution. Several
studies have suggested different ways of facilitating
the recall of distant memories, from highligthing the
importance of visual help (Brady et al, 2008) to
proposing multimodal learning (Seemüller et al,
2012; Udomon et al, 2013), active learning (Prince,
2004; Bachelor et al, 2012), personalized review
124
Federici, S., Medas, C. and Gola, E.
Who Learns Better.
DOI: 10.5220/0006705001240133
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2018), pages 124-133
ISBN: 978-989-758-291-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(Lindsey et al, 2014), and inquiry learning (Schmid
and Bogner, 2015).
One of the methods proposed to improve
retention has been the learning-by-teaching strategy
(Leelawong and Biswas, 2008; Chase et al, 2009;
Murphy-Paul et al, 2011) that states that the best
way to understand something is trying to teach
someone else that topic. By teaching someone
indeed you must have fully understood the internal
mechanisms of the topic and how the individual
parts of the explanation fit together.
What we propose in this paper is along the lines
of active learning and learning-by-teaching
strategies. Indeed students, by using a programming
language, build an interactive model that tests a
specific topic. By using this strategy, they not only
have the possibility of further memorize the topic,
but must fully understand how all parts of the topic
at stake fit together in order to correctly describe
their behaviours by using a programming language.
With this strategy we are enhancing computer-
supported education by programming-based
learning.
In order to test this hypothesis, we have run an
experiment on the students of two 5th grade classes.
The topic selected for the experiment has been one
that the teachers felt as particularly difficult to
remember for students of this grade, namely the
execution of the exponentiation operation.
Our working hypothesis is that, by assembling an
interactive model by themselves, students will
remember for a longer time how it really works, by
putting at work different learning strategies at the
same time (Seemüller et al., 2012; Udomon et al.,
2013).
2 A DIFFICULT TOPIC TO
REMEMBER
Why do students forget so easily what is the
meaning of the mathematical operation of
exponentiation? This is something that always struck
us. Students do not forget how to do a summation or
the multiplication of two numbers, but they forget
very easily what n
m
means.
Does maybe 2
3
mean that we have to multiply 2
by 3 (wrong; Pershan, 2013; Pershan, 2017; Liu,
2017, p.54), or that we have to multiply 3 by itself 2
times (wrong), or maybe that we have to sum 2 to
itself 3 times (wrong) or that we have to multiply 2
by itself 3 times (wrong, Pershan, 2017), or, in the
end, that we have to multiply three 2s by each other
(correct)?
Here you are the correct definition of
exponentiation (MathsIsFun, 2017):
“The exponent of a number says how many
times to use that number in a multiplication.”
To give an example, 2
3
means 2x2x2=4x2=8. So,
what we really have to remember is that the “small
number” at the top (the 3 in our example, called the
“exponent”) says how many times to use the “big
number” at the bottom (the 2 in our example, called
the “base”) in a multiplication.
What is that makes remembering how to
correctly execute exponentiation so difficult with
respect to, let us say, executing a summation or a
multiplication? The operations involved are
relatively simple (you have just to multiply several
numbers) but the meaning slips very easily from the
student’s mind. One possible explanation is that,
whereas summing or multiplying numbers is
something that can happen quite often in the
everyday life of a student, calculating an exponent is
instead something that, until you are not in a high
grade, you do not see so often, except maybe for
calculating the squared of a number, that is the
practical operation of calculating the area of a square
whose sides are a given measure. Another possible
reason is that the definition of exponentiation that
you find in books or websites is often misleading, as
for example in (iCoatchMath, 2017):
“An Exponent is a mathematical notation that
implies the number of times a number is to be
multiplied by itself.”
or in (Liu, 2017, p.53):
“An exponent means the number of times a
quantity is to be multiplied.”
So, students can think that to calculate 2
3
you have
to multiply 2 by itself 3 times, that is you do 3
multiplications, that is 2x2x2x2=16. But this is
clearly wrong. If you think this should be the correct
operation by reading the definition of exponentiation
and you then realize this is not the case by looking at
the examples, you can be confused and this
confusion can impair your recall.
A further source of problem is the possible
confusion (Liu, 2017, p. 54) arising when the student
is exposed to a wrong very first example. If the
student is shown at start that 2
2
=4, they can wrongly
remember that 2
2
is the same than 2x2.
Who Learns Better
125

3 THE EXPERIMENT:
PROGRAMMING AND
EVALUATING
EXPONENTIATION
The experiment involved 36 students from two 5
th
grade classes from a local elementary school. The
experiment started during the same period of the
year when the two classes were studying
exponentiation, that is about at the beginning of the
school year, and was run during school hours
already devoted to mathematics. In order not to
interfere too much with the completion of the
explanation of all mathematics topics usually
explained in 5
th
grade, the teachers required that the
time spent by students in creating interactive
projects should have been limited to at most 3
sessions of 2 hours each. One further session of 2
hours was used to be able to discriminate at the end
of the experiment between the contribution of
computer-based learning and programming-based
learning (see section 3.2).
3.1 Beginning of the Experiment
At the beginning of the experiment the students were
all taught exponentiation in a standard classroom
lesson. Then the students were split in 3 groups in
order to understand the influence, if any, of
computer programming, by using a block language
such as Scratch, on long-term retention of the ability
to correctly solve standard exponentiation problems,
that is exponentiation problems that did not involve
“special cases” were the exponent is 0
i
or when both
the base and the exponent are 0’s
ii
.
3.2 Splitting the Students in Groups
As doing well in the experiment could potentially
involve a lot of distinct factors (previous math
knowledge, concentration, interest and enthusiasm
with respect to technology, etc) and not having
enough time to run a thorough examination at the
beginning of the year of all the students involved in
the experiment, we asked the teachers of the two
classes, that had been working with the kids for 5
years, to split the classes in three roughly similar
groups basing on their general skills.
So, in each class we had group A, that would
have been working with exponentiation both by
following standard explanation and by creating
multimedia interactive projects by means of a block
language; group B, that would have been working
with exponentiation both by following standard
explanation and by playing with multimedia
interactive projects created by their peers; and group
C, that would have been working with
exponentiation only by following standard
explanation (see Table 1). So, we had a total of 12
students in each group.
Table 1: Learning in the different groups.
Group Learning
A Standard lessons
Creation of interactive projects
B Standard lessons
Usage of interactive projects
C Standard lessons only
From group A we wanted to clearly understand if
long-term retention could improve by allowing
students to create by themselves interactive
explanations. Group C instead was the control group
that was learning exponentiation by simply
following the teacher lessons. Group B was a second
control group to understand if just the usage of an
interactive project could have been as good as the
personal creation of an interactive project, that is
allowing us to discriminate between the usage of
digital tools supported by the computer-based
learning approach and the usage of computer
programming in the proposed programming-based
learning approach.
To avoid that the time devoted to learning
exponentiation would have been longer in groups A
and B with respect to group C and longer in group A
with respect to group B -as group A would have
spent several days in creating exponentiation
projects and group B would have spent several hours
in using those projects- students in groups B and C
kept exercising on exponentiation while the students
in the other groups were involved in creating or
using interactive projects. It is worth noting that
students in group A, in the end, spent less time in
exercising on exponentiation than students in groups
B and C, as their peers kept exercising on
exponentiation while they were learning about block
programming.
3.3 Teaching 5
th
Grade Students How
to Build Multimedia Interactive
Projects
In order to allow the students to learn how to build
an interactive project about exponentiation they
were first exposed to projects created by using a
programming language and then they were taught
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
126
the basics of computer programming. We choose a
programming language based on the block
metaphor, Scratch (Maloney et al. 2010),
specifically designed to easily teach computer
programming to children 8-11 and to easily allow to
create colourful interactive objects.
The structure of a visual programming
environment for a block language is very easy and
quick to grasp (figure 2). All “instructions” indeed
are represented by coloured blocks that are visible in
the block area at the left-hand side of the window.
By dragging blocks from the block area to the
central part of the window, users can build
sequences of blocks, called “scripts”, for their
characters to behave and interact as expected.
Figure 2: Creating block sequences by drag-and-drop from
the block area (to the left) to the script area (to the right).
3.3.1 First Session: Arousing Enthusiasm
In the first session we allowed students to play with
several projects created with Scratch. Having only 3
sessions available, we had to arouse students’
enthusiasm very quickly towards the possibility of
creating the projects that they had to develop so to
have them work quickly and effectively. The
projects were all based on the SuperMario
characters. The reaction of the class was what we
had supposed, that is delighted. The first project was
a minigame that allowed them to move Supermario
and make it jump by using arrow keys to collect
coins by hitting boxes and avoiding the Goombas,
the bad guys (figure 3). When answering correctly or
wrongly, the student were getting the classic
Supermario’s “correct” or “wrong” sounds. The
purpose of this project was to make them familiar
with the simple move-and-jump mechanism that we
had chosen to use in the exponentiation project to let
them select what they thought as the correct answer.
This was, of course, more complex than a simple
point-and-click mechanism, but it was something
that a big part of them already knew and loved and
that was eager to use and to program.
Figure 3: Move-and-jump in Supermario minigame.
3.3.2 First Session: Introducing the
Structure of the Final Project
The main project shown in the first session aimed at
showing to the students the structure of the projects
they will have to develop during the next sessions.
By using the same move-and-jump mechanism of
the previous introductory project, this project tested
their knowledge about multiplications (figure 4).
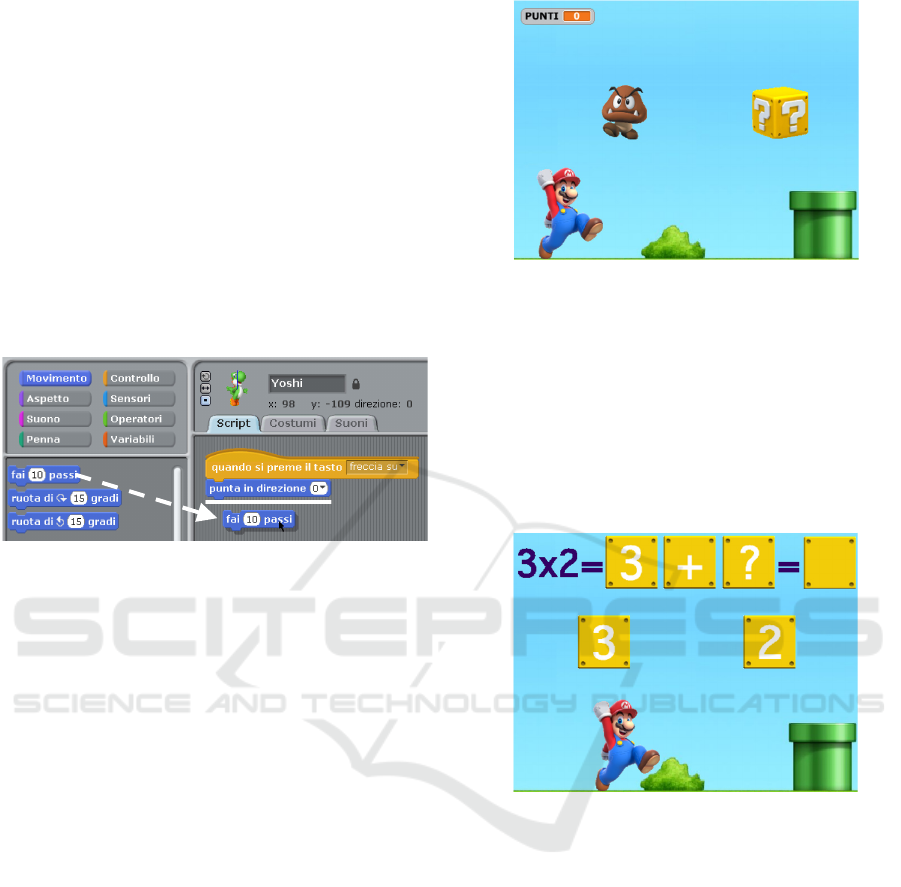
Figure 4: Minigame to test multiplication.
For example, in the exponentiation project, the users
are asked to select the correct operation (figure 5) or
the correct factor (figure 6) by hitting the correct
yellow cube with the Yoshi character.
We started with multiplication as this is an
already well-known topic since 3
rd
grade, but the
structure of this project was the same as the final
project about exponentiation that they had to
develop in their third session.
At the end of the project the students could see a
short minivideo of Supermario defeating the monster
Bowser. The minivideo made the students jump for
happiness.
Who Learns Better
127

Figure 5: Selecting correct operation in exponentiation.
Figure 6: Selecting correct factor in exponentiation.
3.3.3 First Session: Final Free Exploration
The final part of the first session was aimed at
leaving the students free to explore the Scratch
environment. They quickly discovered several
features of Scratch such as how to add new
characters to the projects, how to draw their own
characters or backgrounds by themselves, how to
play sounds, etc. At the end of the first session they
were eager to start developing projects with Scratch.
3.3.4 Second Session: Developing
Multimedia Interactive Projects About
Multiplications
In the second session the students built the testing
project to check multiplications, as shown in figure
4. Knowing the topic very well since 3
rd
grade they
did not have to think about what the project should
illustrate. The project taught how to decompose a
multiplication of n x m as a summation in which the
number n was used m times (figure 7).
Figure 7: “unpacking” 5x4 as the summation of four 5’s.
They learnt how to use a block programming
language by importing pictures of their characters
and their sounds and by creating scripts to describe
the behaviour of the characters by building
sequences of blocks and by finding events to trigger
the behaviours described by those sequences.
At the beginning of this very first session, blocks
and events were identified only after explaining
step-by-step to the students in plain language what
we wanted to happen and showed them how to find
the correct block in the block area and how to build
the correct sequence in the script area.
After a few scripts were built, the students
started to propose themselves how to go on and we
were then mainly busy in following (and correcting,
when necessary) their work.
3.3.5 Third Session: Developing Multimedia
Interactive Projects About
Exponentiation
In the third session the students built the same
testing project but this time about exponentiation.
The structure of the project was the same of the
multiplication project, so they had to express the
exponentiation n
m
as a multiplication in which the
number n was used m times (figure 8).
Figure 8: “unpacking” 2
3
as a multiplication of three 2’s.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
128
As the structure of the two projects was the same
(same blocks, same events, etc) and they already
knew how to use a block programming language,
this time the construction of the project was very
quick. At the end of the session, the students had
time to play with their projects.
They worked mainly by themselves, so that we
had only to help them a few times and correct them
when necessary.
3.3.6 Fourth Session: Playing With
Multimedia Interactive Projects About
Exponentiation
In the fourth session the students from group A and
B played both with the projects built by their peers
in group A and with further projects prepared by us
that they could use in order to test their knowledge
about exponentiation by solving an infinite sequence
of randomly-generated powers.
3.4 Blind-testing Knowledge About
Exponentiation
After the fourth session had ended, the knowledge
acquired by the students of all three groups (A, B
and C) about exponentiation has been tested by
giving them sequences of mixed multiplications and
exponentiations. In order to test how effective
computer programming was on long-term recall of
how to do exponentiation operations, the students
were tested three times, starting immediately after
the end of the four sessions and finishing at the end
of the school year. So, they were tested
• the day immediately after the fourth
session;
• after two weeks from the forth session;
• after six months from the forth session,
without prior notice.
The tests were prepared and administered by the
teachers of the two classes. The results of the three
tests were anonymized (both for privacy reasons and
for blind-testing purposes) and then sent to us. What
it is important to note is that the final test was
administered without giving prior notice to the
students, so that they had no time to refresh their
knowledge about exponentiation.
All three tests showed the same kind of errors.
The errors were mainly due to transforming
exponentiations in:
• summation instead of multiplication, e.g.
2
3
=2+2+2=6 (summation error);
• multiplication of the base times the
exponent, e.g. 2
3
=2x3=6 (times exponent
error);
• multiplication with a wrong number of
factors, e.g. 2
3
=2x2x2x2=16 (number of
factors error).
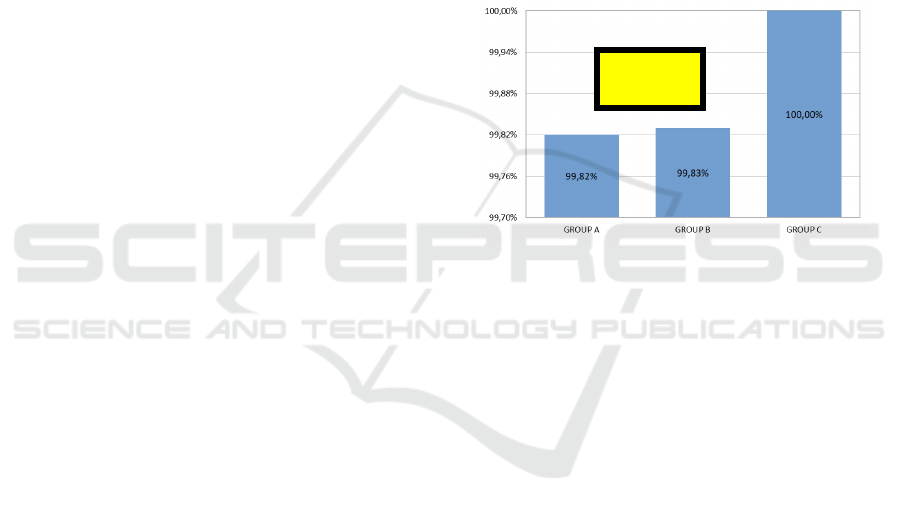
3.4.1 Immediate Test: Results
The results of the first test administered right after
the end of the fourth session were not able to really
discriminate among the three groups (figure 9).
Group A had a correctness rate of 99.82%, group B
99.83% and group C 100%. The difference Δ
between the top and the bottom group was less than
0.2%, which is really non-meaningful.
Figure 9: Results of “immediate” test.
From the results of this first experiment we could
see that all students had learned pretty well how to
calculate the result of an exponentiation. Not
surprisingly, students from group C, which had time
to exercise on exponentiation for 6 more hours while
students from group A were learning about block
languages, did better than any other group. But
being the test very close to the explanation, they all
did very well.
3.4.2 Two-weeks Test: Results
During the two weeks after the first test, the teachers
had time to introduce further topics of Mathematics,
such as decimal numbers and relative numbers, but
this didn’t affect the knowledge of the students
about exponentiation. So, even in the results of the
second test administered after two weeks, the
difference among the three groups was really small
(figure 10). Nonetheless, if results from groups B
and C had only slightly decreased, results from
Group A had instead increased, even if by a
negligible amount. Group A had indeed a
correctness rate of 100%, group B 98.6% and group
C 99.3%. The difference Δ between the top and the
bottom group was anyway less than 2%.
∆<0.2%
Who Learns Better
129
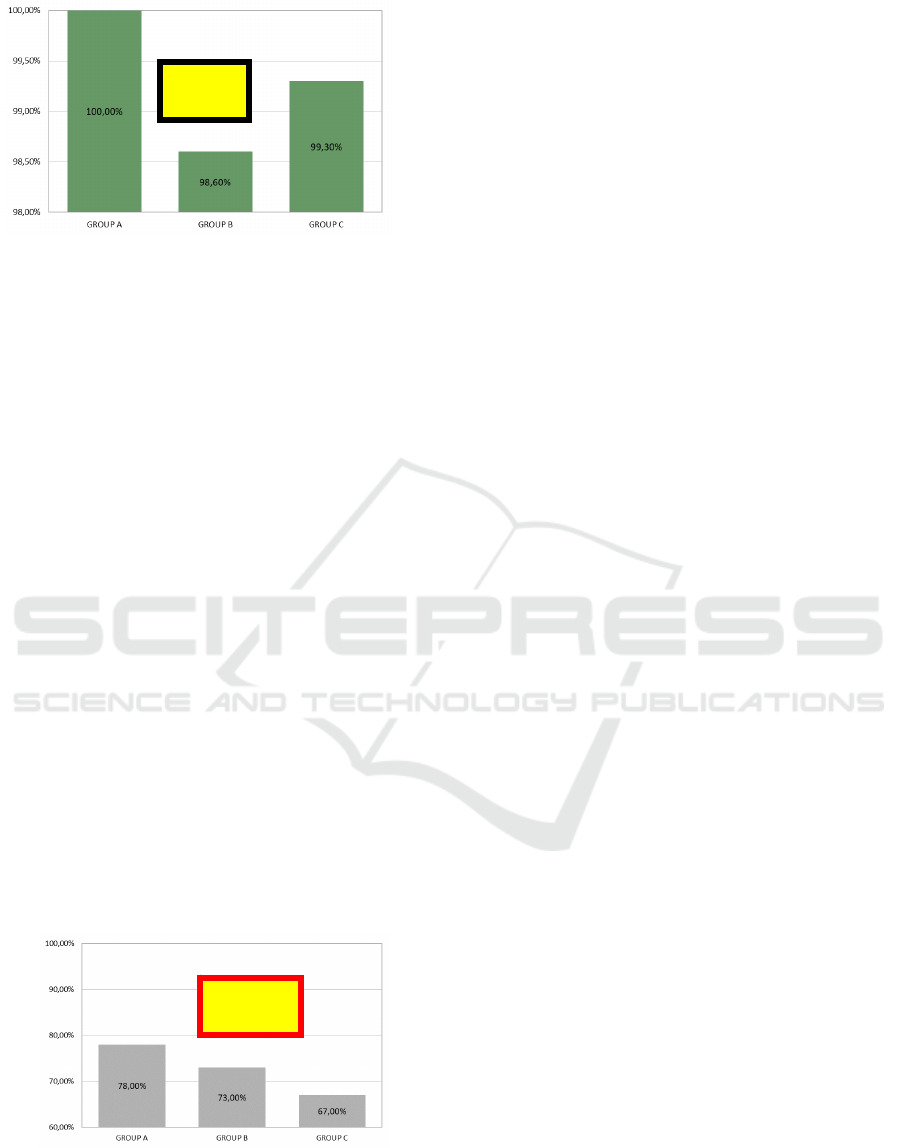
Figure 10: Results of test after two weeks.
All students are still remembering pretty well how to
calculate the result of an exponentiation. Students
from group A showed a slight improvement with
respect to both groups B and C, and students from
group C started showing a small decrease.
3.4.3 Six-month Test: Results
After six months, that is very close to the end of
school year, we prepared a final test without giving
prior notice to the students. The students, since the
end of the second test, had not made further exercise
on exponentiation at school.
What we expected this time was a general, and
substantial, decrease in the correctness rate of the
three groups. But what we were very interested in
was how the students from group A, which had 6
hours less of exercise than students from group C
and 4 hours less than students from group C, would
have done with respect to their peers. The absolute
performance was as expected: all three groups
showed a substantial decrease with respect to the
previous results, showing a clear decrease by more
than 20% for all three groups. The best group, group
A, had this time a correctness rate of about 78%.
The best group this time was group A by far. The
relative performance this time was much better than
we expected, almost surprising.
Figure 11: Results of test after six months.
The differences among the three groups are in
our opinion extremely meaningful (figure 11). If
group A had a correctness rate of 78%, group B had
73% and group C 67%. The difference Δ between
the top and the bottom group was this time more
than 10%.
4 PROGRAMMING-BASED
LEARNING: ANALYSIS OF
THE RESULTS
What follows from the results of the three tests is
that just adding something to the standard classroom
explanation, different from the usual battery of
exercises, improves the long-term retention of the
knowledge of a topic that teachers know as a
difficult one to correctly remember by students. The
positive contribution of computer-based learning is
very-well known.
However, adding self-made, programming-based
interactive explanations gives even better results
than by using computer-based tools created by
others. And this even if, to creates these
explanations, we devote less time to exercising. This
is the positive apport of programming-based
learning.
We explore the possible reasons in the following
sections. We want just to notice here that
programming-based learning does not require, for
every new topic, 3 or 4 more two-hour sessions than
the standard classroom learning. Indeed, we must
remember that the first two-hour session was
devoted to “arousing the enthusiasm” of the students
towards the creation of digital projects and that the
bigger part of the second and third sessions were
devoted to learning how to use Scratch. In our view,
when this computer-supported educational
methodology is acquired by the class, part of the
time spent in teaching and exercising can be
fruitfully replaced by creating interactive
explanations of each given topic.
4.1 Explanation of the Results
Clearly the results of this experiment show that even
less exercise is not a drawback if it is replaced by
other kinds of meaningful activities that gives the
students further insight in what is behind the specific
topic they are studying. A lot of exercise (more than
8 hours spent in doing just exponentiation) proves
certainly effective for a short- or medium-term
evaluation. But then, when time passes by, student
do not remember very well what they have learnt
about the exponentiation operation because they
∆<2%
∆>10%
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
130

have just memorized how to calculate it, but they
have not deeply understood what an exponentiation
does really mean. The students instead, by building
by themselves the kind of interactive projects that
we design for them, are forced to see the elements
that corresponds to the abstract definition of
exponentiation.
So let us go now into some more details in the
kind of project we have designed for both
multiplication and exponentiation. In the following,
given that the structure of the two projects is exactly
the same, we will be discussing the exponentiation
project.
4.1.1 Creating Interactive Objects to
Understand and Remember a Given
Topic
To allow the student to test their knowledge about
exponentiation, we can use a programming language
to build several different kinds of projects. One of
the simplest projects could be just showing the value
of a base and of an exponent randomly selected and
then just compare the user answer with the result of
calculating the power by using the operators of the
programming language, for example the exponent
operator with base e (Euler’s number) and the
natural logarithm operator again with base e
iii
(figure
12).
Figure 12: Calculating 2
3
as e
3 ln 2
by using the e^ and ln
mathematical operators of the Scratch language.
However, using the mathematical operators that are
already available in a programming language, for
example the e^ and ln operators available in Scratch,
clearly does not give us a better understanding of the
exponential operation. It is like using the “x”
multiplication operator of a calculator to calculate
2x3. This does not allow us to learn or understand
more deeply about multiplication.
A good way of using a visual programming
language such as Scratch is instead to create an
interactive model of the problem by creating
interactive objects for each single component of the
problem. To create this model the student will have
then to know how many elements compose the
correct solution. For example, to build the
interactive solution of 2
3
the student will have to
create 3 interactive 2’s and 2 interactive x’s (figure
13).
Figure 13: Calculating 2
3
as the result of two
multiplications of three 2’s.
All these elements are clearly visible in the object
area of Scratch (figure 14) so that for the
programmer are tangible objects.
Figure 14: Interactive objects of the exponentiation project
clearly visible in the object area of Scratch.
So, the deeper learning of the student will come out
due to several concurrent reasons, all concurring to
getting rid of the more common mistakes (“times
exponent” error, “number of factor” error,
“summation” error; see section 3.4) done by the
students:
• the student will have to place on the design
area copies of the base, not the exponent.
This will allow the user to get rid of the
“times exponent” error;
• the student will have to place on the design
area as many copies of the base as
indicated by the exponent. This will allow
the user to get rid of the “number of
factors” error;
• the student will have to place on the design
area copies of the multiplication operator.
This will allow the user to get rid of the
“summation error”;
• the student will have to add to the project
several behaviours that reject the wrong
answers or accept the correct answers given
by the users of the project -when the user
select the correct/wrong factor or the
correct/wrong operation- by playing, for
example, the “correct” and “wrong” sounds
as in the first Supermario minigame. This
Who Learns Better
131

will allow the user to get rid of both the
“summation error” and the “factors error”.
Several different learning strategies are working in
this case together (Udomon et al., 2013, Seemüller et
al., 2012) to build an interactive virtual model that
will help the student to improve the recall of the
topic. Indeed, each element of the correct answer
(each factor, each operation, etc) is “physically”
represented in the project by an interactive object
that can be seen. Furthermore, each element must be
“physically” manipulated by the student (for
example by selecting its picture and by dragging and
dropping it) in order to correctly place it on the
design area. Finally, elements are manipulated in
order to assign them the correct behaviour when the
user of the project will interact with it.
4.2 Applying Programming-based
Learning to Other Disciplines
The strategy discussed in this paper, that allows
students to acquire a deeper understanding of school
topics by programming-based learning and
illustrated via the exponentiation operation that has
been chosen as the topic of this experiment in 5
th
grade classrooms, is not limited to
mathematical/scientific topics.
Other experiments are currently under way by
actively testing how applicable and effective this
very same strategy can be when applied to other
“non-scientific” disciplines such as arts at the high
school level and foreign language learning at the
elementary school. The fundamental part of these
experiments is to find a suitable representation -as
interactive objects- of the elements and concepts
explained in the most complex parts of the standard
classroom lessons for these topics.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we illustrated the positive outcomes of
a recent experiment in two 5
th
grades classes proving
that computer programming can be introduced as an
effective strategy to improve retention of knowledge
of difficult school topics.
The devised strategy is not limited to scientific
topics and can be fruitfully applied to further topics
of all disciplines that are felt as particularly difficult
to remember by students.
The double outcome of the programming-based
learning strategy described in the paper is that not
only long-term retention is significantly improved,
but that students are given at the same time the
chance to learn computational thinking (Wing,
2006), a skill that will be really important in their
future lives.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Stefano Federici expresses his gratitude for the
support of Fondazione Banco di Sardegna within the
project ``Science and its Logics: The
Representation's Dilemma'', Cagliari, number:
F72F16003220002.
All authors would like to thank the school
principal Claudia Aroni of the Santu Nigola
elementary school in Selargius, for her support to
this experimentation, and the teachers Adele Sechi
and Simona Quartu for their help in designing and
administering the experiment.
REFERENCES
Bachelor, R.L., Vaughan, P.M., Wall, C.M., 2012,
Exploring the effects of active learning on retaining
essential concepts in secondary and junior high
classrooms, dissertation thesis, School of Education,
Saint Xavier University, Chicago, Illinois.
Bethune, J., 2011, How to Improve Student Content
Retention: A Tale of Two Classrooms, in
TheNewtonBlog, https://www.knewton.com/resources
/blog/student-resources/how-to-improve-student-
content-retention-a-tale-of-two-classrooms/ (last
retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Boulton, K., 2013, Why is it that students always seem to
understand, but then never remember?, in toTheReal,
https://tothereal.wordpress.com/2013/05/06/why-is-it-
that-students-always-seem-to-understand-but-then-
never-remember/ (last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Brady, T.F., Konkle, T., Alvarez, G.A., Aude, O., 2008,
Visual long-term memory has a massive storage
capacity for object details, in Proceedings of the
National Academy of Science of United States of
America, volume 105, n. 38, p. 14325-14329.
Briggs, L.J., Porteus B., 1965, Increasing long-term
retention of knowledge, final report, American
Institute of Research, Palo Alto.
Chase, C.C., Chin, D.B., Oppezzo, M.A., Schwartz, D.L.,
2009, Teachable Agents and the Protege Effect:
Increasing the Effort towards Learning, in Journal of
Science Education and Technology, volume 18, n. 4,
p. 334-352, Springer, New York.
Chin, D.B., Dohmen, I.M., Schwartz, D.L., 2013, Young
Children Can Learn Scientific Reasoning with
Teachable Agents, in IEEE Transactions on Learning
Technologies, volume 6, n. 3, p. 248-257, IEEE
Computer Society and IEEE Education Society.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
132

Custers E.J., 2008, Long-term retention of basic science
knowledge: a review study, in Advances in Health
Sciences Education, Theory and Practice, volume 15,
n. 1, p. 109-128, Springer.
Darland, D.C., Carmichael, J.S., 2012, Long-Term
Retention of Knowledge and Critical Thinking Skills
in Developmental Biology, in JMBE, Journal of
Microbiology and Biology Education, volume 13, n. 2,
doi: 10.1128/jmbe.v13i2.331.
Deng, F.; Gluckstein, J., 2014, Tools to Improve Long-
Term Retention of Preclinical Knowledge, in
Academic Medicine, Journal of the Association of
American Medical Colleges, volume 89, n. 2, p.195.
Engelbrecht, J., Harding, A., Du Preez, J., 2007, Long-
Term Retention of Basic Mathematical Knowledge
and Skills with Engineering Students, in European
Journal of Engineering Education, volume 32, n. 6, p.
735-744, Taylor & Francis, Ltd., Philadelphia.
Fogel, E.K., Drew, T., 2008, Why Do We Forget Things?,
in Scientific American Online,
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-do-
we-forget-things/ (last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
iCoatchMath, 2017, Definition of Exponent,
http://www.icoachmath.com/math_dictionary/exponen
t.html (last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Kirby, J., 2013, Why don’t students remember what
they’ve learned?, in PragmaticReform,
https://pragmaticreform.wordpress.com/2013/11/16/m
emory/ (last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Leelawong, K., Biswas, G., 2008, Designing Learning by
Teaching Agents: The Betty's Brain System, in
International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in
Education, volume 18, issue 3, p. 181-208, IOS Press
Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Lindsey, R.V., Shroyer, J.D., Pashler, J., Mozer, M.C.,
2014, Improving students’ long-term knowledge
retention through personalized review, Psychological
Science, volume 25, n. 3, p. 639-647, doi:
10.1177/0956797613504302.
Liu, F., 2017, Common Mistakes in Teaching Elementary
Math—And How to Avoid Them, Routledge.
Maloney, J., Resnick, M., Rusk, N., Silverman, B., and
Eastmond, E., 2010, The scratch programming
language and environment, in ACM Transactions on
Computing Education. volume 10, n. 4,
doi=10.1145/1868358.1868363.
MathsIsFun, 2017, Definition of Exponent,
https://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/exponent.htm
l (last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Murphy Paul, A., 2011, The Protégé Effect: Why teaching
someone else is the best way to learn, in Ideas,
http://ideas.time.com/2011/11/30/the-protege-effect/
(last retrieved on 29/10/2017).
Palha J.A., Almeida, A., Correia-Pinto, J., Costa, M.J.,
Ferreira, M.A., Sousa, N., 2015, Longitudinal
evaluation, acceptability and long-term retention of
knowledge on a horizontally integrated organic and
functional systems course, in Perspectives on Medical
Education, volume 4, n. 4, p. 191-195.
Pershan, M., 2017, “Two cubed is eight, but seven squared
is fourteen”, in MathMistakes,
http://mathmistakes.org/category/middle-
school/exponents-middle-school/ (last retrieved on
29/10/2017).
Pershan, M., 2017, Why Kids Mess Up Exponents, in
RationalExpressions,
http://rationalexpressions.blogspot.it/2013/04/figuring-
out-why-kids-mess-up-exponents.html (last retrieved
on 29/10/2017).
Prince, M., 2004, Does Active Learning Work? A Review
of the Research, in The Research Journal of
Engineering Education, volume 93, n. 3, p. 223-231,
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Schmid, S., Bogner, F.X, 2015, Does Inquiry-Learning
Support Long-Term Retention of Knowledge?, in
International Journal of Learning, Teaching and
Educational Research, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 51-70.
Seemüller, A., Müller, E.M., Rösler, F., 2012, EEG-power
and -coherence changes in a unimodal and a
crossmodal working memory task with visual and
kinesthetic stimuli, in International Journal of
Psychophysiology, issue 83, p. 87-95.
Semb, G.B., Ellis, J.A., 1994, Knowledge Taught in
School: What Is Remembered?, in Review of
Educational Research, volume 64, n. 2, p. 253-286
Udomon, I., Xiong, C., Berns, R., Best, K., Vike, N.,
2013, Visual, Audio, and Kinesthetic Effects on
Memory Retention and Recall, in Journal of Advanced
Student Science (JASS), issue 1.
Upadhyay, B., DeFranco, C., 2008, Elementary Students’
Retention of Environmental Science Knowledge:
Connected Science Instruction Versus Direct
Instruction, in Journal of Elementary Science
Education, volume 20, n. 2, p. 23-37, Western Illinois
University.
Wing, J.M. 2006, Computational Thinking, in
Communications of the ACM, volume 49, n. 3, p. 33-
35, ACM.
i
Indeed, when the exponent is 0, there is no series of
multiplications that can be used to calculate the result. So, in
order to be coherent in the successive grades of the school with
the operation of division of powers with the same base, n
0
is 1 for
all values of n
.
ii
When the base and the exponent are both 0’s there are different
interpretations of what the result should be. Usually. the result is
considered undetermined.
iii
In Scratch the exponentiation looks more complex than
necessary, due to the lack of a general exponentiation operator
that is instead available in other common programming languages
such as C/C++
.
Who Learns Better
133
