
The Knowledge of Level of Mosquitoes as Vector Diseases at
Community in the Village Tegal Rejo Sub-district Medan
Perjuangan Medan City
Merina Panggabean
1
, Lambok Siahaan
1
and Yoan Carolina Panggabean
1
1
Parasitology Department; Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Dr. Mansur No.5 Kampus Universitas
Sumatera Utara Medan Indonesia 20155
Keywords: Mosquito, Knowledge, Vector.
Abstract: The incidence of diseases caused by mosquitoes as vector transmission is still high in Indonesia.
Mosquito-borne diseases such as: dengue fever, chikungunya, filariasis, malaria and zika. Until now there
has been no elimination of diseases caused by mosquitoes as vector transmissions succeed. It is difficult to
break the life cycle of mosquitoes. For this reason, it is necessary to conduct research on the level of
community knowledge, especially mothers, against mosquitoes as vector transmitters. Data were obtained
giving questionnaires before and after counseling with quasi experiment study, pre and post test design.
Counseling was carried out for the intervention of mothers' knowledge with lectures and video in May
2018.The population of mothers who came to counseling were 100 peoples. The knowledge level before
intervention were good 12%, moderate 75% and less good 13%. After intervention the level of knowledge
were 62% and moderate 38%, nothing were less good. This research was conducted to mothers as
representatives of the community expected to prevent transmission of diseases by eradicating vectors in or
around the house.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vector is a living things that can transmit infectious
diseases between humans or animals to humans.
Mosquitoes are vectors that most often transmit
disease. Mosquitoes are also one of the animals that
can cause death in the world. The ability of
mosquitoes to carry and spread disease to humans
causes millions of deaths in each case (WHO,
2016). Mosquitoes as vectors can carry diseases
caused by viruses such as dengue fever,
chikungunya, yellow fever and encephalitis. As well
as diseases caused by nematodes such as filariasis
and protozoa such as malaria. The types of
mosquitoes that are the main vectors are usually
Aedes sp, Culex sp, Anopheles sp, and Mansonia sp
(Sembel, 2009).
These vectors are generally blood-sucking
insects that receive disease-causing microorganisms
while sucking human or animal blood, then
inserting these microorganisms in other humans
while sucking blood again. Globally, there are more
than 1 billion cases and more than 1 million deaths
due to vector-borne diseases (WHO, 2015). The
disease incidence which is carried by the mosquito
vector is caused by the high density of mosquito
vectors, especially in Indonesia (Ndione, 2007).
In the case of Chikungunya, there was a
significant decline in 2012 compared to the previous
3 years, namely 1831 cases. One of the factors
causing the decline of the Chikungunya case is the
presence of some regions that have not reported this
case. Clinical cases of filariasis showed an increase
from 2008 to 2011, but in 2012 clinical cases of
filariasis decreased by 163 cases. This is due to the
commencement of the government's filariasis
elimination program (WHO, 2016).
In 2012, the number of patients with dengue
hemorrhagic fever (DHF) in Indonesia was reported
as many as 90,245 cases with the number of deaths
of 816 people. There was an increase in the number
of cases in 2012 compared to 2011 of 65,725 cases
(WHO, 2016). In 2014 until mid-December
recorded DHF patients in 34 provinces in Indonesia
were 71,668 people and 641 of them died (Ministry
of Health Indonesia, 2015).
936
Panggabean, M., Siahaan, L. and Panggabean, Y.
The Knowledge of Level of Mosquitoes as Vector Diseases at Community in the Village Tegal Rejo Sub-district Medan Perjuangan Medan City.
DOI: 10.5220/0010103409360938
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
936-938
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Malaria is still a health problem in Indonesia. In
2015, WHO estimated there were around 214
million new cases of malaria with 438,000 deaths
worldwide. Of the total deaths due to malaria,
around 306,000 occurred in infants (Ministry of
Health Indonesia, 2015).
Mosquito control efforts are important to prevent
outbreaks from mosquito-borne diseases (WHO,
2015). To be able to carry out mosquito control we
must know how the mosquito's life cycle and the
environment as it can cause high mosquito breeding
(Service, 2012). In connection with this, mothers as
representatives of the community play a role in
controlling mosquitoes in house and around the
house. For this reason, research on the level of
knowledge of mothers towards mosquitoes as a
vector of diseases is carried out.
2 METHODS
This study was a quasi-experimental with pre and
post test design. Where this study was conducted by
looking at differences in knowledge before and after
being given counseling with the same material
questionnaire. Counseling here is an intervention for
mothers as respondents representatives of the
community against mosquitoes as vector
transmitters by giving lectures and video screenings.
Counseling is carried out on May 2018 at the office
of the Tegal Rejo Village Head, Medan Perjuangan
District, Medan City.
2.1 Population
The population of this study were 100 mothers as
Respondents who were representatives of their
respective environments. There are 15
neighborhoods in this village. Data collection was
conducted by interview using a questionnaire
containing 20 questions given before and after
counseling. All questions in the questionnaire have
been tested for their validity and reliability. Each
question has a predetermined value. The level of
knowledge consists of 3 categories, namely: good if
75% (> 15 questions), moderate if 40% -75% (8-14
questions) and less good if < 40% (< 7 questions) of
the answers answered correctly.
2.2 Data Analysis
The data from the questionnaires before and after
counseling were answered by the respondents, then
data processing is carried out. Univariate analysis is
done to explain the frequency distribution of each
variable and presented in table.
3 RESULTS
The questionnaires after and before counseling
were analyzed in this study. The number of 100
respondents was attended for this study. Table 1
presents the characteristics of the respondents.
Table 1: Characteristics of respondents.
Variabel f %
Age (yrs)
< 30 6 6
31-40 33 33
41-50 23 23
>50 38 38
Ethnicit
y
Java 42 42
Batak/Mandailin
g
41 41
Mala
y
11 11
Minang 3 3
Sunda 3 3
Education
Elementary school 7 7
Middle school 22 22
High school 64 64
Colle
g
e7 7
Jobs
Housewife 97 97
Teache
r
3 3
Knowledge of mosquiotoes as vector diseases
can be know when respondents answer the
questionnaires correctly. Answered correctly before
and after intervention can be seen on table 2.
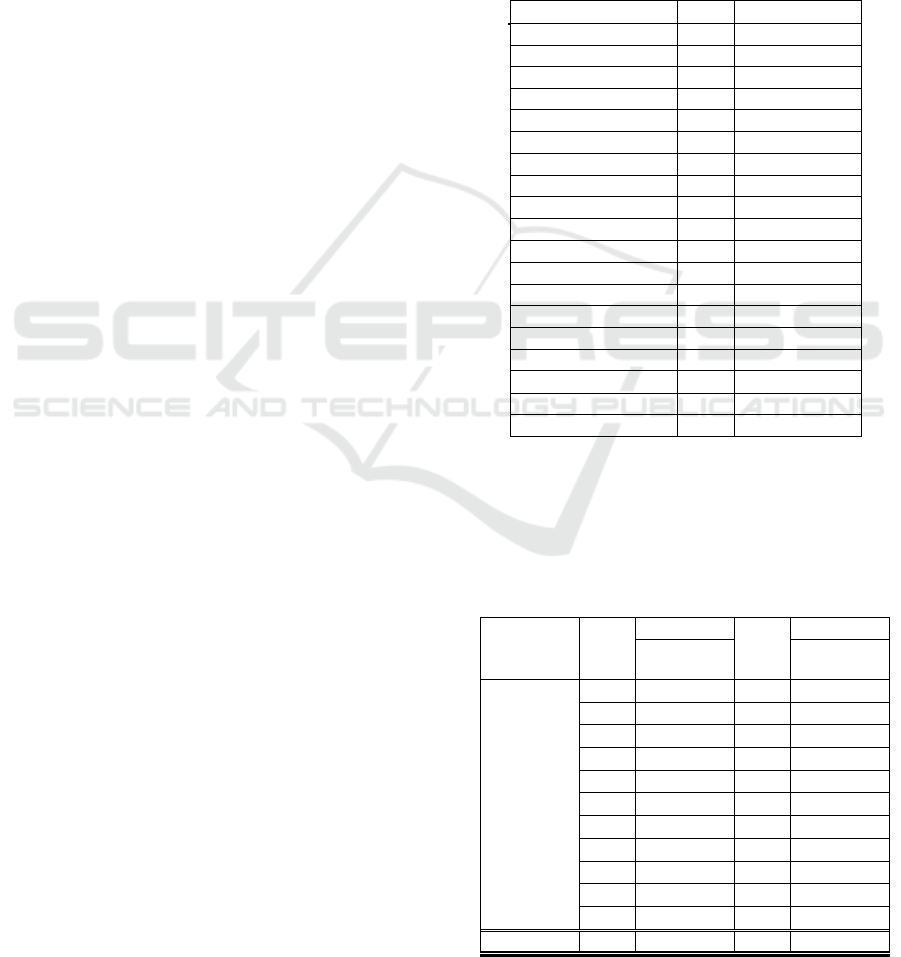
Table 2: Frequency of distribution answered correctly
before and after intervention.
Before Afte
r
f
Numbe
r
of
res
p
ondents
f
Numbe
r
of
res
p
ondents
Answer 7
13
0
0
Correctl
y
8
10
8
3
9
6
9
7
10
9
10
7
11
12
11
3
12
11
12
7
12
16
13
10
14
13
14
1
15
4
15
20
16
6
16
39
17 0 17 3
Total 100
100
100 100
The Knowledge of Level of Mosquitoes as Vector Diseases at Community in the Village Tegal Rejo Sub-district Medan Perjuangan Medan
City
937

The level of knowledge good, moderate and less
good classified from before and after intervention of
the answers correctly (table 3.)
Table 3: Frequency of distribution the knowledge of level
before and after intervention.
Before f Afte
r
f
(%)
(%)
The
knowledge Goo
d
12
Goo
d
62
level Moderate
75
Moderate
38
Less
Goo
d
13
Less Goo
d
0
Total
100
100
4 DISCUSSION
The results obtained showed that there were
variations in the characteristics of respondents based
on age, ethnicity and education.
It can be seen that out of 100 respondents, the
highest number is > 50 years old, with Javanese
ethnicity, Hight School education and generally
housewives (table 1). In general, someone with a
higher education will have a broader knowledge
compared to lower education (Notoatmodjo, 2005).
Table 2, shows that out of the 20 questions
given, the correct answers before the intervention
were 7 questions at 10 respondents and the most
were 16 questions in 6 respondents. After being
given intervention the questions correctly answered
became 17 questions in 3 respondents. Here it can be
seen that respondents education influences the
absorption of an intervention (Notoatmodjo, 2005).
The intervention by lectures and video screenings
interesting for them and become increase answered
correctly.
Interventions on respondents are very useful.
This can be seen in table 3, where before the
intervention the level of knowledge was less good as
13%. After being given this unfavorable
intervention, there was no more, good knowledge
increased by 50% (before intervention 12 % and
after intervention became 62%). While the
knowledge moderate before intervention 75% were
reduced to 38%. Good and moderate knowledge was
influenced by several factors, such as information
sources and educational factors and environmental
factors.The more information was obtained, it would
influence the level of one's knowledge
(Notoatmodjo, 2005 and Notoatmodjo, 2007). From
table 3 it can also be seen that respondents have not
been aware and less concerned about the dangers of
mosquitoes as vector transmitters in their homes
before intervention.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The level of knowledge mothers as respondents at
community representatives before the intervention is
still not good and the most is the level of moderate
knowledge.After intervention,the level of knowledge
of mothers as respondents increased more well
compared to the moderate and there was no more
less good for mosquitoes as a vector of diseasese.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was part of Community Service
supported by the Community Service Universitas
Sumatera Utara from Grand NON
PNBP
Universitas Sumatera Utara Number:
172/UN5.2.3.2.1/PPM/2018.
REFERENCES
Ministry of Health Indonesia., 2015. Health
ProfileIndonesia. doi 351 077 Indonesia.
Ndione, R. D., Omar, F., and Ndiaye, M., 2007. African
Jof Biotech, 6 (24) pp 2846-54.
Notoatmodjo, S., 2005. Metodologi Penelitian
Kesehatan. Edisi revisi. Jakarta. PT Rineka Cipta.
Notoatmodjo, S., 2007. Promosi Kesehatan dan Ilmu
Perilaku. Edisi revisi. Jakarta. PT Rineka Cipta.
Sembel, D., 2009. Medical Entomology. Yogyakarta.
Andi Press.
Service, M. 2012. Medical Entomology for Students,
United Kingdom, Cambridge, University Press, Fifth
Edition,.
WHO. 2015. accessed 8 June 2017 available at
http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/vector_ecolog
y/mosquito-borne-diseases/en/
WHO. 2016. accessed 8 June 2017 available at
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs387/en/
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
938
