
Utilization of Volcanic Ash of Mount Sinabung as a Substitute for
Cement to Flexure Strength of Geopolymer Concrete
Rahmi Karolina
1
, Syahrizal
2
, M. A. P. Handana
2
, Billy Wijaya
2
1
Doctoral student of Civil Engineering Universitas Sumatera Utara
2
Department of Civil Engineering Universitas Sumatera Utara
Keywords: geopolymer concrete, sinabung ash, curing time, flexure strength.
Abstract: Concrete is one of the construction materials that have been commonly used for the construction of buildings,
bridges, roads and so forth. The need for concrete will increase in line with the increasing need of basic human
facilities and infrastructures. Therefore, the production of cement as a binder of concrete increases as well. In
the process of cement production occurs a process of a huge amount of CO2 release into the atmosphere and
then damage the environment which among them cause global warming. To overcome these problems, it’s
necessary to find another material as a substitute for cement. Geopolymer concrete is an alternative to
substitute concrete that uses cement. Geopolymer concrete is made without the use of cement as a concrete
binder, and instead, using sinabung ash which is rich in silica and alumina and can react with alkaline liquids
to produce a binder. In this research, the flexure strength of concrete is tested to a number of samples in the
form of 15x15x60 cm3 block with curing time variation of 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours and 24 hours at 60
o
C
temperature by using oven. From the results, it’s obtained that the graph of flexure strength value increases
with the length of curing time. Maximum flexure strength occurs at 24 hours curing time.
1 INTRODUCTION
(Davidovits, 1999) Geopolymer concrete is a
construction material that is developed and offers
many advantages compared to conventional concrete
where the making process of concrete does not use
cement. The advantages to be obtained from
geopolymer concrete are its ability to withstand fire,
corrosive resistance, reducing air pollution due to
excessive CO2 emissions at the time of cement
production. The base materials for the geopolymer
binder used to create geopolymer concrete can be
obtained from various sources where these materials
have high silica and aluminum content.
In this research the cement substitute binder
used is volcanic ash. Volcanic ash is a fine material
and very small in size, bursting from a erupting
volcano. Volcanic ash has some content that can
support reinforcement in concrete. One of the most
abundant types of material in volcanic ash is silica
(SiO2). This material can react chemically with
alkaline liquids at a certain temperature to form a
cement-like mixed material.
Based on the descriptions described above, the
author will conduct a test by using volcanic ash of
Mount Sinabung as a substitute of cement in concrete
mixture, to be able to know the result of flexure
strength of concrete produced with the base material
of volcanic ash.
2 MATERIALS
Sinabung Ash. Volcanic ash or volcanic sand is a
falling volcanic material that is ejected into the air
during an eruption. The ash and volcanic sand consist
of large to fine-sized rocks, large ones usually falling
around 5-7 km from the crater, while the fine ones can
fall at a distance of hundreds of kilometers or even
thousands of kilometers from the crater that caused
by the wind (Sudaryo dan Sucipto, 2009). The
characteristics of volcanic ash generally contain
major elements (AI, Si, Ca and Fe), minor (I, Mg, Mn,
Na, P, S and Ti), trace levels (Au, As, Ba, Co, Cr, Cu,
Mo, Ni, Pb, S, Sb, Sn, Sr, V and Zn), have broad uses
(AI, Si, Ca, Fe, Ti, V and Zn) and high values (Au).
Based on the content of AI, Ca and Si elements in
332
Karolina, R., Syahrizal, ., Handana, M. and Wijaya, B.
Utilization of Volcanic Ash of Mount Sinabung as a Substitute for Cement to Flexure Strength of Geopolymer Concrete.
DOI: 10.5220/0010094303320337
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
332-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

large ash (56%, 4% and 18% respectively), it is
possible to use the ash as a cement material or
cement-based goods (Wahyuni, 2012)
Table 1: Chemical Contents of Volcanic Ash of
Mount Sinabung Eruption
No Parameter Result (%) Method
1 Silika as
SiO₂
85,6 Gravimetri
2 Aluminium
as Al₂O₃
0,95 Perhitungan
3 Kalsium as
CaO
4,78 Gravimetri
4 Magnesium
as MgO
4,48 Gravimetri
5 Water
content
1,43 Gravimetri
(Source : Balai Riset dan Standarisasi Industri
Medan, Laboraturium Penguji, Kementerian
Perindustrian)
Figure 1: Magnification of Volcanic Ash Samples
with SEM Test
Figure 2: Magnification of Volcanic Ash Samples
with SEM Test
Table 2: Results of EDS Spectrum Analysis of
Volcanic Ash Samples of Mount Sinabung
EI An C Norm (wt%)
C atom
(at%)
Fe 26 37,96 16,72
O 8 33,28 51,16
Si 14 16,81 14,72
C 6 6,12 12,53
Al 13 4,26 3,88
K 19 0,89 0,56
Ca 20 0,69 0,42
Na 11 0,00 0,00
Mg 12 0,00 0,00
Br 35 0,00 0,00
Tl 81 0,00 0,00
(Source : Laboratorium Fisika Universitas Negeri
Medan)
Utilization of Volcanic Ash of Mount Sinabung as a Substitute for Cement to Flexure Strength of Geopolymer Concrete
333
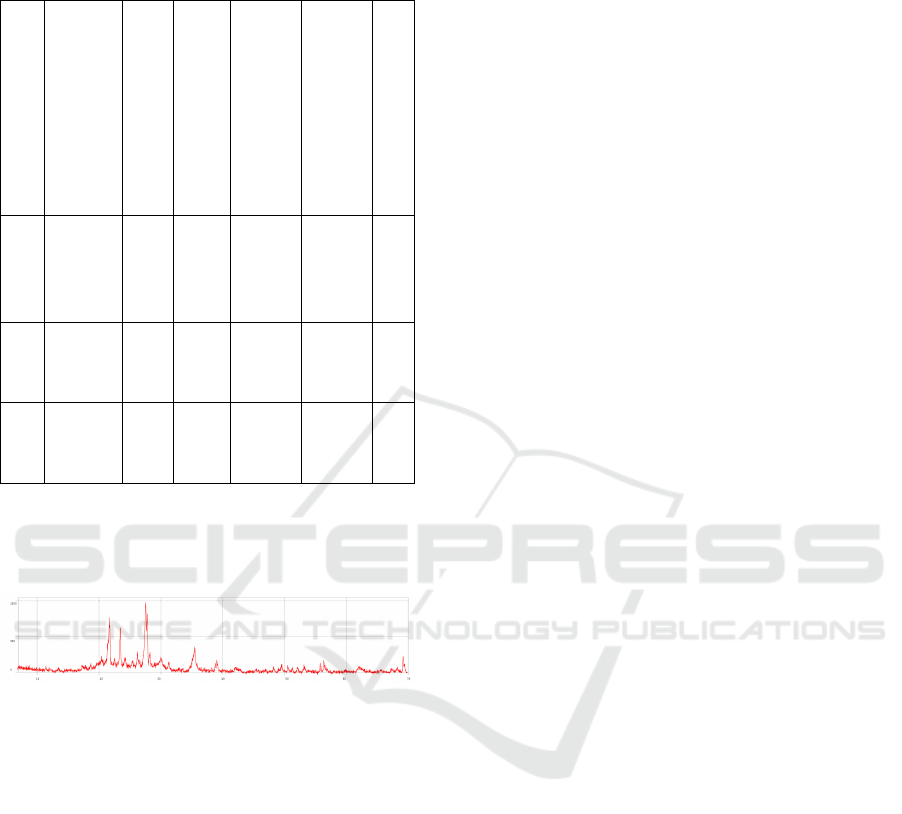
Table 3: Results of X-ray Diffraction Analysis of
Activation Nature of Volcanic Ash
No
2 Theta
(deg)
d
(A)
I/II
FWH
M
(deg)
Intensi
ty
(Coun
ts)
Int
eg
rat
ed
Int
(C
ou
nt
s)
1
27,758
4
3,2
11
12
5
100
0,505
80
297
79
98
2 21,786
4,0
76
19
73 0,412 217
48
31
3
23,559
4
3,7
73
22
48
0,281
1
144
20
25
(Source : Laboratorium Fisika Universitas Negeri
Medan)
Figure 3: Diffraction Pattern of Activation Results of
Volcanic Ash
Figure 3 shows the pattern of X-ray diffraction
between intensities to the volcanic ash element
pattern of modified nature (chemical and physical
activation). The analysis of X-ray diffraction tool is
intended to know the dase and crystal structure, and
identification result crystallinity of a dominant
composition on volcanic ash (Bambang Nurdiansyah,
2017).
From table 3, it can be seen that the maximum
peak is at 2θ = 27.7584 with spacing of 3.21125A and
FWHM 0,50580.
From the results of chemical content
examination above, it is seen that sinabung ash has a
very high silica content. The percentage of this
content indicates that the ash can be used as a
substitute for cement in a concrete mixture.
From the SEM test of volcanic ash samples
above, it can be seen that the morphology of samples
is irregular with varying sizes. And the magnitude of
the volcanic ash particle distribution from the
eruption of Mount Sinabung is 13.49μm - 45.56μm
(Bambang Nurdiansyah, 2017).
Agregates. The fine aggregate (sand) used is sand
from Medan Sunggal with dry, SSD and apparent
specific gravity of 2460 kg / m3 and 2510 kg / m3
and 2590 kg / m3. Coarse aggregate (gravel) is split
with the maximum size of 20 mm with SSD and
apparent specific gravity of 2630 kg / m3, 2680 kg /
m3 and 2770 kg / m3
Admixtures. Admixtures are materials used in
concrete mixture other than water, aggregates (fine
and coarse aggregate), ashes, and alkaline activators
added in concrete mix. In this research is using
highrange water reducer admixture such as Master
Ease 3029 and Accelerator.
[2][3]
Alkaline Activators (Sodium Silicate dan
Sodium Hidroxyde). Alkaline activators to be used
in this research are sodium hydroxide and sodium
silicate. NaOH is a powder with a content of 98%.
Sodium hydroxide serves to react the Si and Al
elements contained in the volcanic ash so as to
produce a strong polymer bonds. Na
2
SiO
4
contains
96% gel-shaped sodium silicate. Sodium silicate
serves to speed up the polymerization reaction.
3 METHOD
(Mulyono, 2004) Research method is stages,
processes, sequences or workflows to get the purpose
of a research conducted. The method used in this
study is an experimental study conducted at the
Concrete Laboratory of Faculty of Engineering of
Department of Civil Engineering of University of
Sumatra Utara. A complete mix design calculation
can be seen in the attachment. From the mix design
results, it is obtained 1m³ concrete mixture proportion
among others are as follows :
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
334
Table 4: The proportion of concrete mixture per m
3
Material Weight
Sinabung Ash 553,57 kg/m³
Sodium Silicate 138,40 kg/m³
Sodium Hidroxyde 230,65 L/m³
Coarse Aggregate 900,16 kg/m³
Sand 808,46 kg/m³
Master Ease 3029 11,07 L/m³
Accelerator 5,54 L/m³
Concrete Flexure Strength. The loading system in
the flexure test, ie the specimen is loaded so that it
will only experience a failure caused by pure flexure
(two point loading system). The flexure strength of
concrete (modulus of rupture) is calculated as
follows:
If the failure occurs in the middle of the span:
[1]
If the collapse occurs in the drag outside of the center
of the span then the following formula is used:
[2]
Where :
Fr = modulus of rupture
P = the maximum load that occurs
L = the effective span length
b = average width of fault specimen
d = average height of fault specimen
a = the average distance from the failure line from
the nearest placement point measured at the
specimen's drag
4 RESULTS AND DISCCUSIONS
Visible Properties
Volume Weight of Geopolimer Concrete. The
volume weight of concrete is the ratio between the
weight of the concrete and its volume. The average
volume weight of the geopolymer concrete can be
seen in table 5 below :
Table 5: Table of average volume weight of
Geopolymer Concrete
No.
Curing
Time
(Hours)
Number
of
Samples
AverageVolume
Weight (kg/m
2
)
1 4 3 2329,04
2 8 3 2381,04
3 12 3 2386,00
4 24 3 2369,41
From the results obtained, the volume weight of
geopolymer concrete volume ranges between
2329,04 kg/m
2
– 2386,00 kg/m
2
. The examination
results of the geopolymer concrete volume weight, it
is included a normal weighted concrete (SNI 03-
2847-2002).
Flexture Strength of Geopolymer Concrete. In this
research, flexure strength test is performed on a beam
of geopolymer concrete with the size of 15 x 15 x 60
2
bd
PL
fr
2
3
bd
Pa
fr
Utilization of Volcanic Ash of Mount Sinabung as a Substitute for Cement to Flexure Strength of Geopolymer Concrete
335
cm at 7 days of age. The results of the average flexure
strength test can be seen in Table 6.
Table 6: Average Flexure Strength of Geopolymer
Concrete
N
o
Curing
Time
(Hours
)
Curing
Temperatur
e (
o
C)
Average
Flexure
Strength
(Mpa)
1 4 60 2,78
2 8 60 3,29
3 12 60 3,79
4 24 60 4,53
[6]
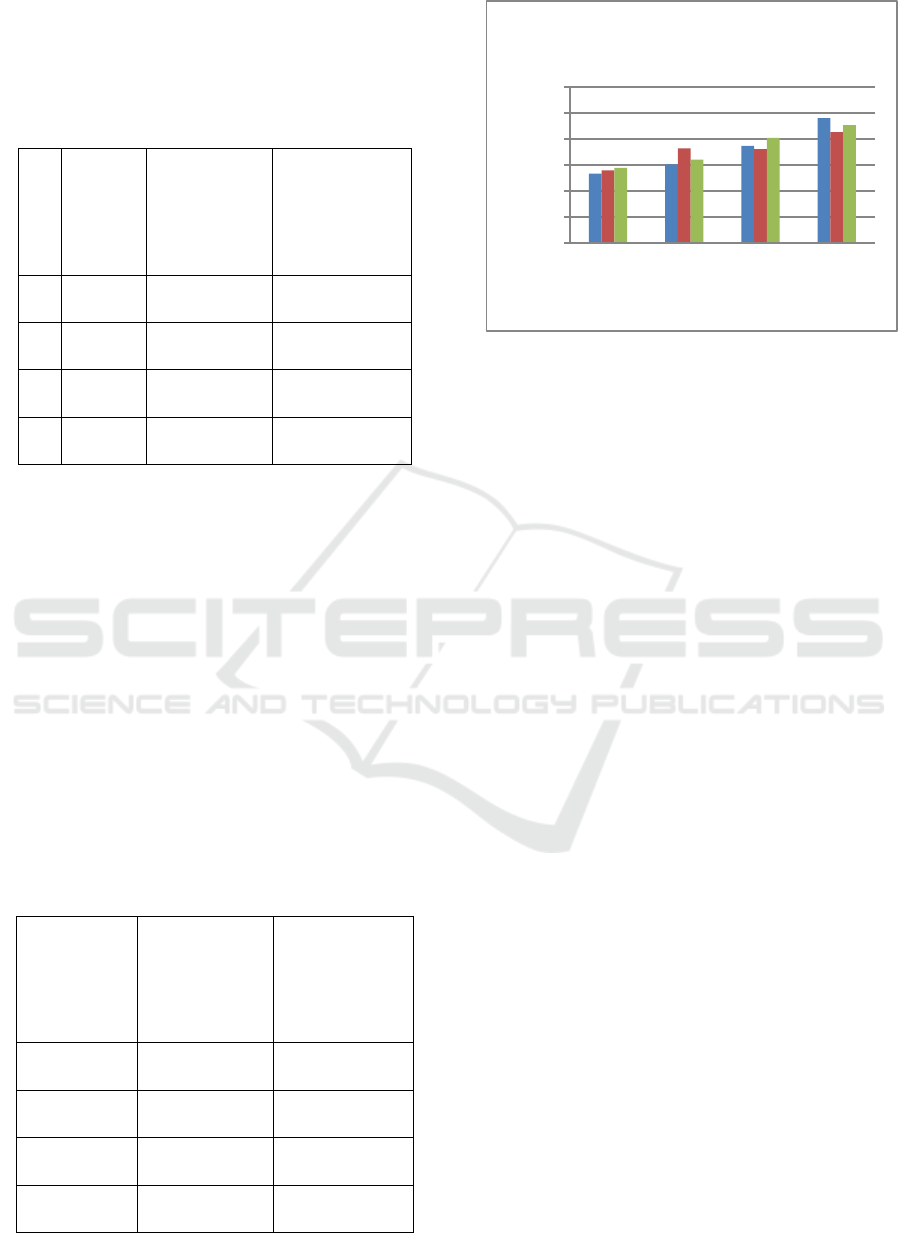
From the table and graph above, it can be seen that
there is an increase of flexural strength of geopolymer
concrete along with the length of treatment time in the
oven (Curing Time) at 60
o
C. The longer the curing
time on the concrete samples, the higher the strength
of the concrete flexure is. Maximum flexure strength
occurs at 24 hours curing time.
From the results of the research of flexure strength of
geopolymer concrete, it is obtained a concrete
conversion value at 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours, to 24
hours curing time.
Table 7: Conversion Table of Geopolymer Concrete
Flexure Strength
Curing
Time
(Hours)
Flexure
Strength
(Mpa)
Conversion
Value of
Flexure
Strength
4 2,78 0,61
8 3,29 0,73
12 3,79 0,84
24 4,53 1,00
Figure 5: Flexure Strength Comparison
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the test results, data processing and analysis, it
can be concluded as follows:
1. Based on the test results, it can be concluded that
the optimum variation is on the variation with
24 hours curing time because it has the highest
flexure strength. For 24 hours curing time
variation, the average flexure strength is 4.53
MPa.
2. Based on the discussion, it can be concluded that
the flexure strength value of geopolymer
concrete increases along with the length of
treatment time in the oven (Curing Time) at
60oC. The average flexure strength of 7days of
age concrete and being ovened for 24 hours has
a flexure strength of . The longer the curing
time on the concrete samples, the higher the
strength of the concrete flexure is. Maximum
flexure strength occurs at 24 hours curing time.
6 SUGGESTIONS
Based on the results obtained in this research, the
author provides some suggestions as follows :
1. Conducting variation of curing temperature
more than 60
o
C and more than 24 hours curing
time and more than 7 days of concrete age to
obtain an optimum flexure strength of concrete.
2,67
3,02
3,73
4,8
2,79
3,64
3,61
4,26
2,88
3,20
4,04
4,53
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
4 Hours 8 Hours 12 Hours 24 Hours
f'c (MPa)
Ovening Time (Hours)
Comparison of Geopolymer
Concrete Flexure Strength
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
336

2. Conducting further research by varying the
molarity of NaOH and the ratio between
Na2SiO3 and NaOH to obtain an optimum
value.
3. Noticing the use of vaseline for formwork of
samples because the incorrect use of vaseline
can cause a sticky samples when opening the
formwork.
4. Conducting research on the mechanism and
method of mixing of geopolymer concrete
materials connected with concrete workability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you to USU Research Institute and
TALENTA USU Research Program 2018 for
funding this research.
REFERENCES
Davidovits, J. (1999). Chemistry of Geopolymeric
Systems, Terminology In: Proceedings of 99
International Conference. eds. Joseph
Davidovits, R. Davidovits & C. James,
France.
Ekaputri, J. J., & Triwulan, T. (2013). Sodium
sebagai Aktivator Fly Ash, Trass dan Lumpur
Sidoarjo dalam Be
GEOPOLIMER, TERHADAP KUAT MEKANIK
BETON. "PENGARUH MOLARITAS
AKTIFATOR ALKALIN TERHADAP
KUAT MEKANIK BETON GEOPOLIMER
DENGAN TRAS SEBAGAI PENGISI."
Karolina, Rahmi, M. Agung Putra, and Tito Agung
Prasetyo. "Optimization of the use of volcanic
ash of Mount Sinabung eruption as the
substitution for fine aggregate." Procedia
Engineering 125 (2015): 669-674.
Mulyono, Tri. "Teknologi Beton." Yogyakarta:
Andi(2004).
Risdanareni, Puput, Adjib Karjanto, Januarti Jaya
Ekaputri, Poppy Puspitasari, and Febriano
Khakim. "Mechanical properties of volcanic
ash based geopolymer concrete." In Materials
Science Forum, vol. 857, pp. 377-381. Trans
Tech Publications, 201
Utilization of Volcanic Ash of Mount Sinabung as a Substitute for Cement to Flexure Strength of Geopolymer Concrete
337
