
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
Adriano Lages dos Santos
1
, Mauricio R. de A. Souza
1
, Eduardo Figueiredo
1
and Marcella Dayrell
2
1
Computer Science Department, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte - MG, Brazil
2
Computer Science Department, State University of Montes Claros, Montes Claros - MG, Brazil
Keywords: Game Elements, Serious Games, Programming, Learning.
Abstract: Serious games have been used as a tool to support learning in several areas and subjects. To achieve its
educational goals, a serious game must consist of a set of game elements that are related to the learning
outcomes. In Computer Science, educators are also using serious games and their elements to enhance
learning of programming-related disciplines, which are often considered challenging by first-year students.
It is important for educators in Computer Science to know what are the types of game elements used in
games to learn programming. Besides that, it is also important to know how game elements are evaluated
and what are the game elements that mostly contribute to learning achievements. In this work, we aim to
verify how serious games and their composing elements are used and evaluated to support learning
programming. To achieve this goal, we conducted a systematic mapping study on the use and evaluation of
game elements for learning programming. Our results indicate that game elements are only evaluated
indirectly by means of their serious games. Furthermore, we identify some shortcomings in game elements
evaluation, such as the lack of evaluation in some primary studies and low number of quantitative studies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Serious games are important tools for many
educational areas. Educators are using games in
universities to improve traditional classes. Serious
games used to learn programming provide students
with a way to reinforce knowledge acquired in
classroom. Students can also learn programming
concepts without use of the educator, allowing
students to learn everywhere (Zhang et al., 2014).
Serious games combine different elements, such
as levels, leaderboards, point system, and bosses, to
achieve its learning goals (Werbach and Hunter,
2012). These game elements, if used properly, can
potentialize learning and student interest (Bedwell et
al., 2012). However, the right combination of
elements may contribute to the success or failure of
a serious game. Additionally, developing a good
game is not an easy task. It demands time and
resources, and requires programming and graphic
design abilities (Folmer, 2007). These factors may
hinder the development and use of games in the
academia.
Computer Science also benefit from the use of
games to provide students a more enjoyable way to
learn the fundaments of programming (Kazimoglu et
al., 2012). In the context of programming education,
the majority of serious games are evaluated using
subjective feedback collected via questionnaires
from the students after play sessions (Petri and
Wangenheim, 2017). However, students evaluate the
games as a whole. They do not evaluate specific
game elements. As a result, data on the effectiveness
of each game element for learning is not gathered.
Thus, educators do not have information about
which game elements have contributed positively
and negatively for learning programming. Such
feedback could provide valuable lessons on how
each game element contribute for students’ learning,
engagement, and motivation when playing serious
games. Therefore, educators would benefit from
guidelines about the use of specific game elements.
In this context, the goal of this paper is to discuss
the use and evaluation of game elements in the
context of learning programming. To achieve this
goal, we conducted a systematic mapping study to
investigate the programming educational literature in
order to: (i) identify the game elements used in
serious games for learning programming; and (ii)
understand how these game elements are evaluated.
Additionally, we expect to identify possible research
gaps and trends for future investigations.
Lages dos Santos, A., R. de A. Souza, M., Figueiredo, E. and Dayrell, M.
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0006682200890101
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2018), pages 89-101
ISBN: 978-989-758-291-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
89

We identified 39 primary studies with 27 game
elements distributed over 43 serious games for
learning programming. As a result, we identified and
mapped the game elements used in these games and
the evaluation strategies used. We did not find any
study that objectively evaluates game elements.
With respect to the evaluation of the serious games,
only a small number of studies provide quantitative
data to support their results.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 provides the current state of art
about game-elements and serious games for learning
programming. In Section 3, we describe the design
of this systematic mapping study. Section 4 presents
the results of the study. Section 5 discusses the
results on how serious games for learning
programming can be used and improved. Section 6
discusses the threats to validity of the study while
we discuss the related work in Section 7. Section 8
concludes this research paper.
2 BACKGROUND
This section presents some game elements, game
based learning approaches, and programming areas.
2.1 Game Elements
Game elements are a set of components that
compose a game (Bedwell et al., 2012). In some
studies, game elements are also called game
attributes (Bedwell et al., 2012). In fact, terminology
and description for game elements are not uniform
in the literature. Souza et al. (2017) discuss the lack
of a standard definition and nomenclature for game
elements. For instance, emblem (Garcia et al., 2017)
and badge (Hamari, 2017) are two names for the
same game element, which are visual rewards given
to the user and identify user achievements in the
game.
Previous works have tried to define a unified
taxonomy for game elements, but there is no
consensus in the community about it (Dicheva et al.,
2015). Several authors propose different strategies to
categorize game elements (Zichermann and
Cunningham, 2011) (Dicheva et al., 2015).
However, several authors (Bedwell, et al. 2012),
(Werbach and Hunter, 2012) end up using their own
definitions, according to the needs of the research.
This lack of standardization in element names makes
it difficult to unify results of studies that use or
evaluate game elements.
Research on which game elements constitute the
core of a game is conducted since the 80s. Previous
work defined that game elements such as, challenge,
curiosity, control, and fantasy, constituted a core of a
game (Malone, 1981) (Malone and Lepper, 1987).
Other works expanded this view to incorporate other
elements, such as roles of a player, conflicts, even
rules, goals, and constraints (Gredler, 1996)
(Thiagarajan, 1999).
Bedwell et al. (2012) present a taxonomy to
define game elements for educational purposes.
They surveyed the literature on game elements
related to education and identified the most recurring
game elements. The work is generalist and it does
not consider specific areas of learning, such as
programming.
Werbach and Hunter (2012) propose a pyramid
that organizes game elements in three categories:
dynamics, mechanics, and components. Components
compose the base of the pyramid, with the
mechanics group in the middle and dynamics on top.
Dynamics contain the main aspects of a serious
game. They are conceptual elements in a serious
game. Examples of elements in this group are:
Constraints, Emotions, Narrative, Progression, and
Relationships. Mechanics contain the basic process
that directs users to engage with content and
continue to drive the action forward. Examples of
mechanics are: Challenges, Feedback, Competition,
and Cooperation. Components are less abstract than
the first two categories and are tools that can be
employed to motivate user in the environment of
interest. Examples are Achievement, Avatar, Badge,
Combat, Leaderboard, and Level.
2.2 Learning Programming
Algorithms are a fundamental knowledge for
students of Computer Science. A good software
system depends of the algorithms chosen and the
various layers of implementation. Design of
algorithms is important to performance of all
software systems. Furthermore, as stated by the 2013
ACM and IEEE Computer Science curricula
(CS2013) (ACM and IEEE, 2013), the study of
algorithms provides insights into the intrinsic nature
of the problem and possible solutions independent of
programming language, hardware, or other
implementation aspects.
According to CS2013, students have to develop
the ability to select the appropriate algorithms for a
set of problems. The knowledge area of CS2013
responsible for defining how algorithms should be
addressed in Computer Science courses is
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
90

“Algorithms and Complexity”. This knowledge area
defines the main skills for students to design,
implement, and debug algorithms to solve problems.
The Algorithms and Complexity knowledge area
is divided in seven sub-areas. Table 1 lists the three
areas considered in this study: (i) algorithmic
strategies, (ii) fundamental data structures and
algorithms, and (iii) advanced data structures,
algorithms, and analysis. We select these three areas
because we are mainly concerned in finding
elements from serious games to learn algorithms and
data structures. The other four areas are related to
automata and complexity analysis. They are: (iv)
basic analysis, (v) basic automata, computability and
complexity, (vi) advanced computation complexity,
and (vii) advanced automata theory and complexity.
3 STUDY DESIGN
This section presents the goal of this study and its
experimental steps. Section 3.1 presents the study
goal and research questions. Section 3.2 explains the
research method and steps we followed. Section 3.3
discusses the search strategy applied to mine
relevant scientific databases. Section 3.4 shows the
selection process filtering only relevant papers for
this study. Lastly, Section 3.5 shows the strategy for
data extraction and summarizing the results.
3.1 Goal and Research Questions
The goal of this study is to identify game elements
existing in serious games for learning programming.
By learning programming, we mean all aspects to
learn algorithms and data structures, from basic
algorithms and data structures to advanced ones.
More formally, we define the goal of this study
based on the GQM (Basili, 1992) as follows: to
identify and analyse game elements from the
purpose of understanding their use and evaluation,
in the context of serious games for learning
programming, from the perspective of researchers,
educators, and students. To achieve this goal, we
defined two research questions (RQ1 and RQ2).
RQ1. What are the game elements in the serious
games for learning programming? The answer is a
list of game elements that are in existing serious
games. We also aim to categorize these elements.
RQ2. What are the empirical strategies and methods
used to evaluate existing game elements? The
expected answer is a mapping between game
elements and the type of empirical studies used to
evaluate them (Wohlin et al., 2000).
3.2 Experimental Steps
To achieve the study goal (Section 3.1), we
conducted a systematic mapping study – SMS. SMS
is a secondary study method that systematically (i.e.,
based on a structured and repeatable process or
protocol) explores and categorizes studies in a
research field. It also provides a structure of the
types of research reports and results that have been
published (Petersen et al., 2007). Additionally, we
expect to identify possible research gaps and trends
for future investigations.
We have conducted the SMS in the period of
May/2017 to September/2017, following four steps
adopted described as follows (Petersen et al., 2007).
Step 1 – Definition of research questions: we
defined two research questions, based on the
study goal, to establish the scope of the
systematic study (Section 3.1);
Step 2 – Conduct search: based on the
research questions, we defined and performed
a replicable method for searching and
retrieving papers in five selected scientific
databases (Section 3.3);
Step 3 – Study selection: we defined and
applied a systematic method for selecting only
the relevant papers for this study (Section 3.4);
Step 4 – Data extraction and analysis: we
Table 1: Selected knowledge areas according to ACM Computer Science Curricula 2013.
Name Description
Algorithmic Strategies - AS Brute-force, greedy, divide-and-conquer, and recursive algorithms. Dynamic programming,
reduction.
Fundamental Data Structures and
Algorithms - FDS
Binary search. Insertion sort, selection sort, shellsort, quicksort, mergesort, heapsort. Binary
heaps. Binary search trees, hashing. Representations of graphs. Graph search, unionfind,
minimum spanning trees, shortest paths. Substring search, pattern matching.
Advanced Data Structures,
Algorithms and Analysis - ADS
Balanced trees, B-trees. Topological sort, strong components, network flow. Convex hull.
Geometric search and intersection. String sorts, tries, Data compression.
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
91

finally summarized the relevant data from the
primary studies (Section 3.5) and present the
study results (Section 4).
Four researchers participated in the planning and
execution of the study: an undergraduate student in
Information Systems, two PhD students in Computer
Science, and a PhD associate professor. Two PhD
students conducted the searches in scientific
databases and conducted the process of inclusion
and exclusion of primary studies. The undergraduate
student participated in the phase of extraction of
information from the selected studies. All phases
were supervised by the PhD associate professor,
which validated all stages of the study and
participated in discussions on the SMS strategy.
3.3 Search Strategy
To identify possible relevant primary studies for data
extraction, the search was based on (i) trial searches
using combinations of keywords derived from the
study goal and (ii) the execution of automatic
searches in the scientific databases using search
strings. Initially, we selected relevant keywords
related to three major concepts: (a) education; (b)
algorithms and data structures; and (c) games. The
resulting keywords per major concept were:
Education: teach; learn, education, train;
Algorithms and data structures: algorithm, data
structures, program;
Games: game, edutainment, playful;
We defined search strings by grouping keywords
in the same domain with the logic operator “OR”
and grouping the three major concepts with the logic
operator “AND”. We then executed automatic
searches in five scientific databases, using and
adapting (when necessary) the search string. The
databases were ACM Digital Library (ACM, 2017),
IEEE Xplore (IEEE, 2017), Science Direct (Elsevier,
2017), Springer Link (Springer, 2017), and Wiley
Online Library (Wiley, 2017). We selected these
databases because they have a large amount of
relevant conferences and journals indexed for
Computer Science. We limited the results of
automatic searches to return only papers written in
English and published from 2007 to 2016, due to the
high number of results retrieved. We do not include
2017 because this year has not yet finished.
3.4 Study Selection
We filtered the studies retrieved from automatic
searches to exclude papers not aligned with the
study goals. In this step, the four researchers defined
and applied the following inclusion and exclusion
criteria.
Inclusion Criteria: Studies whose main focus
was on proposal, usage, discussion or evaluation of
serious games for learning programming in
undergraduate courses.
Exclusion Criteria: Papers not written in
English; studies whose the main focus was
elementary and high school education; studies
formatted as short papers (less than 3 pages); studies
not published as either journals or conference
papers; and duplicated studies.
The study selection process was executed in two
phases: (i) in the first selection phase, we read titles
and abstracts and removed studies that did not
comply with inclusion criteria; (ii) in the second
selection phase, we downloaded all papers, read
their introduction and conclusion, and removed
studies that matched any exclusion criteria.
Table 2 presents the number of papers selected in
each phase. It is important to observe that the
automatic searches returned a high number of
primary studies (#papers column in Table 2). This
high number of results is expected by the use of
general terms in the search string, such as algorithm
and programming. In particular, these terms
commonly appear in other contexts not related with
programming. Due to the high number of results, we
only evaluated the first 500 records of each database.
Figure 1 shows the overlapping results between
databases. In case of different papers reporting the
same study (e.g., journal and conference papers with
Table 2: Results of search in selected scientific databases.
Source #Papers* 1
st
Selection 2
nd
Selection
ACM Digital Library 143,577 51 10
IEEE Xplore 658,195 136 21
Science Direct 36,956 9 1
Springer Lin
k
78,921 14 4
Wiley Online Library 112,347 8 3
Total 1,029,996 218 39
* Given this high number of results, we evaluate only the first 500 records of each database.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
92

the same title), only the most recent and/or most
complete was kept in the final list of primary
studies.
IEEE Xplore ACM DL
Springer Link
15
5
5
3
1
Wiley Online
Library
Science Direct
1
3
1
0
Figure 1: Distribution of primary studies per database.
3.5 Data Extraction and Summary
To evaluate the primary studies found in literature,
we used a set of quality criteria (Kitchenham et al.,
2007) detailed in the appendix. These criteria are
used to evaluate the primary studies, regarding their
methodology, results, evaluation, quality of
references, and others. To answer RQ1, we used the
strategy to classify and map the groups of game
elements found (Deterding et al., 2011). This
strategy defines three groups of game elements:
components, dynamics, and mechanics.
Regarding the data analysis and evaluation
(RQ2), we adopted the classifications proposed by
Wohlin et al. (2000). That is, we investigated (i) if
the evaluation strategies rely on quantitative or
qualitative analysis of the data and (ii) what
empirical strategy is used – i.e., case study,
experiment, or survey. We consider a quantitative
study when it relies on statistical analysis of the
data. Studies are considered qualitative when only
qualitative discussions are made.
4 RESULTS
In this section, we present the results of the
systematic mapping study. Section 4.1 provides an
overview of the primary studies selected for this
study. Section 4.2 shows the results of a quality
assessment of the selected primary studies. Sections
4.3 and 4.4 describe the results for the research
questions RQ1 to RQ2, respectively. Considering
the space restrictions and the double blind revision
process, we provide an anonymous online appendix
in GitHub (https://github.com/csedu2018doubleblind
/csedu2018doubleblind) with the data that support
our results.
4.1 Overview
We selected 39 primary studies published between
2007 to 2016. Figure 2 presents a histogram with the
frequency of selected primary studies per year. This
result suggests that serious games for learning
programming in computer science courses are
balanced between years. That is, 5 primary studies
were selected per year, except for the years of 2008,
2011, 2013, and 2016.
Our results found 43 serious games distributed
over 39 primary studies. In fact, we expected that the
number of primary studies describing serious games
to learning programming would be higher and we
consider 43 a small number. We also found several
serious games for this purpose available online, yet
not published, such as CodinGame (CodinGame,
2017), Code Wars (Code Wars, 2017), Codemancer
(Codemancer, 2017), and Code Warriors (Code
Warriors, 2017). In this study, we did not consider
these games since our focus is to evaluate primary
studies indexed in scientific bases.
Figure 2: Timeline of primary studies.
The distribution of studies was 20.5% in journals
(8 studies) and 79.5% (31 studies) in conferences.
Table 3 summarizes the most recurring publication
venues and their respective counting of selected
primary studies. The conferences and journals with
greater occurrences of primary studies were FIE (3
studies), SIGSE, ITHET and IEEE Transactions on
Education (2 studies each). We listed only
publication venues that have two or more primary
studies selected in this study.
Table 3: Main venues of primary studies.
# Studies Publication Venues
3 IEEE Frontiers in Education (FIE)
2
ACM Technical Symposium on Computer
Science Education (SIGSE)
2
IEEE Information technology Based Higher
Education and Training (ITHET)
2 IEEE Transactions on Education
In the supplementary online material, we
provided the complete list of primary studies
(https://github.com/csedu2018doubleblind/csedu201
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
93
8doubleblind). In the remaining of this paper, we
used unique identifications (AuthorName<year>)
when referring to primary studies. For instance,
Bishop2015 refers to the paper “Code Hunt:
Experience with Coding Contests at Scale”
published in proceedings of the International
Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE) in
2015.
4.2 Quality of Selected Studies
We used quality criteria to evaluate primary studies
with respect to their methodology, objectives,
results, references, and other points (Kitchenham et
al., 2007). We adopted seven quality criteria, to
evaluate the primary studies: (i) Does the primary
study clearly describe educational goals? (ii) Has the
research methodology been appropriate to address
the research objectives? (iii) Is the primary study
proper referenced? (iv) Has the proposed game been
tested with students? (v) Was there an appropriate
assessment of the data collected? (vi) Does the work
present results consistent with its educational
objectives? (vii) Does the study compare their
proposals with related work?
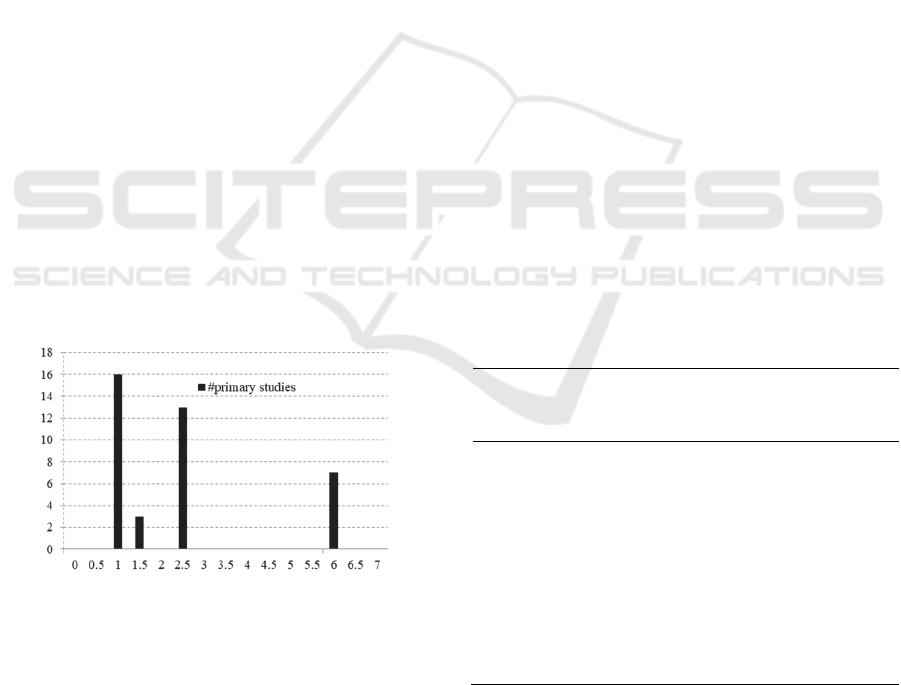
Figure 3 presents the results of the quality
evaluation. A study scores one point for each
criterion if it fully satisfies that criterion, 0.5 point if
it partially satisfies it, or zero if the criterion is not
satisfied. The total score of each primary study is the
sum of the scores for all quality criteria. Therefore,
the total value a primary study can range from zero
to seven.
Figure 3: Quality evaluation of the primary studies.
According to Figure 3, 16 primary studies score
a total of one point in quality criteria, three studies
score 1.5 point, 13 primary studies score 2.5 points,
and 7 studies scores 6 points. No study scored points
in quality criteria which checks if a primary study
compares their proposal with others. The quality
criterion with higher attendance was related to the
clear description of educational goals. The other five
quality criteria had low accordance with the primary
studies. We observed an overall low quality
considering our criteria. That is, only six studies
obtained more than 70% of the points in the quality
criteria established for this study. The main
shortcomings we observed is that they do not expose
the outcomes of the proposed approach. They
neither explain the methodology they followed to
develop their games nor their evaluation strategy.
4.3 RQ1 - Game Elements
This section discusses the results for the first
research question: “RQ1. What are the game
elements in the serious games for learning
programming?”
We found 27 game elements distributed over 43
serious games. Table 4 lists these game elements and
classify them in three categories: dynamics,
components, and mechanics (Werbach and Hunter,
2012). The number inside parenthesis after each
game element corresponds to the number of games
that the element has been found. In the group of
dynamics, four elements were found, being Fantasy
the most used element (17 games in total). In the
group of components, we found nine elements. The
most used elements in this group are Level (36
games), Quest (16 games) and Avatar (14 games).
On the other hand, we found 14 elements in the
group of mechanics. Goal (21 games) and Point
System (16 games) are the most used elements of the
mechanics group.
Table 4: Game elements found in serious games.
Game
Elements
Group
Game Elements
Components Level (36), Quest (16), Avatar (14), Virtual
Good (5), Boss Fight (4), Hint (4),
Leaderboard (3), Combat (1), Card (1).
Dynamics Fantasy (17), Meaning (5), Constraint (4),
Progression (3).
Mechanics Goal (21), Point System (16), Reminder (6),
Time Pressure (5), Change Difficult (4),
Progressive Disclosure (3), Competition (3),
Achievement (3), Win State (3), Cooperation
(2), Resource Acquisition (2), Badge (2),
Loss Aversion (1), Turns (1).
We note in Table 4, that only six elements (i.e.,
Avatar, Fantasy, Goal, Level, Point System, and
Quest) were used more than ten times. On the other
hand, each game uses only a few elements. That is,
the average of 8 game elements per game. In Section
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
94
5, we further discuss about the usage of game
elements.
4.4 RQ2 - Evaluation of Game
Elements
This section discusses the results for the second
research question: “RQ2. What is the evaluation
methods used to evaluate the game elements existing
in literature?”
In short, we found no study that directly evaluate
game elements. The primary studies described
evaluation strategies that focused on the game as a
whole. However, we believe that evaluating each
game element individually is important because they
are directly related to how players interact with the
game. In addition, evaluating the game elements
may give us insights on what game elements are
more impactful for a specific audience (in our case,
students learning programming, for instance). This
in-depth analysis may also provide objective results
on why such elements are important in creating a
better playing/learning experience.
Given this negative response for RQ2, we opted
to investigate how the serious games, in which the
game elements are found (RQ1), were evaluated. We
mapped two facets: the type of empirical study and
the empirical strategy. The type of empirical study
means whether the game elements were found in
qualitative or quantitative studies. The empirical
strategies indicate if the primary study reports a case
study, an experiment, or a survey.
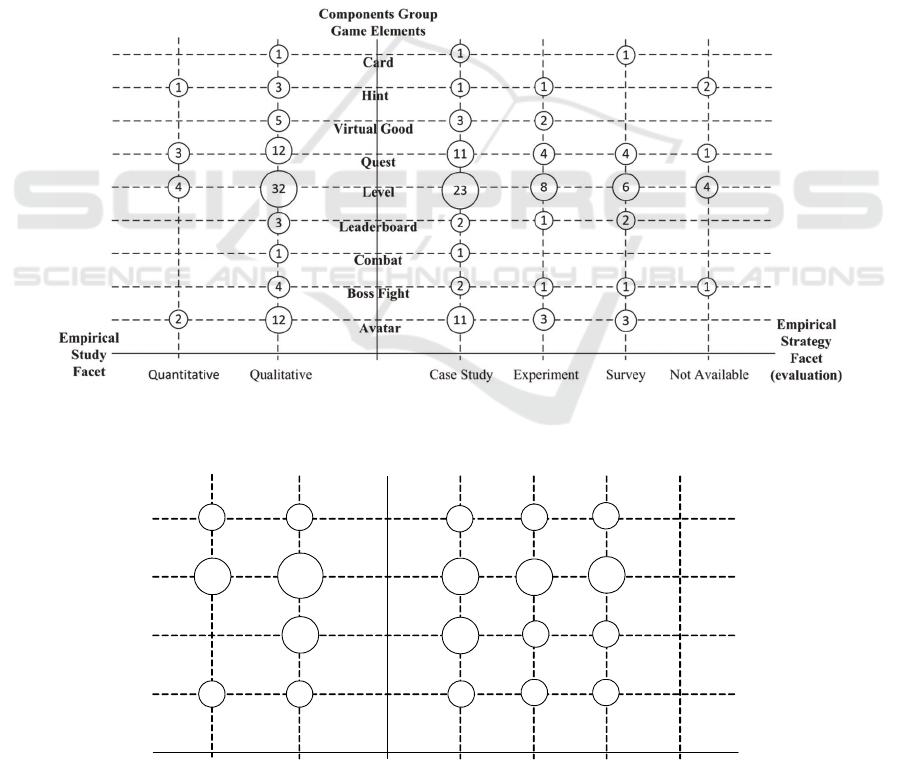
Figures 4, 5, and 6 map game elements
(components, dynamics, and mechanics,
respectively) to the type of empirical study and
Figure 4: Game elements of the components group and evaluation strategies.
Figure 5: Game elements of the dynamics group and evaluation strategies.
Dynamics Group
Game Elements
Empirical
Study
Facet
Empirical
Strategy
Facet
(evaluation)
SurveyCase Study Experiment Not AvailableQuanti tative Qualitative
1 2
5
12
1 3
5
1
1
3
5
9
7
1
4
1
1
2
1
Progression
Meaning
Fantasy
Constraint
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
95

Figure 6: Game elements of the mechanics group and evaluation strategies.
empirical strategy adopted in the primary studies in
which they are found. The numbers inside bubbles in
the facet of empirical study represent the number of
elements per study type. For example, the element
Level appears in 36 studies: 32 qualitative studies
and 4 quantitative studies. In the empirical strategy
facet, the number inside bubbles means the number
of times that a game element appears in studies that
adopt one of the empirical strategies listed. If a study
does not report any evaluation method, we report
that evaluation of the game element is not available.
Usually, studies describe case studies where
educators apply the games in classrooms, and
describe their observations. Surveys are used to
collect feedback from students playing games. Only
few studies Chaffin2009, Sindre2009, Eagle2009,
Hicks2010, Laguna2014 and Bishop 2015 provide
quantitative data to support their results. However,
none of these evaluation strategies mention any link
between game elements and the observed outcomes.
In total, 19 studies used both experiment and
survey empirical strategies and 21 studies used both
Case Study and Survey to evaluate game elements.
There was no case of studies that used experiment
and case study together, as well as, there were no
case of studies that used the three strategies at same
time to evaluate their game elements.
With respect to the types of empirical studies, we
found a total of 6 quantitative studies and 33
qualitative studies. These numbers may indicate that
researchers are focusing more on collecting and
describing perceptions on the game experiences than
on providing statistical evidences of the
effectiveness of their approaches.
We also verified the number of primary studies
that conducted tests of the proposed serious games
with users. We found 22 primary studies that tested
game with users (56% of total studies), versus 17
studies that have not tested serious games with users
(44% of total). About studies that tested serious
games with users, 15 studies tested the proposed
serious games with a number of users between 1 to
50, while 4 studies tested with a number of users
between of 51 to 100 and 3 studies performed tests
with more than 101 users. The low number of
studies with a reasonable population size is a
possible reason for the preference for qualitative
studies.
5 DISCUSSION
This section discusses the results of Section 4.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
96

5.1 Quality of the Studies and Serious
Games Found in the Literature
We consider that the number of serious games to
learn programming found in literature is small. We
found 43 serious games in 39 primary studies. This
small number of serious games contradicts the
common sense, since there are several serious games
to learn programming available on the internet
(some of them are mentioned in Section 4.1). Our
hypothesis about this number of serious games to
learning programming present in scientific studies is
due to three reasons. First, the research of serious
games for learning programming is recent (we found
relevant results from 2007), and researchers and
educators are still developing new ideas and over
time. Second, developing a game involves high
financial, time and personnel costs that may be
deterrent for educators (Folmer, 2007). Third,
serious games to learn programming are properties
of private companies seeking profit and may not be
interested in publishing scientific studies. In our
study, we found only one game related to a private
company: Code Hunt (Bishop2015), from Microsoft.
Code Hunt is free.
In Section 4.2, we show the results of the quality
evaluation of the primary studies found. Only seven
studies scored more than 70% on the proposed
quality criteria. The majority of the primary studies
found have some shortcomings, regarding their
methodology, evaluation with subjects, assessment
of data collected during test with students and
description of game and how it works. Despite the
fact that this quality assessment is related to the
purpose of this present study, and to the attendance
of the primary studies to our research questions,
these criteria should be considered by researchers
and educators when writing similar studies.
The simplicity of the serious games caught our
attention. Several serious games are only one screen
games, such as, Binary Search Game, JeliotConAn,
and Gaps 1.0. As mentioned before, the quality of
serious games might be related to the costs to
develop a game. Hence, some researchers and
educators do not have enough resources to develop a
high-quality game. However, as far as we are
concerned, no primary study reported difficulties
and challenges in developing serious games for
learning programming.
On the other hand, we found studies and serious
games with high quality. Code Hunt, a game to learn
programming, is a game that presents puzzles to
users, and the user has tips, examples and user guide
to help the user to understand the game and its
mechanics. Furthermore, Code Hunt scored 6 points
in our quality evaluation. The game Lost in Space
(Laguna2014) is an example of good game
developed by researchers and educators. The game
is well structured and it has been tested with
students. In addition, the data collected was assessed
with statistical tests. Laguna2014 scored 6 points in
our quality evaluation.
Regarding ACM CS2013 areas, only two areas
are covered by the serious games found in the
primary studies. The area with more coverage was
the area of FDS – Fundamental Data Structures with
41 proposed serious games to learning programming
in this area. The area of ADS – Advanced Data
Structures had two proposed serious games. This
result can be related to the fact that educators are
concerned with development of serious games to
help students learn the fundamentals of
programming. Since, the programming fundamentals
are the core knowledge for many other areas of
computer science.
5.2 Few Game Elements are used in
Serious Games
We note that only a group of six elements (avatar,
fantasy, goal, level, point system and quest) were
used in more than ten serious games. We found
other 21 game elements that are scarcely used in the
primary studies. The average number of game
elements per game is eight. We consider this number
low; since we have an elevated number of game
elements available in literature, although the number
of game elements used does not necessarily defines
the quality of games. We can speculate that the
development of these games is often driven by
researchers and educators, who are not game
designers, or have little experience with this
discipline.
The lack of evaluation of game elements
prevents us from discussing which game elements
are more important, or from measuring how much
the addition of new elements would improve the
evaluation of a game by its users. We are not aware
of the correct amount of elements a game must have
to achieve greater success among users.
5.3 Shortcomings in Game Elements
Evaluation
Some primary studies such as Rais2011a and
Hakulinen2012 and other 22 studies (56% of total)
tested the proposed serious games with users.
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
97

However, the majority of studies do not adequately
evaluate serious games for learning programming
with users. For example, Rais2001, Karapinar2012,
and Jiau2009 do not evaluate the opinions of the
users about the proposed serious games for learning
programming. In total, only eight studies (20% of
total studies) report the opinion of users, as said by
users, about the proposed game. Other studies that
surveyed users only report in the results that users
like the game and that educational objectives are
achieved or that the result of game was successful,
without further evidences. The studies that presented
these shortcomings are in the group of 33 qualitative
studies found in our systematic mapping study.
In some primary studies Alhazabi2001,
Barnes2007, Chaffin2009, Eagle2009, Rossiou2007,
Zhang2014, Zhang2015 and Melero2012, students
reported that the use of serious games is effective.
Some studies report that the traditional classes to
learn programming with slides and blackboard
overwhelm students Barnes2007, Chaffin2009.
Students need to practice coding, not only at home,
but also in the classroom. Students have doubts and
these concerns can be shared with educator and
other colleagues in classroom. With serious games,
students report that the learning became pleasant,
with more chances for the student to overcome the
fear of learning programming and demystifying its
difficulty.
Only six primary studies present a quantitative
research. These studies are: Chaffin2009,
Sindre2009, Eagle2009, Hicks2010, Laguna2014
and Bishop 2015. These primary studies present a
well structure research paper, allied with controlled
experiment, consistent, statistical analysis of the data
obtained from experiment with users. We believe
that researchers focus on describing preliminary
results to share their experiences and somehow show
that their game was used in an academic
environment, even if it lacks a more comprehensive
analysis of the quality of the game.
We believe that there is an opportunity to capture
additional insights on how students interact with
serious games and what is the link between game
elements and the reception of the games.
6 THREATS TO VALIDITY
This section discusses the different threats to validity
of this study with respect to the four groups of
threats to validity (Wohlin et al., 2012): internal
validity, external validity, construct validity, and
conclusion validity. We also discuss how the threats
are addressed to minimize the probability of their
impact on our results.
Internal validity. The reliability has been addressed
as much as possible by involving three researchers,
and by having a strict protocol which was piloted
and hence evaluated. If the study is replicated by
another set of researchers, it is possible that some
studies that were removed in this review could be
included. Similarly, some studies we selected could
be excluded by others. However, in general we
believe that the internal validity of this study is high
given the use of a systematic procedure, repetition of
the search protocol by two researchers, and
discussion between three researchers.
External validity. A major external validity to this
mapping study was the identification of primary
studies. The search for the primary studies was
conducted in five scientific databases, namely ACM
Digital Library, IEEE Xplore, Science Direct, Wiley
Online Library, and Springer Link to capture as
much as possible relevant studies and to avoid all
sorts of bias. However, the quality of search engines
could have influenced the completeness of the
identified primary studies. For instance, our search
may have missed studies whose authors have used
other terms to specify their proposed games for
learning programming. In addition, we search for
relevant terms only in the title and abstract of their
papers.
Construct Validity. A construct validity threat
could be biased judgment. In this study, the decision
of which studies to include or to exclude and how to
categorize the studies could have been biased and
thus pose a threat. For instance, a possible threat in
the selection process is to exclude some relevant
studies. To minimize this threat, both the processes
of inclusion and exclusion were piloted by at least
two researchers. Furthermore, potentially relevant
studies that were excluded were documented for
further verification.
Conclusion Validity. From the reviewers’
perspective, a potential threat to conclusion validity
is the reliability of the data extraction from the
primary studies, since not all information was
obvious to answer the research questions and some
data had to be inferred. Therefore, to ensure the
validity, sometime cross-discussions among the
paper authors took place to reach a common
agreement. Furthermore, in the event of a
disagreement between two researchers, a third
reviewer acted as an arbitrator to ensure a position to
be reached.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
98

7 RELATED WORK
In this section, we discuss the related research on the
use and evaluation of serious games and their
elements to learn programming in superior
education.
Regarding the identification of how game
elements are evaluated in relation of empirical
strategies, to the best of our effort, we did not
identify any study that proposes this type of work to
the date of our investigations. No primary study
considered evaluating the game elements that
composed a game. Instead, authors only evaluated
the serious games as a whole entity.
We found studies that proposes frameworks to
evaluate the quality of serious games in all areas of
computer science, with a focus on software
engineering games (Petri et al, 2017), and serious
games to learning programming. This type of
evaluation does not consider the game elements that
compose a game, since these elements are related to
cognitive learning outcomes (Wilson, et al, 2009).
These works consider game attributes, such as ease
of use, graphical interface, if the game helps user to
improve the process of making decisions, and others.
Some questions on what motivates the user in the
game are investigated, such as which rewards to use
and what levels are more challenging. However,
other elements that contributed to the learning were
not evaluated, such as, card, badge and
achievements.
Some research evaluates the relationship
between game elements and learning outcomes for
all educational purposes (Bedwell et al, 2012)
(Garris et al., 2002). However, these works have
some shortcomings, such as, making conclusions of
learning outcomes and game elements through case
study using one game in non-academic
environments. In addition, there is a lack of
experiments with a considerable number of students,
as well as evaluating the results using statistical
tools.
Research in literature about serious games to
learning programming provides opportunities to
research what game elements are more effective to
learning programming, since we do not find any
study that addresses this type of research. Another
opportunity for research is a creation of guidelines to
evaluate game elements in learning programming
and the development of a framework that provides
information about what game elements should be
used in different types of contexts to learning
programming.
8 CONCLUSIONS
This study presented a systematic mapping study to
identify how game elements are used to support
learning programming. We mined five scientific
databases (IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library,
Springer Link, Wiley Online Library and Science
Direct) and retrieved 39 primary studies, from 2007
to 2016. These primary studies describe 43 serious
games with 27 game elements distributed over them.
Some recurring issues in learning programming
motivate the use of game-related approaches that
require students to experience real-world issues of
software development. It is difficult to provide
convincing examples of some aspects of
programming in traditional lectures and practical
projects, given the limitations of these formats.
Game-related approaches have been used to
overcome some of these limitations. The use of
serious games brings to students the possibility to
practice with pleasure and make programming fun
even in academic contexts.
The main challenge of this study was to evaluate
the primary studies found. Since many studies do not
adequately report their methodologies, as well as all
the characteristics of the proposed serious games. A
considerable number of studies do not clearly
structure their learning goals. Many studies also do
not adequately evaluate the proposed serious games
with students. No study found directly evaluated the
link between game elements and learning outcomes
for learning programming. More studies are required
to assess the effectiveness of specific game
elements.
The number of studies with serious games to
learn programming in superior education was low in
scientific publications. The majority of online
serious games are not published in scientific articles.
The scientific community of serious games to learn
programming need more serious games shared in
scientific venues. We expect to provide educators
and researchers an overview of the state of the art in
the literature of serious games to learn
programming, and highlight that there is room for
new research, and there is a need for researchers to
publish their results.
For future work, we plan to evaluate how game
elements are related to learning outcomes,
conducting experiments using serious games in
academic context, and evaluate how the elements of
these games contribute to learning.
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
99

REFERENCES
ACM and IEEE, 2013. Computer Science Curricula 2013:
Curriculum Guidelines for Undergraduate Degree
Programs in Computer Science.
ACM, 2017. https://dl.acm.org/. Accessed in 14/09/2017.
Basili, V., 1992. Software modeling and measurement: the
Goal/Question/Metric paradigm. Techical Report.
pages 24.
Bedwell, W. L., Pavlas, D., Heyne, K., Lazzara, H. E.,
Salas, E., 2012. Toward a Taxonomy Linking Game
Attributes to Learning: An Empirical Study.
Simulation & Gaming An Interdisciplinary Journal,
43(6), 729–760.
Code Combat, 2017. https://codecombat.com/. Accessed
in 14/09/2017.
Code Hunt, 2017. https://www.codehunt.com/. Accessed
in 14/09/2017.
Code Wars, 2017. https://www.codewars.com/. Accessed
in 14/09/2017.
CodeMancer, 2017. http://codemancergame.com/.
Accessed in 14/09/2017.
Coding Game, 2017. https://www.codingame.com/.
Accessed in 14/09/2017.
Deterding, S and Dixon, D., 2011. Gamification: Using
game design elements in non-gaming contexts. In
Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing
Systems (CHI).
Dicheva, D., Dichev C., Agre G., Angelova G., 2015.
Gamification in Education: A Systematic Mapping
Study. Educational Technology & Society, 18(3), 75–
88.
Folmer, E., 2017. Component Based Game Development
– A Solution to Escalating Costs and Expanding
Deadlines? In Proceedings of 10th International
Symposium Component-Based Software Engineering
(CBSE), 66-73.
García, F., Mario, P. P., Cerdeira-Pena, A., Penabad, M.,
2017. A framework for gamification in software
engineering. Journal of Systems and Software (JSS),
132, 21-40.
Garris, R., Ahlers, R., Driskell, J. E. (2002). Games,
motivation and learning: A research and practice
model. Simulation & Gaming: An Interdisciplinary
Journal, 33, 441-467.
Gredler, M. E., 1996. Educational games and simulation:
A technology in search of a research paradigm.
Handbook of research for educational communications
and technology (pp. 521-540).
Habgood, M. P. J., Ainsworth, S. E., Benford, S. (2005).
Endogenous fantasy and learning in digital games.
Simulation & Gaming: An Interdisciplinary Journal,
36, 483-498.
Hamari, J., 2017. Do badges increase user activity? A field
experiment on the effects of gamification. In
Computers in Human Behavior, 469-478, Elsevier.
IEEE, 2017. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/home.jsp.
Accessed in 14/09/2017.
Kazimoglu, C. Kiernan, M. Bacon, L. and MacKinnon, L.,
2012. Learning programming at the computational
thinking level via digital game-play. Procedia
Computer Science, 9, 522-531.
Khenissi, M. A., Essalmi, F., and Jemni, M., 2014.
Comparison between serious games and learning
version of existing games. In Proceedings of the 6th
World Conference on Educational Sciences, pp. 06-09.
Kitchenham, B. and Charters, S., 2007. Guidelines for
performing systematic literature reviews in software
engineering, Technical Report EBSE-2007-01, School
of Computer Science and Mathematics, Keele
University
Malone, T. W., 1981. Towards a theory of intrinsically
motivation instruction. Cognitive Science, 4, 333-369.
Malone, T. W., Lepper, M. R., 1987. Making learning fun:
A taxonomy of intrinsic motivations for learning. In
Aptitude, learning and instruction: Vol. 3. Cognitive
and affective process and analyses (pp. 223-253).
Orehovački, T., Babić, S., 2015. Inspecting Quality of
Games Designed for Learning programming. In
International Conference on Learning and
Collaboration Technologies (LCT).
Petersen, K., Feldt, R., Mujtaba, S., Mattsson, M., 2007.
Systematic mapping studies in software engineering.
In 12th International Conference on Evaluation and
Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE).
Petri, G. and Wangenheim G. C., 2017. How games for
computing education are evaluated? A systematic
literature review. In Computers & Education, 107
(2017) 68-90.
Science Direct, 2017. http://www.sciencedirect.com/.
Accessed in 14/09/2017.
Souza, M. R., Furtini Veado, L., Teles Moreira, R.,
Figueiredo, E., Costa, H. A. X., 2017. Games for
learning: bridging game-related education methods to
software engineering knowledge areas. In proceedings
of the 39th International Conference on Software
Engineering (ICSE), 170-179.
Springer, 2017. https://link.springer.com/. Accessed in
14/09/2017.
Thiagarajan, S., 1999. Team activities for learning and
performance. Handbook of human performance
technology (pp. 518-544).
Werbach, K. and Hunter, D., 2012. For the win: How
game thinking can revolutionize your business,
Wharton Digital Press.
Wiley, 2017. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/. Accessed in
14/09/2017.
Wilson, K. A., Bedwell L. W., Salas, E., Burke, S. C,
Estock, J. L., Orvis, K. L., Conkey, C., 2009.
Relationships Between Game Attributes and Learning
Outcomes: Review and Research Proposals. In
Simulation & Gaming: An Interdisciplinary Journal,
40 (2) 217-266.
Wohlin, C., Runeson, P., Höst, M., Ohlsson, M. C.,
Regnell, B., Wesslén, A., 2000. Experimentation in
Software Engineering: An Introduction. Kluwer
Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA, USA.
Zhang, F. Kaufman, D. and Fraser, S. 2014. Using video
games in computer science education. European
Scientific Journal, vol. 10, No 22, 37-52.
CSEDU 2018 - 10th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
100

Zichermann, G. and Cunningham, C., 2011. Gamification
by Design: Implementing Game Mechanics in Web
and Mobile Apps. O’Reilly Media.
Game Elements for Learning Programming: A Mapping Study
101
