
Standardization and Phytochemoical Screening of Syzygium
polyanthum Wight Leaf and Myrmecodia pendans Simplicia
Tri Widyawati
1*
, M. Aron Pase
2
, Milahayati Daulay
3
, Imam Bagus Sumantri
4
1
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutic, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155,
Indonesia
2
Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
3
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia8
4
Department of Pharmacy Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20222, Indonesia
Keywords: Syzygium polyanthum, Myrmecodia pendans, standardization, phytochemical, simplicia.
Abstract: Syzygium polyanthum Wight (SP) leaf and Myrmecodia pendans (MP) have been widely reported to have
beneficial pharmacological activites. To obtain consistent and reliable results from preparations derived from
medicinal plants, preparation including standardization and extraction process is important. The present study
aims to determine the yields of standardization and phytochemical screening of (SP) and MP (MP) simplisia.
Standardization of SP and MP showed as follows: total water : 8.61.13% and 9.2 1.13%, total water soluble
simplicia 10.2 0.57% and 35.4 7.8%, total ethanol soluble simplicia 25.6 1.15% and 12.3 1.52% and
total ash 0.981.01% and 15.2 2.69% respectively. Both simplicia consisted of alkaloid, tannin, saponin,
triterpene/steroid, flavonoid and glicosyde.
1 INTRODUCTION
Syzygium polyanthum Wight (SP) is one of medicinal
plants that has been widely investigated to elucidate
its benefit pharmacological activity such as
antidiabetic and antioxidant (Widyawati et al, 2015;
Widyawati et al, 2016). Myrmecodia pendans (MP),
an epiphytic plant that belonging of Hydophytinae
(Rubiceae) family (Sudiono et al, 2015), is originated
of local society in Papua island (Gartika et al, 2018).
Various diseases including cancer, tumors, gout,
diarrhea and diabetes have been claimed can be cured
by this plant (Supriatno, 2014). Standardization is a
crucial step for the development of a consistent
biological activity, chemical profile, or simply a
quality assurance program for production and
manufacturing of herbal drugs preparation of any
herbal formulation (Bajpai et al, 2012). The present
study aims to compare the standardization of SP and
MP.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Syzygium Polyanthum Leaves and
Myrmecodia Pendans Collection
and Preparation
Syzygium polyanthum Wight (SP) leaves were
collected from Titi Kuning Medan, Indonesia. The
fresh leaves were washed in running water and dried
in temperature room. The dried leaves then were
ground into powder. Dried of Myrmecodia pendans
(MP) were supplied from Fakfak, West Papua.
Similar procedure as SP was conducted to obtain MP
simplicia
2.2 Standardization and Phytochemical
Screening Procedures
Standardization of both simplicia including
determination of total water, total water soluble ash,
total ethanol soluble ash and total ash was conducted
based on “Materia Medika Indonesia (MMI)”
(Depkes RI, 1995). Qualitative phytochemical
screening to trace alkaloida, glycoside, saponin was
114
Widyawati, T., Pase, M., Daulay, M. and Sumantri, I.
Standardization and Phytochemoical Screening of Syzygium polyanthum Wight Leaf and Myrmecodia pendans Simplicia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010099801140116
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
114-116
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
based on MMI as well, while procedure by
Farnsworth (1996) was used to identify the presence
of tannin, flavonoid, steroida/triterpenoida and
glycoside.
3 RESULTS
Table 1 showed that the percentage of total water of
both SP and MP was almost comparable ie
8.61.13% and 9.21.13% of each. Total water
soluble ash of MP (35.4%) was higher than SP
(10.20.57%). Total ash of MP (15.22.69%) was
also higher than SP (0.981.01%). Total ethanol
soluble ash of SP (25.61.15%) was higher than MP
(12.31.52%).
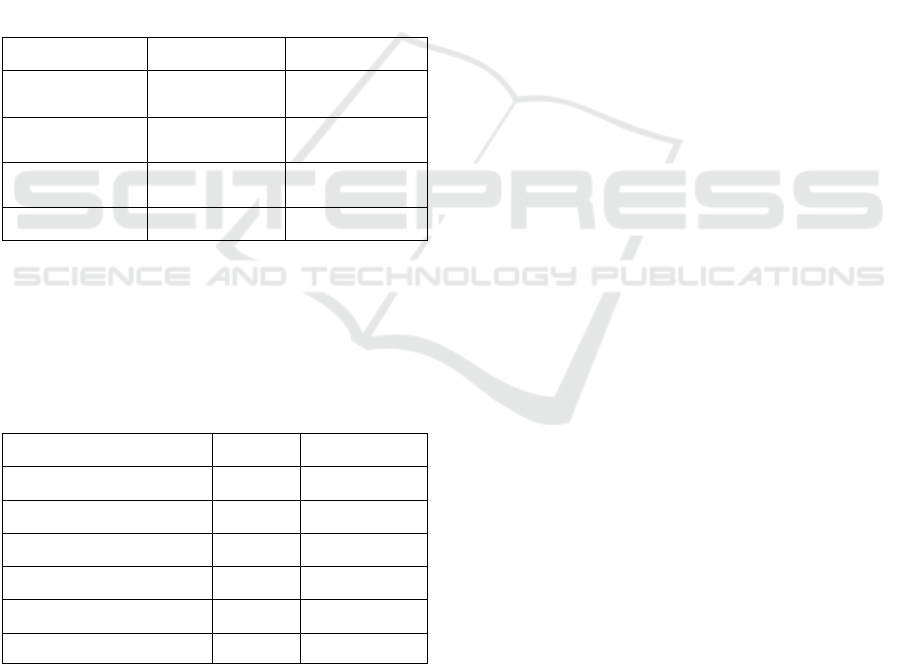
Table 1: Standardization of Syzygium polyanthum
(Wight)(SP) leaf and Myrmecodia pendans (MP) simplicia
SP (%) MP (%)
Total water 8.6 1.13 9.2 1.13
Total water
soluble simplicia
10.2 0.57 35.4 7.8
Total ethanol
soluble simplicia
25.6 1.15 12.3 1.52
Total ash 0.98 1.01 15.2 2.69
Phytochemical screening of SP and MP simpicia
traced the presence of alkaloid, tannin, saponin,
triterpene/steroid, flavonoid and glycoside (Table 2).
Table 1: Phytochemical screening of Syzygium polyanthum
(Wight)(SP) leaf and Myrmecodia pendans (MP) simplicia
Chemical class SP MP
Alkaloid (+) (+)
Tannin (+) (+)
Saponin (+) (+)
Triterpene/Steroid (+) (+)
Flavonoid (+) (+)
Glycoside (+) (+)
Plants are valuable for modern medicine development
(Hariharan and Subburaju, 2012). Standardization of
medicinal plant under development plays a very
important role in identifying its purity and quality
(Ahmad et al, 2013). According to Shalija and Banji
(2014) the macroscopic and microscopic description
of a medicinal plant, the degree of purity of such
materials should be carried out before any studies are
undertaken.
The total water content determines the stability of the
extract and the subsequent formulation. The
percentage of total water of both SP (8.61.13%) and
MP (9.21.13%) that below 10% were in the normal
level. Water content in extract less than 10% aims to
avoid the rapid growth of fungus in the samples.
Determination of water- and ethanol soluble extract is
a classical approach to estimate the level of active
compounds based on the polarity properties. Through
the determination can be calculated the percentage of
polar to non polar in the samples. The sum of water
soluble extract and ethanol soluble extract should not
be more than 100%. The presents study showed that
the total water soluble simplicia of MP (35.47.8%)
was higher than SP (10.20.57%). Thus, the total
ethanol soluble ash of SP (25.61.15%) was higher
than MP (12.31.52%). The present study assumed
that simplicia of MP was more polar than SP.
The present study identified the presence of following
chemical compounds ie alkaloid, tannin, saponin,
triterpene/steroid, flavonoid and glycoside. This
result supported the previous study that reported the
similar compounds were found in both plants.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Standardization of SP and MP simplicia meets MMI
criteria. Both simplicia of SP and MP contained of
alkaloid, tannin, saponin, triterpene/steroid, flavonoid
and glycoside acetate.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ministry of
Research and Technology and Higher Education
Republic of Indonesia, Research and Community
Service, Universitas Sumatera Utara for supporting
this study (DRPM 2018
No.263/UN5..2.3.1/PPM/KP-DRPM/2018).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Standardization and Phytochemoical Screening of Syzygium polyanthum Wight Leaf and Myrmecodia pendans Simplicia
115

REFERENCES
Ahmad, T., Singh, S., B., Pandey, S., 2013. Phytochemical
screening and physicochemical parameters of crude
drugs: A brief review. International Journal of Pharma
Research & Review. 2(12), 53-60.
Bajpai, R., Jain, N., Pathak, A., K., 2012. Standardization
of ethanolic extract of Cucurbita maxima seed. Journal
of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 92-95.
Depkes RI., 1995. Materia Medika Indonesia. Jilid VI.
Jakarta: Departemen Kesehatan RI. 300-306, 321, 325,
333-337.
Farnsworth, N., R., 1996. Biological and phytochemical
screening of plants. Journal of Pharmaceuticals
Science. Chicago: Reheis Chemical Company 55(3).
1996; 247-268.
Gartika, M., Wartadewi, Mariam, M., S., Kurnia, D., Satari,
M., H., 2018. Antibacterial of terpenoid: a from sarang
semut (Myrmecodia pendans) against streptococcus
mutans. International Journal of ChemTech Research.
11 (01), 228-233.
Hariharan, P., Subburaju, T., 2012. Medicinal plants and
its standardization – A global and industrial overview.
Global Journal of Medicinal Plant Research. 2012;
1(1): 10-13.
Shailaja, V., Banji, D., 2014. Evaluation of standardisation
parameters, pharmacognostic study, preliminary
phytochemical screening and in vitro antidiabetic
activity of Emblica officinalis fruits as per WHO
guidelines. Journal of Pharmacognosy and
Phytochemistry. 3(4).
Sudiono, J., Oka, C., T., Trisfilha, P., 2015. The scientific
base of Myrmecodia pendans as herbal remedies. Br J
Med Medic Res. 8(3), 230-237.
Supriatno., 2014. Antitumor activity of Papua’s
Myrmecodia pendens in human oral tongue squamous
cell carcinoma cell line through induction of cyclin-
dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kp1 and suppression of
cycklin E. J of Cancer Res and Ther. 2014; 2, 3: 48-53.
Widyawati, T., Yusoff, N., A., Asmawi, M., Z., Ahmad, M.,
2015. Antihyperglycemic effect of methanol extract of
Syzygium polyanthum (Wight.) leaf in streptozotocin-
induced diabetic rats. Nutrients. 7(9), 7764-7780.
Widyawati, T., Roslan, N., A., B., Yusoff, N., A., Asmawi,
M., Z., Ahmad, M., 2016. The evaluation of
antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of
Eugenia polyantha leaves extracts. International
Journal of ChemTech Research. 465-471.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
116
