
Effect of Ethanol Extract of Celery (Apium graveolens L) against
Urea and Creatinine Level in Male Wistar Rats on Ethylene Glycol
Induced Nephrolithiasis
Marline Nainggolan
1*
, Kasmirul Ramlan Sinaga
2
, Siti Morin Sinaga
3
, Sony Eka
Nugraha
1
1
Department of Pharmaceutial Biology,
Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155 Indonesia.
2
Department of Pharmaceutical Technology,
Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia.
3
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry,
Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia.
Keywords: Nephrolithiasis, Ethylene Glycol, Celery, Urea, Creatinine
Abstract: The use of celery in Indonesia was known as cooking spice to enrich the taste of food, has not been widely
used as herbal medicine either in the form of juice or extract. The Pre-clinical testing of celery herbs in addition
to diuretics it is also to treat sore eyes, sprains, rheumatism, hypertension, and as a hair tonic. The celery Herb
is rich in the content of flavonoids and potassium that can be used to dilute kidney stones. The aim of this
study was to investigate effect of ethanol extract of celery (Apium graveolens L) against urea and creatinine
level in male wistar rats on ethylene glycol induced nephrolithiasis. In vivo test was performed male wistar
which divided into 6 groups. Group I as normal control without any tratment, Group II as negative control
was induced ethylene glycol, Group III as positive control was given Batugin Elixir, Group IV, V and VI were
given ethanol extract of celery a dose of 50, 100 and 150 mg/kgBW respectively. Blood was collected by
cardiac puncture then measured level of urea and creatinine. The data were analyzed statistically using
ANOVA (analysis of variance). The results showed that ethanol extract of celery has an effective activity at
a dose of 150 mg / kgBW (P < 0.05) to negative group in decreasing level of urea and creatinine male wistar
rats on ethylene glycol induced nephrolithiasis and it showed a dose-dependent manner.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urolithiasis is a formation of crystal stone that formed
in the kidney and known as nephrolithiasis, its stone
also found in the urinary tract, bladder and ureters
(Selvam et al., 2001). The prevalence of urolithiasis
>10% with expected recurrence rate of >50%. The
incidence of nephrolithiasis in worldwide is high, and
around 80% of nephrolithiasis cases are found as form
of calcium oxalate or mixed with stone of calcium
phosphate (Brikowski et al., 2008).
Epidemiological
studies reported that the cases of nephrolithiasis
disease are higher between the ages of 20–40 in both
in men and women, men is more prevalent as 12%
than in women as 6% (Lopez et al, 2010).
Various study regarding to nephrolithiasis disease
has been isvestigated, such as radiological treatment
and laboratory determination. Both are not efficiently
to determine the mechanisms and causes of stone
deposite in the kidney and urinary tract (Tiselius et
al., 1980). However, some factors that would be
responsible induced kidney stone formation have
been studied recently (Curhan et al, 1997). It is
reported that the urine is saturated with material
compund which is a insoluble substance, it is leads to
formation of crystals and aggregate into stone form
(Sakhaee et al, 1993).
The nephrolithiasis needs
curative and preventive treatment. Nowdays, there are
no good modern medicine, that can dissolve stone
form in the part of kidney or urinary tract, therefore
the physicians is considering to alternative medicine
or treatment to heal the nephrolithiasis disease (Coe
at al, 1992).
The other medical treatment of
nephrolithiasis was surgical removal treatment of the
stones (Uribarri et al, 1989). Recently treatment
including extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
(ESWL) adn percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
are not guarantee the recurrence of the disease
(Srisubat et al., 2009). Moreover, it can cause various
side effects such as bleeding, increasing blood
742
Nainggolan, M., Sinaga, K., Sinaga, S. and Nugraha, S.
Effect of Ethanol Extract of Celery (Apium graveolens L) against Urea and Creatinine Level in Male Wistar Rats on Ethylene Glycol Induced Nephrolithiasis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010087107420746
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
742-746
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

pressure and also kidney fibrosis (Wadhwa et al,
2007).
In the traditional cure, most of the sources
were taken from plants which has been proved
empirically in community that it is believe to heal
many disease. Herbal medicines are known have
lower side effects and efficacious than modern
medicine and it also reduce the prevalent of the
recurrece cases. Phytochemical properties such as
flavonoids spread widely in plants, and its biological
effect such as antioxidant have been reported in
various studies such as,
cancer, coronary heart
diseases and
diabetes (Hopper et al., 2008).
Herbal
Medicine have lower side effects compare to
chemical modern drugs because its antioxidant
activity has a role in lowering the toxicity of drugs
(Bent et al, 2004).
Today herbal medicine are used as
an alternative treatment to chemical drugs including
in treating nephrolithiasis (Butterweck and Khan,
2009).
Recent studies reported that the high content
of flavonoids plant could effectively inhibit the
formation of kidney stone in form of CaOx stones in
vivo and in vitro, correlating with its biological
activity such as anti-inflammatory, diuretic,
antioxidant, antibacterial properties and other
protective activity (Rad et al, 2011). Based on the
explanation, it showed that the flavonoids or
flavonoid-rich plant extracts has potential activitiy as
anti-nephrolithiasis.
Celery (Apium graveolens L) is a apiaceae family
plant, and grow in Europe and the tropical and sub
tropical regions of Africa and Asia. Beneficial
compounds are found in celery such as flavonoids
vitamins A and C, frocoumarin glycosides, limonene
and, selinene (Sowbhagya, 2014). Flavonoids content
of celery are the reason that celery has potential as
anti-urolithiasis activities
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Chemical
Ethanol 96%, aqudest, ethylene glycol, ammonium
chloride, Creatinine kit, Ureum kit
2.2 Plant Collection
Celery herb (Apium graveolens L) was collected from
local market at Padang Bulan, Northern Sumatra,
Indonesia. The plant samples authenticated by
Indonesian Institute of Science, Research Center of
Biology, Bogor, Indonesia.
2.3 Extraction of Celery Herb
An amount of 500 g dried Celery herb were crushed
in a blender, then macerated in ethanol 80 % for 5
days thereafter countinue to remecerated for 2 days.
The solvent was evaporated at low pressure with a
temperature of not more than 40 ° C using a Rotary
evaporator, then dried using freeze dryer (Nugraha et
al, 2018).
2.4 Phytochemical Screening of
Ethanol Extract Celery Herb
Phytochemical screening carried out on ethanol
extract celery herb includes examining the chemical
secondary metabolites of alkaloids, flavonoids,
glycosides, tannins, saponins, triterpenoids, and
steroids
2.5 Animals and Blood Sample
An amount of 30 male wistar rats used in this study,
weighing around of 180-220 g. The blood sample
was collected by cardiac puncture.
2.6 Experimental Design
The animals were given solution of 0.75% ethylene
glycol and also solution of 2% ammonium chloride
as much as 1% body weight orally to induce
Nephrolithiasis for 14 days.
Group I : as nornal control
Group II : as negative control (Na-CMC 0,5 %)
Group III : as positive control. Rats were received
Batugin Elixir 0.5 ml/ 200 g BW
Group IV : Rats were received ethanol extract of
celery herb at a dose of 50 mg/kg BW
Group V : Rats were received ethanol extract of
celery herb celery at a dose of 100 mg/kg BW
Group VI : Rats were received ethanol extract of
celery herb at a dose of 150 mg/kg BW
Treatment was given orally after ethylene
glycol induced. Treatment were given as long as 10
days, than in the day of 11, the blood was collected
from cardiac to determine the level of urea and
creatinine. Determination level of urea and creatinine
were measured using “Cobas Integra”.
2.7 Statistical Data Analysis
Data were analyzed using ANOVA and continue to
Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. Significance P
values were set at 0.05. Values for all measurements
are expressed as the mean ± SD
Effect of Ethanol Extract of Celery (Apium graveolens L) against Urea and Creatinine Level in Male Wistar Rats on Ethylene Glycol
Induced Nephrolithiasis
743
3 RESULT
3.1 Phytochemical Screening
Qualitative analysis of the various phytochemical
properties in the celery herb were done by qualitative
determination methods. the celery herb contains of
glycosides, alkaloids, steroids, tannins and flavonoids
compounds.
3.2 Level of Urea and Creatinine
Level of urea and creatinine was illustrated the
effectiveness of ethanol extract of celery herb to
inhibit nephrolithiasis that caused by ethylen glycol
induction. The level of urea and creatinine showed in
table 1 and table 2. Some study showed that ethylene
glycol induced the formation of kidney stone form in
albino Wistar rat. The process of supersaturation in
the urine which is contact to various forming
compound is the major factors in the kidney stone
deposition (Brikowski et al., 2008).
Using ethylene
glycol as an inducer of kidney stone formation is the
most suitable method and it is similar to kidney stone
that found in humans which cause the kidney damage
(Brikowski et al., 2008). Degradation of renal
function characterized by elevated levels of urea and
creatinine (Meier et al, 2004). In the present study, we
investigated the effect of celery (Apium graveolens L)
ethanol extract against urea and creatinine level in
male wistar rats on ethylene glycol induced
nephrolithiasis.
Urea is the final product of protein metabolism
and amino acids containing nitrogen One of the
important roles of the kidneys is to eliminate these
potentially toxic substances from the body. If there is
a decrease in kidney function, the blood urea nitrogen
level (BUN) increases ( Meier et al., 2004). BUN
measurements was one of kidney health marker.
Measurement of blood serum urea level of rats was
done to determine the effect of induction of ethylene
glycol 0.75% and 2% ammonium chloride to kidney
damage, and the effect of variation dose ethanol
extract celery herb on blood serum urea level of rat.
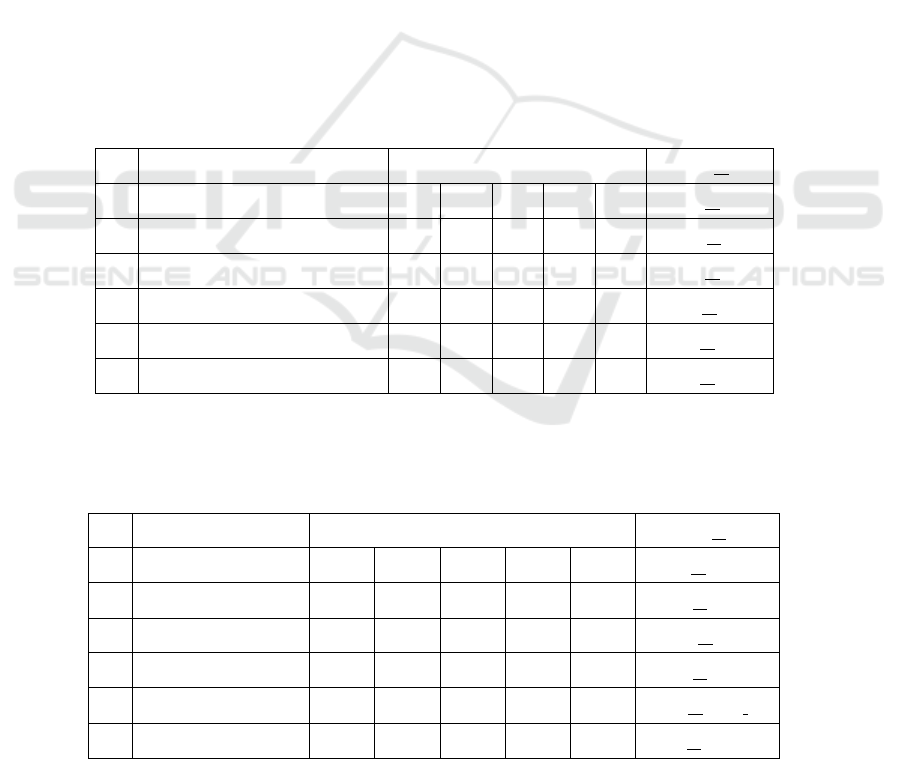
Table 1: Level of urea
No Group Level of urea Mean + SD
1 Normal control 40 41 41 42 39 40.6 + 1.1*
2 Negative control 57 56 58 55 56 56.4 + 1.1
#
3 Positive control 43 44 42 42 43 42.8 + 0.8*
4 Extract 50 mg/kgbw 47 48 50 49 47 48.2 + 1.3*
#
5 Extract 100 mg/kgbw 47 45 45 46 44 45.4 + 1.1 *
#
6 Extract 150 mg/kgbw 39 42 43 41 37 40.4 + 2.4 *
#
Where
* (Significantly different to negative control) P<0.05
# (Significantly different to positive control) P<0.05
Table 1: Level of creatinine
No Group Level of creatinine Mean + SD
1 Normal control 0.26 0.27 0.27 0.25 0.24 0.25 + 0.013 *
2 Negative control 0.45 0.49 0.48 0.45 0.48 0.47 + 0.018
#
3 Positive control 0.24 0.23 0.24 0.25 0.24 0.24 + 0.07*
4 Extract 50 mg/kgbw 0.37 0.44 0.45 0.42 0.45 0.42 + 0.033
#
5 Extract 100 mg/kgbw 0.37 0.40 0.39 0.35 0.37 0.37 + 0.019 *
#
6 Extract 150 mg/kgbw 0.33 0.30 0.28 0.29 0.30 0.30+ 0.018 *
Where
* (Significantly different to negative control) P<0.05
# (Significantly different to positive control) P<0.05
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
744

Creatinine was a metabolism molecule product
which is produced from the muscle metabolism.
Creatinine was an important molecule in the process
of energy production in the muscle, it is produced
from creatine. Every day, about 2% of the creatine
in the body, it was converted into creatinine form
(Horio, 2014). This molecules are transported into
the kidneys through blood vessel. The kidneys filter
out and remove of the creatinine in the urine. The
creatinine was a reliable indicator to determine the
function of.kidney.
The results of rat blood serum testing in each
group were statistically analyzed by spss to compare
the differences between treatment groups to negative
control and positive control. Based on Table 1, it
showed that the effective dose of ethanol extract
celery herb was 150 mg/kg BW and it showed dose
dependent manner. Level of urea in treatment group
of ethanol extract 150 mg/kgBW was 40.6 showed
there was no different to positive control (P>0.05)
and significant different to negative control (P<0.05).
Table 2 showed that effective dose of ethanol
extract celery herb to creatinine level of rat induced
ethylen glycol was 150 mg/kgBW with level of
creatinine was 0.30. Level of creatinine was not
different to positive control (P>0.05) and significant
different to negative control (P<0.05). Content of
flavonoids in ethanol extract celery herb prevents
oxidative stress in the kidney by increasing
glutathione s-transferase (GSH) antioxidant activity ,
increasing GSH synthesis and trapping directly ROS
formed by donating H atoms to free radicals resulting
in non-reactive free radical compounds and non-
reactive radical flavonol compounds that can
improve kidney function (Kang et al, 2016). In this
research, elevation of urea and creatinine were
decreased by treatment with ethanol extract celery
herb and thereby improved kidney functions in
nephrolithiatic condition.
4 CONCLUSION
Ethanol extract of celery herb at the dose of 50,100
and 150 mg/kgbw have effect in decreasing level of
urea and creatinine. Treatment dose which has
effective activity was 150 mg/kgbw and it showed
dose dependent manner.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Research funded by Universitas Sumatera Utara in
accordance to the contract of research
implementation TALENTA Universitas Sumatera
Utara funding year 2018 No. 2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/
2018, date : 16 March 2018.
REFERENCES
Bent, S. and Ko, R., 2004. Commonly used herbal
medicines in the United States: a review. The American
journal of medicine, 116(7), pp.478-485.
Brikowski, T.H., Lotan, Y. and Pearle, M.S., 2008.
Climate-related increase in the prevalence of
urolithiasis in the United States. Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences.
Butterweck, V. and Khan, S.R., 2009. Herbal medicines in
the management of urolithiasis: alternative or
complementary?. Planta medica, 75(10), p.1095.
Coe, F.L., Parks, J.H. and Asplin, J.R., 1992. The
pathogenesis and treatment of kidney stones. New
England Journal of Medicine, 327(16), pp.1141-1152.
Curhan, G.C., Willett, W.C., Speizer, F.E., Spiegelman, D.
and Stampfer, M.J., 1997. Comparison of dietary
calcium with supplemental calcium and other nutrients
as factors affecting the risk for kidney stones in
women. Annals of Internal Medicine, 126(7), pp.497-
504.
Hooper, L., Kroon, P.A., Rimm, E.B., Cohn, J.S., Harvey,
I., Le Cornu, K.A., Ryder, J.J., Hall, W.L. and Cassidy,
A., 2008. Flavonoids, flavonoid-rich foods, and
cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. The American journal of clinical
nutrition, 88(1), pp.38-50.
Horio, M., 2014. New topics regarding equations for GFR
estimation based on serum creatinine and cystatin C.
Rinsho byori. The Japanese journal of clinical
pathology, 62(2), pp.153-162.
Kang, J.T., Moon, J.H., Choi, J.Y., Park, S.J., Kim, S.J.,
Saadeldin, I.M. and Lee, B.C., 2016. Effect of
antioxidant flavonoids (quercetin and taxifolin) on in
vitro maturation of porcine oocytes. Asian-
Australasian journal of animal sciences, 29(3),
p.352.
López, M. and Hoppe, B., 2010. History, epidemiology and
regional diversities of urolithiasis. Pediatric
nephrology, 25(1), p.49.
Meier, J.J., Nauck, M.A., Kranz, D., Holst, J.J., Deacon,
C.F., Gaeckler, D., Schmidt, W.E. and Gallwitz, B.,
2004. Secretion, degradation, and elimination of
glucagon-like peptide 1 and gastric inhibitory
polypeptide in patients with chronic renal
insufficiency and healthy control subjects. Diabetes,
53(3), pp.654-662.
Meier, J.J., Nauck, M.A., Kranz, D., Holst, J.J., Deacon,
C.F., Gaeckler, D., Schmidt, W.E. and Gallwitz, B.,
Effect of Ethanol Extract of Celery (Apium graveolens L) against Urea and Creatinine Level in Male Wistar Rats on Ethylene Glycol
Induced Nephrolithiasis
745

2004. Secretion, degradation, and elimination of
glucagon-like peptide 1 and gastric inhibitory
polypeptide in patients with chronic renal
insufficiency and healthy control subjects. Diabetes,
53(3), pp.654-662.
Nugraha, S.E., Suwarso, E. and Yuandani, Y., 2018,
January. In Vitro Hemostatic Activity Of Ethanol
Extract Of Beet Root (Beta Vulgaris L) In Blood Of
Male Albino Rat. In International Conference on
Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research (ICPCR).
Rad, A.K., Rajaei, Z., Mohammadian, N., Valiollahi, S.
and Sonei, M., 2011. The beneficial effect of
Cynodon dactylon fractions on ethylene glycol-
induced kidney calculi in rats. Urology journal, 8(3),
pp.179-184.
Sakhaee, K., Harvey, J.A., Padalino, P.K., Whitson, P. and
Pak, C.Y., 1993. The potential role of salt abuse on
the risk for kidney stone formation. The Journal of
urology, 150(2), pp.310-312.
Selvam, R., Kalaiselvi, P., Govindaraj, A., Murugan, V.B.
and Kumar, A.S., 2001. Effect of A. lanata leaf
extract and Vediuppu chunnam on the urinary risk
factors of calcium oxalate urolithiasis during
experimental hyperoxaluria. Pharmacological
Research, 43(1), pp.89-93.
Sowbhagya, H.B., 2014. Chemistry, technology, and
nutraceutical functions of celery (Apium graveolens
L.): an overview. Critical reviews in food science and
nutrition, 54(3), pp.389-398.
Srisubat, A., Potisat, S., Lojanapiwat, B., Setthawong, V.
and Laopaiboon, M., 2009. Extracorporeal shock
wave lithotripsy (ESWL) versus percutaneous
nephrolithotomy (PCNL) or retrograde intrarenal
surgery (RIRS) for kidney stones. Cochrane
Database of Systematic Reviews, (4).
Tiselius, H.G., Ahlstrand, C. and Larsson, L., 1980. Urine
composition in patients with urolithiasis during
treatment with magnesium oxide. Urological
research, 8(4), pp.197-200.
Uribarri, J., Oh, M.S. and Carroll, H.J., 1989. The first
kidney stone. Annals of internal medicine, 111(12),
pp.1006-1009.
Wadhwa, P., Aron, M., Bal, C.S., Dhanpatty, B. and Gupta,
N.P., 2007. Critical prospective appraisal of renal
morphology and function in children undergoing
shockwave lithotripsy and percutaneous
nephrolithotomy. Journal of endourology, 21(9),
pp.961-966.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
746
