
Histopathologic Feature and Vitamin D Receptor Expression of
Benign Breast Tumor
Mega Sari Sitorus
1
, Dwi Rita Anggraini
1
, Lita Feriyawati
1
1
Departement of Anatomy, Medical Faculty, Universitas Sumatera Utara
Keywords: VDR, Benign Breast Tumor, Fibroadenoma.
Abstract: Many studies say that vitamin D levels are useful as a protection that can decrease the risk of breast cancer,
colon, prostate and ovarian cancers. But some say it's not related. But how the expression of benign breast
tumor never been reported. The existence of VDR can be showed by its expression through
immunohistochemistry. This report will describe the expression of VDR in benign breasst tumor which the
most is fibroadenoma mamma. Pathological tissue samples were obtained from 50 patients suffered with
benign breast lesion that treated in Grandmed Hospital. There are 50 females, the mean age was 24,1, ranging
from 12 to 42 years of age. All of the Hematoksilin Eosin staining slides are examined by pathologist using
light microscope and concluded as fibroadenomas. The presence and location VDR is detected by
immunostaining with VDR Antibody (D-6) from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. One of the most common benign
tumors in the breast around 30 years old is fibroadenomas. In this study it is found that 34 patients (68%)
under 30 years old. The expression of VDR in the fibroadenomas are strong : 42 tumours (82%), moderate:
4(8%, low: 3 (6%), negative: 1(2%). Most of them are VDR positif expression. From the figure 4 we can see
that the VDR is placed in the nuclear dan cell membrane of the cells. Stromal cells doesn’t show expression
of VDR. This discribe that only epithelial cell of breast glandular this receptor.
1 INTRODUCTION
Usually, the tumor that grows in the breast are benign.
Attention is more given to malignant breast lesion
because breast cancer is the most common
malignancy among women in the world. Actually,
benign beast tumor are more frequent than malignant
lesions (Guray, 2006). Fibroadenoma of the breast is
a relatively frequently occurring tumor. It can occur
in any age of women, but the peak incidence is in
twenty until thirty tears of age. Although often
considered a benign tumor, several reports describe a
higher risk of subsequent breast carcinoma in patients
diagnosed with fibroadenoma (Kuijper, 2001).
The study during the two decades before has
mentioned that the variety biological actions of 1,25-
dihydroyxyvitamin D
3
(1,25(OH)
2
D
3
/ Calcitriol) are
triggered by exactly changes in gene expression
which are assisted by intracellular vitamin D receptor
(VDR)(Pike JW, 2010). Mostly of breast tumors
(58%) displayed moderate to strong VDR expression.
An aggressive tumor display inversely related to
VDR expression (A-Azhri, 2017).
A fat soluble vitamin D consist of steroid
molecular structures (Yosephine B, 2016). Sunlight
exposure is the main source of vitamin D for human.
Ultraviolet B light from the sun will penetrate the
skin, change 7-dehydrocholesterol from
keratinocytes and fibroblasts in plasma membranes to
be previtamin D3. In the plasma membrane,
previtamin D3 will be converted rapidly to vitamin
D3, then released into the extracellular space. In the
skin Vitamin D3 is bounded vitamin D-binding
protein. While vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 from the
diet therapy bound with vitamin D binding protein
and lipoprotein. In the liver, vitamin D2 and D3 are
hydroxylated to be 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25 (OH)
D]. 25 (OH) D is the main form of circulation. This
form molecule is used to measure the vitamin D
status. 25 (OH) D is still inactive form and should be
hydroxylized at carbon 1 to be 1,25-
dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25 (OH) 2D/calcitriol] by the
kidney and other tissues, including the breast (Katie
MO, 2017).
1,25 (OH) 2D has endocrine role to control
calcium metabolism by increasing absorption and
mobilizing calcium from bone (Holick MF, 2018).
880
Sitorus, M., Anggraini, D. and Feriyawati, L.
Histopathologic Feature and Vitamin D Receptor Expression of Benign Breast Tumor.
DOI: 10.5220/0010098208800883
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
880-883
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Other sources of vitamin D are very few gets from
foods including oily fish, such as salmon, mackerel,
tuna, and sardines. Vegetable foods generally contain
low vitamin D. Now there are many kinds of foods
which contain fortified vitamin D, particularly milk
products, biscuits, orange juice, yogurt and cereals.
Some foods, such as milk, bread, cereals, are fortified
with vitamin D (Yosephine B, 2016; Holick MF,
2018).
Actions of 1,25 (OH)2D are mediated by the VDR.
It consists of three domains: the C-terminal ligand
binding domain, N-terminal DNA binding domain,
and hinge region binding binds these two domains
together (Bikle DD, 2014). VDR belongs to the
nuclear subfamily receptors acts as transcription
factors into the target cells after making a dimer with
retinoid X receptors (RXR). After dimerization, the
compound molecule binds to VDR(Gil A, 2018). In
the intestine and bone this action to augment intestinal
calcium absorption and influence osteoclast activity.
Prostate, colon, and breast express 1-hydroxylase,
non-calcium regulating tissues locally convert
25(OH)D to 1,25(OH)2D which regulate cell
proliferation and differentiation, to possibly decrease
the risk of cell transformation into a malignant lesion.
Almost tissues and cells in the body have vitamin D
receptor. The presence of 1,25(OH)2D to be one of the
most potent regulators of cellular growth in normal
condition and cancer cells (Stechschulte SA, 2009).
Many studies say that vitamin D levels are useful
as a protection that can decrease the risk of colon
cancer, breast, prostate and ovarian cancers. But some
say it's not related (Gil A, 2018). But how the
expression of benign breast tumor never been
reported.
The existence of VDR can be showed by its
expression through immunohistochemistry. This
report will describe the expression of VDR in benign
breasst tumor which the most is fibroadenoma
mamma.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
Pathological tissue samples were obtained from 50
patients suffered with benign breast lesion that treated
in Grandmed Hospital. There are 50 females, the
mean age was 24,1, ranging from 12 to 42 years of
age. All of the Hematoksilin Eosin staining slides are
examined by pathologist using light microscope and
concluded as fibroadenomas. The presence and
location VDR is detected by immunostaining with
VDR Antibody (D-6) from Santa Cruz
Biotechnology.
Table 1: Characteristics of the patients.
Age of patients with fibroadenoma mammae
10
–
14
y
ears 2 (4.0%)
15
–
19
y
ears 10 (20.0%)
20
–
24
y
ears 18 (36.0%)
25
–
29
y
ears 4 (8.0%)
30
–
34
y
ears 7(14.0%)
35
–
39
y
ears 5(10.0%)
40
–
44
y
ears 4(8.0%)
Immunohistochemistry and Evaluation
In this study, the samples are from formalin-fixed
paraffin embedded pathological tissue. The VDR
expression were studied by immunostaining using
monoclonal antibodies VDR Antibody (D-6) from
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, according the standards
protocols used in laboratories of Murni Teguh
Hospital .
VDR immunostaining intensity of fibroadenoma
was examined semiquantitatively by two independent
observers from 0 to 3 arbitrary units with 0 as
negative (0), weak/low (1), moderate (2) and strong
(Pike JW, 2010). VDR staining intensity in
fibroadenoma lesions was evaluated with reference to
intense reddish-pink basal layer of normal skin
epidermis, scored as strong. Light reddish-pink and
light pink stained cells were scored as cells with
moderate or weak VDR expression, correspondingly.
The VDR expression was assessed for cytoplasm and
nuclei of cells separately (Brozyna AA, 2011).
Figure 1: Representative images of vitamin D receptor
(VDR) protein expression, classified by immunoreactive
score (IRS) (Al-Zahri J, 2017).
3 RESULTS
The most common benign tumors of the breast in
woman is fibroadenomas. This tumor usually attack
woman under 30 years old. In this study it is found
that 34 patients (68%) under 30 years old.
Microscopically, fibroadenoma is a benign tumor
with biphasic features consist of epithelial and
stromal components (Lee M, 2015).
The microscopic features showed in figure 2. The
tumour consists of epithelial component as a
Histopathologic Feature and Vitamin D Receptor Expression of Benign Breast Tumor
881
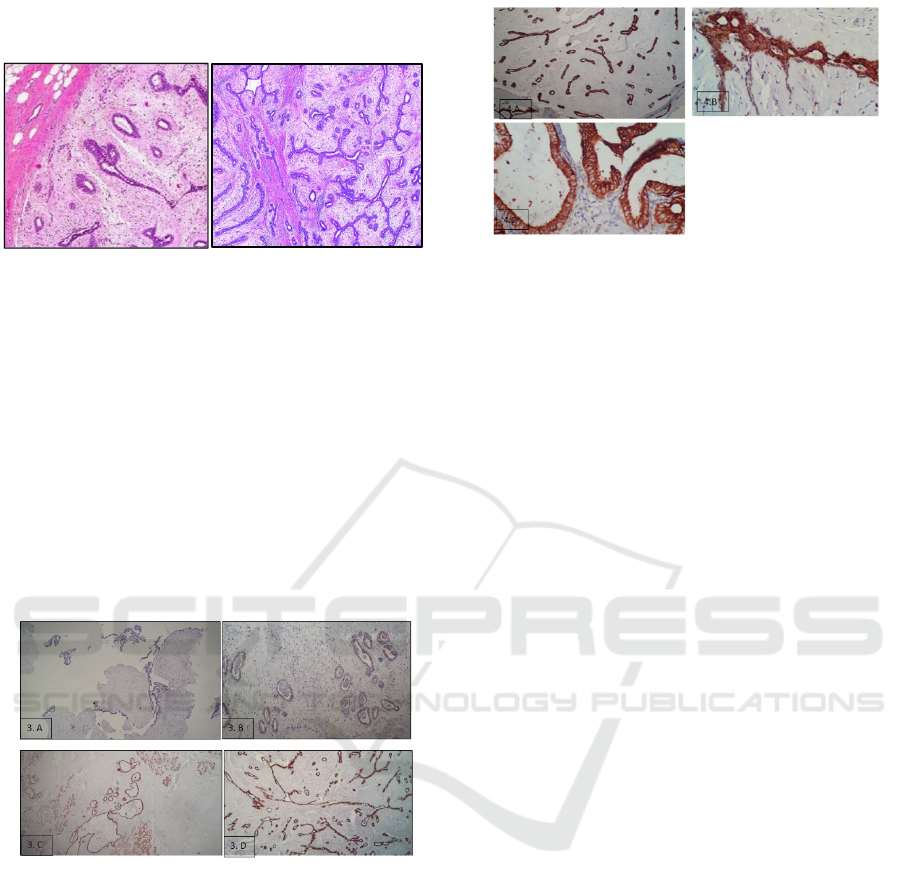
glandular slit or tubular form and propiferative
stromal component.
Figure 2: Pathologic view of fibroadenomas.
Most of the of fibroadenomas present as a single
mass (70%). Others are as multiple masses around
10%–25%. Characteristic of fibroadenomas are a
painless, mobile, smooth, and rubbery mass with
distinct borders. The size usually ranging from 1 cm
to 3 cm, on the upper outer quadrant of the breast. It
can also be very small unpalpable mass that it is only
seen on microscopic examination. Simetimes can be
larger than 10 cm and may cause breast asymmetry
and significant esthetic problem of the breast. The
finding existence of VDR in other tissue beside gut
and skeletal are observed in this study in benign
breast tumor (figure 3).
Figure 3. VDR expressions in fibroadenomas, A. Negative,
B. Low, C. Moderate, E. Strong (100x).
4 DISCUSSION
Fibroadenomas is the most benign breast tumour in
woman. Usually they are found in young middle age,
below 30 years old. In this study found that 68%
tumours are found under 30 years old. As a benign
breast tumor, fibroadenoma is also thought to
represent a set of hyperplastic breast lobules called
“aberrations of normal development and involution”.
This lesion is a hormone-dependent neoplasm that
lactates during pregnancy and also get involuting
along with the rest of the breast in perimenopause.
Figure 4. Distribution of VDR Expression (100x).
The expression of VDR in the fibroadenomas are
strong : 42 tumours (82%), moderate: 4(8%, low: 3
(6%), negative: 1(2%). Most of them are VDR positif
expression. From the figure 4 we can see that the
VDR is placed in the nuclear dan cell membrane of
the cells. Stromal cells doesn’t show expression of
VDR. This discribe that only epithelial cell of breast
glandular this receptor.
5 CONCLUSION
The histopathologic feature of benign breast tumor
mostly is fibroadenoma mammae. The glandular dan
stromal cells proliferates resemble the cleft like
appearence. With imunohistochemistry can detect
that vitamin D receptor also expressed in the
epithelial cells, both in nuclei and cytoplasm.
REFERENCES
Al-Azhri J, Zhang Y, Bshara W, Zirpoli G, McCann SE,
Khoury T
,
Morrison CD, Edge SB, Ambrosone CB, Yao
S. 2017. Tumor Expression of Vitamin D Receptor and
Breast Cancer Histopathological Characteristics and
Prognosis. Clin Cancer Res, 1;23(1):97-103.
Bikle DD, 2014. Vitamin D Metabolism, Mechanism of
Action, and Clinical Applications. Chem Biol; 21(3):
319–329.
Brożyna AA, Jozwicki W, Janjetovic Z, Slominski AT.
2011. Expression of vitamin D receptor (VDR)
decreases during progression of pigmented skin lesions.
Hum Pathol. ; 42(5): 618–631.
Gil A, Plaza-Diaz J, Mesa MD. 2018. Vitamin D: Classic
and Novel Actions. Ann Nutr Metab;72:87–95.
Guray DM, Sah AA. 2006. Benign Breast Diseases:
Classification, Diagnosis, and Management. The
Oncologist;11:435–449.
Holick MF. 2018. Vitamin D and Sunlight: Strategies for
Cancer Prevention and Other Health Benefits. Clinical
Journal of the American Society of
Nephrology;3(5):1548-1554.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
882

Katie MO, Brien, Sandler DP, Taylor JA, Weinberg CR.
2017. Serum Vitamin D and Risk of Breast Cancer
within Five Years. Environmental Health Perspectives;
077004(1-9). is available at
https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP943.
Kuijper A, Mommers EC, van der Wall E, van Diest PJ.
2001. Histopathology of Fibroadenoma of the Breast.
Am J Clin Pathol;115:736-742.
Lee M, Soltanian HT, 2015. Breast fibroadenomas in
adolescents: current perspectives. Adolesc Health Med
Ther;6:159–163.
Pike JW, Meyer MB. 2010. The Vitamin D Receptor: New
Paradigms for the Regulation of Gene Expression by
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D
3.
Endocrinol Metab Clin
North Am.; 39(2): 255–269.
Stechschulte SA, Kirsner RS, Federman DG. 2009. Vitamin
D: Bone and Beyond, Rationale and Recommendations
for Supplementation. The American Journal of
Medicine;122(9): 793-802.
Yosephin B , Anwar F, Riyadi H, Khomsan A, Elly N. 2016.
Food Sources Of Vitamin D And Its Deficiency In
Worker Women. 4th Asian Academic Society
International Conference (AASIC);233-239. Available
at
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306392153_f
ood_sources_of_vitamin_d_and_its_deficiency_in_wo
rker_women.
Histopathologic Feature and Vitamin D Receptor Expression of Benign Breast Tumor
883
