
Optimization of Garbage Hauling Route in Medan Kota District
using Saving Matrix Method to Minimize Cost
Khalida Syahputri
1
, Rahmi M. Sari
1
, Mangara M. Tambunan
1
, Indah Rizkya
1
, Ikhsan Siregar
1
and
Josua P. Simanjuntak
1
1
Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Sumatea Utara, Jl. Almamater, Padang Bulan, Medan,
Indonesia
Keywords: Garbage Hauling Route.
Abstract: Medan Kota district is one of the district with the highest population density in the city. This has resulted in
the high rate of garbage heap in the Medan Kota that must be managed. Limitations of the means of
transporting garbage resulted in the accumulation of garbage in various TPS in Medan district. The purpose
of this research, applying Saving Matrix method to optimize the route of transporting garbage in the city field.
This method enables route optimization with respect to vehicle capacity and garbage volume for each TPS.
The data used is the distance between Pool with the point of point of TPS and the distance between the points
of TPS, the amount of garbage volume of each TPS point, and the capacity of the vehicle. The route
optimization using Saving Algorithm will result in a route that minimizes the cost of fuel by the amount of
garbage transported more. The route generated by using the Savings Algorithm to successfully save the
distance as far as 95 Km and save the cost of Rp. 59.525.416 / year.
1 INTRODUCTION
Rate of garbage heap in developing countries will
always be high. This was influenced by high levels of
population, industrialization, urbanization, and
economic growth.
Economic garbage management
consists of garbage reduction and garbage handling
efforts. garbage reduction efforts consist of limiting
garbage heap, recycling waste, and reuse of waste.
garbage management efforts include sorting,
collection, transporting, processing, and final
processing (Bozkurt, 2015).
Medan Kota district is
one of the biggest sub-district in Medan with the
population of 118.405 people and is categorized as
solid city based on SNI 19. In Medan Kota sub-
district, there are shopping area, trade, market that is
Sambu Market Center, sports facility that is Teladan
Stadium (C. Bozkurt, 2015).
The Increasing number of residents in Medan
Kota district, will also increase the amount of garbage
volume in Medan city. Based on the results of recap
at department of public works and housing (DPUP)
municipalities, the volume of garbage in Medan Kota
district from year to year also increased. So it is
necessary to do proper garbage management. The
process of transporting garbage is done by way of
garbage transportation from garbage bins that were
spread in every public road. Because of the limited
number of transport vehicles, then the process of
transporting garbage can only be executed as much as
one time round in one day from the base to every
particular service area and then taken to the landfill
and ended up in the base and not optimal journey
truck transport truck that resulted in garbage
accumulation in some regions (Kinobe, 2016).
There were many factors that could influence in
the process of transporting garbage from the starting
point, in this case DPUP to the end point of the
landfill, including the capacity of transport means, the
volume of garbage in each TPS and the distance
travelled in the transport process. The garbage
transport process should each pay attention to the
capacity of each vehicle and the demand capacity
(waste) on each route the issue of garbage distribution
involves several major considerations including
vehicle routes, vehicles to minimize distribution
costs, so as to expand the service area from garbage
collection with limited fleets).
The problem of distribution routes was a very
much discussed problem in terms of optimization
such as about traveling salesman problems and
vehicle routing problems and for that has been done a
lot of research to discuss the problem VRP in order to
Syahputri, K., Sari, R., Tambunan, M., Rizkya, I., Siregar, I. and Simanjuntak, J.
Optimization of Garbage Hauling Route in Medan Kota District using Saving Matrix Method to Minimize Cost.
DOI: 10.5220/0010077702170221
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
217-221
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
217

obtain the optimal technique to solve the problem
(Hannan, 2018). Traveling salesman problems and
routing issues vehicles are a very complex problem in
the field of logistics distribution because they should
involve a minimum cost design, determining the
delivery route from start to finish and determining the
start of the depot and the end of the depot
(Armenzani, 2017). The solutions generated on the
VRP problem are increased exponentially and to find
the optimal solution in VRP problems can be solved
by using heuristic methods that the proposed heuristic
approach allows us to deal with problems in a short
time using the heuristic method (Heechul, 2016).
Clarke and Wright create a heuristic algorithm to
complete the VRP based on the concept of austerity
which provide optimal solution and easy way to
calculate and easier to comprehend. The concept of
this savings was with the concept of cost that can be
obtained by combining the two routes to the top and
making it one. This was shown in the figure below
where 0 represents the depot and i, j as the customer
(Fathoni, 2017) of modified saving algorithms to
create feasible solutions for VRPP. The idea was to
first serve each customer with a special route, and
then combine the route pairs as long as the positive
savings can be realized and the vehicle's capacity was
not violated. In each iteration, we combine pairs with
the highest savings. To combine the two routes r1 and
r2, we only consider the edge incidence to the depot
and remove one side of r1 and one side r2. Then, we
replace it with an edge directly connecting the
appropriate customer i from r1 and j r2 (Babaee,
2018). The Saving Matrix method was the method
used to determine the route of product distribution to
the marketing area by determining the distribution
route to be traveled and the number of vehicles
routing based on the capacity in order to obtain the
shortest route and minimal transportation cost. The
Saving Matrix method was also one of the techniques
used to schedule a limited number of vehicles from
facilities with a different maximum capacity. The
austerity matrix shows the savings that occur when
combining two possible TPS into one truck so that it
can save the distance, time, and transportation costs
(Babaee, 2018).
2 METHODOLOGY
This research was conducted in the district of Medan
Kota. The object studied was the route of transporting
garbage from the pool to the TPS and from the TPS
to the landfill located in Marelan Raya Street, Market
V TPA Plunge, Rengas Island, Medan Marelan. The
data collected to conduct the research is the data of
the number of temporary garbage disposal sites, the
number of consumer demand or the volume of
landfills.from the data obtained will be processed
using Clarke and Wright Saving Matrix method, the
route of garbage transportation in sub-district of city
was divided into 4 polls where each poll has different
number of different TPS for each POOL
The first step done in this research was to create a
matrix that contains distance between TPS the
distance between each pair of locations to visit.
Determining the distance was based on the distance
of each TPS where the location of each TPS can be
symbolized as notation, Juanda street was symbolized
by A1, Sisingamangaraja street symbolized by A2,
Mahkamah street symbolized by A3, Tengah street
symbolized by A4, Samarinda symbolized with
Rahmadsyah by A6 , Raja street symbolized by B1,
Pelangi steet symbolized by B2, Turi street
symbolized by B3, Gedung Arca street symbolized by
B4, Halat street symbolized by B5, Halat street
symbolized by B6, Juanda street symbolized by B7,
H M Joni street symbolized by B8, Seksama street
symbolized by C1, Saudara street symbolized by C2,
Bahagia street symbolized by C3, Kemiri 1 street
symbolized by C4, Kemiri 2 street symbolized by C5,
Pelajar street symbolized by D1, Jati street
symbolized by D2, Aman street symbolized by D3,
Meranti street symbolized D4. Sakti Lubis street
symbolized by D5, Pintu Air street symbolized by
D6, Busi street symbolized by D7, Gg Pegawas
symbolized by D8, Bali street symbolized by D9,
Sempurna symbolized by E1, Santun street
symbolized by E2, Laksana street symbolized by E3,
Amalium street symbolized by I4, and Rahmadsyah
street symbolized by E5. The second stage is to create
a distance-saving Matrix that shows the savings that
occur when combining two possible TPS into one
truck so that it can save the distance, time, and
transportation costs.
S (x, y) = Dist (Center, x) + Dist (Center,
y
) - Dist (x,
y
)
(1)
Third stage. Allocate TPS points to a transport
route. The first step of each TPS was allocated to
different trucks or routes. The second step was to
combine two routes based on the saving distance
obtained using the largest Saving Matrix formula and
check whether the merger was feasible or not. It was
said to be appropriate if the total shipments that
should be passed through the route do not exceed the
capacity of the conveyance. The integration of the
route was focused on saving the greatest distance to
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
218
obtain the distance efficiency, so the time spent will
be faster.
The fourth stage. This stage aims to minimize the
travel distance that must be transported each means
of conveyance. To get an optimal transportation
route, can be done two stages of determining the
initial delivery route for each vehicle and make
improvements to the route that is not feasible. The
fifth stage. Calculates the fuel cost of each total
distance with the fuel consumption for each garbage
truck average of 3km / liter and the diesel price is Rp
5,150.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Truck Transportation Garbage
Route in Medan Kota District
In this research, the data consists of Primary Data and
Secondary Data. Primary data collected were among
others: truck route of garbage transport during
operational time and location of service area; truck
capacity; and the amount of garbage heap in each
service area. Secondary data collected were: number
and type of garbage truck, truck data (type, police
number, and year of output); data speed of truck
(speed), time of loading and unloading of waste,
garbage transport vehicle in sub district Medan of 7
unit consisting of:
1. In pool A there was 1 unit of truck garbage of
capacity 8m
3
2. In pool B there were 2 units of 8m
3
capacity truck.
3. In pool C there was 1 unit of 8m
3
capacity truck.
4. In pool D there were 2 units of 8m
3
capacity truck.
5. In pool E there was 1 unit of 8m
3
capacity truck.
Research determination of garbage dumping route
in sub-district of Medan Kota with the capacity of
8m
3
garbage
truck
which the actual route from
garbage collection in sub-district of Medan Kota.
On the actual route the garbage truck that was in
each pool only runs every TPS once a day and when
the volume of garbage meet the capacity of the truck,
not yet lifted will resume on the next day, on Monday
the truck in pool E will lift the garbage at A1-A2-A3
point with a volume of 7.5 after lifting the truck truck
will depart to TPA, and for the garbage located at A5-
A4-A6 will be taken the next day because each truck
there was only one ritation per day. After using
Clarke method and Wright Saving Matrix could be
obtained new route which can be seen in Table 2.
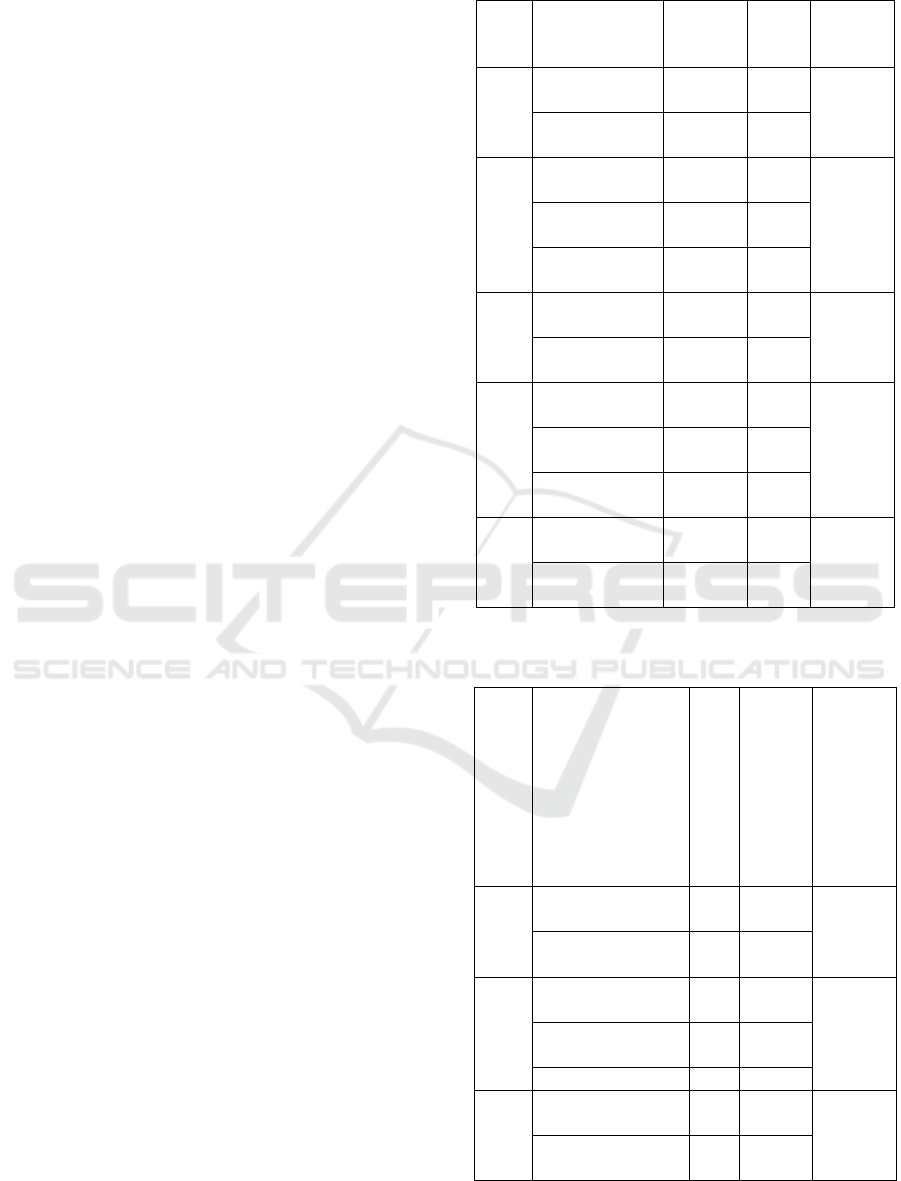
Tabel 1: Actual Route
Pool Route
Volume
Transpo
rted (m
3)
Dista
nce
(km)
Cost
Pool
A
A0-A1-A2-
A3-X-A0
7,5
46,60
Rp468.
135
A0-A5-A4-
A6-X-A0
7,5
44,3
Pool
B
B0-B4-B7-B3-
X-B0 7
62,3
Rp829.
923
B0-B6-B1-B8-
X-B0 8
50,75
B0-B5-B2-X-
B0 5,5
48,1
Pool
C
C0-C1-C4-C2-
X-C0 7
53,90
Rp545.
128
C0-C3-C5-X-
C0 6,
51,95
Pool
D
D0-D6-D2-
D7-X-D0 7,5
53,9
Rp841.
510
D0-D3-D5-
D1-X-D0 8
56,9
D0-D9-D4-
D8-X-D0 7
52,6
Pool
E
E0-E4-E2-E1-
X-E0
7,5
58,70
Rp628.
815
E0-E4-E3-X-
E0
4,5
63,40
Tabel 2: Actual Route
Pool Route
Vol
um
e
Tra
nsp
orte
d
(m
3
)
Distan
ce
(km)
Cost
Pool
A
A0-A4-A1-A3-X-
A0
7
42,40
Rp418.
438
A0-A2-A6-A5-X-
A0
8
38,85
Pool
B
B0-B4-B6-B7-X-
B0 8 43,75
Rp695.
250
B0-B2-B3-B8-X-
B0 7,5 43,75
B0-B1-B5-X-B0 6 47,50
Pool
C
B0-C5-C1-C2-X-
C0 6,5 49,00
Rp489.
250
C0-C4-C3-X-C0 6,5 46,00
Optimization of Garbage Hauling Route in Medan Kota District using Saving Matrix Method to Minimize Cost
219
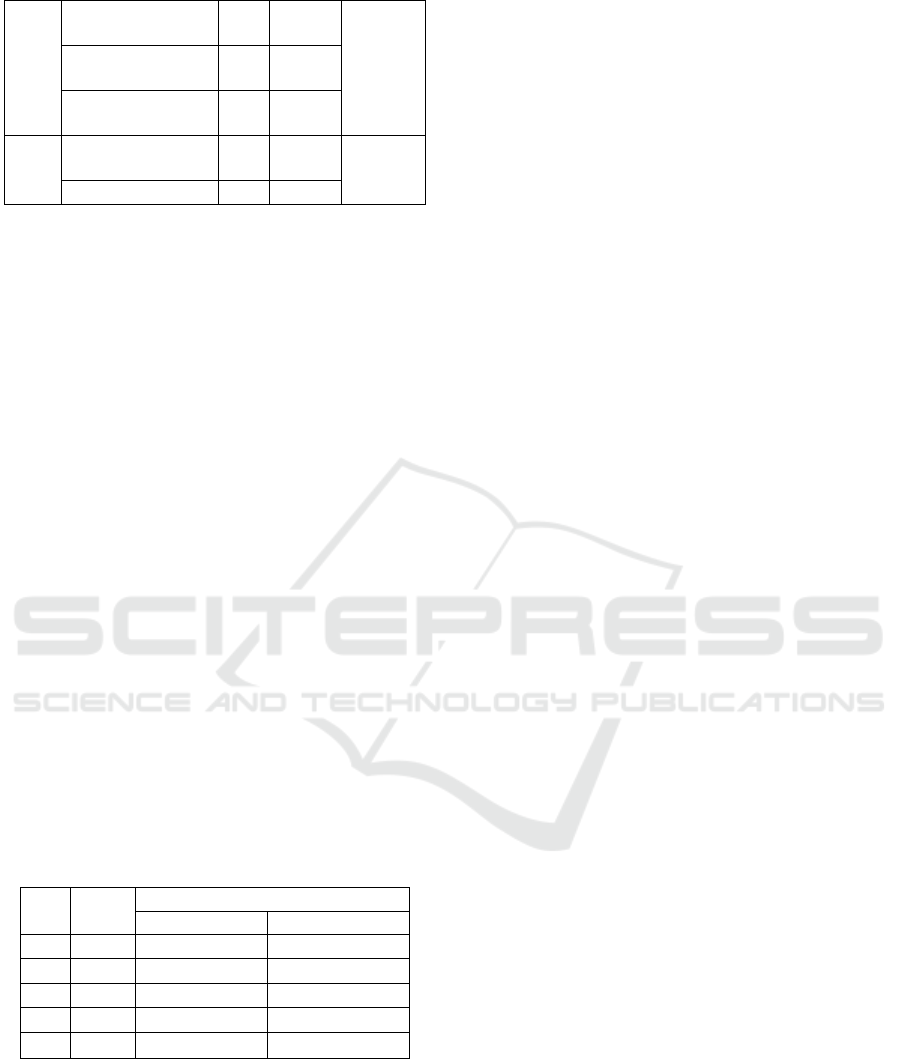
Pool
D
D0-D8-D7-D6-X-
D0 8 53,15
Rp831.
210
D0-D1-D9-D3-X-
D0 8 57,70
D0-D4-D5-D2-X-
D0 6,5 50,55
Pool
E
E0-E3-E5-E4-X-
E0
7
51,70
Rp587.
100
E0-E1-E2-X-E0 5,5
62,30
From the Table 1. Can be seen that there were 5
garbage truck pools that serve garbage collection in
each TPS in the Medan Kota district, the results
obtained were the garbage in the coverage TPS of
pools E, F, G, H and I can be trapped in one day 2
garbage hauling and in pools F and H there were 3
routes that must be trucked by garbage trucks but in
pools F and H each have 2 different trucks with other
pools that have only one truck, the determination of
the route of garbage by using Saving Matrix method
was based on the volume and capacity of garbage
truckers. On the trucking trip, each truck will do two
ritations a day if the truck was only one ritual in one
day, the garbage in each TPS is all due to the limited
number of trucks and the limited capacity of the
conveyance at each pool.
3.2 Comparison of the Total Actual
Cost with the Cost of the Proposed
Route
Based on the determination of the cost of truck
transporting garbage using saving matrix method,
then compare between actual route and with the
regular route.
Table 3: Comparison Of Total Actual Cost With Cost Of
Proposed Route
No Pool
Total Distance (km)
Actual Proposal
1 E Rp468.135 Rp418.438
2 F Rp829.923 Rp695.250
3 G Rp545.128 Rp489.250
4 H Rp841,510 Rp831.210
5 I Rp628.815 Rp587.100
From the table it can be seen that the total fuel cost
of the actual route is greater than the total cost of the
proposed route with savings of 8.8%. Peter
Majercak's research on the determination of the
distribution route of goods to each consumer by
considering the capacity of the truck using the Clark
and Wright's Savings Algorithm method successfully
minimizes the delivery distance of the product to the
consumer. Clark and Wright's Savings Algorithm
methods have also managed to minimize waste
transport distance between TPS in Medan Kota
District.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The total traveled distance by all trucks so far in
Medan Town sub-district is 643.4 km. After using the
saving matrix method the total traveled distance
become 586.65 km km. The total fuel cost incurred
by the urban district is Rp. 3.313.000,- per month.
After using the saving matrix method the total cost of
board materials issued to RP. 3.021.000,- per month.
The percentage of total cost savings is 8.8%, The
results shows that the route and cost of fuel with
saving matrix method is minimized.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been fully supported by TALENTA
Research Program (Universitas Sumatera Utara),
No:2590/UN5.1.R/PPM/2018, March 16th, 2018
REFERENCES
Cuma Bozkurt, 2015. International Journal Of Energy
Economics And Policy Vol 5, No 2.
Cuma Bozkurt.” Industrial-waste management in
developing countries: The case of Lebanon Volume 61,
Issue 4, April 2015.
Kinobe,j.r dkk, 2016. Habitat International Volume 49,
October 2015, Pages 126-137
M.A.Hannan, M.A 2018. Waste Management Volume 71,
January 2018. Pages 31-41
Gendreau Michel.” Efficiently Solving Very Large Scale
Routing Problems4 Florian Arnold1”, diakses dari
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Florian_Arnold/p
ublication/322317599
Armenzoni 2017. Distribution Journal of Advanced
Transportation Volume 2017.
Heechul Bae 2016, Mathematical Modelling 40(13-14)
Fathoni, Ali, 2017. International Journal of New
Technology and Research Volume-3, Issue-10
Babaee dkk 2018 , Sustainability 2018. 10(5), 1366
Fisher, M.L. 1995. “Vehicle Routing in Operations
Research and Management Science”Vol.8.
Amsterdam, New York, Elsevier
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
220

Majercak,Peter. 2016. Application of Clark and Wright´s
Savings Algorithm Model to Solve Routing Problem in
Supply Logistics Vol 25 (2), PP.125-145
Uchoa, E., Pecin, D., Pessoa, A., Poggi, M., Vidal, T., and
Subramanian, A. 2017. European Journal of
Operational Research, 257(3):845-858.
Optimization of Garbage Hauling Route in Medan Kota District using Saving Matrix Method to Minimize Cost
221
