
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous
Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water
Vapour
Susilawati
1,2
, Anwar Dharma Sembiring
1
, Fransiskus Waruwu
1
, and Siti Khanifah
1
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155,
Indonesia
2
Pusat Unggulan Inovasi Green Chitosan dan Material Maju, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: Clay, Active Charcoal, Porous Ceramic, and Water Vapour Filter.
Abstract: Have made a porous ceramic which was formed by clay and active charcoal with casting technique. The clay
which was used comes from the village Iraonogeba regency of Moroó in West of Nias. The active charcoal
which is used is active Aquasorb® 1000. The clay and active charcoal sifted with the sieve mesh 200. Then
the clay wa activated chemically using the solution H
2
SO
4
6% and physically can be activated at a temperature
of 300
0
C. Ceramic was formed by the technique of slip casting with comparison of variation of clay: charcoal
active 100% : 0 percent ; 90% : 10% ; 80% : 20% ; 70% : 30% and 60% : 40%. The ceramics was sintering
with sintering temperature 1000
0
C with variation of holding time 2 hours ; 3 hours and 4 hours. Ceramics
characterized to get the value of mechanical properties (pressure and hardness); the size of the diameter of the
pores, womb elements (SEM-EDX) and the value of the water vapour adsorption. The results of this
characterization shows that the optimum variations there are on the mixtures of clay and active charcoal 80%
: 20% with a holding time of 2 hours with pressure = 9.8 MPa and hardness = 184,73 MPa ; the size of the
diameter of the pores on average = 8,606 µm and womb elements (EDX) namely elements O = 58,11% ; Si
= 24,04% ; Al = 12,33% ; Na = 3,06% ; K = 2.51% ; Ca = 2.22 % ; Fe = 2.01% ; Mg = 1.60 percent and C =
1.54%. water vapour adsorption test shows the value of the maximum hydrogen concentration passed =
61,87% on minutes- 77 with maximum output voltage = 3.09 Volts on minutes 98.
1 INTRODUCTION
Has been widely known that the pottery is one of the
first artificial material made by human beings as a
result of burning the clay in the fire to produce
artificial stone (Buys and Oakley, 2014) clay that
burned in the fire was then known as ceramics.
Ceramics have some attractive properties compared
to metals and poymers, is make them useful for
specific applications. Their physical properties have
been utilized for many applications. In other
applications their mechanical properties acres
Washington (Munz and Fett, 2013). Now ceramic
products has been expanded and has a wide range of
variation one of the porous ceramic. Porous Ceramic
is a component of the glomerular filtration which is
very useful in various applications and is designed to
eliminate concentrate grade which has the size of the
micrometer to nanometer from various fluid. Whereas
total and the distribution of the size of the pores is the
most important aspect of the porous media and
effected on most of the characteristics of the porous
media such as elasticity and mechanical properties,
the movement and the flow of the fluid (Kuila and
Prasad, 2013). Whereas the total important to
improve permeability and high surface area provided
for the adsorption of the vapour of gas (Prenzel et al,
2014). The way of filtering can be consist of the
surface filtration and the inside filtration (cake
filtration) ) (Hammel et al, 2014).
Adsorption as surface filtration occurs when a
solid surface left open to gas or fluid, which is defined
as material enrichment or a rise in the density of the
liquid in the region around the interface (Rouquerol
et al, 2013). Ceramic Adsorption to gas occurs on the
pores of the ceramic surface until the condition where
1062
Susilawati, ., Sembiring, A., Waruwu, F. and Khanifah, S.
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water Vapour.
DOI: 10.5220/0010098410621069
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
1062-1069
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
the pores is fully charged by the gas or in other words
is on the state of the saturated.
Mechanical characteristics such as a pressure and
hardness is one of the nature of the material that is
very important. Various studies have previously
using the mixture of clay with carbon (active carbon/
active charcoal) (Phonpuak, 2012; Sarkar, 2012; Shen
et al., 2014; Wang, 2013; Yates, 2012). (Susilawati
et. al., 2017) has studied the use of natural zeolite with
cocoa skin filler as a water vapor filter in the
electrolysis process
In this experiment a porous ceramic as water
vapour filter characterised the nature of the
mechanism made from clay and active charcoal that
have pores of that very much spread in all parts of the
ceramics, which eventually produce ceramic that is
weak with the mechanical nature of the weak. This is
the main problem of this experiment. Porous ceramic
needed not only have the nature of a good physic but
must also have a good mechanical nature. Mechanical
nature which is tested in this experiment is a pressure
and hardness. The pressure of ceramics tested using
Maekawa Testing Machine Tokyo Japan Type MR-
20-CT while hardness of ceramics tested using
Hardness Tester Matsuzawa Seiki Co,LTD No, 71C4.
After strong mechanics characterised, ceramics
porous structure will further be observed morphology
surface.
The size of the pores and elements analysis using
SEM EDX Zeiss types. For applications, ceramics
will be tested for filtering the water vapor using the
filter KIT is equipped with a hydrogen sensors
TGS821.
2 EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
Porous Ceramic is made from clay and active
charcoal. Clay which is used comes from the village
Iraonogeba, Regency of Moroó in West of Nias and
the active charcoal which is used is active Aquasorb®
1000 charcoal. The clay and active charcoal sifted
with the sieve mesh 200. The clay activated
chemically using the solution H
2
SO
4
6% and
continued with the activation of physics at a
temperature of 300
0
C. Ceramic is formed with the
technique of slip casting with comparison of
variation of clay mixtures : active charcoal 100% : 0%
; 90% : 10% ; 80% : 20% ; 70% : 30% and 60% : 40%.
Ceramics were sintering with sintering temperature
1000
0
C with variation of holding time 2 hours ; 3
hours and 4 hours. Ceramics characterised to get the
value of mechanical properties (pressure and
hardness); the size of the diameter of the pores,
unsure elements (SEM-EDX) and the value of the
water vapor adsorption.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Mechanical Test
The results of the mechanical test of porous ceramic
is shown in the Figure 1 and Figure 2.
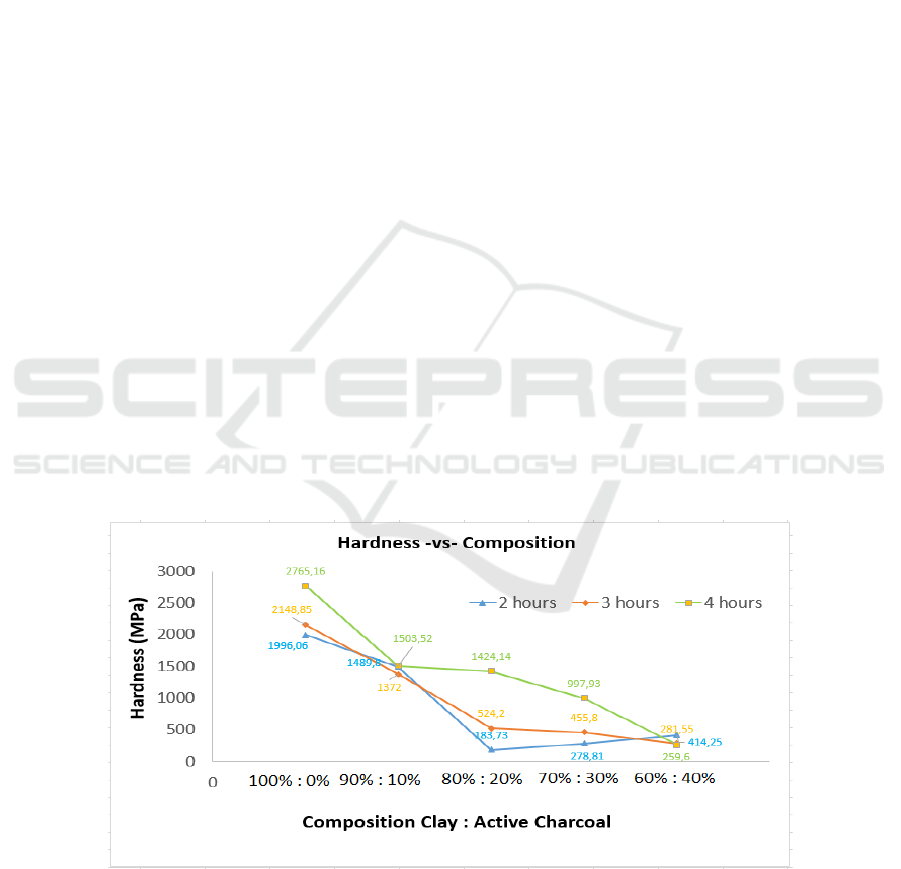
Figure 1 : Chart of Hardness VS Composition.
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water
Vapour
1063
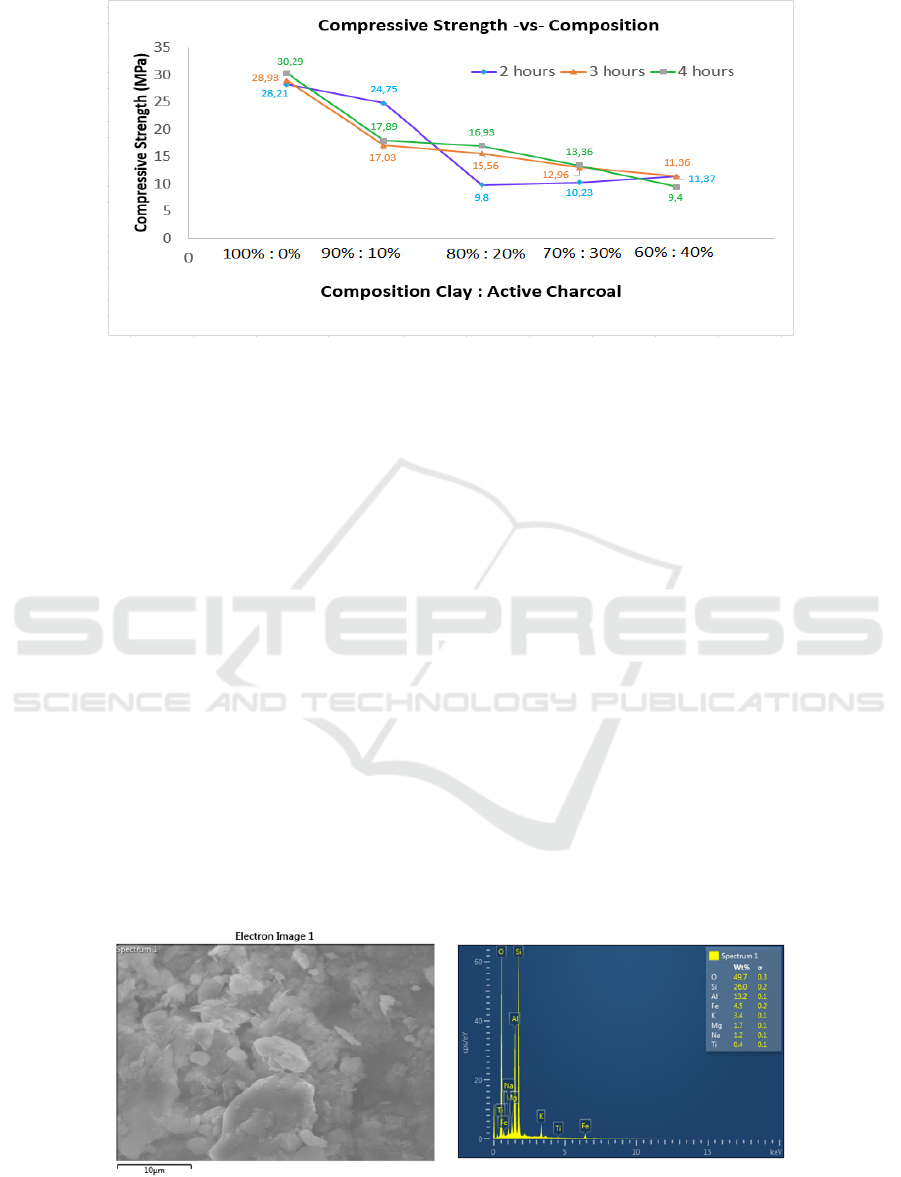
Figure 2 : Chart of Compresive Strength VS Composition.
From the results of compressive strength and
hardness test can be taken from the following
conclusion that ceramics which is form by clay and
active charcoal have strong value of compressive
strength and hardness that maximum at mixed
variations 90% : 10 % with holding time 4 hours (due
to the variation of a mixture of 100% : 0% do not have
a mixture of active charcoal in it) while the lowest
value is on the variation of a mixture of 80%:20%
with holding time 2 hours. But the desired porous
ceramic is ceramic that have many pores to be able to
accommodate the water vapor when doing the
filtration rate or in other words due to the porous
ceramic required have pores then by itself the value
of mechanical nature compressive strength and
hardness) will be low (Yuan, et al, 2016).
Therefore, then the optimum ceramic on this trial is
on ceramics mixed variations 80% : 20% with a
mixture of holding time 2 hours with pressure value
= 9.8 MPa (Figure 1) and value of violence = 184,73
MPa (Figure 2) while for comparison taken ceramics
with the value of the mechanical properties that high
on the variation of a mixture of 90% : 10% with a
holding time of 4 hours with strong value press =
17.89 MPa and the value of hardness = 1503,52 MPa
or 1,50352 GPa. In the Figure can also be seen that
the addition of active charcoal is on a mixture of
ceramic coating will reduce the value of mechanical
properties (either hardness or compressive strength)
where the value of the best mechanical properties of
ceramics found in a mixture of 100% : 0% without
adding active charcoal and the value of the lowest
mechanical nature there is on a mixture of 60% : 40%.
Based on previous research reference (Yuan, et al,
2016) can be seen that the ceramic that is produced
has a worth compressive strength between 13,72±2.2
- 43.5±3.3 MPa and also on the research (Yalcin and
Sevinc, 2000) hardness of ceramics has a value
between 0.79±0.02 - 8.25±0.09 GPa. So when
compared to the ceramic coating on this research is
worthy said as a porous ceramic.
3.2 SEM-EDX
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
1064
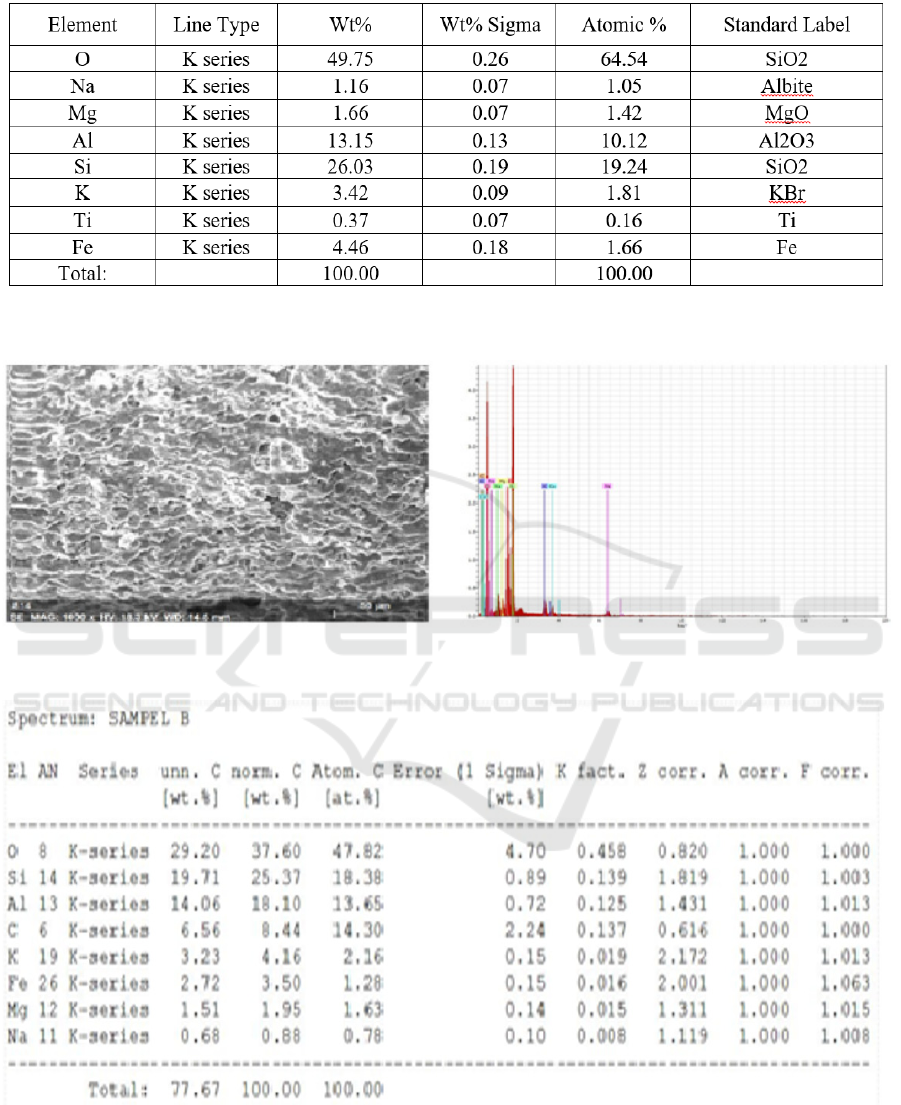
(a)
(b)
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water
Vapour
1065
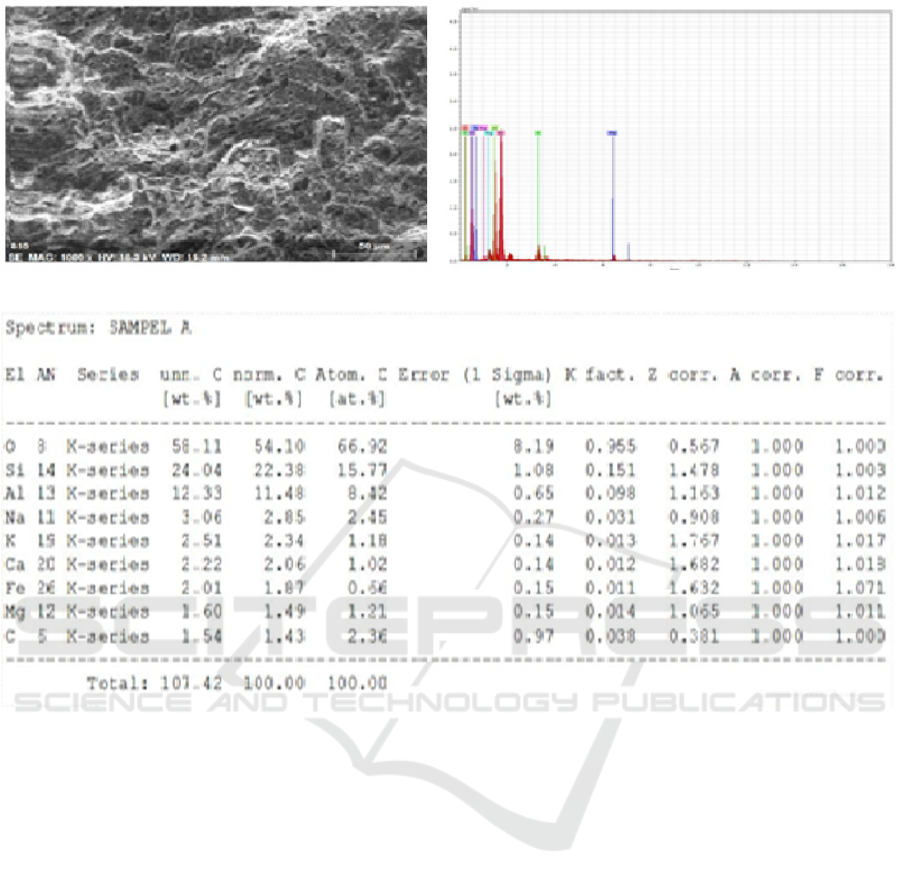
(c)
Figure 3 : SEM - EDX test results (a) clay without charcoal (b) clay: activated charcoal with 80%: 20% mixed variation, with
a holding time of 2 hours (c) clay: activated charcoal with 90%: 10% mixed variation, with a holding time of 4 hours.
From the observations of the morphology of the
ceramic surface can be used as an example of 80%:
20% mixture with a holding time of 2 hours has larger
and more pores compared to 90%: 10% mixture with
a 4 hour holding time which has pores which is far
less and not evenly distributed.
While the results of the analysis using EDX can
be used to mix 80%: 20% with a holding time of 2
hours which is equal to = 58.11% compared to a
mixture of 90%: 10% with a 4 hour holding time of =
29, 20% where oxygen indicates that the porosity (eg
oxygen from free air trapped in
the pores) in the
80%: 20% Mixture with 2 hours holding time is far
more than the 90%: 10% mixture with a 4 hour
holding time. When compared to the concentration of
oxygen in clay soil that has not been activated it can
be seen the amount of oxygen in the mixture of 80%:
20% with a holding time of 2 hours compared to
before the mixed clay is 90%: 10% with holding time
4 hours before clay is activated.
This reinforces that the 80%: 20% mixture with a 2
hour holding time is a better mixture.
From the reading of EDX elements, it can also be
seen that the content of Ti in clay that was previously
read by 0.37% was no longer found in 80%: 20%
mixture with a holding time of 2 hours and a mixture
of 90%: 10% with a holding time of 4 hours. This
shows that chemical activation and technology can
eliminate impurities but can also increase the surface
area and porosity of raw clay (Toor et al, 2015). In
addition, SEM-EDX also measured pore diameters at
3 different pores . Pore diameter measurements using
SEM EDX are shown in the following figure with
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
1066
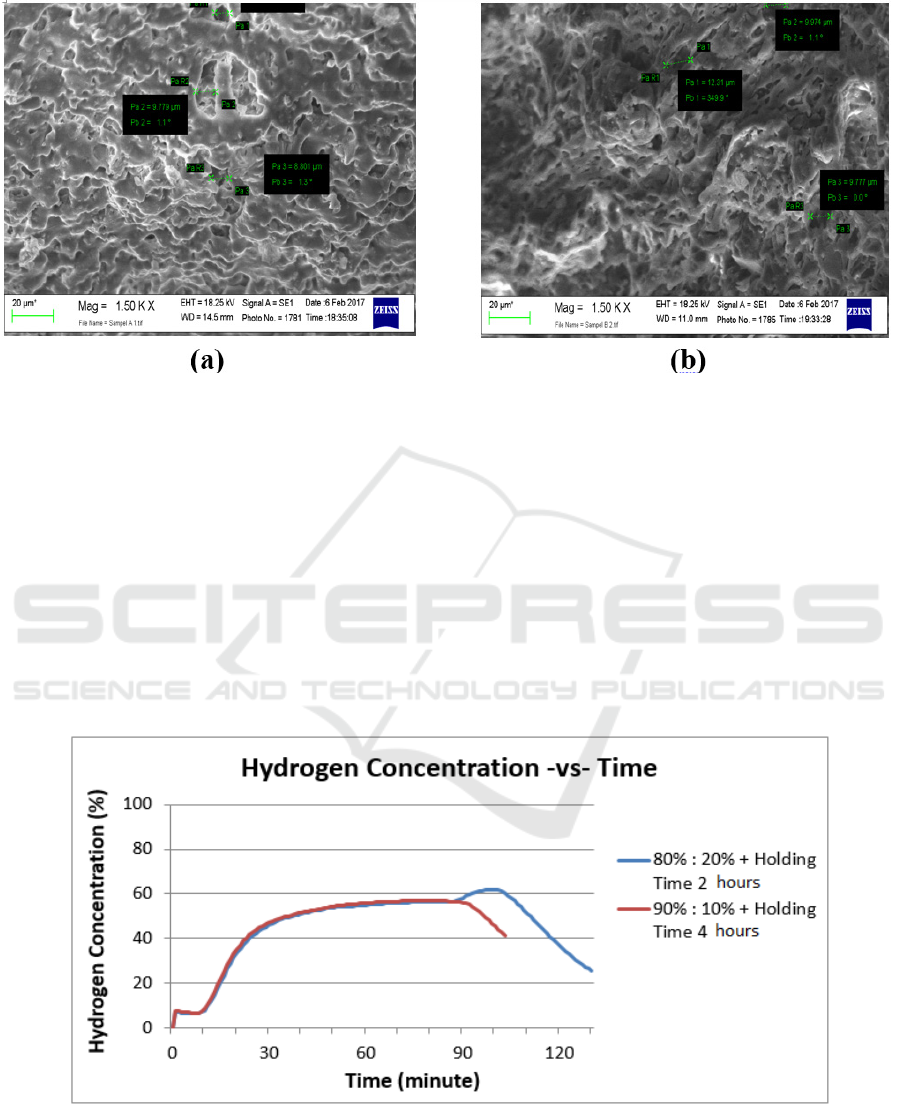
Figure 4 : Results of SEM observations for pore diameters with 1500 times magnification (a) samples with a mixture of 80%:
20%, 2-hour holding time, and (b) samples with a mixture of 90%: 10% 4-hour holding time.
From the results of the diameter size measurement
of the pores using SEM can be seen that the plates
with a mixture of variations 80% : 20% with holding
time 2 hours have the size of the diameter of the pores
average = 8,606 µm.
While ceramics with mixed variations 90% : 10%
with holding time 4 hours have the size of the
diameter of the pores on average = 10.
Have no evidence that the depiction of the
multitude of pores which is actually on the ceramic
coating is complex because of the extent of the
spreading of the size and shape of the pores and the
complexity of the network of pores .
From the measurement result proved both
variation of these ceramics including ceramic coating
type of macroporous ceramic due to the ceramic has
the size of the pores greater than 50 nm (d >50 nm).
3.3 Water Vapour Adsorption Test
(a)
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water
Vapour
1067
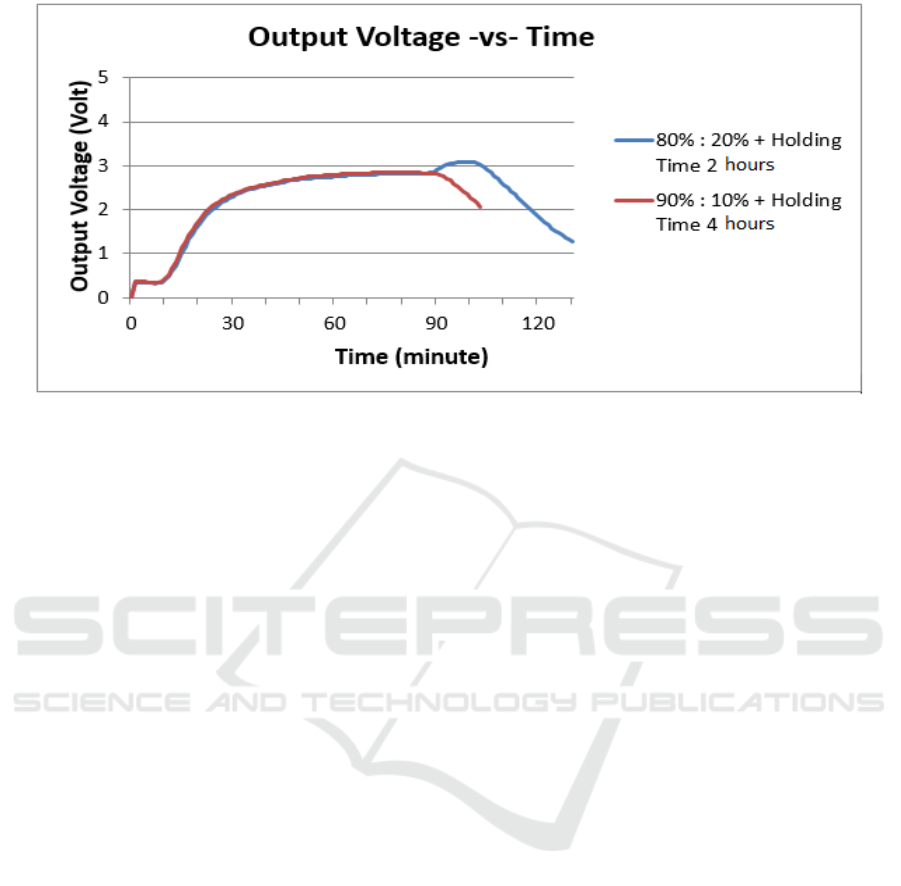
(b)
Figure 5 : Charts of The Water Vapour Adsorption based on (a) Hydrogen Concentration (b) Output Voltage.
Based on the results of the water vapor adsorption test
can be seen that the variation of a mixture of 80% :
20% with holding time 2 hours that the hydrogen
concentration which is read by the censorship is
61,87% with output voltage 3.09 Volts on minutes to
98 while on the variation of a mixture of 90% : 10%
with holding time 4 hours the test results shows that
the concentration of hydrogen which is read by the
censorship is 57,08% on minutes to 77 with output
voltage of 3.09 Volts on minutes to 98 . From the
results of this test, it can be concluded that the
application of the water vapour filter turns to
ceramics with the basic materials of clay and active
charcoal variation by a mixture of 80% : 20% with
holding time 2 hours better in filtering the water
vapour.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Ceramics with the basic materials of clay and active
charcoal can be used as a water vapor filter with the
optimum mixture variations 80% : 20% with a
holding time of 2 hours is supported by mechanical
data test (pressure and hardness), observation SHEM-
EDX (morphology surface, the size of the diameter of
the pores and the analysis of unsures elements). From
the test of the water vapour adsorption also proves
that a mixture of 80% : 20% with a holding time of 2
hours is the optimum variations that can be filtering
the water vapour.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are very grateful to Universitas Sumatera
Utara for its funding according to TALENTA
research contract 2018 with number
2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/2017 on March 16
th
, 2018.
REFERENCES
Buys, S. and Oakley, V., 2014. Conservation and
restoration of ceramics. Routledge.
Hammel, E.C., Ighodaro, O.R. and Okoli, O.I., 2014.
Processing and properties of advanced porous
ceramics: an application based review. Ceramics
International, 40(10), pp.15351-15370.
Kuila, U. and Prasad, M., 2013. Specific surface area and
pore size distribution in clays and shales. Geophysical
Prospecting, 61(2), pp.341-362.
Munz, D., & Fett, T. 2013. Ceramics: mechanical
properties, failure behaviour, materials selection (Vol.
36). Springer Science & Business Media.
Phonphuak, N. and Thiansem, S., 2012. Using charcoal to
increase properties and durability of fired test
briquettes. Construction and Building Materials, 29,
pp.612-618.
Prenzel, T., Guedes, T.L.M., Schlüter, F., Wilhelm, M. and
Rezwan, K., 2014. Tailoring surfaces of hybrid
ceramics for gas adsorption–From alkanes to CO 2.
Separation and Purification Technology, 129, pp.80-
89.
Rouquerol, J., Rouquerol, F., Llewellyn, P., Maurin, G., &
Sing, K. S. 2013. Adsorption by powders and porous
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
1068

solids: principles, methodology and applications.
Academic press.
Sarkar, S., Bandyopadhyay, S., Larbot, A. and Cerneaux,
S., 2012. New clay–alumina porous capillary supports
for filtration application. Journal of membrane science,
392, pp.130-136.
Shen, Y., Zhao, P. and Shao, Q., 2014. Porous silica and
carbon derived materials from rice husk pyrolysis char.
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 188, pp.46-
76.
Susilawati, Tulus I. N., Fynnisa Z., and Hamonangan N.
2017. Hydrogen purification using natural pahae zeolit
and cocoa rind based filter. International Journal of
Applied Engineering Research 12 (13), 3914-3918.
Toor, M., Jin, B., Dai, S., & Vimonses, V. 2015. Activating
natural bentonite as a cost-effective adsorbent for
removal of Congo-red in wastewater. Journal of
Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 21, 653-661.
Wang, A., Gao, X., Giese, R.F. and Chung, D.D.L., 2013.
A ceramic–carbon hybrid as a high-temperature
structural monolith and reinforcing filler and binder for
carbon/carbon composites. Carbon, 59, pp.76-92.
Yalçın, N., & Sevinc, V. 2000. Studies of the surface area
and porosity of activated carbons prepared from rice
husks. Carbon, 38(14), 1943-1945.
Yates, M., Martín-Luengo, M.A., Argomaniz, L.V. and
Velasco, S.N., 2012. Design of activated carbon–clay
composites for effluent decontamination. Microporous
and Mesoporous Materials, 154, pp.87-92.
Yuan, B, Li, H. X, Wang, G., Yu, J. B., Ma, W. K, filter.
Journal of Alloys and Compunds, 684, 613-615
Yuan, B., Li, H. X., Wang, G., Yu, J. B., Ma, W. K., Liu,
L. F., ... & Shen, Z. J. 2016. Preparation and properties
of porous silicon carbide based ceramic
The Effect of the Mixture Variation and Holding Time to the Porous Ceramics based from Clay and Active Charcoal as a Filter of Water
Vapour
1069
