
Evaluating Green and Resilient Supplier Performance:
AHP-Fuzzy Topsis Decision-Making Approach
Ahmed Mohammed, Irina Harris
,
Anthony Soroka, Naim Mohamed and Tim Ramjaun
Cardiff Business School, Cardiff University, Aberconway Building, Colum Dr, CF10 3EU, Cardiff, U.K.
Keywords: Supplier Selection, Green Development, Supply Chain Resilience.
Abstract: This paper presents an approach for evaluating and ranking suppliers with respect to their traditional, green
and resilience (TGR) characteristics. A set of criteria/sub-criteria were identified within a unified framework
and their relative importance weighted using the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) algorithm. In addition,
the suppliers were evaluated and ranked based on their performance towards the identified TGR criteria using
the fuzzy technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution (FTOPSIS) algorithm. The
applicability and effectiveness of the proposed approach was proved through a real case study by revealing a
comparatively meaningful ranking of suppliers. The study provides a noteworthy aid to management who
understand the necessity of building supply chain resilience while concurrently pursuing ‘go green’
responsibilities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The supplier selection decision-making process
represents a key activity in supply chain management
since purchasing expenses exceed fifty percent of all
firms’ costs (Mohammed et al., 2017a). Supplier
selection refers to a multi-criteria decision-making
problem in evaluating suppliers’ performance with
respect to several criteria in order to purchase
materials from the most appropriate source. Despite
the importance of price, other evaluation criteria
should be considered such as reliable delivery, which
will ultimately effect productivity and efficiency
within a production environment and therefore
overall costs. Dickson (1966) highlighted 23
parameters that can be used by decision-makers to
assess suppliers, Ha and Krishnan (2008) updated
these and suggested several additional criteria.
Nevertheless, the most prevalent traditional business
criteria are quality, cost, and delivery. Popular green
criteria include: environmental management systems,
resource consumption, eco-design and waste
management. Further supplier selection criteria can
be found in Weber et al. (1991); Govindan et al.
(2015); and Aissaoui et al. (2007).
Presently, there are ever increasing
responsibilities placed on companies to consider the
environmental impact of their supply chain activities
(Mohammed et al., 2017b and 2015; Konur et al.,
2016). Green supply chain management is the activity
of purchasing, producing, marketing and performing
various packaging and logistical activities that takes
into account environmental implications
(Mohamemd et al., 2017c). However, suppliers tend
to represent inevitable sources of external risk
(Rajesh and Ravi, 2015). Purchasing managers may
consider traditional and more recently green criteria
when assessing suppliers while neglecting resilience
(Kannan et al., 2015). Resilience is the capability of
the system to efficiently adapt an expected
disruptions and back to its normal process, is a vital
aspect of any supply chain management (Torabi et al.,
2015). Following an earthquake in Japan (2011),
Apple was unable to produce the iPad 2 due to lack of
flash memory and super-thin battery (BBC News, 18
Mar 2011) caused by an unanticipated disruption to
the supply chain. This particular event also
interrupted the automotive sector and retail supply
chains in the UK (Hall, 16 Apr 2010). Recently,
hurricane Sandy led to massive disruptions in US
supply chains (Torabi et al., 2015; Burnson, 30 Oct
2012). To protect their business, purchasing
managers should include resilience in to their
decision-making criteria (Torabi et al., 2015).
Resilience criteria is represented by a supplier’s
capability to cope with risk and unexpected events
more efficiently and quickly than other suppliers. The
current work considers resilience criteria identified
Mohammed, A., Harris, I., Soroka, A., Mohamed, N. and Ramjaun, T.
Evaluating Green and Resilient Supplier Performance: AHP-Fuzzy Topsis Decision-Making Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0006619902090216
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2018), pages 209-216
ISBN: 978-989-758-285-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
209

and analysed by Purvis et al. (2016). The latter
proposed a framework for the development and
implementation of a resilient supply chain strategy,
which illustrates the relevance of various
management paradigms. The authors considered four
pillars (enablers) as key factors to improve supply
chain resilience: redundancy, agility, leanness and
flexibility (RALF). However, visibility was
suggested as an essential resilience criterion by the
purchasing manager for our case study.
Since additional criteria, such as environmental
sustainability and resilience are paramount to
building a successful and competitive supply chain,
supplier selection complexity has increased. A novel
approach is required, which incorporates three main
criteria: traditional business, green and resilience.
Despite the significant quantity of research already
conducted around these topics, the vast majority of
current literature considers the green and resilience
aspects of supplier selection independently.
This paper addresses the knowledge gap by
proposing a unified supplier selection approach that
considers traditional, green and resilience criteria
simultaneously. The evaluation criteria were
identified from the literature and based on discussions
with the purchasing manager from our case study.
The development of this approach can be detailed into
three phases. In phase one, the main traditional, green
and resilience criteria and their sub-criteria were
identified in a unified framework. Phase two, AHP
was used to integrate judgments from a decision
maker with the purpose of determining the weights of
the criteria and sub-criteria. In the third phase,
FTOPSIS was applied to evaluate and rank suppliers
based on their TGR performance. The robustness of
the proposed approach is validated within a case
study for a manufacturing company and the work
contributed to providing a framework for the supplier
selection strategy, which incorporates traditional,
green and resilience criteria.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Previous studies on supplier selection consider
traditional criteria to be more extensive than the less
established, green supplier selection (Govindan et al.,
2015; Amindoust et al., 2012). Most Recently,
Govindan et al. (2015) reviewed published research
from 1997 to 2011 on MCDM and mathematical
modelling used for green supplier selection problems.
Shen et al. (2013) proposed a fuzzy approach for
evaluating the green suppliers. Büyüközkan and Çifçi
(2010) developed a fuzzy analytic network process
(ANP)-based approach within a multi-person
decision making scheme under incomplete preference
relationships. Kuo and Lin (2011) proposed an
integrated approach using ANP and DEA for green
supplier evaluation. Akman (2015) suggested a two-
step supplier-assessment framework to evaluate
green suppliers. Kannan et al. (2015) investigated a
green supplier selection problem in a plastic company
using a fuzzy axiomatic design approach. Govindan
and Sivakumar (2016) developed an integrated multi-
criteria decision-making and multi-objective linear
programming approach as an aid to select the best
green supplier. Songa et al. (2017) proposed an
integrated approach for evaluating suppliers with
respect to economic, green and social criteria using
the merit of pairwise comparison method in
determining relative importance, the strength of
decision making trial and evaluation laboratory
(DEMATEL) in manipulating the complex and
intertwined problems with fewer data, and the rough
number's advantage in flexibly dealing with vague
information.
Supply chain management includes a variety of
complex activities subject to disruptions caused by
unexpected incidents. Improving supply chain
resilience is crucial for managing potential
disruptions (Torabi et al., 2015). The reviewed
literature showed that research studies using
quantitative approaches to solve resilient supplier
problem are limited. Mitra et al. (2009) and Sawik
(2013) identified several pillars and criteria that
should be considered for selecting resilient suppliers.
Haldar et al. (2014) developed a fuzzy MCDM
approach for supplier selection considering the
importance degrees of specific attributes as linguistic
variables formulated by triangular and trapezoidal
fuzzy numbers. Torabi et al. (2015) proposed a fuzzy
stochastic bi-objective optimization model to solve a
supplier selection and order allocation problem to
improve the supply chain resilience under operational
and disruption risks. Sahu et al. (2016) proposed a
supplier evaluation decision support system using the
VIKOR method considering general and resiliency
criteria. Pramanik et al. (2016) presented a fuzzy
MCDM approach as an aid to developing a resilient
supplier selection activity. Klibi and Martel (2012)
formulated a mixed integer programming model for
handling supplier selection and order allocation
problem. Sawik (2013) designed a mixed-integer
programming model to solve a supplier selection
problem in a supply chain under disruption risks.
ICORES 2018 - 7th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
210
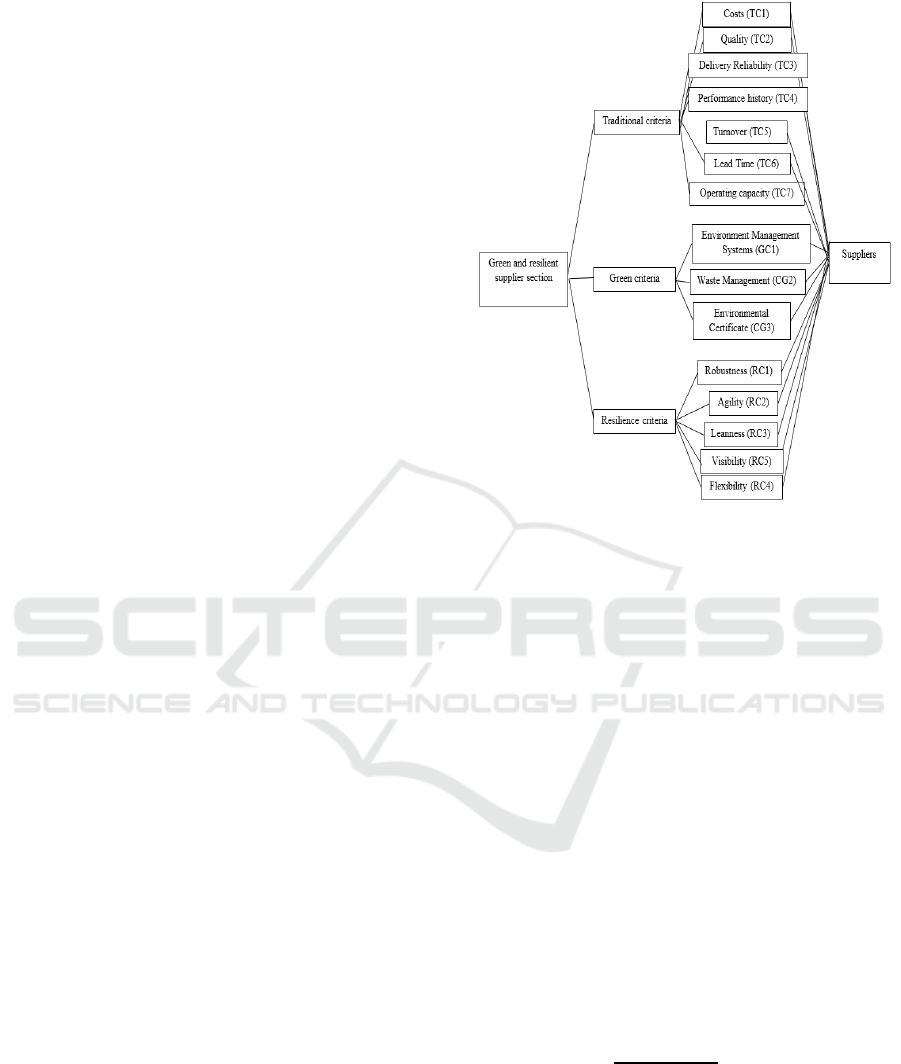
3 DEVELOPED GREEN AND
RESILIENT SUPPLIER
SELECTION APPROACH
A laboratory instrumentation Original Equipment
Manufacturer wants to develop a resilient supplier
selection approach for evaluating their current
suppliers in order to plan for unexpected events.
Additionally, the company is keen to take ownership
of their environmental responsibilities. This research
supports the company’s requirements through
development of a supplier selection approach to
facilitate evaluation and ranking of suppliers based on
their performance with respect to traditional, green
and resilience criteria. Figure 1 shows the hierarchical
supplier selection framework developed for this task.
The traditional sub-criteria include: cost, quality,
delivery reliability, performance history, turnover,
lead time, and operating capacity. The green sub-
criteria include: environmental management system,
waste management and environment related
certificate. The resilience sub-criteria include:
flexibility, leanness, agility robustness and visibility
(FLARV). AHP used linguistic expert assessment to
determine the importance weight for each criteria and
sub-criteria. FTOPSIS was then adapted towards
evaluating suppliers based on their performance
towards the criteria shown in Figure 1. Subsequently,
the ranking order of suppliers was determined based
on evaluation derived from FTOPSIS.
3.1 AHP
AHP is a multi-criteria decision making algorithm,
developed for considering both qualitative and
quantitative aspects of evaluation (Saaty, 1977). It
attempts to reduce complex decisions to a series of
pairwise comparisons and then reveals the final
weights. In this work, AHP was applied for
determining the importance weight for each TGR
criteria and sub-criteria. Table 1 shows the evaluation
scale in terms of linguistic variables that were used to
perform pairwise comparisons among TGR criteria
and sub-criteria. Decision makers need to give their
opinion about the importance of every criteria and
sub-criteria. AHP was implemented as follows:
Figure 1: Criteria and sub-criteria for the traditional, green
and resilient supplier selection.
1. Use a decision maker’s preference to build a pair-
wise comparison matrix (A) using the evaluation
scale shown in Table 1:
1,2 1,
2,1 2,
,1 ,2
1
1
; 1, 2, 3,..., ; 1, 2, 3, ...,
... ... ...
1
j
j
ii
aa
aa
A i I j J
aa
(1)
where I refers to the number of suppliers and J refers
to the number of criteria.
2. Sum each column of A as follows:
,
i ij
jJ
Column S a
(2)
3. Build the normalised decision matrix (R) by
dividing each value in matrix A by the sum of its
column:
S
i
A
R
Column
(3)
4. Determine the weight w
j
of each criterion by
calculating the average of its weight with respect
to other criteria:
Evaluating Green and Resilient Supplier Performance: AHP-Fuzzy Topsis Decision-Making Approach
211

Table 1: Evaluation scale in linguistic variables.
Scale
Linguistic Variable
1
Equally important (EI)
3
Weakly important (WI)
5
Strongly more important (SMI)
7
Very strongly important (VSI)
9
Extremely important (EI)
1
I
i
i
i
rowS
w
J
(4)
3.2 Fuzzy TOPSIS
Hwang and Yoon (1981) developed TOPSIS to select
an alternative based on its distance to the ideal
solution and the negative ideal solution. FTOPSIS is
an extension of TOPSIS developed by Chen (2006) to
handle the uncertainty in the linguistic assessment. In
this work, after determining the importance weight
for each green and resilient criteria and sub-criteria,
Fuzzy TOPSIS was applied to evaluate and rank
suppliers with respect to their TGR performance. It is
noteworthy to mention that fuzzy TOPSIS was used
rather TOPSIS to cope with uncertain evaluation of
some suppliers. Table 2 presents the linguistic
variables and the correspondent triangular fuzzy
numbers that were used to rank the alternatives
considering each criterion. Decision makers need to
give their opinions about the performance of every
supplier based on TGR criteria. FTOPSIS was
implemented as follows:
Eq. (6) is used to normalise the fuzzy decision
matrix to get the normalised decision matrix ( ):
~~
ij
nxm
Rr
(5)
where
~
222
,,
ij ij ij
ij
ij ij ij
iii
a n m
r
mmm
(6)
The weights of the criteria (w
j
) obtained from the
AHP approach need to be multiplied by the elements
of the normalised decision matrix (
~
R
) to form the
weighted normalised decision matrix (
~
V
).
~~
ij
nxm
Vv
(7)
where
~
ij
v
is obtained using the following equation:
~~
ij
ij
j
v r x w
(8)
The fuzzy positive and negative ideal solutions are
determined using Eqs. 9 and 10, respectively (Roy et
al., 2004).
~ ~ ~ ~
12
, ,...,
n
A v v v
(9)
~ ~ ~ ~
12
, ,...,
n
A v v v
(10)
The distance of supplier ‘I’ from the fuzzy positive
ideal solution (
i
d
) and the fuzzy negative ideal
solution (
i
d
) are calculated as follows:
~
~
, ;
,;
i v ij j
jn
i v ij j
jn
d d v v
d d v v
(11)
where
j
v
and
j
v
are fuzzy positive and negative
ideal points for criterion ‘j’, respectively.
Based on
and
ii
dd
, the fuzzy closeness
coefficient (CC) for each supplier is then determined
using Eq. 12. The supplier with the highest CC (varies
between 0 and 1) is selected as the best green and
resilient supplier.
i
ii
d
CC
dd
(12)
Table 2: Linguistic variables and their TFN used for
evaluating and ranking suppliers.
Linguistic variable
Triangular fuzzy number
Very low (VL)
(1, 1, 3)
Low (L)
(1, 3, 5)
Medium (M)
(3, 5, 7)
High (H)
(5, 7, 9)
Very high (VH)
(7, 9, 9)
~
R
ICORES 2018 - 7th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
212

4 APPLICATION: A REAL CASE
STUDY
In To validate the applicability and effectiveness of
the developed methodology, it was applied with a
manufacturing company (Company A, henceforth)
that design and produce thermal desorption and time-
of-flight mass spectrometry instrumentation in the
UK. Their products are used for a variety of
applications such as: environmental monitoring,
detection of chemical warfare agents, quality control
& safety of food products, aroma profiling and
environmental forensics. Company A aims to develop
a purchasing strategy that helps in evaluating their
current supplier with respect to green and resilience
performance in addition to the traditional business
criteria such as cost and quality. Company A aim to
meet their growth target by 2020, however, current
and projected turnover have not been revealed upon
the company’s request. Our novel approach to
supplier selection has been applied in this case study
to help the purchasing manager: (1) develop a unified
TGR purchasing strategy and (2) evaluate their
current supply chain resilience in term of suppliers’
performance towards the previously defined TGR
criteria (Figure 1).
The purchasing manager (PM) was invited to
select a number of suppliers to validate the proposed
approach in evaluating their performance towards the
identified criteria illustrated in Figure 1. The PM has
more than 18 years procurement experience. Two
deep discussions (each about 2 hours) were held to
explain, discuss and evaluate the TGR criteria, sub
criteria and five suppliers’ (S) performance.
In the first step, AHP was implemented to
determine the importance weight for each TGR
criteria and sub-criteria. Thus, the PM was invited to
perform a pairwise comparison among TGR criteria
and sub-criteria using the linguistic variables
presented in Table 1. A pair-wise comparison matrix
was built via the correspondence scale evaluation
(refer to Table 1) as shown in Table 3. Eqs.1-4 were
then applied to determine the importance weights of
each criteria and sub-criteria which are presented in
Table 4. According to the calculations shown in Table
4, the weight of traditional criteria is 0.263293; the
weight of green criteria is 0.051821; and the weight
of resilience criteria is 0.684886. The resilience
criteria obtained the highest weight followed by the
traditional and then green pillar. Thus, the resilience
criteria are deemed to be the most important
compared with the other traditional and green criteria.
The PM confirmed that the company’s current
strategy was to build a resilient supply chain rather
Table 3: Decision matrix among TGR criteria.
TGR criteria
Traditional
Green
Resilience
Traditional
1
9
1/5
Green
1/9
1
1/9
Resilience
5
9
1
than selecting suppliers according to performance
towards traditional criteria such as costs and quality.
After determining the importance for each TGR
criterion, fuzzy TOPSIS was implemented to obtain
the ranking order of suppliers based on their TGR
performance. The PM was invited for another
interview to evaluate the performance of selected
suppliers with respect to each sub-criterion using the
evaluation scale presented in Table 2. Table 5 shows
the linguistic evolution of suppliers towards their
TGR performance. Fuzzy TOPSIS was applied using
Eqs 5-12 to determine the matrix of normalized and
weighted normalized triangular fuzzy numbers in
addition to the positive ideal solution (
i
D
) and the
negative ideal solution (
i
D
). The closeness
coefficient (CC) for each supplier is determined by
the obtained distances using Eq. 12. Table 6 shows
the performance evaluation and rank of suppliers with
respect to each TGR criterion, which is represented
graphically, Figure 2. According to the obtained
results, S
2
revealed the highest TGR performance
with a closeness coefficient of 0.89373. Comparing
with the other suppliers the closeness coefficient of S
4
(0.733641), S
2
(0.489352), S
5
(0.432518) and S
3
(0.117511) were respectively in rank after S
1
.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work presents a unified traditional business,
green and resilient supplier selection approach. The
framework was developed by identifying traditional,
green and resilience criteria and sub-criteria. Two
steps were followed to evaluate and rank suppliers.
Firstly, AHP was applied to determine the importance
weight of each criterion and sub-criterion based on
the linguistic evaluation of a purchasing manager.
The AHP results indicate that the resilience criteria
are deemed the most important for company A,
followed by traditional and green, respectively.
Secondly, fuzzy TOPSIS was applied to reveal the
order ranking of suppliers based on their TGR
performance with respect to the importance weight of
each criterion and sub-criterion. Based on the
obtained suppliers’ performance, we recommended
that company A works with some of their suppliers
(e.g. S
3
and S
5
) to improve their resilience. The results
Evaluating Green and Resilient Supplier Performance: AHP-Fuzzy Topsis Decision-Making Approach
213
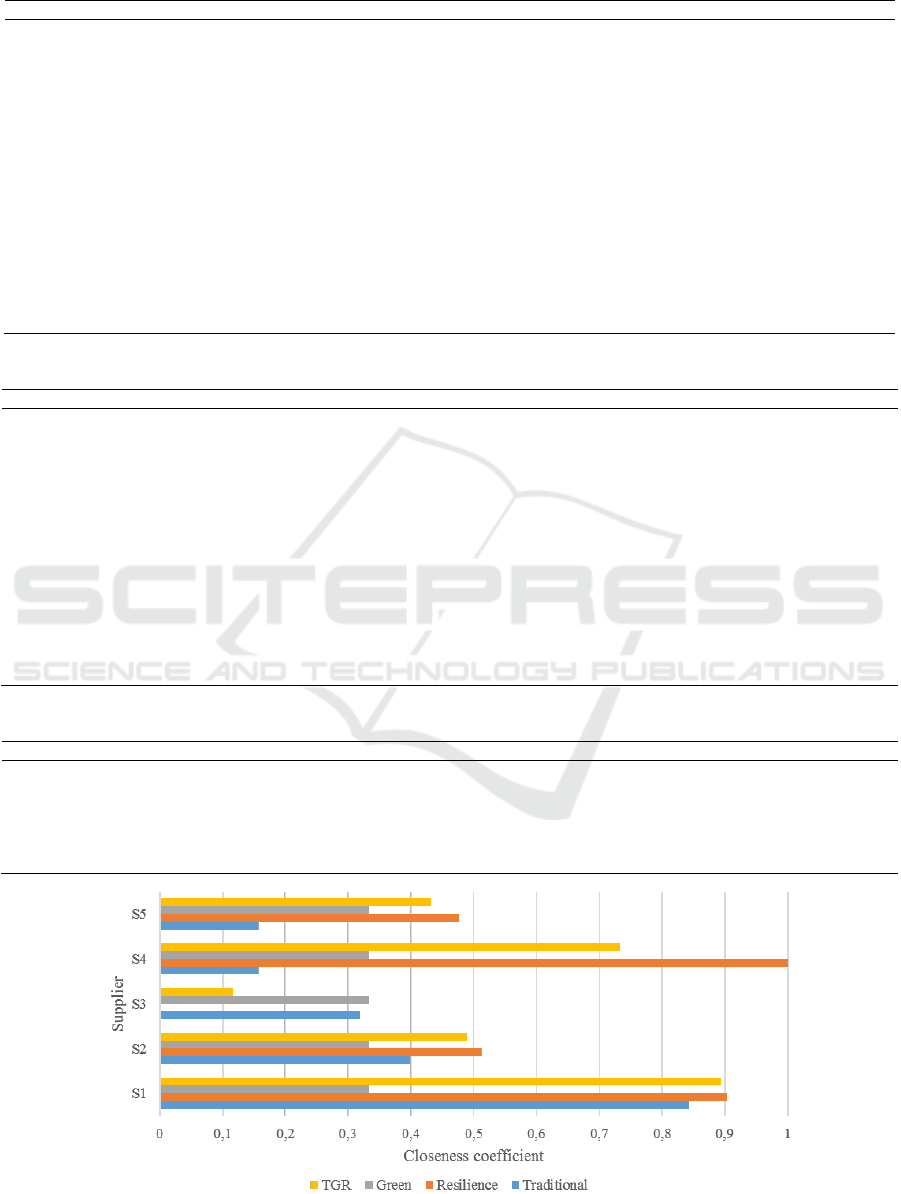
Table 4: Weights of TGR criteria and sub-criteria obtained by AHP.
Criteria
IW
Ranking
Sub-criteria
IW
Ranking
Traditional
0.263293
2
TC1
0.188584
2
TC2
0.148292
4
TC3
0.146552
5
TC4
0.02105
7
TC5
0.082984
6
TC6
0.250322
1
TC7
0.162216
3
Green
0.051821
3
GC1
0.481354
1
GC2
0.282937
2
GC3
0.235709
3
Resilience
0.684886
1
RC1
0.033343
5
RC2
0.192122
3
RC3
0.093336
4
RC4
0.429723
1
RC5
0.251476
2
Table 5: Evaluation of suppliers towards their traditional, green and resilience performance.
Criteria
Sub-criteria
S
l
S
2
S
3
S
4
S
5
Traditional
TC1
H
H
M
M
M
TC2
M
M
M
M
M
TC3
M
M
M
M
M
TC4
VL
L
M
M
M
TC5
H
L
M
L
L
TC6
M
M
M
M
M
TC7
H
M
M
M
M
Green
GC1
M
M
M
M
M
GC2
M
M
M
M
M
GC3
M
M
M
M
M
Resilience
RC1
M
M
M
H
L
RC2
H
H
M
M
L
RC3
M
M
M
L
L
RC4
H
M
L
H
L
RC5
L
L
L
M
L
Table 6: Closeness coefficient and distances from the positive ideal/negative ideal solutions related to suppliers.
S
1
S
2
S
3
S
4
S
5
i
D
0.008212
0.008212
0.068047
0.023736
0.042167
i
D
0.069065
0.069065
0.009061
0.065376
0.032138
CC
0.89373
0.489352
0.117511
0.733641
0.432518
rank
1
3
5
2
4
Figure 2: A graphical comparison of suppliers’ closeness coefficient performance with respect to TGR criteria individually.
ICORES 2018 - 7th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
214

demonstrate the applicability of the novel approach in
assisting the purchasing manager at company A to
produce a green and resilient purchasing strategy
through supplier evaluation.
The developed methodology can be applied to
other companies as a tool to measure the healthiness
of their supply chain in terms of resilience and green
performance. Furthermore, it mediates the
uncertainty in experts’ opinions through the use of
fuzzy evaluation.
Ongoing work includes the incorporation of social
criteria to those already studied here. Finally, the
authors are developing a multi-objective optimization
model to help decision makers in solving order
allocation problem with respect to TGR performance
of suppliers.
REFERENCES
Akman, G., 2015. Evaluating suppliers to include green
supplier development programs via fuzzy c-means and
VIKOR methods. Comput. Ind. Eng. 86, 69–82.
BBC News, 18 Mar 2011. Japan disaster: Supply shortages
in three months. BBC News. (accessed 11.02.17).
Bing, X., Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J., Chaabane, A., van der
Vorst, J., 2015. Global reverse supply chain redesign
for household plastic waste under the emission trading
scheme. J. Clean. Prod. 103, 28-39. Aissaoui, N.,
Haouari, M., Hassini, E., 2007. Supplier selection and
order lot sizing modeling: a review. Com. Oper. Res.
34, 3516–3540.
Burnson, P., 30 October 2012. Nation’s Supply Chains
Disrupted by Hurricane Sandy. Logistics Management.
(accessed 14.06.17).
Büyüközkan and Çifçi, 2010 G. Büyüközkan, G. Çifçi.
Evaluation of the green supply chain management
practices: a fuzzy ANP approach. Production Planning
& Control, iFirst (2010), pp. 1-14
Chen, C.T., Lin, C.T., Huang, S.F., 2006. A fuzzy approach
for supplier evaluation and selection in supply chain
management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 102, 289–301.
Dickson, G., 1966. An analysis of vendor selection systems
and decisions, J. Purch. 2(1), 5–17.
Govindan, K., Rajendran, S., Sarkis, J., Murugesan, P.,
2015. Multi criteria decision making approaches for
green supplier evaluation and selection: a literature
review. J. Clean. Prod. 98, 66–83.
Govindan, K., Sivakumar, R., 2016. Green supplier
selection and order allocation in a low-carbon paper
industry: integrated multi-criteria heterogeneous
decision making and multi-objective linear
programming approaches. Ann. Oper. Res. 238, 243–
276.
Ha, S.H., Krishnan, R., 2008. A hybrid approach to supplier
selection for the maintenance of a competitive supply
chain. Expe. Sys. with Appl. 34, 1303–1311.
Haldar, A., Ray, A., Banerjee, D., Ghosh, S., 2014. Resi-
lient supplier selection under a fuzzy environment. Int.
J. Manage. Sci. Eng. Manage. 9 (2), 147–156.
Hall, J., 16 Apr 2010. Volcanic Ash Cloud Leaves Shops
Facing Shortages of Fruit, Vegetables and Medicine.
The Daily Telegraph.
Hwang, C.L, Yoon, K., 1981. Multiple attribute decision
making: methods and applications. New York:
Springer-Verlag.
Kannan, D., Govindan, K., Rajendran, S., 2015. Fuzzy
axiomatic design approach based green supplier
selection: a case study from singapore. J. Clean. Prod.
96, 194–208.
Klibi, W.; Martel, A. Scenario-based Supply Chain
Network risk modeling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 223,
644–658.
Konur, D., Campbell, J.F., Monfared, J.A., 2016. Economic
and environmental considerations in a stochastic
inventory control model with order splitting under
different delivery schedules among suppliers. Omega,
71, 46–65.
Kuo, R.J., Y.J. Lin. Supplier selection using analytic
network process and data envelopment analysis.
International. Journal of Production Research (2011),
pp. 1-12iFirst.
Mitra, K.; Gudi, R.D.; Patwardhan, S.C.; Sardar, G.
Towards resilient supply chains: Uncertainty analysis
using fuzzy mathematical programming. Chem. Eng.
Res. Des. 2009, 87, 967–981.
Mohammed A. and Wang Q. 2015. Integrity of an RFID-
enabled HMSC Network. Proceedings of the Third
International Conference on Digital Enterprise and
Information Systems, Shenzhen, China, 2015a, 79-86.
Mohammed A. and Wang Q. and Li X. 2017a. Developing
a meat supply chain network design using a multi-
objective possibilistic programming approach. British
Food Journal, 119, 3, 690-706.
Mohammed, A. and Wang, Q., 2017b. The fuzzy multi-
objective distribution planner for a green meat supply
chain. International J. Pro Eco., 184, 47–58
Mohammed, A., Wang, Q., Alyahya, S. and Binnette, N.
2017c. Design and optimization of an RFID-enabled
automated warehousing system under uncertainties: A
multi-criterion fuzzy programming approach. The
International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing
Technology. 91 (5), 1661-1670.
Pramanik, D., Subhash, N., Haldar, A., Mondal, S.C.,
Naskar, S.N., Ray. A., 2017. Resilient supplier
selection using AHP-TOPSIS-QFD under a fuzzy
environment. International Journal of Management
Science and Engineering Management, 12 (1), 45-54.
Purvis, L., Spall, S., Naim, M. and Spiegler, V. 2016.
Developing a resilient supply chain strategy during
‘boom’ and ‘bust’, Production Planning & Control,
27:7-8, 579-590.
Rajesh, R.; Ravi, V. Supplier selection in resilient supply
chains: A grey relational analysis approach. J. Clean.
Prod. 2015, 86, 343–359.
Saaty, T. L. (1977). A scaling method for priorities in
hierarchical structures. Journal of Mathematical
Psychology, 15(3), 234–281.
Evaluating Green and Resilient Supplier Performance: AHP-Fuzzy Topsis Decision-Making Approach
215

Sahu, A.K., Datta, S., Mahapatra, S.S., 2016. Evaluation
and selection of resilient suppliers in fuzzy
environment: Exploration of fuzzy-VIKOR.
Benchmarking: An International Journal, 23 (3), 651-
673.
Sawik, T. Selection of resilient supply portfolio under
disruption risks. Omega 2013, 41, 259–269.
Shen, L., Olfat, L., Govindan, K., Khodaverdi, R. and
Diabat, A. (2013), “A fuzzy multi criteria approach for
evaluating green supplier’s performance in green
supply chain with linguistic preferences”, Resources,
Conservation and Recycling, Vol. 74 No. 1, pp. 170-
179.
Songa, W., Xub, Z. and Liu, H-C. 2017. Developing
sustainable supplier selection criteria for solar air-
conditioner manufacturer: An integrated approach.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 79 (2017)
1461–1471.
Torabi, S.A., Baghersad, M., Mansouri, S.A., 2015.
Resilient supplier selection and order allocation under
operational and disruption risks. Transportation
Research Part E 79, 22–48.
Weber, C.A., Current, J.R., Benton, W.C., 1991. Vender
selection criteria and methods, Eur. J. Oper. Res. 50 (1),
2–18.
ICORES 2018 - 7th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
216
