
Influence of Tannin Concentration from Banana Peel as Iron
Inhibition in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
R. Tambun
1*
, Y. F. Pakpahan
1
, E. Christamore
1
and B. Haryanto
1
1
Department of Chemical Engineering, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Padang Bulan, Medan 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: Banana Peel, Tannin, Corrosion Rate, Inhibition Efficiency.
Abstract: Banana peel contains tannin that could be used as corrosion protection of iron. This study aims to determine
the effect of tannin from banana peel on corrosion inhibition of iron plate in 3% hydrochloric acid solution.
The banana peel used in this study is unripe Awak Banana peel. The variables observed are soaking method,
inhibitor concentration and immersion time, and the parameters studied are corrosion rate of iron and
corrosion inhibition efficiency. In this experiment, the lowest corrosion rate and highest inhibition efficiency
are obtained on immersion of iron for 12 days in hydrochloric acid solution and addition of 9 g of tannin
inhibitor. In this condition the corrosion rate is 7.2578 mpy and the corrosion inhibition efficiency is 97.79%.
The results showed that tannin from Awak banana peel could be used as corrosion inhibition of iron in
hydrochloric acid solution.
1 INTRODUCTION
Corrosion is the most common problem found on a
daily life, both in the household and in industry.
Corrosion is the degradation of the destruction of the
quality of metallic properties through a natural
electrochemical reaction and it happens because of
chemical phenomena with the environment.
Corrosion can’t be stopped but can be controlled, so
various attempts are done to inhibit corrosion
(Darmokoesoemo et al., 2018). Organic inhibitors or
commonly referred to as green inhibitors are a safe
type of inhibitor because they have an eco-friendly or
biodegradable, economical, and widely available in
nature. The plants that can be used as organic
inhibitors are plants that have antioxidant properties,
such as containing flavonoid compounds, tannins,
ascorbic acid, phenolic, and others (Chancay and
Poosaran, 2009).
In this study, the corrosion inhibitor used is unripe
Awak banana peel (Musa paradisiacal var. Awak).
Unripe banana peels have a tannin content about
6.48%, almost mature banana peels about 4.97 % and
ripe banana peel about 4.69% (Tartrakoon et al.,
1999). Tannins protect the iron from corrosion in
hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution due to the
adsorption of tannins onto the iron surface (Agi et al.,
2018; Madhu et al., 2018). Tannin inhibits the
oxidation of Fe
2 +
ions to iron oxides and avoid
corrosion inhibition (Al-Amiery et al., 2014). Banana
peel is very potential to be used as a corrosion
inhibitor because it has high antioxidant (Gopal et al.,
2015). Wang, et al. vary the addition of a corrosion
inhibitor concentration and the results obtained that
the efficiency of the inhibitor is higher with
increasing inhibitor concentration (Wang et al.,
2016). Al-Moubaraki, et al. vary the time of
immersion metal plates in the media and the results
obtained that the longer the immersion time, the
corrosion rate of metal will be higher (Al-moubaraki
et al., 2015). Based on the above study, this study is
aimed to develop banana peel tannin as iron corrosion
inhibitor in HCl medium. In this experiment, the
influence of tannin concentration from Awak banana
peel and duration of immersion of iron in HCl
solution will be investigated experimentally.
2 METHODS
2.1 Qualitative Analysis of Tannins on
Extracts
Materials used in this study are iron specimen (Fe)
with the size 1 cm x 2 cm x 0.2 cm, 3% HCl solution
of 50 ml as medium, Awak banana peel (Musa
Tambun, R., Pakpahan, Y., Christamore, E. and Haryanto, B.
Influence of Tannin Concentration from Banana Peel as Iron Inhibition in Hydrochloric Acid Solution.
DOI: 10.5220/0010087502970301
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
297-301
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
297

paradisiacal var. Awak) from Pringgan Market
Medan, distilled water, methanol, FeCl
3
, ethyl
acetate, and the equipment used in this research
include beaker glass, rotary vacuum evaporator,
Whatman no 41 filter paper, oven, blender, and
analytical balance. In this experiment, the smooth
iron surface is washed with detergent and distilled
water, then dried in an oven at 110 ° C for 2 hours so
that the iron does not contain water.
In this study, the unripe Awak banana peel is dried
in the air to remove the water content then the banana
peel is cut into small pieces about 1 cm, then dried in
the sun for 3 days. Banana peel is put in an oven at 80
o
C. Banana peel is blended to be powder and sieved
by using sieve tray of 50 mesh. The powder is
macerated with methanol at a ratio of 7:1 for 24 hours
then filtered by using filter paper of Whatman no
41. The filtrate is removed with a rotary vacuum
evaporator at a temperature of 65
o
C into a paste
form. The crude extract is analyzed qualitatively. The
crude extract of banana peel is dissolved with ethyl
acetate, stirred until dissolved, then settled to form
precipitate. The precipitate is filtered and then
washed again with ethyl acetate until the filtrate is
clear. The insoluble precipitate in ethyl acetate is
tannin. Iron is then immersed in a 3% HCl of 50 ml
without the presence of tannin and with additions of
1 gram, 3 gram, 5 gram, 7 gram, and 9 gram of tannin.
The immersion durations are 3 days, 6 days, 9 days,
and 12 days. Then the rate of corrosion reaction and
the corrosion inhibition efficiency are calculated.
The corrosion rate, CR (mils/year or mpy) is
determined by equation (1) (Ali and Hamedh, 2016):
CR=
KW
DAt
(1)
where K is constant (3.45 x 10
6
), W is mass loss (g),
D is density (g/cm
3
), A is surface area (cm
2
), and t is
immersion time (hours).
The corrosion inhibition efficiency is determined by
equation (2) (Ali and Hamedh, 2016):
Inhibition Efficiency (%) =
C
R0
-C
Ri
C
R0
x 100 % (2)
where C
R
is corrosion rate with inhibitor (mils/year)
and C
R
is corrosion rate without inhibitor
(mils/year).
Corrosion rate determination is carried out by
following the steps:
1. After the corrosion process is carried out within
a certain time, the pH of the medium is
measured with a pH meter and set as the final
pH
2. Corrosion products are removed from corrosion
media, and dried in an oven at 110
o
C for 2
hours, then weighed as final mass
2.2 Tannins Content Analysis with
UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
Determination of tannin levels in Awak banana peel
is carried out using UV-Vis Spectrophotometer, and
absorbance is observed in wave numbers 765 nm.
2.3 Immersion of Iron Plate in HCl
Solution without Inhibitors
Immersion of iron plate in HCl solution without
inhibitor is carried out in accordance with the
following steps:
1. The mass of the iron plate is weighed as the
initial mass
2. The iron plate is soaked in 50 mL of 3% HCl
solution
3. The pH of the medium is measured with a pH
meter and set as the initial pH
4. The iron plate that has been soaked is stored for
3 days, 6 days, 9 days, and 12 days, then the
corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency are
determined by equation 1 and equation 2.
2.4 Immersion of Iron Plate in HCl
Solution with Addition of Inhibitors
Immersion of iron plate in HCl solution with inhibitor
is carried out in accordance with the following steps:
1. The mass of the iron plate is weighed as the
initial mass
2. The iron plate is soaked in 50 mL of 3% HCl
solution
3. Awak banana peel tannins are added 1 g, 3 g, 5
g, 7 g, and 9 g, respectively
4. The pH of the medium is measured with a pH
meter and set as the initial pH
5. The iron plate that has been soaked is stored for
3 days, 6 days, 9 days, and 12 days, then the
corrosion rate and inhibition efficiency are
determined by equation 1 and equation 2.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
298
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Fourier Transform-Infrared
(FTIR) Analysis of Awak Banana
Peel
In this study, FTIR is used to analyze chemical
compounds of Awak banana peel compound. Based
on the analysis, the banana peel compound could be
seen in Figure 1. This figure shows us the presence
of hydroxyl group (OH) in the area of 3398.5 cm
-1
.
This FTIR result analysis is similar to the results
obtained by Zhao, et al., 2017 (Zhao et al., 2018).
Hence, this FTIR result analysis indicates that Awak
banana peel contains tannins.
Figure 1: FTIR Analysis of Awak banana peel.
3.2 Tannins Content Analysis Awak
Banana Peel with UV-Vis
Spectrophotometer
Analysis using UV-Vis spectrophotometer is a
qualitative analysis to determine the levels of tannins
contained in the Awak banana peel. The
spectrophotometer is operated at a wave number of
765 nm for its absorbance. Tannins on banana peels
are identified by observing the maximum wave
number absorbed by the Awak banana peel extract.
The results of UV-Vis spectrophotometer analysis on
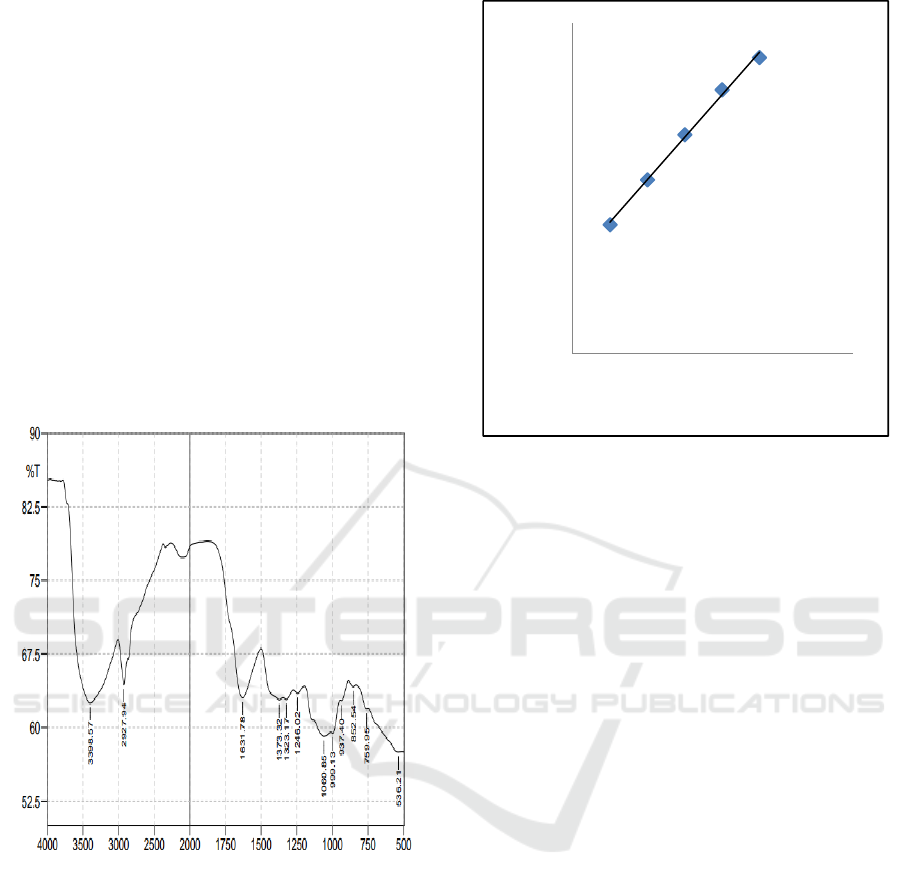
the Awak banana peel extract are seen in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Standard Curve of UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
Analysis.
3.3 Effect of Tannin Concentration of
Banana Peel on Corrosion Rate of
Iron
The effect of tannin concentration of banana peel on
corrosion rate of iron could be seen in Figure 3. The
presence of tannin is very influential to reduce the
corrosion rate of iron in HCl solution. This result is
consistent with the theory that the absorption at the
metal surface increases with increasing inhibitor
concentration (Umoren et al., 2015). The presence of
electrons in the oxygen atoms of the hydroxyl group
of inhibitors increase the interaction of the inhibitors
formed on the iron surface. The presence of a
hydroxyl group in the inhibitor molecule could
decrease the corrosion rate (Hassan and Zaafarany,
2013). The lowest corrosion rate is obtained on
immersion of iron for 12 days in HCl solution and
addition of 9 g of tannin inhibitor. In this condition,
the corrosion rate is 7.2578 mpy. Hence, the tannin
from Awak banana peel could be used as corrosion
inhibition of iron in HCl solution.
y = 0,005x + 0,242
R² = 0,996
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0 50 100 150
Absorbance
Gallic acid concentration (ppm)
Tannin
Influence of Tannin Concentration from Banana Peel as Iron Inhibition in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
299
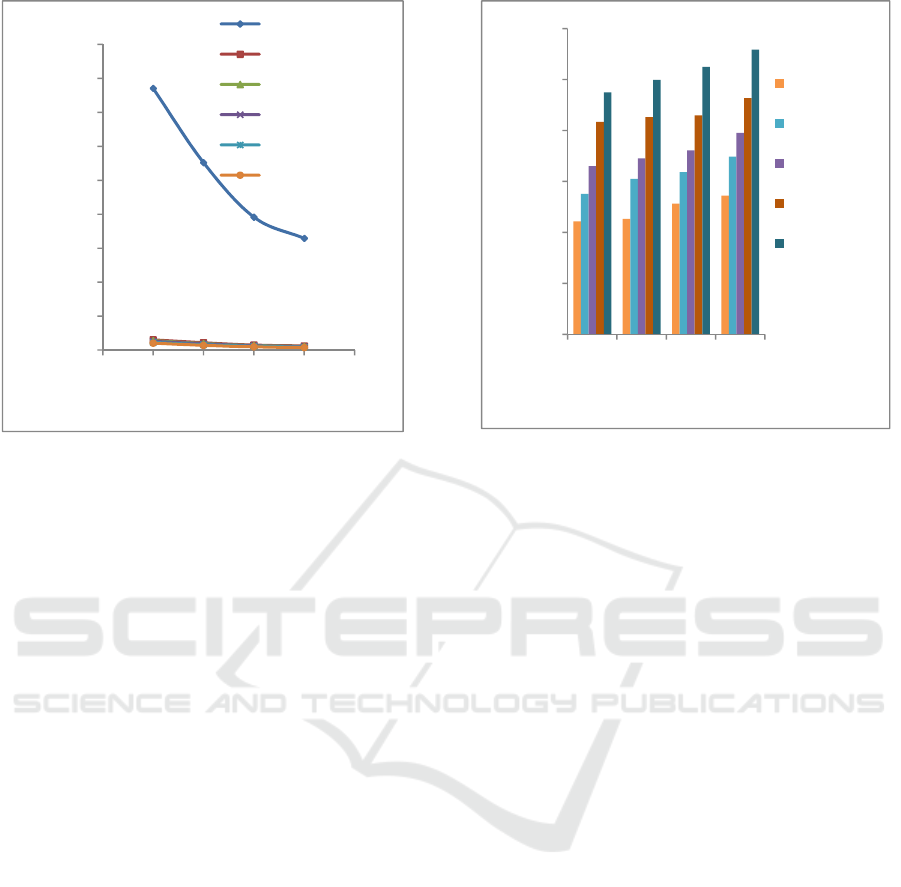
Figure 3: Effect of Tannin Concentration of Banana Peel on
Corrosion Rate of Iron.
3.4 Effect of Tannin Concentration of
Banana Peel on Inhibition
Efficiency of Iron
Figure 4 describes the effect of tannin concentration
of banana peel on inhibition efficiency of iron. This
figure shows us that the highest inhibition efficiency
is achieved in addition tannin of 9 g and the lowest in
addition tannin of 1 g. In this condition the corrosion
inhibition efficiency is 97.79%. The inhibition
efficiency of iron increases with the increase of tannin
content. This result in accordance with the theory that
the inhibition efficiency depends on the concentration
of tannin and the duration of contact between metal
with corrosive medium (Khadom et al., 2018 and
Rondang et al., 2015.
Figure 4: Effect of Tannin Concentration of Banana Peel
on Inhibition Efficiency of Iron.
4 CONCLUSION
The corrosion rate of iron plate decreases with the
addition of tannin inhibitor from Awak banana peel
in a corrosive media of 3% HCl solution. The
corrosion rate decrease with the increase of tannin
content and the inhibition efficiency of iron increases
with the increase of tannin content. The lowest
corrosion rate about 7.2578 mpy and the highest
inhibition efficiency about 97.79 % are achieved on
the addition of tannin inhibitor of 9 g and immersion
duration of 12 days.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This study is supported by Universitas Sumatera
Utara under TALENTA Fundamental Research
Scheme 2018, No: 2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/2017, dated
March 16, 2018.
REFERENCES
Agi, A., Junin, R., Zakariah, M. I. 2018. Effect of
Temperature and Acid Concentration on Rhizophora
Mucronata Tannin as a Corrosion Inhibitor. Journal of
Bio- and Tribo-Corrosion 4(5): 1-10.
Al-Amiery, A.A., Kadhum, A.A.H., Kadihum, A., Abu
Bakar Mohamad, A.B., How CK, Junaedi, S. 2014.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
03691215
Corrosion rate (mpy)
Time (days)
without inhibitors
tannin of 1 g
tannin of 3 g
tannin of 5 g
tannin of 7 g
tannin of 9 g
95.0
95.5
96.0
96.5
97.0
97.5
98.0
36912
Inhibition Efficiency (%)
Time (days)
tannin of 1 g
tannin of 3 g
tannin of 5 g
tannin of 7 g
tannin of 9 g
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
300

Inhibition of Mild Steel Corrosion in Sulfuric Acid
Solution by New Schiff Base. Materials 7(2): 787-804.
Ali, S.M., Hamedh, A. A. L. 2016. Control of Zinc
Corrosion in Acidic Media : Green Fenugreek Inhibitor.
Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China
26(11): 3034-3045.
Al-Moubaraki, A., Al-Judaibi, A., Asiri, M. 2015.
Corrosion of C-Steel in the Red Sea: Effect of
Immersion Time and Inhibitor Concentration.
International Journal of Electrochemical Science 10:
4252-4278.
Chanchay, N., Poosaran, N. 2009. The Reduction of
Mimosine and tannin contents in leaves of Leucaena
Leucocephala. Asian Journal of Food and Agro-
Industry Special Issue: S137-S144.
Darmokoesoemo, H., Suyanto, Anggara, L.S.,
Amenaghawon, N., Kusuma, H.S. 2018. Application of
Carbonxymethyl Chitosan-Benzaldehyde as
Anticorrosion Agent on Steel. Internasional Journal of
Chemical Engineering 2018: 1-9.
Gopal, J., Shadma, A., Shanthi, S., Rajiv, P. 2015. Musa
Paradisica Peel Extract as Green Corrosion Inhibitor for
Mild Steel in HCl solution. Corrosion Science 90: 107-
117.
Hassan, R.M., Zaafarany, I.A. 2013. Kinetics of Corrosion
of Aluminum in Acidic Media by Water-Solube Natural
Polymeric Pectates as Anionic Polyelectrolyte
Inhibitors. Materials 6(6): 2436-2451.
Khadom, A.A., Ahmed, N. A., Nagham, A. A. 2018.
Xanthium strumarium leaves extracts as a friendly
corrosion inhibitor of low carbon steel in hydrochloric
acid: Kinetics and mathematical studies. South African
Journal of Chemical Engineering 25: 13-21.
Madhu, T., Vinod, K. G., Ram, A.S., Gopal, J.,Rajiv, P.
2018. Donor−π−Acceptor-Type Configured,
Dimethylamino-Based Organic Push−Pull
Chromophores for Effective Reduction of Mild Steel
Corrosion Loss in 1 M HCl. ACS Omega 3: 4081−4093
Rondang, T., Harry P. L., Panca, N., Nimrod, S. 2015.
Inhibition Ability Comparation of Guava Leaves
Tannin, Extract of Guava Leaves, and Guava Leaves
Powder as Iron Corrosion Inhibition in HCl Solution.
Jurnal Kimia dan Kemasan, 37(2): 73-78.
Tartrakoon, T., Nitima, C., Therdchai, V., Udo, M. 1999.
The Nutritive Value of Banana Peel (Musa sapieutum
L.) in Growing Pigs. Deutscher Tropentag in Berlin
Session: Sustainable Technology Development in
Animal Agriculture.
Umoren, S.A., Obot, I.B., Gasem, Z.M. 2015. Adsorption
and Corrosion Inhibition Characteristics of Strawberty
Fruit Extract at Steel/Acids Interfaces: Experimental
and Theoretical Approaches. Ionics 21(4): 1171- 1186.
Wang, H., Gao, M., Guo, Y., Yang, Y., Hu, R. 2016. A
Natural Extract of Tobacco Rob as Scale and Corrosion
Inhibitor on Artificial Seawater.
Desalination 398: 198-
207.
Zhao, B., Han, W., Zhang, W., Shi, B. 2018. Corrosion
Inhibition Performance of Tannis for Mild Steel in
Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Research on Chemical
Intermediates 44(1): 407- 423.
Influence of Tannin Concentration from Banana Peel as Iron Inhibition in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
301
