
The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial
Intention
Fadli
1
, Yasmin Chairunisa
1
Muchtar and Inneke Qamariah
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, 9 Dr. Mansur Street, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Entrepreneurship Education, Entrepreneurial Intention.
Abstract: Unemployment problem is one of the most common problems in developing countries. Indonesia with
population of about 258.7 million possess unemployment rate of 5.61%. Meanwhile, neighboring country
like Singapore owns a lower unemployment rate of 2.1%. One way to cope with a high number of
unemployment is by creating entrepreneurship. With entrepreneurship, someone will be a job creator not a
job seeker, which will reduce the dependency level on employment providers. A joint effort from various
parties is needed to build a condition which allows the rapid growth of entrepreneurship. At the same time,
university as one of main pillars in generating the successor of the nation is also responsible in increasing
the number of entrepreneurships. There are a wide variety of entrepreneurial education compositions
formulated by the university to attract the interest of the students, which encourage them to choose
entrepreneurship as a career. This research aims to analyze the effect of entrepreneurship education on
entrepreneurial intention. Result shows that entrepreneurship education have a positive and significant effect
on entrepreneurial intention. In general, in order to increase the entrepreneurial intention, it should focus on
the improvement of entrepreneurship education.
1 INTRODUCTION
Unemployment problem is one of the most common
problems in developing countries. As well as
Indonesia with population of about 258.7 million
which possess unemployment rate of 5.61%.
Meanwhile, neighboring country like Singapore
owns a lower unemployment rate of 2.1%. A high
level of unemployment is raising concerns as it can
lead to more severe socio-economic problems.
One way to cope with a high number of
unemployment is by creating entrepreneurship. With
entrepreneurship, someone will be a job creator not a
job seeker, which will reduce the dependency level
on employment providers. Therefore, a joint effort
from various parties is needed to build a condition
which allows the rapid growth of entrepreneurship.
One of the government’s active roles in promoting
the growth of entrepreneurship is through Nascent
Enterpreneurship Program (Program Wirausaha
Pemula) and National Enterpreneurship Movement
(Gerakan Kewirausahaan Nasional) since 2013 by
the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs
(Departemen Koperasi dan UKM).
At the same time, university as one of main
pillars in generating the successor of the nation is
also responsible in increasing the number of
entrepreneurships. There are a wide variety of
entrepreneurial education compositions formulated
by the university to attract the interest of the
students, which encourage them to choose
entrepreneurship as a career. Izedonmi and Okafor
(2010) explored the education of Nigerian students,
found a positive effect towards intentions. It was
discovered that eventhough joinning in the
entreprenuerial education, it was not automatically
lead to the intentions of entrepreneurial.
In this context, therefore it is vital to investigate
the valuable contribution of higher education
towards the entrepreneurial intentions of students.
Hence, the objective of this paper is to investigate
the effect of entrepreneurship education on students’
entrepreneurial intentions.
The objective of this research is to analyze the
effect of entrepreneurship education on
entrepreneurial intention of University students in
Universitas Sumatera Utara.
1566
Fadli, ., Muchtar, Y. and Qamariah, I.
The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention.
DOI: 10.5220/0010089115661569
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
1566-1569
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Entrepreneurship Education on
Entrepreneurial Intention
Entrepreneurial intention is a cognitive illustration
of an objective a person wants to achieve with a
greater effort. It includes the development of a plan
that someone seeks and utilizes to achieve their
goals (Tubbs & Ekeberg, 1991). Entrepreneurial
intention has been described as “a conscious state of
mind that directs attention (and therefore experience
and action) toward a specific object (goal) or
pathway to achieve it (means)” (Bird, 1989, p. 8).
In this regard Katz (2003), and Lautenschläger
and Haase (2011) disclosed that the popularity of
entrepreneurship as part of business education is
increasing at university and college level, and it is
becoming popular as well around the globe. Last few
decades, entrepreneurship has emerged as a widely
taught subject to the university graduates.
Spiteri and Maringe (2014) classified four
important elements that express the nature of
entrepreneurial education in universities in Europe:
pedagogy; assessment; content; and role model
lecturer. In another study, satisfaction of university
students in Indonesia was examined in terms of the
content of learning and teaching, methodology of
teaching and expected results with the
implementation of entrepreneurship education
(Abduh, Maritz, & Rushworth, 2012). Vukovic,
Kedmenec and Korent (2015) posited four different
ideas or stages of entrepreneurship education:
entrepreneurial awareness education; education for
newly business; entrepreneurial dynamism
education; and continue education for entrepreneurs.
Entrepreneurship education is designed to instill
the competency, skill, and value needed to recognize
the business opportunity, as well as organize and
establish a new business (Brown in Izedonmi and
Okafor, 2010). The competence obtained by the
students is not only limited to the competence to sell
product or service as in the mindset of the people
who consider entrepreneurs as traders. Based on a
research performed by Oguntimehin and Olaniran
(2017), entrepreneurship education is a significant
contributor to entrepreneurial intention.
Hypothesis 1A: Entrepreneurship Education has
a positive and significant effect on Entrepreneurial
Intention.
Figure 1: Research Framework.
3 METHOD AND RESULT
The type of research conducted is causal associative
(causality). The population in this research is 4279
students from Faculty of Economics and Business,
Faculty of Public Health, Faculty of Engineering
batch 2015 and 2016 in University of Sumatera
Utara that had already received entrepreneurship
courses. As these faculties have an entrepreneurship
curriculum and the students are willing to be
entrepreneurs. Samples are selected by utilizing the
simple random sampling. A simple random sample
is a subset of a statistical population in which each
member of the subset has an equal probability of
being chosen.
The dimensions of Entrepreneurship Education
are (1) Subject, (2) Education Facilities, (3) Practice,
and (4) Lecturers Competence. And the indicators
are business management, finance, human resources
and innovation, laboratory, books and journals,
business plan, observation and product
innovation/process, teaching method, and
experience.
The dimensions of Entrepreneurial Intention to
capture behaviour intention towards starting
business are (1) Preparation to develop product or
services, (2) Preparation to develop teamwork, (3)
Preparation to look for a building or equipment, (4)
Business plan, and (5) Financial Investment.
The samples were taken with slovin method by
the formula as followed:
N =
N =
N =
N =
= 97,71
In this research the number of the samples are
rounded up to 100 university students.
Here is the table of distribution of samples of
faculties and batches:
Entrepreneurship
Education
Entrepreneurial
Intention
The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention
1567
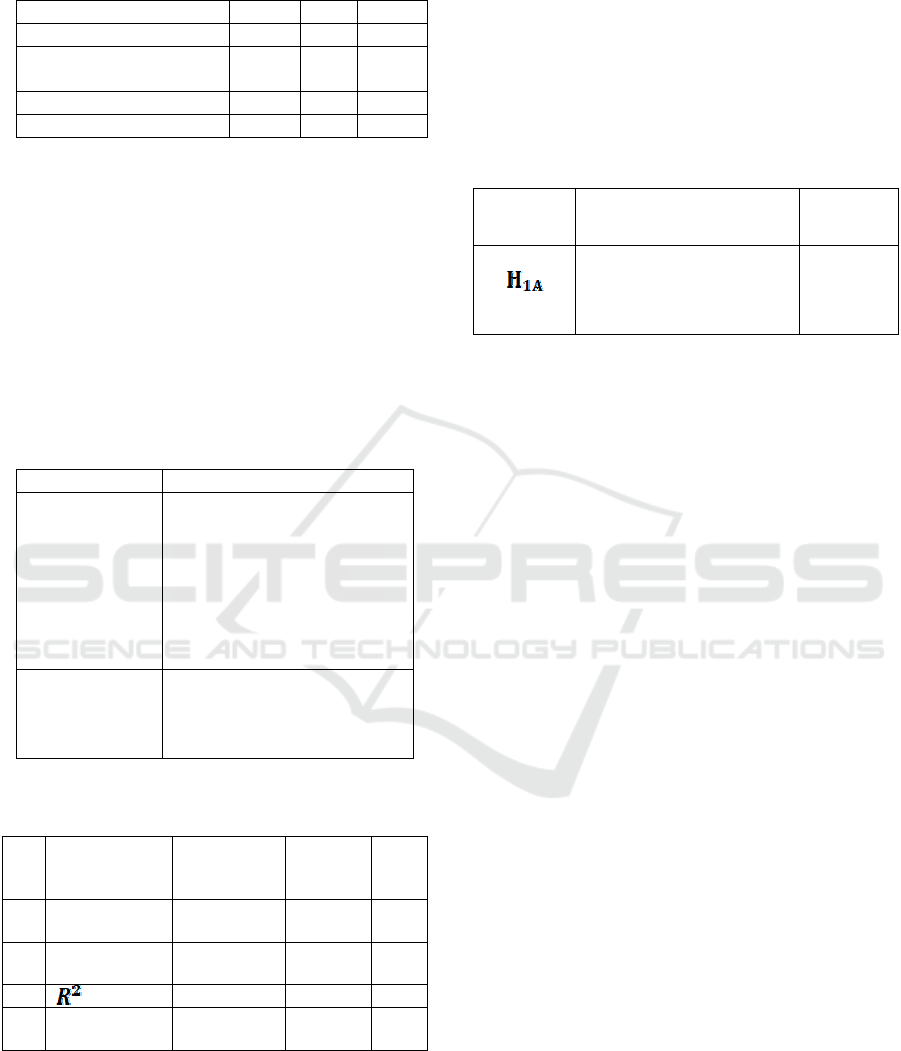
Table 1: Sample Based on Proportion of Faculties and
Batches.
Faculties 2015 2016 Total
Faculty of Public Health 12 7 19
Faculty of Economics and
Business
24 25 49
Faculty of Engineering 15 17 32
Total 51 49 100
Source: Processed Data (2018)
This research used two types of data resources,
which are: (1) Distribution of Questionnaires, and
(2) Documentations Studies. Simple linear
regression analysis is used as data analysis technique
to discover the influence of the independent
variables which is Entrepreneurship Education to the
dependent variable that is Entrepreneurial Intentions
in University Students. Also, this research is using
descriptive statistical analysis method and depth
interview as data analysis techniques.
Table 2: Operational Definition.
Variable Operational Definition
Entrepreneurship
Education
Entrepreneurship education is a
program to increase the
awareness and understanding
of entrepreneurship as a
process as well as to increase
students’ awareness of
Entrepreneurship as a career
possibility.
Entrepreneurial
Intention
Entrepreneurial intention is a
cognitive illustration of an
objective a person wants to
achieve with a greater effort.
Table 3: The Result of Simple Linear Regression
Analysis.
No Variables Coefficients t-Values
Sign
ifica
nt
1 Constant 5.510 3.300 0.00
1
2 Entrepreneurs
hi
p
Education
0.217 7.989 0.00
0
3
= 0.394
4 (F-Statistic =
63.825)
0.00
0
It is found the Simple Regression Analysis
Model is:
Y = 5.510 + 0.217EE + e
Table 4.10 shows partially Entrepreneurship
Education (Sig. = 0.000 < 0.05) is significantly
affecting Entrepreneurial Intention.
The coefficient determination of this research is
0.394, which means that Entrepreneurship Education
contributed 39.4% to explain Entrepreneurial
Intention. While the remaining of 60.6% is
explained by other variables.
Table 4: Summary of Hypothesis Tests.
Hypothesis
No.
Statement Decision
Entrepreneurship Education
has a positive and
significant effect on
Entrepreneurial Intention.
Supported
Entrepreneurship education have positive and
significant impact on entrepreneurial intention
among university students. It may explain the
improvement of entrepreneurship education will
generate the entrepreneurial intention. University
students are inspired to be entrepreneur through the
best quality of curriculum, lecturer and the
availability of laboratory facilities in the faculty. As
stated by Wennberg and Berglund (2008) most
program of university have tried to increase the
awareness of students to focus on develop new
ventures. Yet, it remains big question what is
specific educations program are most effective to
increase entrepreneurial intention. However,
Universitas Sumatera Utara has develop strong
foundation to instill the entrepreneurial mindset
among the students through various entrepreneurial
program.
According to Liñán & Chen (2009),
entrepreneurial intention has a very important role
when deciding to start a business venturing, as
evidenced by a significant number of scientific
papers dealing with this issue. In order for a person
to become an entrepreneur, he/she must first show a
certain degree of entrepreneurial intent (Bird, 1988).
The existence of entrepreneurial intention is a
reliable predictor of entrepreneurial behavior and
entrepreneurship (Koe, 2016).
Although we have focused in university
education, the entrepreneurial education may not be
only related to development process of becoming an
entrepreneur or tied to the specifics stages of starting
a business. It even has crucial contribution to
economic development, spirit to start their own
business and many more.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
1568

We also found that students engaged in practice
base methods of teaching for entrepreneurship
programs such as the entrepreneurship week,
business consultancy program and student
entrepreneurship center have higher intentions to
start their own businesses in the future. However,
there is no significant difference between students
from business program and non-business program in
terms of entrepreneurial intention. It is quite
surprising since the degree of entrepreneurship
education contents are higher for business program
students than non-business program.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusion of this research is entrepreneurship
education have a positive and significant effect on
entrepreneurial intention. In general, in order to
increase the entrepreneurial intention, it should focus
on the improvement of entrepreneurship education.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to express the gratitude to
Universitas Sumatera Utara for the financial support
for this research. That support has given us a great
opportunity to present this paper in the ICOSTEERR
2018. Moreover, we would like to gratefully
acknowledge the contribution of research reviewers,
Faculty of Economics and Business, and all the
research team members for the completion of this
paper.
REFERENCES
Abduh, M., Maritz, A., & Rushworth, S. (2012). An
evaluation of entrepreneurship education in Indonesia:
a case study of Bengkulu University. The International
Journal of Organizational Innovation, 4(4), 21-47.
Bird, B. (1988). Implementing entrepreneurial ideas: The
case for intentions. Academy of Management Review,
13, 442-453.
Bird, B.J. (1989), Entrepreneurial Behavior, Scott
Foresman and Co., Glenview, IL.
Caird, S. (1990). What does it mean to be enterprising?
British Journal of Management, 1(3), 117-145.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8551.1990.tb00002.x.
Hamidi, D.Y., Wennberg, K. & Berglund, H. (2008).
Creativity in entrepreneurship education. Journal of
Small Business and Enterprise Development, 15(2),
304-320.
IAC Integral Assets Consulting. (2006). Youth
Entrepreneurship: Theory. Practice and Field
Development. A Background Paper Prepared for the
W. K. Kellogg Foundation Youth and Education Unit.
Iglesias, S. P. P., Jambrino, M. C., Velsco, A. P., &
Kokash, H. (2016). Impact of entrepreneurship
programmes on university students. Education +
Training, 58(2), 209-228. https://doi.org/10.1108/ET-
01-2015-0004
Izedonmi, P. F. and Okafor, C. 2010. The Effect Of
Entrepreneurship Education On Students’
Entrepreneurial Intentions. Global Journal of
Management and Business Research, Vol. 10 Issue 6
(Ver 1.0).
Katz, J.A. (2003), “The Chronology and Intellectual
Trajectory of American Entrepreneurship Education
1876 – 1999”, Journal of Business Venturing, Vol. 18
No. 2, pp. 283–300.
Koe, W. L. (2016). The relationship between Individual
Entrepreneurial Orientation (IEO) and entrepreneurial
intention. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship
Research, 6(1), 13.
Lautenschläger, A. and Haase, H. (2011), “The Myth of
Entrepreneurship Education: Seven Arguments against
Teaching Business Creation at Universities”, Journal
of Entrepreneurship Education, Vol. 14, pp. 147–161.
Liñán, F., & Chen, Y. W. (2009). Development and Cross-
Cultural Application of a SpeciM c Instrument to
Measure Entrepreneurial Intention. Entrepreneurship
Theory and Practice, 33(3), 593-617.
Oguntimehin, Y. A., and Olaniran, O. O. 2017. The
Relationship Between Entrepreneurship Education and
Students’ Entrepreneurial Intentions in Ogun State-
owned Universities, Nigeria. British Journal of
Education, 5(3), 9-20.
Spiteri, S., & Maringe, F. (2014). EU entrepreneurial
learning: perspectives of university students. Journal
of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the
Global Economy, 8(1), 51-70.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JEC-07-2013-0023
Tubbs, M.E. and Ekeberg, S.E. 1991. The Role of
Intentions in Work Motivation: Implications For Goal-
Setting Theory and Research, Academy of
Management Review, 16 (1), 180-199.
Vukovic, K., Kedmenec, I., & Korent, D. (2015). The
Impact of exposure to entrepreneurship education on
student entrepreneurial intentions. Croatian Journal of
Education, 17(4), 1009-1036.
Wennberg, K. J., and Berglund, H. 2008. Creativity in
Entrepreneurship Education. Journal of Small
Business and Enterprise Development.
www.bps.go.id.
The Effect of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention
1569
