
Risk Factors of Non-communicable Diseases in Medan City
E. Mutiara
1
, Syarifah
2
and L. D. Arde
1
1
Department
of Population and Biostatistics, Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jalan Universitas,
Medan, Indonesia
2
Department
of Health Education and Health Behavior, Faculty of Public Health, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jalan
Universitas, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Non-communicable Diseases, Risk Factors, Measurement.
Abstract: Although achievements have been achieved to anticipate and control non-communicable diseases (NCDs),
the frequency of these diseases are basically greater. The purpose of this study was to assess risk factors of
non-communicable diseases in Medan City, in 2017. Using a cross-sectional design, the selected sample
was recruited purposively consisting of 440 individuals. The selected individual was approached in the
interview and the related questionnaire is filled out. Only 154 were included in the collection of
measurement data, namely systolic and diastolic blood data, weight, height, uric acid, blood glucose and
cholesterol. Chi-square and independent t test were used to analyze data. Obesity was seen in 16.3% and
8.7% of female and male respondents. There was no significant difference in the proportion of obesity
between female and male respondents. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure were estimated at 129.3 and
82.9 mmHg on average and were evenly distributed in female and male. And 32.5% of respondents were
smokers and 17.5% of respondents had drunk alcohol. Risk factors for non-communicable diseases were not
evenly distributed in male and female. Moderate physical activity, overweight, obesity and high blood
pressure were more common in female, while smoking and alcohol consumption were more common in
male.
1 INTRODUCTION
Some non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like
cancer, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory
diseases, and diabetes are the worldwide primary
determinant of death, kill 41 million people each
year same with 71% of deaths worldwide. Nearly
three quarters of all NCDs death, and over 85% of
the 15 million people died too early (between the
ages of 30 and 69 years), both in low and middle-
income countries. These NCDs are caused by
modifiable behavioural risk factors like unhealthy
diet, lack of physical activity, tobacco use and using
alcohol, which consecutively caused some impacts
like overweight and obesity, raised blood pressure,
and also cholesterol (WHO, 2018).
Although success has been achieved in the recent
years in reducing NCDs, the cases of these diseases
have became greater unquestionably. Globally
cardiovascular disease account for most NCD
deaths, or 17.9 million people yearly, followed by
cancers (9.0 million), respiratory infections (3.9
million), and the last is diabetes (1.6 million) (WHO,
2011).
Prevalence of NCDs in Indonesia based on
Riskesdas (Basic Health Research) 2013,
hypertension aged ˃ 18 years (25.8%), Coronary
Heart Disease (CHD) aged ≥ 15 years (1.5%), heart
failure (0.3%), chronic renal failure (0.2%), kidney
stones (0.6%), rheumatism (24.7%), stroke (12.1
‰), injuries of all ages (8.2%), asthma (4.5%),
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
aged ≥ 30 years (3.8%), cancer (1.4 ‰), Diabetes
Mellitus (2.1%), hyperthyroid aged ≥ 15 years on
the basis of diagnosis (0.4%), and injury due to land
transportation (47.7%). While some risk factors for
NCDs, obesity in men aged ˃18 years (19.7%) and
in women (32.9%), central obesity (26.6%), tobacco
consumption aged ≥15 years (36.3 %), less
vegetable consumption (93.5%). Meanwhile
prevalence of NCDs in North Sumatera Province
based on Riskesdas 2013, hypertension (6.7%),
CHD (1.1%), heart failure (0.3%), chronic renal
failure (0.2%), kidney stones (0, 3%), stroke (10.3
‰), asthma (2.4%), COPD (3.6%), cancer (1.0 ‰),
Mutiara, E., Syarifah, . and Arde, L.
Risk Factors of Non-communicable Diseases in Medan City.
DOI: 10.5220/0010081006210627
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
621-627
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
621
diabetes mellitus (2.3%), hyperthyroid (0.3 %), and
joint disease (19.2%) (Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembangan Kesehatan, 2013).
In Indonesia, many policies, strategies and/or
plans of action have been done to prevent and
control NCDs according to WHO’s approach to
Major NCDs involving general risk factors. At the
community level, Integrated NCD Education Posts
(Posbindu PTM) have been established, where early
detection of risks are conducted and community
activities and education are held towards achieving
Clean and Healthy Living Behavior. At the
healthcare level, strengthening measures have been
taken on the PUSKESMAS as the community’s first
contact point with the health system. It is recognized
that currently the referral system is not organized
effectively, and will be continually be improved
along with refinements to the National Health
Insurance program (JKN), which is the
manifestation of the Universal Health Coverage
(UHC) that has been implemented since 1 January
2014. However, the above efforts are not sufficient,
as cross-sector participation is still limited. So the
increasing prevalence of NCDs in Indonesia
especially in Medan during the last few decades is
occurring, both with respect to morbidity and
mortality. It is understood that NCD is related to
social determinants for health, particularly with
regard to risks associated with behavior and
environment (Directorat General Disease Control
and Environmental Sanitation, 2016).
Because the frequency of noncommunicable
diseases are expanding and their risk factors can be
controlled, so this study aimed to understand the
NCD risk factors in Medan City in 2017 to offer
applicable action to prevent NCD.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study using cross-sectional design, selected
samples were recruited purposively by using
POSBINDU sampling unit (11 POSBINDU, each
POSBINDU consisted of 40 persons, totally 440
samples) from the whole Medan City. Selected
individuals were approached in designated interview
and fill the related questionnaires. The questionnaire
contained questions about personal information as
well as the information about all risk factors related
to non-communicable diseases.
Height was measured using a staturemeter
installed on the wall and the individuals were asked
to stand up in front of the staturemeter without shoes
while looking forward and their head and ankles
were stuck to the back wall. Weight was measured
using an analogue scale. The participants were asked
to stand on the scale without shoes and with the least
clothing. BMI was calculated by dividing weight
(kg) by square height (m
2
).
Data entering were done and analyzed using the
statistical software. Chi-square, Fisher exact, and
independent t tests were used as appropriated and P
values less than 0.05 were results were presented as
numbers (percents) and mean ± standard deviations.
3 RESULTS
The socio-demographic characteristics of the
respondents can be seen in Table 1. Most female
respondents (71.0%), with an average age of 44.2
years (+17.2 years) and as many as 60.2% in the
reproductive life range of 15-49 years. The ethnic's
of respondent's fathers and mothers are mostly
Javanese each as many as 44,5% and 45,5%
respectively. Most respondents have high school
education (46.8%) and many work as domestic
workers (25.9%).
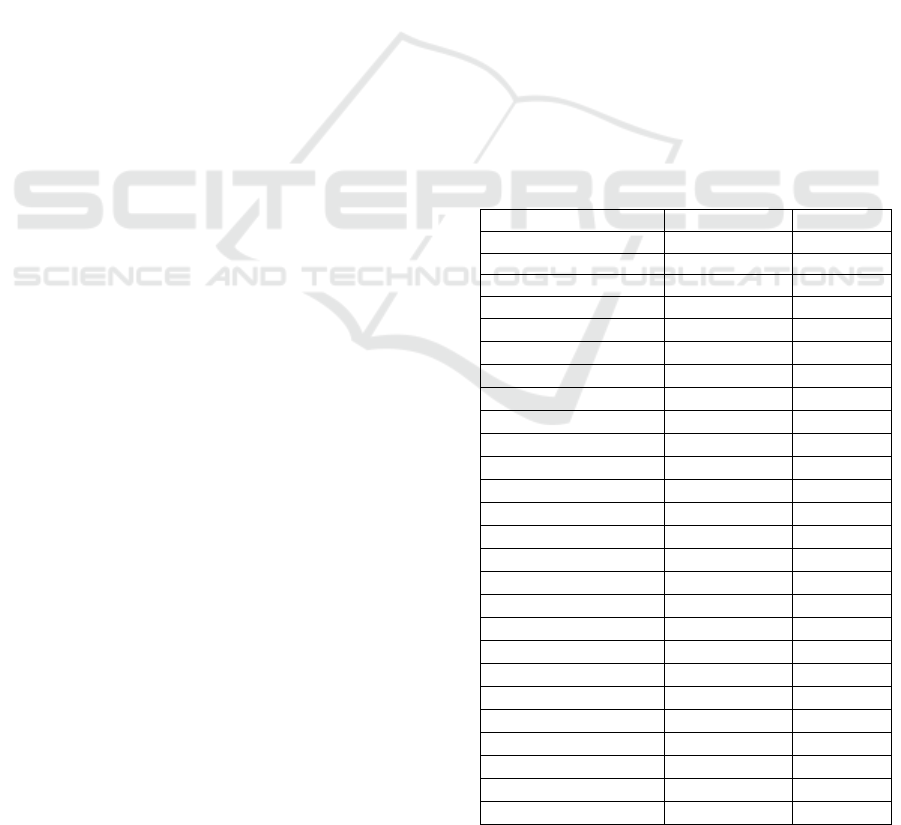
Table 1: Characteristics of Respondents' Socio
Demography
Characteristics Frequenc
y
%
Sex
Male 126 28.6
Female 314 71.4
Age (years)
15 – 24
76 17.3
25 – 34 65 14.8
35 – 44 84 19.1
45 – 54 83 18.9
55 – 64 65 14.8
65 – 74 52 11.8
75+ 15 3.4
Fathers’s ethnic
Javanese 196 44.5
Sundanese 24 5.5
Betawi 4 0.9
Bataknese 90 20.5
Minang 27 6.1
Melayu 25 5.7
Ambon 2 0.5
Madura 1 0.2
Banjar 6 1.4
Acehnese 9 2.0
India 9 2.0
Chinese 7 1.6
Others 40 9.1
Mother’s Ethnic
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
622
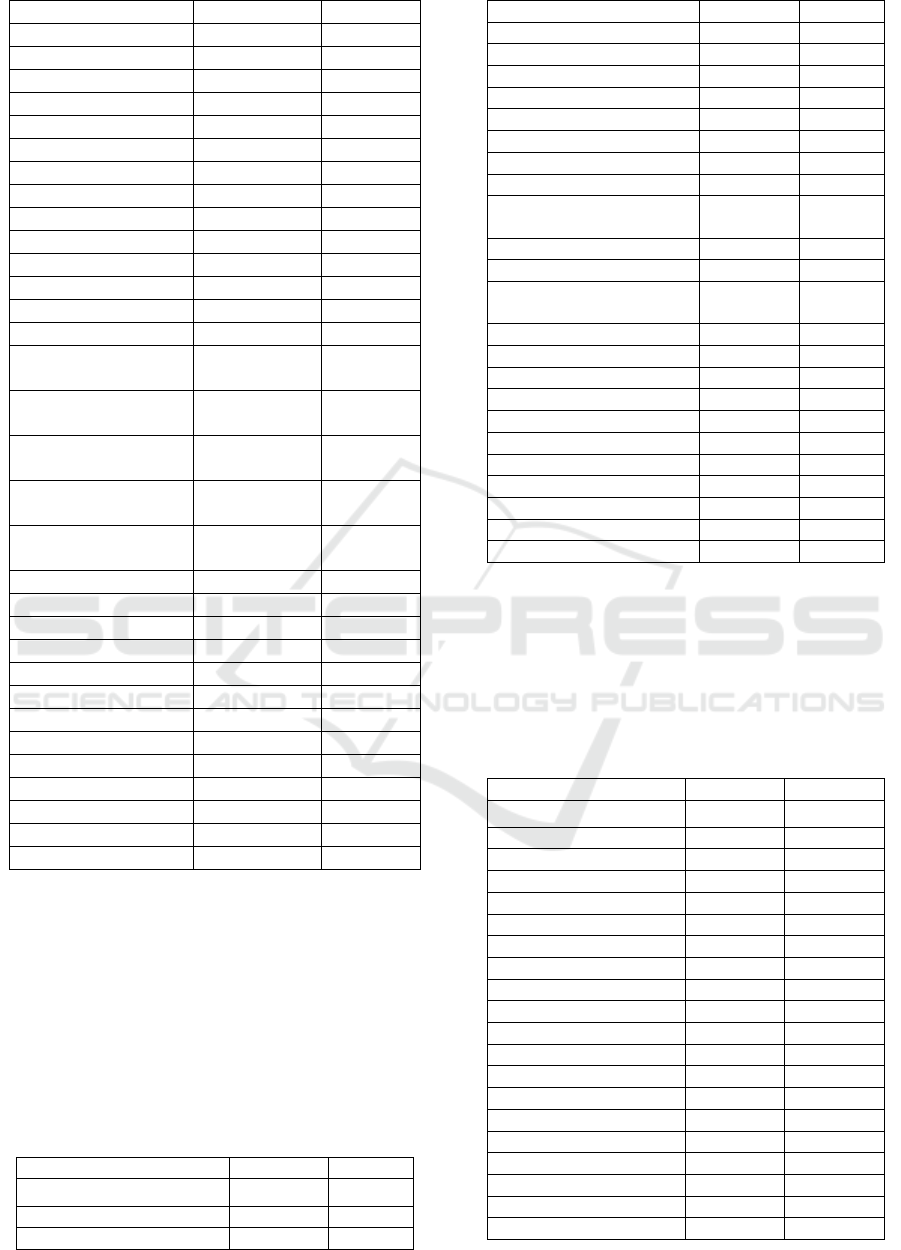
Javanese 200 45.5
Sundanese 31 7.0
Betawi 3 0.7
Bataknese 88 20.0
Minang 30 6.8
Melayu 21 4.8
Ambon 1 0.2
Madura 1 0.2
Banjar 8 1.8
Acehnese 1 0.2
India 9 2.0
Chinese 5 1.1
Others 42 9.5
Last Education
No school 9 2.0
Not completed in
Elementary School
33 7.5
Graduated from
Elementary School
63 14.3
Graduated from
Junior High School
93 21.1
Graduated from
Senior High School
206 46.8
Graduated from
Higher Education
36 8.2
Occupation
Driver 10 2.3
Domestic workers 114 25.9
Student 21 4.8
Army/Police 1 0.2
Civil Servant 7 1.6
Enterpreneurs 80 18.2
Private Employees 19 4.3
Farmer 1 0.2
Factory Workers 6 1.4
ConstructerWorkers 7 1.6
Retired 14 3.2
Others 160 36.3
3.1 Description of Health Status of
Respondents
Health status of respondents can be seen in Table 2
below. When it was viewed from the health status,
hypertension was the most common illness (18.2%),
then diabetes mellitus (5.9%) and coronary heart
disease (4.8%). In general the current health status
of respondents is good (83.4%).
Table 2: Health Status of Respondents
Health Status Fre
q
uenc
y
%
Coronary Heart Disease
Yes 21 4.8
No 419 95.2
Stroke
Yes 10 2.3
No 430 97.7
Diabetes Mellitus
Yes 26 5.9
No 414 93.9
Cance
r
Yes 7 1.6
No 433 98.4
Obstructive Pulmonary
Disease
Yes 0 0.0
No 440 100.0
Chronic Bronchitis
Disease
Yes 1 0.2
No 439 99.8
Em
p
h
y
sema
Yes 0 0.0
No 440 100.0
Asthma
Yes 2 0.5
No 438 99.5
H
yp
ertension
Yes 80 18.2
No 360 81.8
3.2 Description of Non Communicable
Disease Risk Factors
The following table showed the risk factors of non-
communicable diseases in Medan City
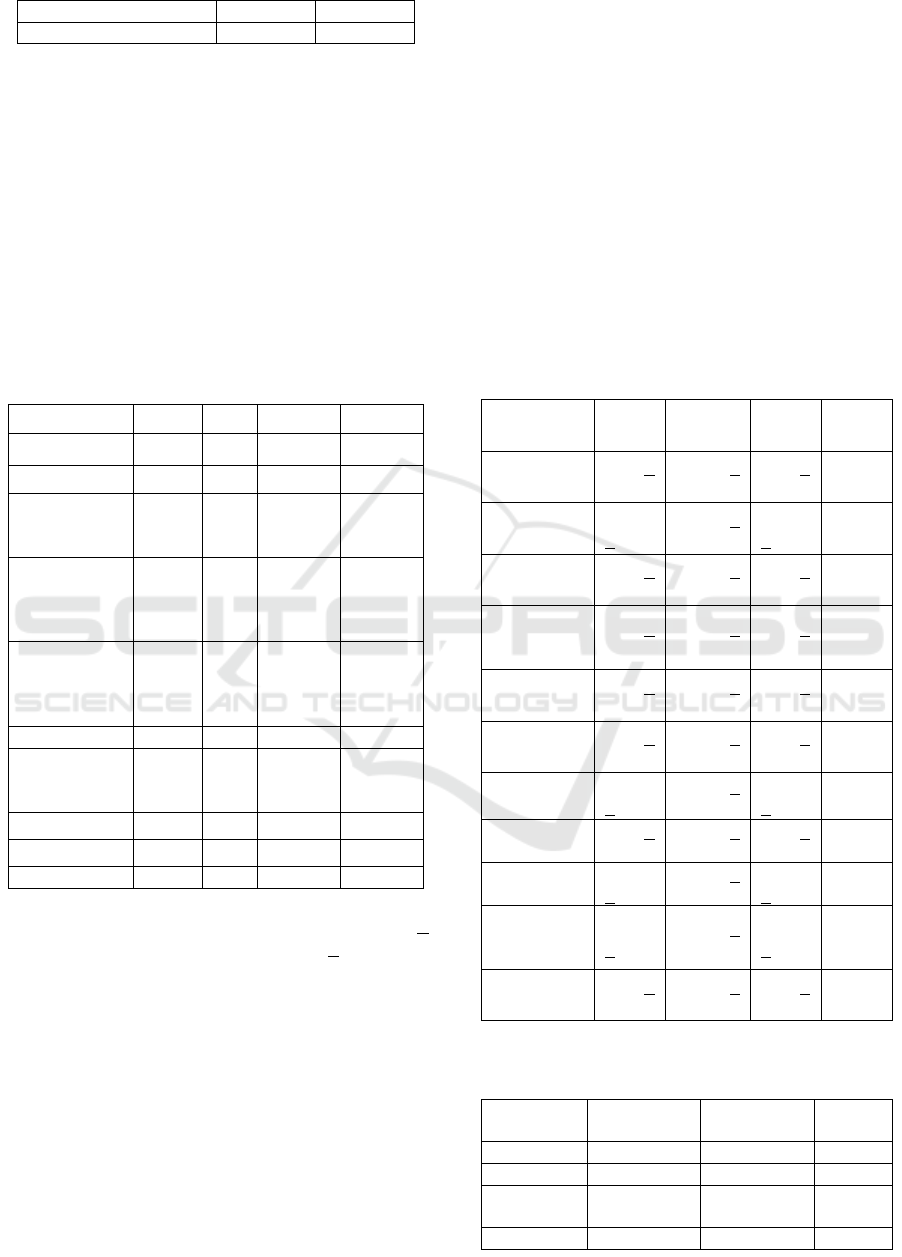
Table 3: Distribution of Non Communicable Diseases
Risk Factors
Risk Factors Frequenc
y
%
Oil to cook
Coconut Oil 17 3.9
Coconut Oil Packa
g
in
g
78 17.7
Palm Oil Bulkin
g
191 43.4
Palm Oil Packa
g
in
g
154 35.0
Flavoring MSG
Always 197 44.8
Sometime 122 27.7
Eve
r
19 4.3
Neve
r
102 23.1
Smoking Habit
Yes 143 32.5
No 297 67.5
Passive Smookin
g
Yes 246 55.9
No 194 44.1
Alcohol Consumption
Yes 77 17.5
No 363 82.5
Workin
g
Activit
y
Risk Factors of Non-communicable Diseases in Medan City
623
Heav
y
37 8.4
Moderate 403 91.6
The most prevalent NCD risk factors were
cooking oil bulking (43.4%), always using flavoring
(44.8%), most of whom had household members
smoking (55.9%).
3.3 Description of Measurement
Results
Of the 440 respondents, 154 respondents (35.0%)
were willing to measure height, weight, waist
circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic
blood pressure, pulse, blood sugar, uric acid and
cholesterol levels.
Table 4: Description of Measurement Results
Measurement Mean SD Min Max
Height (cm) 154.7 8,1 135 175,5
Weight (kg) 59.0 11,8 34 95
Waist
circumferenc
e (cm)
86.8 11,4 56 115
Systolic
Blood
Pressure
(
mmH
g)
129,3 22,7 90 200
Diastolic
Blood
Pressure
(
mmH
g)
82,9 9,7 50 120
Pulse 82,2 4,3 40 97
Blood
glucosa
(
m
g
/dL
)
144,9 81,0 69 462
Uric acid
7,1 5,7 3,4 7,1
Cholesterol
225,4 60,8 104 392
BMI (kg/m
2
) 24.7 4.9 13.4 38.5
When it was viewed by sex, the mean age (+
SD) of the respondents was 44.2 years (+17.2 years)
with no significant difference between men and
women (p = 0.563). The mean height values differed
significantly between males and females but the
mean values of body weight and waist
circumference did not differ significantly, 15.1% of
respondents had BMI > 30 (8.7% male and 16.3
female). Mean systolic blood pressure was higher in
male respondents but there was no significant
difference in mean systolic blood pressure and
diastolic blood pressure between men and women.
In total, 19.1% of respondents had systolic blood
pressure > 140 mmHg and 12.5% had diastolic
blood pressure > 90 mmHg.
Respondents use cooking oil for cooking
(35.0%) and always use flavoring for cooking
(44.8%). A total of 32.6% of the studied population
reported smoking (78.6% in males and 14.1% in
females), which showed a significant difference
between men and women (p <0.001). Similarly in
alcohol consumption, there was a significant
difference in proportion between men (42.9%) and
women (7.3%). The results of this study also show
that there is a significant difference between men
and women in terms of heavy physical activity in the
workplace (18.3% in males and 4.5% in females).
While for the sport, who do moderate activities only
32.5% in men and 26.1% in women.
Table 5: Comparison of Mean (+ SD) Quantitative
Variables between Male and Female in Medan City, 2017
Variable Male Female Total p
Age (years)
43,4 +
18,3
44,5 +
16,8
44,2 +
17,2
0,563
Height (cm)
162.2
+ 6.3
153.4 +
7.7
154.7
+ 8.1
<
0.001
Weight (kg)
60.9 +
13.8
58.6 +
11.4
59.0 +
11.8
0.398
Waist Cir-
cumference
(cm)
84.3 +
12.4
87.3 +
11.2
86.8 +
11.4
0.242
Pulse
83.2 +
3.9
82.0 +
4.3
82.2 +
4.3
0.217
BMI
(kg/m
2
)
15.6 +
13.1
21.0 +
12.6
20.1 +
12.8
0.062
Sistolic BP
(mmHg)
133.5
+ 19.5
128.5 +
23.2
129.3
+ 22.7
0.337
Diastolic BP
(mmHg)
81.7 +
8.3
83.1 +
10.0
82.9 +
9.7
0.547
Cholesterol
(mg/dL)
204.4
+ 56.2
229.3 +
61.0
225.4
+ 60.8
0.079
Blood
Glukosa
(mg/dL)
147.0
+ 63.0
144.0 +
83.5
144.7
+ 81.0
0.867
Uric Acid
(mg/dL)
7.9 +
2.0
7.0 +
6.1
7.1 +
5.7
0.475
Table 6: Distribution of NCD Risk Factors between Male
and Female in Medan City, 2017
Risk
Factors
Male Female p
Oil to cook
Coconut oil 6
(
4,8%
)
11
(
3,5%
)
0,705
Coconut oil
p
ackaging
25 (19,8%) 53 (16,9%)
Palm oil 50
(
39,7%
)
141
(
44,9%
)
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
624
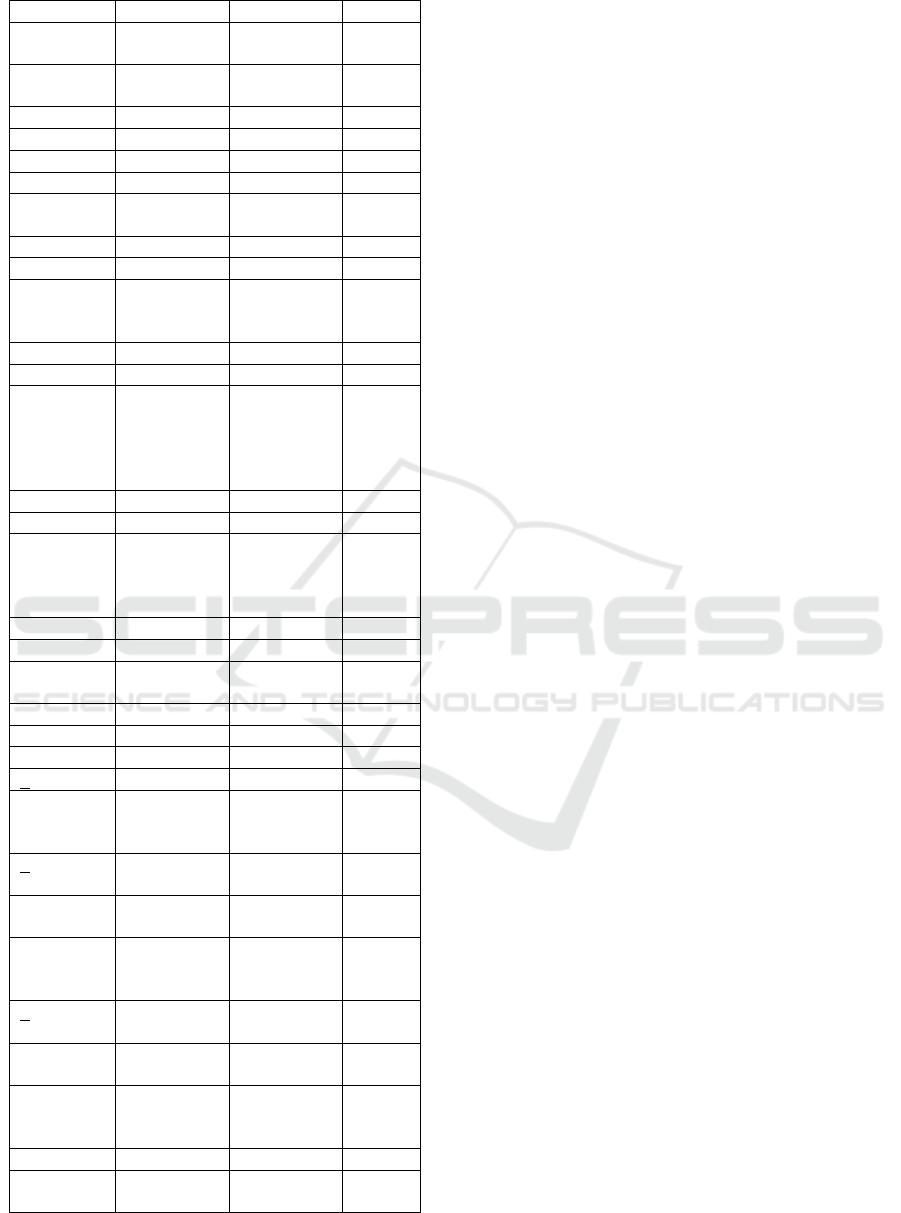
b
ulkin
g
Palm oil
p
acka
g
in
g
45 (35,7%) 109 (34,7%)
Flavoring
MSG
Alwa
y
s 54
(
42,9%
)
143
(
45,5%
)
0,941
Sometime 37
(
29,4%
)
85
(
27,1%
)
Eve
r
6
(
4,8%
)
13
(
4,1%
)
Neve
r
29 (23,0%) 73 (23,2%)
Ever
smoke
Yes 99
(
78,6%
)
44
(
14,0%
)
< 0,001
No 27 (21,4%) 270 (86,0%)
Ever
consume
alcohol
Yes 54
(
42,9%
)
23
(
7,3%
)
< 0,001
No 72
(
57,1%
)
291
(
92,7%
)
Heavy
physical
activity
when
workin
g
Yes 23 (18,3%) 14 ( 4,5%) < 0,001
No 103 (81,7%) 300 (95,5%)
Moderate
physicial
avticity
when sport
Yes 41 (32,5%) 82 (26,1%) 0,174
No 85 (67,5%) 232 (73,9%)
Body Mass
Index
<18,5 4 (17,4%) 9 ( 7,0%) 0,293
18,5
–
24,9 12
(
52,2%
)
61
(
47,3%
)
25,0
–
29,9 5
(
21,7%
)
38
(
29,5%
)
> 30 2
(
8,7%
)
21
(
16,3%
)
Systolic
Blood
Pressure
< 140
mmH
g
18 (78,3%) 105 (81,4%) 0,725
> 140
mmH
g
5 (21,7%) 24 (18,6%)
Diastolic
Blood
Pressure
< 90
mmH
g
21 (91,3%) 112 (86,8%) 0,549
> 90
mmHg
2 ( 8,7%) 17 (13,2%)
Waist
Circumfe-
rence
Normal 13
(
56,5%
)
28
(
21,7%
)
< 0,001
Abdominal
Obesity
10 (43,5%) 101 (78,3%)
4 DISCUSSION
The incidence and prevalence of Non
Communicable Diseases (NCD) has increased over
the past decade. The disease is the most important
cause of death and illness in developed and
developing countries. According to WHO report in
2014, eight controlled risk factors (smoking, high
salt/sodium intake, alcohol consumption, poor
physical activity, hypertension, overweight/obesity,
hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia, account for 70%
of deaths in the world (WHO, 2014). In this study,
the risk factors for non-communicable diseases in
440 respondents in Medan City were overweight and
obesity correlated with cardiovascular disease, and
some cancers as well as increased obesity and
overweight caused death rates and morbidity also
increased. In this study 8.7% of men and 16.3% of
women had BMI> 30. Also 21.7% of men and
29.5% of women were overweight. Southeast Asia,
the highest prevalence of obesity has been reported
from Brunei (16.6% in males and 29.7% in females)
followed by Laos with 12.6% prevalence in males
and 3.3% pad a woman (Dans, 2011). In the Middle
East, the prevalence is reported to be 30.0% and
16.6% respectively in women and men (Shara,
2010). Research in Iran Fars Province obtained the
prevalence of BMI > 30 as much as 93.4% in males
and 20.3% in females. Also 32.8% of men and
35.0% of women were overweight, indicating a high
prevalence of obesity and overweight from the
population studied (Akbarzadeh, 2016). In a 2001
study of Muslims living in urban areas in Palestine,
the prevalence of obesity in women was greater than
in men (49% vs 30%). Research in Medan City
shows that the prevalence of overweight is quite
high compared to the prevalence of obesity, which
can lead to an increase in the prevalence of chronic
diseases. A person who is overweight may soon
become fat if inactive and run a diet is not right.
They should be treated the same as the obese to
control overweight.
In addition to BMI, waist circumference is one of
the important risk factors, which should also be
considered. Body fat distribution is an important risk
factor associated with obesity. Excess abdominal fat
is associated with an increased risk of
cardiometabolic disease. However, the exact
measurement of abdominal fat levels requires the
use of expensive radiological devices. Therefore,
waist circumference is often used as an alternative
marker of abdominal fat mass. This is because the
waist circumference correlates with abdominal fat
mass (subcutaneous and intraabdominal) and is
Risk Factors of Non-communicable Diseases in Medan City
625

associated with cardiometabolic disease (Klein,
2007). The waist circumference can provide a
simple measurement of central obesity. The waist
circumference data in males is categorized to be
normal (<90 cm) and abdominal obesity (> 90 cm)
and in women categorized to normal (<80 cm) and
abdominal obesity (> 80 cm) [10]. As found in this
study, the prevalence of abdominal obesity was
higher in females (78.3%) than in men (48.5%),
similar to the prevalence of obesity higher in
females than in males (16.3% and 8.7%). Thus
women should be closely monitored to control these
risk factors.
Until now, hypertension is still a big challenge in
Indonesia. Hypertension is a condition that is often
found in primary health care health. This is a health
problem with a high prevalence of 25.8%, in
accordance with RISKESDAS 2013 data
(PUSDATIN, 2014). In addition, hypertension
control is inadequate even though effective drugs are
widely available. Long-term persistent blood
pressure can cause damage to the kidneys (kidney
failure), heart (coronary heart disease) and brain
(causing stroke) if not detected early and receive
adequate treatment. Many hypertensive patients with
uncontrolled blood pressure and the number
continues to increase. Hypertension accounts for
about 12.8% of total global mortality (WHO, 2017).
The results showed the mean systolic blood pressure
was 133.5 and 128.5 mmHg in both men and
women. Compared with findings in Iranian Fars
Province (systolic blood pressure is 122.4 and 119.2
mmHg in men and women) the rate in Medan city is
quite high. The prevalence of hypertension in
women is higher than that of men (21.0% and
11.1%). Reports from the Middle East show that the
prevalence of hypertension in women is more than
male (23.0% and 20.0%) (Shara, 2010).
Globally 12% of adult deaths over 30 years old
are caused by tobacco. In 2004, some 5 million
adults over 30 years old died directly from tobacco
use (active and passive smoking) worldwide. The
proportion of tobacco mortality is higher in males
than in females. Globally, 14% of deaths of PTM
cases in adults over 30 years are due to tobacco
(WHO, 2012). In this study 78.6% of men and
14.1% of women had smoked. Current prevalence of
smoking in Southeast Asian countries varies from
36% in Singapore to 64% in Laos. However in
women, smoking prevalence varies from 2% in
Vietnam to 15% in Thailand, Laos, and Myanmar
(Dans, 2011).
The high incidence of non-communicable
diseases (NCD) is caused by unhealthy lifestyles,
one of which is lack of physical activity. The density
of busyness and high mobility make people less
allocate time to exercise. In addition advanced
technology increasingly facilitate the community in
meeting the needs, so that activities that require
movement of the body was reduced. The lack of
physical activity also resulted in the changing trend
of NCD, which initially suffered only by the elderly
age group, but has now been found in the young age
group (0-15 years) and productive age group (15-65
years). The study found that only 28.0% of the
respondents had moderate exercise whereas the
proportion of moderate exercise men (32.5%) was
higher than the proportion of women (26.1%). Men
were significantly more involved in heavy physical
activity in their workplace (18.3%) than women
(4.5%). More male involvement in heavy activity
can be explained largely by the nature of their work
(drivers, factory workers, construction workers,
private employees and self-employed/service),
which may require more activity. But about sporting
activities, lack of knowledge about the importance
of exercise and the lack of appropriate sports
facilities may be one contributing factor that causes
low exercise activity in women.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Most respondents have hypertension (18.2%),
diabetes (5.9%), and Coronary Heart Disease
(4.8%). Meanwhile most of NCD risk factors were
using palm oil bulking to cook (43.4%), always use
flavoring MSG (44.8%), and household member
smoke (55.9%). NCD risk factors which had
significance diffrence between male and female
were height, smoking habit, alcohol consumption,
physical activity and waist circumference.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Direktorat Riset dan
Pengembangan Masyarakat Direktorat Jenderal
Penguatan Riset dan Pengembangan, Kementerian
Riset, Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi, under
contract: 003/SP2H/LT/DRPM/ IV/2017 date 20
April 2017.
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
626

REFERENCES
Akbarzadeh M, Almasi-Hashiani A, Farahmand M., 2016.
The Prevalence of Risk Factors of Non-communicable
diseases in Fars Province. IJNS ; 1(1): 23-29.
Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan,
Kementerian Kesehatan RI, 2013. Riset Kesehatan
Dasar, Jakarta
Dans A, Ng N, Varghese C, Tai ES, Firestone R, Bonita
R. The rise of chronic noncommunicable diseases in
southeast Asia: time for action. The Lancet. 2011;
377(9766):680-9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61506-
1.
Directorate General of Disease Control and Environmental
Sanitation, Ministry of Health of The Republic of
Indonesia, 2016. National Strategic Action Plan for
The Prevention and Control of NonCommunicable
Diseases (RAN PP-PTM) 2016-2019, Jakarta.
Klein S, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, Kelley DE, Leibel
RL, Nonas C, Kahn R. 2007. Waist Circumference
and cardiometabolic risk: a consensus statement from
shaping America’s health: Association for Weight
Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, The
Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition;
and the American Diabetes Association. Am J Clin
Nutr 85:1197–202.
Pusat Data dan Informasi (PUSDATIN) Kesehatan
Kementerian Kesehatan RI, 2014. Hipertensi,
Infodatin: 1-8.
Shara NM. Cardiovascular disease in Middle Eastern
women. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular
Diseases. 2010; 20(6):412-8. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.
2010.01.013. PMID:20554171.
World Health Organization. 2008. Waist Circumference
and waist-hip ratio: report of a WHO expert
consultation. Geneva: WHO Technical Report Series.
World Health Organization, 2011. New WHO report:
deaths from noncommunicable diseases on the rise,
with developing world hit hardest, available at
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2011/
ncds_20110427/en/, accessed 1 June 2018.
World Health Organization, 2012. WHO Global Report :
Mortality atrributable to tobacco, Geneva.
World Health Organization, 2014. Noncommunicable
diseases, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/ factsheets/
fs355/en/, diakses 26 Nopember 2017.
World Health Organization, 2017. Raised blood pressure,
http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/blood_pressu
re_prevalence_text/en/, diakses 26 Nopember 2017.
World Health Organization, 2018. Noncommunicable
Disease, available at http://www. who.int/news-
room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases,
accessed 1 June 2018.
Risk Factors of Non-communicable Diseases in Medan City
627
