
Exposure of Germas Information by using Phones Preventing
Non-communicable Disease for Millennials, Medan City
Lita Sri Andayani
1
, Ernawati Nasution
1
, Eddy Syahrial
1
1
Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Sumatera Utara,Universitas Street Number 21, USU Medan 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: GERMAS (Healthy Life Style Movement) Information, Millenials, Preventing, Non-Communicable Disease.
Abstract: Millennials are people born in 1980 - 2000, with characteristic internet addiction, cell phones, digital
technologies, lazy moving, less physical activity, consumingjunk food, riskof having non-communicable
diseases(NCDs).Research objective is to analyzethe correlationbetweenGERMAS information exposure
andprevention ofNCDsby implementing threeprioritiesof GERMAS. This study usedcross-sectional
designwith 100 sample.The results found that there was a correlation between exposure of GERMAS
information and physical activity (p = 0.040); there was a correlation on eatingvegetables and fruits (p =
0.022), but no correlation on health examinationperiodically(p = 0.606). We also found the correlation
onGERMASactions (p = 0,032) with GERMAS information exposure, and correlation GERMAS knowledge (p
= 0.015) and GERMASaction (p = 0,000) towardNCDs prevention. There was a correlationbetween the use
of smartphones and NCDs prevention (p = 0.012).We can conclude that GERMAS information exposure has
a correlation with physical activity and eating fruits but not with periodic medical examination. There is
correlationbetween GERMAS knowledge and action toNCDs prevention, also there iscorrelationusing of
phoneto NCDs prevention.It is recommended to use GERMAS application on smartphone to empower
millennialsin NCDs prevention.
1 INTRODUCTION
Millennial generation arepeople bornin 1980 and
2000. the generation currently aged the range of 18-
38 years, who grow characterized Increasing
recognition themselves, have high confidence
(Hobart, 2014) and marked technological
developments that enter everyday life (Sari, 2015).
Theeducated and understood generation of the
technology, internet addiction, self-confidence and
high self esteem andopened and tolerant of change,
marked the increase in using and familiarity with
communications, media, and digital technologies
(Kilber et al, 2014).
Technological developments cause lifestyle
changes, such as physical activity (lazy exercise),
tend to be "mager" or lazy moving , spending hours
in front of computer screen, smoking, sleeping late,
eating lots of junk food . The behavioral changes
create a higher risk of health problems such as
obesity, hypertention, type 2 diabets, a heart disease,
stroke and mental illness. Basic Health Research
(2013) shows the prevalence of hypertension in
Indonesia at age ≥18 years of 25.8 % . Prevalence of
DM disease 2.1% (Ministry of Health, 2013)up from
1.1% (Balitbangkes, 2014), with average of North
Sumatera1.76%, Medan city 2.72%. Thestroke
disease had been concerningyoung people, namely
inpatientacuteischemic stroke in men and women in
18- 34 years old increasedby 50% period 2003-2012
(Balitbangkes, 2014).
The view of the proportion of enough physical
activity in Indonesia average 8.25%, North Sumatra
7.20%, Medan 15.15%. Proportion of sedentary
behavior ≥ 6 hours per day 24.1% (Ministry of
Health, 2013). Lack of physical activity will be
associated by the incidence of obesity. The Average
ofPrevalence of obesity in Indonesia 26.60%, North
Sumatra average 29.56%, Medan 37.53%
(Balitbangkes, 2014). The proportion of the national
average consumption behavior is less vegetables and
or fruits 93.5 % . Behavior of food consumption is
risky to population ≥10 years old food and sweet
drinks (53,1%), and fatty foods (40,7%) (Ministry of
Health, 2013).
The increasingof NCDs incidence will correlate
the increaseof health care financing; decreased
community productivity; the declining
Andayani, L., Nasution, E. and Syahrial, E.
Exposure of Germas Information by using Phones Preventing Non-communicable Disease for Millennials, Medan City.
DOI: 10.5220/0010084807030707
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
703-707
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
703

competitiveness of the state that ultimately affects the
socioeconomic conditions of society. Ministry of
Health, Indonesia has launched a HEALTHY
PEOPLE MOVEMENT (GERMAS). GERMAS as a
health promotion effort in changing humanbehavior
in preventing the incidence of non-communicable
diseases (NCDs) . GERMAS supported by
Presidential Instruction of Indonesia in 2017 with 3
priority actions: 1) Physical Activity, 2) Consumption
of Fruits and Vegetables, 3) Conduct periodic health
examination.
The Research objective to analyze the correlation
of GERMAS information exposure with 3 priority
GERMAS actions, GERMAS behavioral correlation
with NCDs prevention measures, the use of mobile
phone correlations with NCDsprevention.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
Type cross-sectional study, carried out in Medan city.
Research population throughout productive age 15-
39 years of 842,484. Number of sample 100 people
taken with simple random sampling. Data are
collected by interviewing respondents using
questionnaires .
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 The Correlation GERMAS
Information Exposures to Three
Priority GERMAS Actions
Spread of GERMAS information intensively
conducted by Ministry of Health through social media
and other information media such as television or
advertising services. This information is the basic
stage to reduce morbidity and mortality rates in terms
of NCDsprevention.
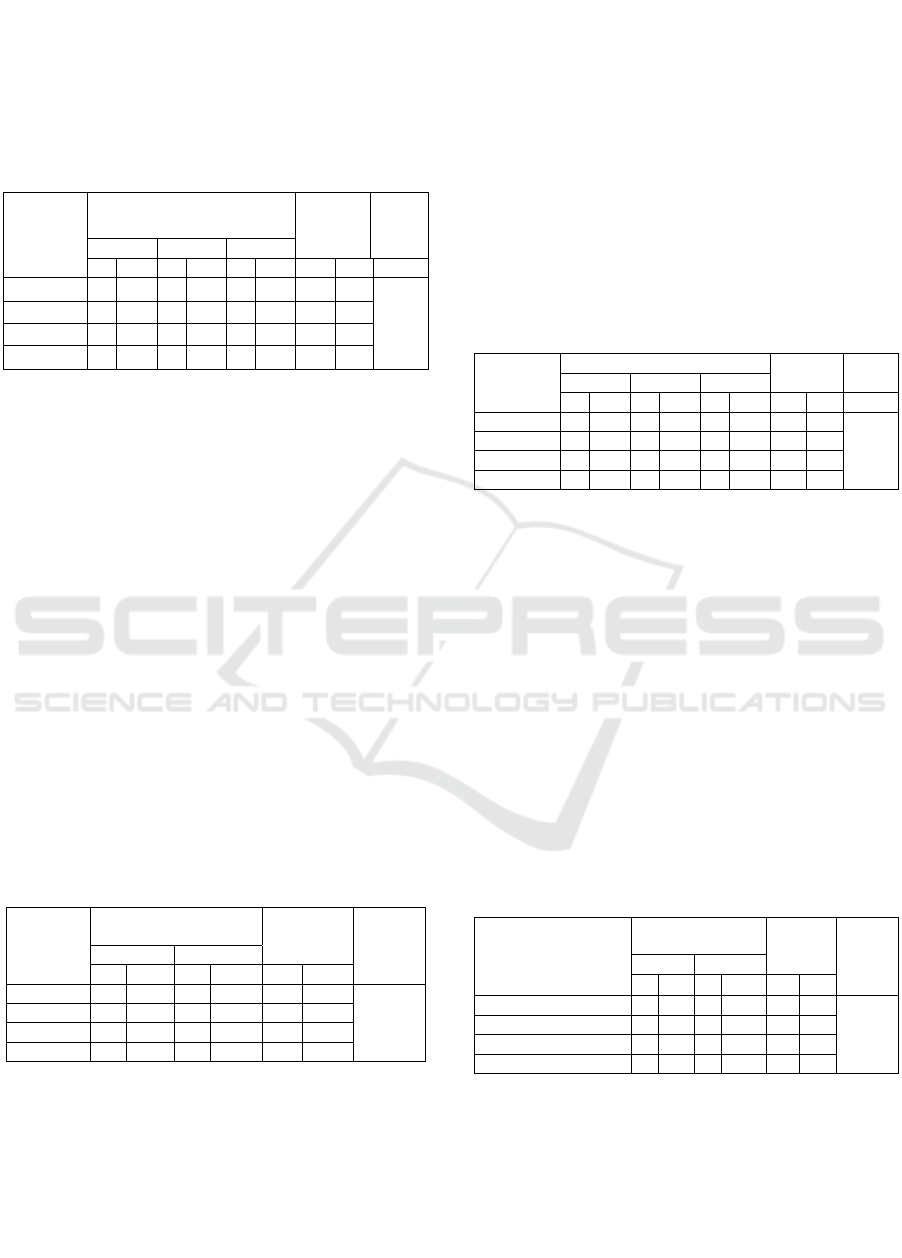
From table 1, The analysis shows that p value =
0,040 <α (0,05), it means there is a correlation
theGERMAS information exposure to physical
activity activity.
Table 1: Correlation of GERMAS information exposure to
physical activity measures
GERMAS
Information
Exposure
Physical Activity
Actions
Total
p
value
Bad Goo
d
n % n %
n
%
B
ad 18 72.0 7 28.0 25 100
0.040
E
nough 15 93.8 1 6.3 16 100
G
oo
d
36 61.0 23 39.0 59 100.0
T
otal 69 69.0 31 31.0 100 100.0
Physical activity is a human activity to move.
Regular physical activity and become one of the
habits will improve physical endurance. The "active"
physical activity criterion is an individual who
performs moderate or moderate physical activity or
both, while the "less active" criterion is an individual
who does not engage in moderate or severe physical
activity. Performing regular activity (aerobic physical
activity for 30-45 minutes / day) is known to be very
effective in reducing the relative risk of hypertension
by up to 19% to 30% (Ministry of Health, 2013).
Damanik Research (2014), there is a correlation
between physical activity and food consumption
patterns with more nutritional incidents in USU
students (Nugroho et al, 2016), there is a correlation
of physical activity with hypertension and there is a
correlation of nutritional status with hypertension of
employees in Subdistrict Tomohon Utara .
Millennials tend to perform sedentary behavior.
The sedentary behavior is sitting or lying down
everyday life either at work (work in front of
computer, reading, etc.), at home (watching TV,
playing games, etc.), traveling / transportation (bus,
train, motor) , but not including bedtime. Sedentary
behavior can increase the risk of obesity. Sedentary
behavior in children is often followed by higher snack
consumption and low energy expenditure, which is a
trigger factor for obesity (Mansjoer, 1999), also
(Negri et al, 1991), an increase in high blood pressure
in adolescents who perform activities more than 2
hours each day .
It is an increasing trend of overweight and obesity
in children and adolescents due to decreased physical
activity and increased sedentary behavior such as
watching TV and using a video or a game computer.It
is in line with the opinion of an expert panel of the
American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) that
obesity is directly related to the number of hours spent
watching television (Marshall, 20014)..
Results of a research (Paruntu et al, 2015),regular
and consistence physical activity shows a reciprocal
correlation with coronary heart disease and has a
positive effect on quality of life and other
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
704
psychological variables. Most of Teenagers in
California intervene to raise the level of physical
activity. The physical environment plays a very
important role in the level of physical activity in
adolescents (Mayosi, 2009).
Table 2 : Correlation of GERMAS information exposure to
vegetables and fruits action
GERMAS
Information
Exposure
Action of Eating Vegetables
and Fruits
Total p value
Bad Enough Goo
d
n % n % n % n %
Bad 7 28.0 11 44.0 7 28 25 100
0.02
2
Enough 9 56.3 4 25.0 3 18.8 16 100
Good 12 20.3 38 64.4 9 15.3 59 100
Total 28 28.0 53 53.0 19 19.0 100 100
From the table above, analysis result shows that
the p value = 0,040 <α (0.05), there is a correlationthe
GERMAS exposure information to the act of eating
vegetables and fruits. The more information received
the more likely it will be for the individual to act. A
research from (Reynolds, 2004) the correlation of
nutrition knowledge with the habit of eating fruits and
vegetables to students in Bogor.
The results of the study, the importance of fruits
and vegetables in reducing cancer risk (Block et al,
1999)and cardiovascular disease (Key et al,
1997).Eating 5 servings of fruit and vegetables in a
day will benefit for the health (Foerster et al, 1995).
Similarly, increased consumption of fruits and
vegetables has been recommended by the UK and
other European authorities (Department of Health,
1994), (Schiffman, 2000), and (Takeunchi, 2017)has
recommended a minimum daily intake for adults of
400g of fruits and vegetables in a day.
Table 3 : Correlation of GERMAS information exposure to
action medical examinationPeriodically
GERMAS
Information
Exposure
Regular Health Check
Measures
Total p value
Bad Goo
d
n % n % n %
B
ad 20 80.0 5 20.0 25 100
0.606
E
nough 14 87.5 2 12.5 16 100
G
oo
d
52 88.1 7 11.9 59 100
T
otal 86 86.0 14 14.0 100 100
Routine screening / screening activities as a
prevention must be taken by every resident of age>
15 and above to detect early behavioral risk factors
that may lead to heart disease, cancer, diabets and
chronic lung disease, sensory disorders and mental
disorders.
From Table 3, analysis result shows that the p
value = 0.606> α (0.05), there was no association
between exposure to the action information
GERMAS periodic health checks on GERMAS.
Information about GERMAS has a positive impact on
people's health, namely to reduce the burden of
infectious and non-infectious diseases. The impact of
such exposure may be associated with the increasing
number of people who check their health regularly to
health center. The purpose of it to identify the risk
factors and early disease signs, prevent disease in the
future through early intervention (Larsen, 2012).
Table 4: Correlation of GERMAS information exposure
toGERMAS actions
GERMAS
Information
Exposure
GERMAS action Total p value
Bad Enough Goo
d
n % n % n % n %
Bad 11 44.0 10 40.0 4 16.0 25 100
0.03
2
Enough 10 62.5 4 25.0 2 12.5 16 100
Goo
d
15 25.4 38 64.4 6 10.2 59 100
Total 36 36.0 52 52.0 12 12.0 100 100
From the table above, analysis reslut shows that
the p value = 0.032 <α (0.05), there is a correlation
between GERMAS informationexposure with
GERMAS action. The more information is received
by individual knowledge will also increase so that it
triggers the individual to act. Action is an attitude not
yet automatically manifested in an action.
3.2 Correlation of GERMAS Behavior
to Action of NCDs Prevention
From table 5, p acyl analysis shows that the p value =
0.015 <α (0.05), there is a correlationthe GERMAS
knowledge aboutaction of NCDs Prevention.
Table 5 : Correlation of GERMAS knowledge with Action
of NCDs prevention
GERMASKnowledge
Action of NCDs
Prevention
Total
p
value
Bad Goo
d
n % n %
n
%
Bad 0 0.0 1 100.0 1 100
0.015
Enough 10
4
0.0 15 60.0 25 100
Goo
d
10 13.5 64 86.5 74 100
Total 20
2
0.0 80 80.0 100 100
From table 5, analysis result shows that the p
value = 0.000 <α (0.05), which means there is a
correlationthe GERMAS knowledge to NCDs
preventionwith this case supported research [16], an
increase in the burden of disease over the next decade
in South Africa in the absence of NCDs prevention
actions, by means of advocacy and effective action.
Exposure of Germas Information by using Phones Preventing Non-communicable Disease for Millennials, Medan City
705
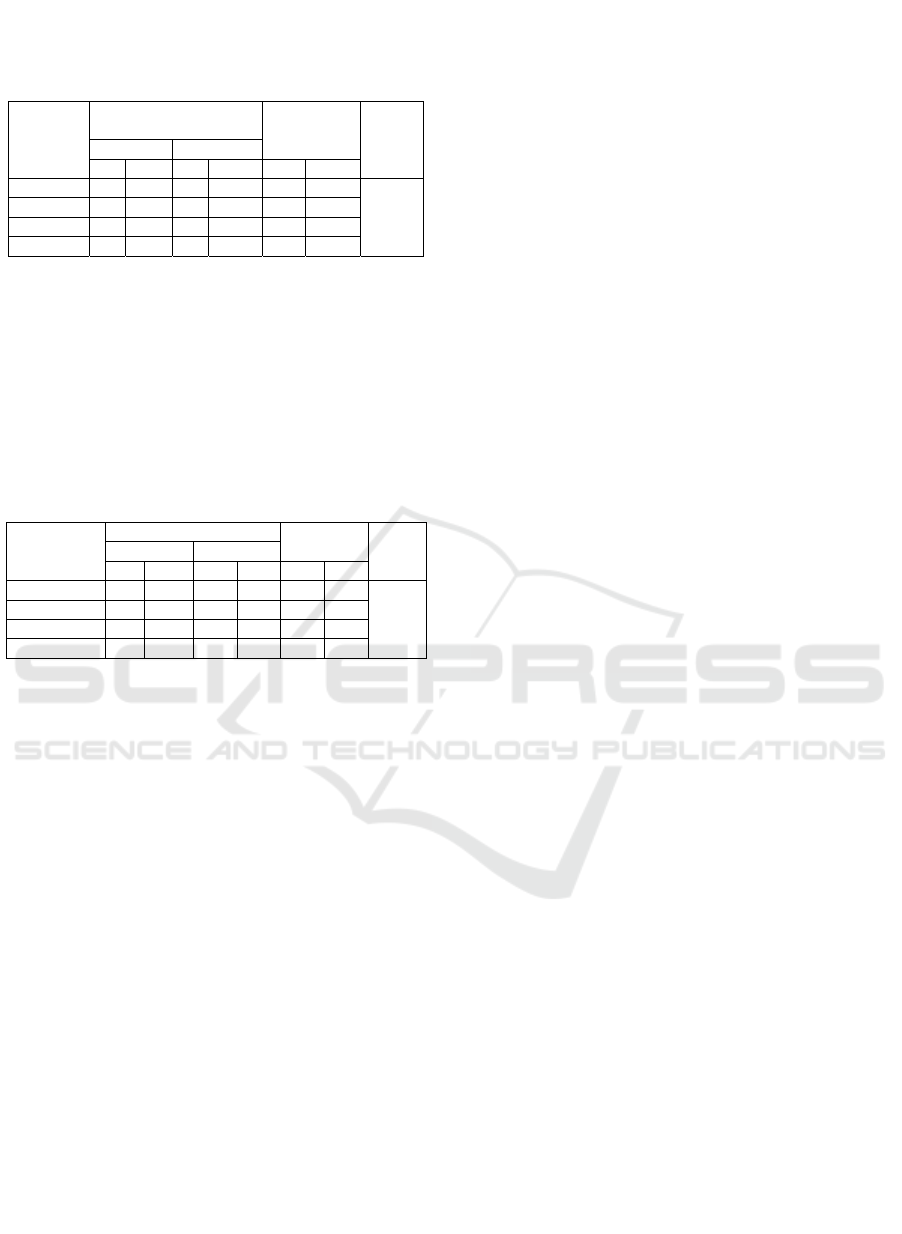
Table 6 : Correlation of GERMAS actions with Action of
NCDs prevention
GERMAS
action
Action of NCDs
prevention
Total p
value
Bad Goo
d
n % n % n %
Bad 16 44.4 20 55.6 36 10
0,000
Enough 4 7.7 48 92.3 52 100
Goo
d
0 0.0 12 100.0 12 100
Total 20 20.0 80 80.0 100 100
3.3 Smartphone Usage Correlation with
NCDs Prevention
From table 7, analysis result shows that the p value
= 0.012 <α (0.05), which means that there is a
correlation the use of smart phones with NCDs
prevention.
Table 7 . Smart phone usage correlation with NCDs
prevention measures
Smartphone
Usage
N
CDs Prevention Measure
s
Total p
value
Bad Goo
d
n % n % n %
Bad 2 66.7 1 33.3 3 100
0.012
Enough 11 29.7 26 70.3 37 100
Goo
d
7 11.7 53 88.3 60 100
Total 20 20.0 80 80.0 100 100
Nowadays, people communicate and get
information by usingthe smart phones. All features
are already available on the service. Smartphones are
currently used as medi a health information. The
Research that supporting it (Dennison et all, 2013),
health behaviorinterventions bydeveloping health
applications insmartphone. They said (Scottish,
1993)a smartphone web worthy of educational
material to support the practice of antenatal perineal
massage in pregnant women.
The determination of the technology is very high
students show that they use a smartphone with new
technology and innovation in accordance with the era
or the present. The study (Bianchi et al, 2005)shows
that youth groups tend to experiment with new
technologies and show off technological addictions
that can be used with existing features in mobile
phones.
4 CONCLUSIONS
There is a correlation of GERMAS information
exposure to the action of physical activity, eating
fruits and vegetables and examinating the health
periodicly, also a correlation GERMAS knowledge
and action to NCDs prevention, and there is a
correlation the mobile phone usage to NCDs
prevention. Based on the above conclusions it is
suggested GERMAS information can be done by
using the application on smart phones to empower
millennial generation on NCDs prevention effort.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Directorate of
Research and Community Service of
DirectorateDirectorateGeneral for Research and
Development of the Ministry of Research,
Technology and Higher Education for the funding
support of this research with contract number:
226/UN5.2.3.1/PPM/KP-DRPM/2018.
REFERENCES
Balitbangkes Ministry of Health RI, 2014. Public Health
Development Index 2013 (HDI). Jakarta. Agency for
Health Research and Development.
Bianchi, A. and Phillips J, 2005. Psychological Predictors
of Problem Mobile Phone Use. Australia. Psychology
of Department, Monash University.
Block, G., et al, 1999. Fruit, Vegetables and Cancer
Prevention: a review of the epidemiological evidence.
Nutrition and Cancer, 18, 1-29.
Damanik, et al, 2014.Risk Factors That Cause More
Nutrition Incidents In Students Of The Faculty Of
Public Health USU. Medan, Journal of North Sumatera
University.
Dennison, Laura, et al, 2013. Opportunities and Challenges
for Smartphones Applications in Supporting Health
Behavior Change: Qualitative Study . J Med Internet
Res ; 15 (4):
e86.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3
636318/?report=printable.
Department ofHealth, 2004. Poor livingconditionsHealth
Survey train. Jakarta. Ministry of Health report.
Department Of Health, 1994. Nutritional Aspects of
Cardiovascular Disease. London. HMSO.
Foerster, S., et al, 1995. California's "5 a day- for batter
health!" Campaign: an innovative population-based
effort to effect large-scale dietary change. American
Journal of Preventive Medicine, 11, 124-131.
Hobart, Buddy, 2014. Understanding Generation Y.
Solution 21 New Jersey. Princenton One.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
706

Ministry of Health Indonesia, 2013. Basic Health Research
2013. Jakarta.Balitbangkes Ministry of Health.
Key, T., et al, 1996 Dietary Habits and Mortality in 11000
Vegetarians and Health Conscious People: Result of a
17 years follow up British Medical Journal 313, 775-
778.
Kilber, J., Barclay, A., and Ohmer, D, 2014. Seven Tips for
Managing Generation Y. Journal of Management
Policy and Practice 15: 4,80-9.
Larsen C, and Friends., 2012. Regular Health Checks:
Cross-Sectional Survey . Nordic Cochrane Center,
Rigshospitalet and University of Copenhagen.
Copenhagen, Denmark.
Mansjoer A, 1999. Hypertension in Indonesia, Ed. Kapita
Selekta Medicine. Jakarta: Media Aesculapius; p.518-
21.
Marshall, S., Biddle, S., Gorely, T., 2004. Relationships
Between Media Use, Body Fatness and Physical
Activity in Children and Youth: A Meta-Analysis.
International Journal of Obesity, 28, 1238-1246.
Mayosi, B , 2009 The Burden of Non-Communicable
Diseases in South Africa . Series.
Mota, Jorge., Et al, 2005. Perceived Neighborhood
Environments and Physical Activity in Adolescents.
University of Porto Portugal.
Negri, E., et al, 1991. Vegetable and Fruit Consumption
and Cancer Risk International Journal of Cancer, 48,
350-354.
Nugroho, et al, 2016. Description of Risk Factors of
Increased Blood Pressure in Adolescents Age 12-14
Years (Study At Al Islam Islamic Junior High School 14
Semarang. Journal of Public Health (E-Journal)
Volume 4, Number 1, January 2016 (ISSN: 2356-3346)
http://ejournal-s1.undip.ac.id/index.php/jkm.
Paruntu, et al, 2015. Relationship Physical Activity,
Nutritional Status, and Hypertension In Employees in
District Tomohon North Nutrition Journal Vol 7. No
1.http://ejurnal.poltekkesmanado.ac.id/index.php/gizid
o/article/view/270/285.
Reynolds, Kim., Killen, Joel., 2004. Psychosocial
Predictors of Physical Activity in Adolesc ents.
Stanford University. Stanford, California 94305 USA.
Sari, Kiki, 2015. Knowledge of Nutrition Related to
Degenerative Disease, Consumption Pattern and
Physical Activity of IPB Students. Bogor Agricultural
University.
Schiffman, Lean, Leslie Lazar Kanuk, 2000. Consumer
Behavior Seventh Edition New Jersey: Patience Hall
International, Inc.
Scottish Office, 1993. The Scottish Diet. EdinburghHMSO.
Takeuchi and Horiuchi, 2017. Feasibility of a Smartphone
website to support antenatal Perineal massage in
pregnant women BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
(2017) 17: 354. DOI 10.1186 / s12884-017-1536-9.
World Health Organization, 1990 Diet, Nutrition, and
Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Report of a WHO
study group Geneva WHO (Technical Report Series-
797).
Exposure of Germas Information by using Phones Preventing Non-communicable Disease for Millennials, Medan City
707
