
The Association between Tuberculosis Cytology through Eosinophilic
Mass with Dark Brown Particles against Various Bacterial Strains
Delyuzar
1
, Bintang Yinke Magdalena Sinaga
2
, and Rina Yunita
3
1
Departement of Anatomycal Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia.
2
Departement of Pulmonology,Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia.
3
Departement of Mirobiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Tuberculosis, cytology, eosinophilic mass.
Abstract: Diagnosis of tuberculosis cytology through eosinophilic mass with dark brown particles has been shown to
establish the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. The eosinophilic mass with dark brown particles is not
a classic histopathological of tuberculosis infection, there are allegations that this picture is related to a
decrease in the patient's immune system. Many HIV TB patients do not provide a classic TB picture on
pathology examination. Mycobacterium avium is associated with TB infection in HIV AIDS patients. The
ability to accurately detect tuberculosis infection is very important in line with USU's research strategic plan
with the specialty in the field of Tropical Science and Medicine in controlling tuberculosis infection,
especially in patients with reduced immune system. Fine needle biopsy was performed twice for cytologic
and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) examination. Statistical analysis was done using Pearson’s Chi
square test. Out of 194 cases, 50% were suspicious for tuberculous lymphadenitis and 51% were proved to
be positive M. tuberculosis. Ther was also a trend association between eosinophilic mass and M. avium. All
suspected cases of tuberculous lymphadenitis showed eosinophilic mass on microscopic examination of
FNA cytology. Our findings suggest the potential of eosinophilic mass as a new diagnostic criteria for TB.
This can be the basis of further research on eosinophilic mass.
1 INTRODUCTIONS
Tuberculosis (TB) is still an Indonesian major
problem. Indonesia is the second country in the
world to have the most cases(321,308 total cases
from 242 million inhabitants, 2011). As the fourth
country in the cause of the death TB also ranks in
Indonesia. Therefore, it needs to research more
deeply both for diagnostics and therapy (WHO,
2016). An increase in human resources is needed,
include ability of the health workers to find cases
and overcome them to decrease tuberculosis
transmissions (Delyuzar, 2006). A fast way to detect
M. tuberculosis infection will help accelerate early
diagnosis in patients who are clinically suspected
tuberculosis patients and immediately followed by
appropriate management (Lalvani, 2001).
Lymphadenitis TB (LTB) can be performed
cytology through fine needle aspiration biopsy
(FNAB). Diagnostic criteria that have been used to
diagnose tuberculosis cytologically are found
epithelioid type histiocyte cells and cells with
multiple nuclei of the Langhans type (Ammari,
2003). Sarwar A. (2004) explained that in addition
to the Langhans cell (multinuclear giant cell) also
contains caseous necrosis. PurohitManju (2007)
using PCR as the gold standard received anti-
MPT64 immunohistochemistry techniques in TB in
the abdomen and lymph nodes of sensitivity,
specificity, positive predictive value and negative
predictive values were 92%, 97%, 98%, and 85%.
Immunistochemistry with anti-MPT64 antiserum
can be done relatively quickly, sensitively, and
specifically to establish a diagnosis of TB (Tubbs
2009). To establish a diagnosis of tuberculosis
lymphadenitis can also be done culture, smear with
ZiehlNeelsen staining in addition to
histopathological features both classical and
immunohistochemistry (Robbins, 2003).
This study uses gold standard biomolecular
examination of PCR, so that it complements each
other to assess the accuracy of fine needle biopsy
cytology diagnostics on unusual TB features
852
Delyuzar, ., Sinaga, B. and Yunita, R.
The Association between Tuberculosis Cytology through Eosinophilic Mass with Dark Brown Particles against Various Bacterial Strains.
DOI: 10.5220/0010094708520855
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
852-855
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
(eosinophilic mass with dark brown particles), as a
new criteria of cytology picture of tuberculosis.
2 OBJECTIVES
The aimed of this study is to analyze the association
between eosinophilic mass and M. tuberculosis.
3 METHODS
This cross-sectional study was carried out in RSUP
HAM Medan/Department of Anatomical Pathology,
Faculty of Medicine USU Medan or who came to
Anatomical Pathology Department, while the
examination according to WHO recommendations,
PCR was conducted at the USU Integrated
Laboratory. The research was done after getting
permission from Ethical Committee of Medical
Faculty USU Medan. Specimen from FNA was done
using a 23 gauge needle, 10 ml syringe and pistol
(Comeco, Sweden). Aspirate was directly smeared
and stained with May-GrunwaldGiemsa stain.
Second FNA procedure was performed to obtain
aspirate for PCR examination.
PCR was used to confirm the presence of M.
tuberculosis and prove the cytological diagnosis of
the first FNA procedure. The
followingmycobacterial and nonmycobacterial
reference bacterial strains were obtained from the
American Type Culture Collection (ATCC;
Rockville, Md.) used in PCR amplification and
grown according to the instructions of ATCC: M.
tuberculosis and M. avium. M. tuberculosis Primers,
A pair of 24-base synthetic oligonucleotides that
bracket a 165-base region of a gene codes for a 65-
kilodalton antigen was synthesized. The sequences
of the oligonucleotide primers were (from the 5' to
the 3' ends) CTAG
GTCGGGACGGTGAGGCCAGG and
CATTGCGAAGT GATTCCTCCGGAT. Another
oligonucleotide of 40 bases in length located
between the two primers was synthesized to be used
as an internal probe, and its sequence was (from the
5' to the3' ends) M. avium Primers, a 427-base
region.
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS
22 version (SPSS Inc., Chicago) with a 95%
confidence interval. Pearson’s Chi square test with
significance p<0.05 was applied to assess the
association between eosinophilic amorphous mass
and tuberculous.
4 RESULTS
Out of the total 194 patients with lumps on the neck,
18.6% of cases was clinically diagnosed as abscess,
31.4% as non-specific lymphadenitis, 50% as
suspicuous for tuberculous lymphadenitis (Table 1).
Table 1: Baseline characteristics of the samples
Characteristics Clinical dia
g
nosis Number
(
%
)
Abscess 36 (18.6%)
Non-specific lymphadenitis 61 (31.4%)
Suspicious for tuberculous
l
y
m
p
hadenitis
97 (50%)
Table 2: Association of eosinofilic mass with M.
tuberculosis PCR results.
PCR
Eosino
p
hilic mass
Presence Absence
M.TB (+) 94 1
M. TB (-) 3 96
Table 3: Association of eosinofilic mass with M. avium
PCR results.
PCR Eosinophilic mass
Presence Absence
M. avium
(
+
)
61 2
M. avium
(
-
)
36 95
There was a significant association between
eosinophilic mass with M. Tuberculosis p value <
0.001 (Table 2).There was also a trend association
between eosinophilic mass with M. avium (Table 3).
Tuberculosis infection proved positive through
PCR in 51% of cases (Figure 1).All suspected cases
of tuberculous lymphadenitis showed eosinophilic
mass on microscopic examination of FNA cytology
(Figure 2).
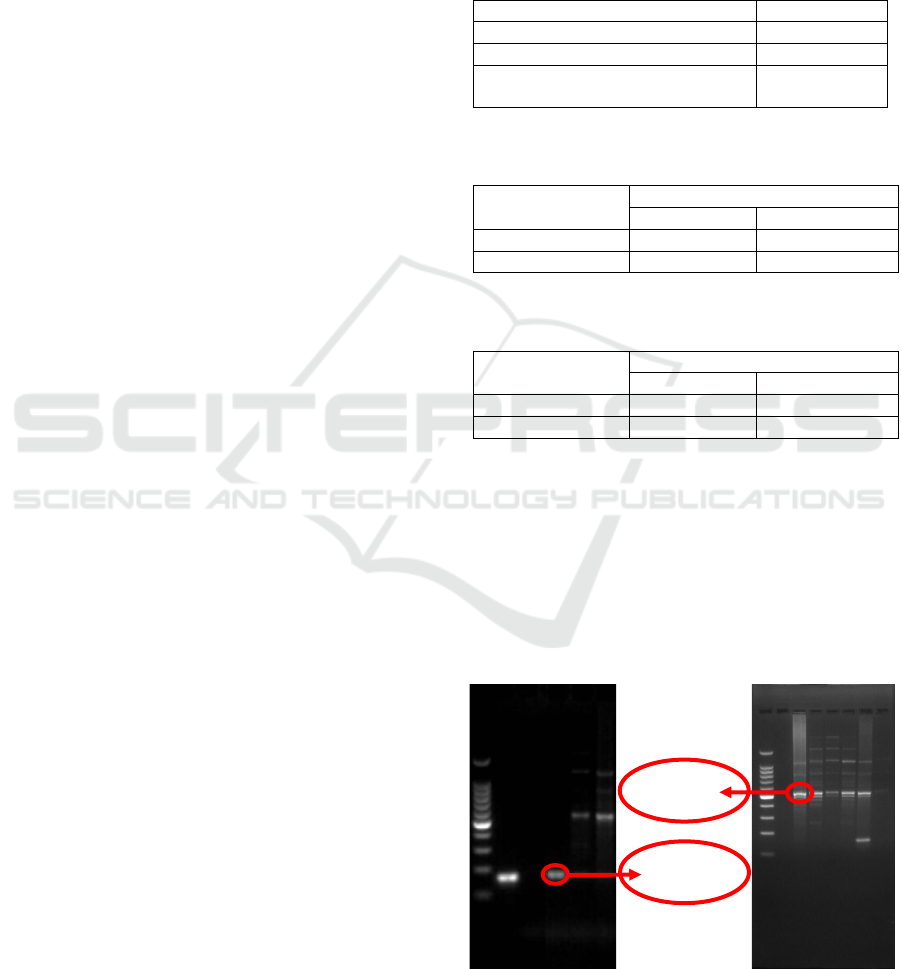
Figure 1: 165 base pairs indicates the presence of M.
tuberculosis and 427 base pairs indicates the presence of
M. avium on PCR
427bp
165bp
The Association between Tuberculosis Cytology through Eosinophilic Mass with Dark Brown Particles against Various Bacterial Strains
853

Figure 2: Eosinophilic mass in cytologic specimen
5
DISCUSSIONS
Patel study (2016), 50% of the samples were non-
specific lymphadenitis, thirty-six percent was TB
and ten percent was abscess, whereas in this study
194 cases (50%) of eosinophilic mass were
suspected of Tuberculosis. As control, 31,44% were
non-specific lymphadenitis and 18,56% abscess.
PCR examination, as gold standard, found 95
positive samples of M. tuberculosis and 99 negative
M. tuberculosis samples.
Microscopically the typical picture tissue of the
mycobacterium tuberculosis lesion is granuloma or
caseous necrosis. Granulomas are a collection of
macrophages (macrophages). Macrophages also
called histiocytes can fuse to form multinucleated
giant cells, magrophages in granulomas are often
called ephiteloid. Epitheloid macrofages are
different from magrophages, usually because they
have an elongated core similar to a shoe sole, the
core is larger and the cytoplasm is more pink, this
change occurs because the magrophage is activated
by the antigen. Granulomas may be accompanied by
other components including lymphocytes,
neutrophils, eosinophils, multinucleted giant cells
and fibroblasts. Actually granulomas are not only
caused by m.tuberculosis but also due to leprosy,
histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, coccidioidomycosis,
and blastomycosis. Non-infectious granulomas can
be found in sarcoidosis, Crohn's disiase, berylliosis,
Wagener's granulomatosis, Churg-Staruss syndroma
and others. Cytology features that contain many
macrophages are the most common reactive,
infectious and sarcoidosis processes, other
conditions can occur in carcinoma with post
obstructive pneumonia, infarct and should be
differentiated also with Langerhan cell histocytosis
(Renshaw, 2005).
Granulomas in tuberculosis tend to form necrosis
(caseatingtubercule) although there is no form of
necrosis, accompanied by multinucleated giant cells
with a nucleus on the edge on one side to form
horseshoe/Langhans giant cell (Underwood, 2009).
Krisnan (2001) reported different cytologic features
in HIV patients he called negative images with a
negative rod shape and blue black ground, with no
classic features found in LTB patients.
Lubis (2008) found structures of eosinophilic
mass with dark brown particles cytologically in
patients clinically untreated with TB treatment.
Lisdine's research, et al (2003) using Kudoch's
reaction to obtain a spotted eosinophilic fine
granular necrotic mass can be used as a basis for
diagnosing extrapulmonary tuberculosis with
probability values of 97%, 91% specificity and 94%
accuracy. From the results of this study means the
patches found in the pussy microscopically have
meaning meaning, where if the encounter of these
spots means that the cause of the lesion tuberculosis
germs, while not encountered these spots are not the
cause of tuberculosis.
Eliandy (2010) examined the appearance of
antigens using rabbit polyclonal to Mycobacterium
tuberculosis antibody (ab905), Abcam. The
appearance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was seen
in 14 cases with small oval-shaped bodies within
macrophages, 21 cases with dark patches, 1 case
with non-specific chronic inflammation, and 7 cases
with abscesses. Lubis et al (2010), examined the
difference in the number of positive IHC displays in
lesions with small oval-shaped bodies in
macrophages and nonspecific chronic inflammation,
and there was a difference in the proportion of
positive IHC displays in lesions with dark patches of
mass amorphous granular eosinophilic ears and
abscesses (
Sarwar A et al. 2004).
But there are still
pros and cons about the use of
Immunocytochemistry in this cytology so it needs to
be reinforced with other techniques more accurate,
researchers use the PCR technique as a gold
standard. Raviglione and O'Brien (2010) mentioned
that granuloma features are not usually found in
HIV-infected patients, whereas granulomas are
characteristic of TB lesions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
There was an associate between eosinophilic mass
and M. tuberculosis. It indicates the possibility of
this cytologic features as a new diagnostic criteria
for tuberculous infection. There was also a trend
association between eosinophilic mass and M.
avium. It indicates the possibility of this cytologic
features for Mycobacteriumtuberculosis and
Mycobacterium nontuberculosis infection.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
854

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by the Ministry of
Research, Technology, and Higher Education
Republic of Indonesia, Universitas Sumatera Utara,
Research Institution, Number:
27/UN5.2.3.1/PPM/KP-DRPM/2018.
REFERENCES
Ammari FF, Bani Hani AH, Ghariebeh KI., 2003.
Tuberculosis of thelymph glands of the neck: a limited
role for surgery. Otolaryngol Head and Neck Surg,
128 (4): 576-580.
Delyuzar, Arbaningsih SR, Ruswardi., 2006.
Empowerment human resources against tuberculosis
in North Sumatera: a FIDELIS initiativeThe
International Jornal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease,
10 (11).
Eliandy S, Lubis HMND, Delyuzar., 2011.
HubunganGambaranBercak-bercakGelap (Dark
Specks) padaLatarBelakang Material Nekrotik
Granular Eosinofilikdengan Kadar CD4
Penderitadengan Kadar CD4
PenderitaLimfadenitisTuberkulosisServikalis yang
Disertai HIV/AIDS.Tesis Program DokterSpesialis.
Available from: http://repository.usu.ac.id/
handle/123456789/26585.
Krisnan R, Iyengar, Basu, Debdatta, 2001. Negative
Immages in the Fine Neddle Aspiration Cytologic
Diagnosis of Mycobacterial Infections. Malaysian
J.Pathol . 23 (2): 89-92.
Lalvani A et al. 2001. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection by enumerationof antigen-
spesific T cells.Am J respirCrit Care med; 163: 824-
828.
Lisdine, Lubis HMND. Massa Nekrotik Bergranul Halus
Eosinofilik Berbercak-bercak sebagai Pembeda Abses
Tuberkulosa dan Abses non Tuberkulosa. Available
from:http://repository.usu.ac.id/bitstream/123456789/6
302/1/patologi-lisdine.pdf.
Lubis HMND, Lubis HML, Lisdine, Hastuti NW, 2008.
Dark specks and eosinophilic granular necrotic
material as differentiating factors between tuberculous
and nontubercolousabcesses. Indonesian Journal of
Pathology; 17 (2): 49-52.
Patel VK, Sheth R, Shah K, 2016. A retrospective study
on role of fine needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis
of cervical lymphadenopathy. International Journal of
Medical Science and Public Health; 5 (8): 1588-1591.
Purohit MR, Mustafa T, Wiker HG, Morkve O., 2007.
Immunohistochemical diagnosis of abdominal and
lymph node tuberculosis by detectingMycobacterium
tuberculosis complex specific antigen
MPT64.DiagnPathol. 2: 36.
Raviglione, Mario C, O’Brien RJ., 2010. Tuberculosis in:
Harrison’s Infectious Diseases. Editor: Dennis L.
Kasper, Anthony S. Fauci. McGraw Hill Companies.
:596-617.
Renshaw, Andrew., 2005. Macrophage rich pattern In:
Aspiration Cytology A Pattern Recognition Approach,
Elsevier Saunders: 47-48.
Robbins SL and Cotran RS., 2003. Tuberculosis in:
Pathologic Basis of Disease. Seventh edition. New
York.
Sarwar A et al., 2004. Spectrum of Morphological
Changes in TuberculousLimfadenitis. International
Journal of Pathology, 2: 85-89.
Tubbs, Raymond R, Stoler, Mark H., 2009. Molecular
Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in Tissue. Cell and
Tissue Based Molecular Pathology. Churchill
Livingstone Elsevier: 182-193.
Underwood, JCE., 2009. Cross SS. Inflamation In:
General and Systemic Pathology, Fifth Edition,
Churchill Livingstone Elsevier: 200-219.
WHO., 2016. Global Tuberculosis Report: 32.
The Association between Tuberculosis Cytology through Eosinophilic Mass with Dark Brown Particles against Various Bacterial Strains
855
