
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of MDR1 C1236T Gene and Its
Association with Neutropenia Event in Breast Cancer Patients
Treated b
y
Chemotera
py
S. Syarifah
1*
, T. Widyawati
1
,
D. Hasni
2
and D. R. Anggraini
3
1
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutic, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155,
Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Baiturrahmah, Padang, Indonesia
3
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: Neutropenia, Polymorphism, Breast cancer.
Abstract: Neutropenia event was one of the side effect which could be occurred in breast cancer patients receiving
chemotherapy. MDR1 gene is a gene that encoded P-glycoprotein (P-gp), an active efflux pump for a variety
of carcinogens and cytostatics. It has been suggested that MDR1 polymorphisms C1236T contribute to the
variability of therapeutic outcome and side effects. The present study was conducted to investigate the
association of C1236T polymorphisms in MDR1 gene with neutropenia incidence in breast cancer patients
treated with antracycline based chemotherapy. As many as 144 Indonesian women’ isolated DNA samples
were amplified using the PCR method. The analysis process of MDR1 C1236T polymorphism were done by
using PCR-RFLP method. The frequencies of MDR1 C1236T genotype for homozygous CC, heterozygous
CT and variant TT was 13 (9,03%), 93 (64,58%), and 38(26,39%) respectively. There was no association
between MDR1 C1236T polymorphisms with neutropenia event (p > 0.05). However, 69 patients (47.9%)
.suffered for neutropenia event. Limitation: the data of patients were collected only after 3 cycles of
chemotherapy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The incidence of breast cancer increased every year,
especially in developing countries due to the
increased of life expectancy, lifestyle, urbanization,
and the majority of cases detected when it is already
achieved in advanced stage (World Cancer Research,
2015). Chemotherapy as one of the important things
in the management of breast cancer patients increased
life expectancy but also various side effects
(Vulsteke, 2013). Neutropenia event is one of the side
effects which can be harmful to the patients due to
increased of infection’s risk and delayed
chemotherapy (Fung, 2009).
The pharmacogenomic studies have contributed
significant advances on how genetic patterns can be
used to predict the efficacy and safety of
chemotherapy in breast cancer (Franke, 2010). The
presence of genetic polymorphisms in the MDR1
C1236T gene in exon 12 which encoded P-
glycoprotein (P-gp) associated with the increased of
neutropenia incidence due to chemotherapy. P-gp is a
transporter protein that acts as an active effluent
pump for various toxins including carcinogens and
medicines such as antineoplastic drugs like
doxorubicin and taxan. Interestingly, P-gp is mainly
expressed in bone marrow and peripheral leukocytes,
the presence of P-gp in bone marrow and peripheral
leukocytes certainly has a protective effect of cells
against drug accumulation into cells (Tazzite, 2016).
Several studies showed the relation of MDR1
polymorphism with hematological toxicities, but the
results was inconsistent and there was no many data
about MDR1 polymorphism in Indonesia
(Milojkovic, 2016).
Therefore, we evaluated the relationship of
C1236T polymorphism with degree of neutropenia
both individually breast cancer patients who treated
by doxorubicin based chemotherapy. The results of
this study are expected to provide information related
to the role of pharmacogenomics in response to
treatment.
Syarifah, S., Widyawati, T., Hasni, D. and Anggraini, D.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of MDR1 C1236T Gene and Its Association with Neutropenia Event in Breast Cancer Patients Treated by Chemoterapy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010092808330836
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
833-836
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
833
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
We conducted a cohort study recruited 144 breast
cancer patients receiving anthracycline base
chemotherapy in Adam Malik Hospital.
2.1 Study Area
This study was conducted at Adam Malik Hospital
and Facullty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera
Utara.
2.2 Samplings
Protocol of this study has been approved by Medical
Ethics Committee Universitas Sumatera Utara
(No. 386/TGL/FK/KEPK FK USU-RSUP
HAM/2018).
2.2.1 Recruiting Methods
Subjects of this study were purposively selected
according to the inclusion criteria. Most of the
subjects who had been diagnosed and treated by
anthracycline base chemotherapy at Adam Malik
Hospital were recruited for this study.
2.2.2 Subjects Characteristics
This study has recruited 144 breast cancer patients.
The characteristic of the patients fulfil the inclusion
criteria: had histologically confirmed breast cancer,
had been planned to receive anthracycline base
regimen of chemotherapy, ages 16– 68 years old, had
normal liver function and kidney function, had a
normal complete blood count (CBC).
2.2.3 Data Collection
The data of subjects’s characteristic and neutropenia
were collected from medical records for three cycles
of chemotherapy. The data of MDR1 C1236T
polymorphism were collected using PCR-RFLP
method. DNA Amplification of MDR1 C1236T using
GoTaq® Green Master Mix (Promega) of 12.5 μl,
primer of exon forward 12 MDR1 5-
'GCCACAGTCTGCCCACTC-3 'and reverse exon
12 MDR1 5-'CCCATCGAAAAGAAATTAAG-3',
respectively 1 μl, nuclease free water as much as 7.5
μl and 3 μl DNA with final volume is 25 μl. The
amplification process consisted of an initiation
denaturation stage, followed by a 30-second
denaturation step, annealing stage, extension stage
and elongation stage for 10 minutes (Syarifah, 2016)
3 RESULTS
The results consist of characteristic of subjects,
frequency of allele and genotype of MDR1 C1236T
polymorphism, the association of MDR1 C1236T
polymorphism with neutropenia.
3.1 Characteristic of Subjects
This study include 144 subjects. We found five
ethnics include Bataknese, Malay,
Javanese,Acehnese and others (Tionghoa and India).
The majority of the subjects were Bataknese (52,8%),
the group of age were 40-50 years old (39,6%), had
job as housewives (63,9%). Most of the subjects were
detected at late stage (61,8%) and 69 patients suffered
for neutropenia after 3 cycles of chemotherapy
(47,9%)[Table 1].
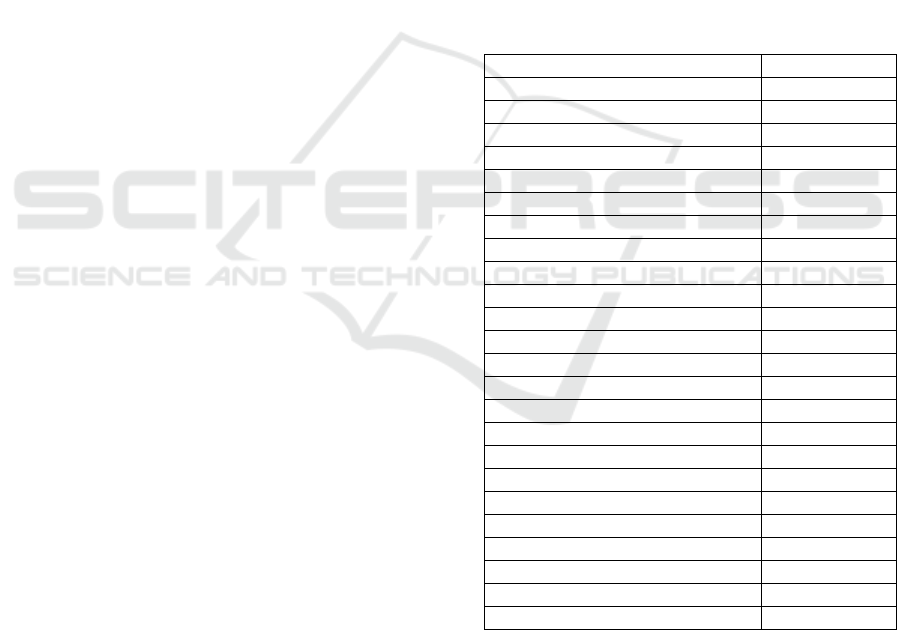
Table 1: Characteristic of subjects
Variables N (%)
Group of age
<40 14(8.5)
40-50 57(39.6)
51-60 54(37.5)
>60 18(11.8)
Ethnic
Bataknese 76(52.8)
Javanese 40(27.8)
Acehnese 14(9.7)
Malay 11(7.6)
Others 3(8.4)
Job
Housewives 92(63.9)
Public Employee 35(24.3)
Private Employee 10(6.9)
Farmer 7 (4.9)
Stages of breast cancer
II 41(28.5)
III 89(61.8)
IV 14(9.7)
Degree of neutropenia
Normal 75(52.1)
Degree 1-2 52(36.1)
Degree 3-4 17(11.8)
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
834
3.2 Frequency of Allele and Genotype of
MDR1 C1236T Polymorphism
Frequency of allele and genotype can be seen below
[Table 2]
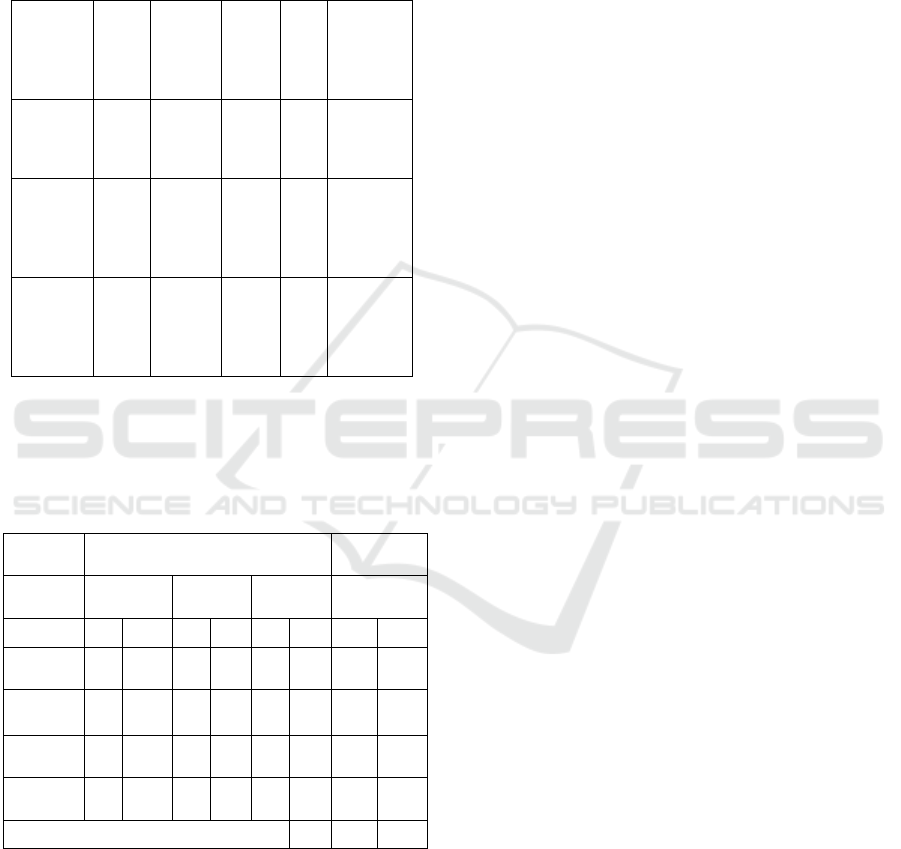
Table 2: Frequency of allele and genotype of MDR1
C1236T polymorphism
Polymo
rphism
Gen
otyp
e
n (%)
Allel
e
(%
)
Hardy-
Weinber
g p
C1236T CC
13
(9.02)
CT
93
(64.58
)
C 62 0,61
TT
38
(26.38
)
T 38
3.3 The Association of MDR1 C1236T
Polymorphism with Neutropenia
The association of MDR1 C1236T polymorphism
with neutropenia can be seen below [Table 3]
C1236
T
Degree of Neutropenia
Total
Normal
Degree
1-2
Degree
3-4
n % n % n % n %
CC 7 4.8 5
3.
4
1
0.
6
13 34
CT
4
7
32.
6
3
6
25
1
0
6.
9
93
53.
1
TT
2
1
14.
6
1
1
7.
6
6
4.
2
38
12.
9
Tot
al
7
5
52
5
2
36
1
7
12
14
4
100
P: 0.096 (Kruskal- wallis Test)
4 DISCUSSION
The C allele frequencies tend to be higher than T
allele in C1236T. Based on the distribution of
polymorphism, the frequency of alleles and genotype
in this study more closely related to Asian
populations than Caucasians. In this study, p> 0,05
shows that there is no significant genotype and allele
frequency deviation based on Hardy-Weinberg
Equilibrium.In this study, as shown in Table 3, 52
subjects (36%) had mild neutropenia (1-2 degrees)
and 17 people (12%) had severe neutropenia (grade
3-4). C1236T polymorphisms had no significant
association with neutropenia (p> 0.05). The results of
this study are in line with a study which shows no
significant association between MDR1
polymorphism and bone marrow suppression events
(Cizmarikova, 2010). Studies conducted) in 121
cancer patients who received paclitaxel
chemotherapy also showed that there was no
association between MDR1 polymorphism with the
incidence of neutropenia of grade 3 and 4 (Chang,
2010). The results of this study contradict the studies
which indicate that the homozygous variant of TT has
a relationship to the incidence of severe neutropenia
(Taheri, 2010) (Sissung, 2006). The presence of a TT
variant is known to cause lower P-gp expression. The
absence of any association between MDR1 C1236T
with the occurrence of neutropenia may be due to
other influencing factors such as the presence of other
gene polymorphisms and the influence of MDR1
C3435T, C1236T polymorphism, it is known that the
common haplotype in the MDR1 gene were C3435T,
C1236T and G2677T (Syarifah, 2016)
5 CONCLUSION
In this study, all forms of GG,GT and TT
polymorphisms in G2677T were found. There was no
significant association between MDR1 G2677T
polymorphisms with neutropenia grading. Advanced
research is needed with larger sample quantities to
confirm and compare the results obtained with respect
to gene polymorphisms related to treatment response.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge to the
Universitas Sumatera Utara for supporting this study.
The research was supported by the research grant
TALENTA USU of The Year 2018 Contract Number
2590 / UN5.1.R / PPM / 2018, date 16 March 2018.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of MDR1 C1236T Gene and Its Association with Neutropenia Event in Breast Cancer Patients Treated by
Chemoterapy
835

REFERENCES
Chang H, Rha SY, Jeung HC, et al. 2010. Association of
the ABCB1 3435C>T polymorphism and treatment
outcomes in advanced gastric cancer patients treated
with paclitaxel- based chemotherapy. Oncol Rep, 23,
271-8
Cizmarikova M, Wagnerova M, Schonova L, Habalova V,
Kohut A, Linkova A, Sarissky M, Mojzis J, Mirossay L,
Mirossay A. 2010. MDR1 (C3435T) polymorphism:
relation to the risk of breast cancer and therapeutic
outcome. Pharmacogenomics J.;10(1):62–9.
Fung KL, Gottesman MM. 2009. A synonymous
polymorphism in a common MDR1 haplotypes shapes
protein function. Biochim Biophys Acta.
Franke RM, Gardner ER, Sparreboom A. 2010.
Pharmacogenetics of Drug Transporters. Curr Pharm
Des.;16:220–30.
Milojkovic M, Stojnev S, Jovanovic I, Ljubisavljevic S, et
al. 2011. Frequency of the C1236T, G2677T/A and
C3435T MDR1 gene polymorphisms in the Serbian
population.. Pharmacol. Rep. 63: 808-814.
Sissung TM, Mross K, Steinberg SM, Behringer D, Figg
WD, Sparreboom A, et al. 2006. Association of ABCB1
genotypes with paclitaxel-mediated peripheral
neuropathy and neutropenia. Eur J Cancer.;42:2893–6.
Syarifah S, Siregar KB, Siregar Y. 2016. Association of
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 gene
C3435T polymorphism with neutropenia in breast
cancer patients treated with chemotherapy.Med J
Indones 25 156-62
Taheri M, Mahjoubi F, Omranipour R. 2010. Effect of
MDR1 polymorphism on multidrug resistance
expression in breast cancer patients. Genet Mo
lRes.;9(1):34–40.
Tazzite A, Kassogue Y, Diakité B, Jouhadi H, Dehbi H,
Benider A and Nadifi S. 2016. Association between
ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk:
a Moroccan case-control study and meta-analysis.
BMC Genet 17 126
Vulsteke C, Lambrechts D, Dieudonné A, Hatse S,
Brouwers B, Brussel T Van, Neven P, Belmans A,
Schöffski P and Paridaens R.2013. Genetic variability
in the multidrug resistance associated protein-1
(ABCC1/MRP1) predicts hematological toxicity in
breast cancer patients receiving (neo-)adjuvant
chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin and
cyclophosphamide (FEC). Annals of Oncology.
World Cancer Research.2015.Breast Cancer Prevention
and Control.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
836
