
Increase Medicine Adherecence TB Patient with Ners-Short Message
Service Intervenstion (N-SMSI)
Reni Asmara Ariga
1
, Siti Zahara Nasution
1
, Rina Amelia
2
and Siti Saidah Nasution
1
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Prof. Maas Street No. 3 Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, dr. Mansyur Street No. 5 Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Medicine Adherecence, TB Patient, Ners-Short Message Service Intervention (N-SMSI).
Abstract: The high rates of pulmonary TB incidence worldwide are common due to poor patient adherence. Drug
adherence is one of the important indicators in the successful treatment of a disease. The purpose of this
study was to determine the effect of Ners-Short Message Service Intervention (N-SMSI) on the adherence
of taking medication to patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. This research design is Quasi experiment pre-
post test desaiqn with control group. Samples are taken by Consecutive Sampling. The results of this study
found that there was a difference between control and intervention groups before and after Ners-Short
Message Service Intervention (N-SMSI), ie in the control group as much as 47.2% obedient and the
intervention group as much as 80.6% obedient. N-SMSI (Ners-Short Message Service Intervention) can
improve medication adherence of pulmonary tuberculosis patients. The action is so important that it is not
just adherence to taking medication, but to the behavior of patients or TB patients' habits. So increase the
cure rate and reduce the rate of transmission and ultimately improve the quality of life.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. It has infected as many as one-third of
the world's population. Tuberculosis cases are
increasing and many are not successfully be cured,
especially in countries grouped in 22 countries with
major tuberculosis problems ( Badan Litbangkes
Kemenkes RI, 2011)
Pulmonary TB patients are estimated to be only
10 to 20 cases among the 100,000 population,
whereas the mortality rate ranges from 1 to 5 deaths
per 100,000 population in development countries.
Africa is estimated to reach 165 new cases among
100,000 populations, and in Asia 110 among
100,000 populations. Asian populations are more
than Africa, the number of pulmonary patient in
Asian 3,7 times more than Africa
Data on World Lung TB patients by 2015
according to the World Health Organization (WHO)
reached 10.4 million people, up from just 9.6
million. Indonesia is ranked second largest among
patients with pulmonary TB after India with a total
of 2.8 million cases, followed by Indonesia with
1.02 million cases and China with 918 thousand
cases (WHO, 2015)
The discovery of new cases of Pulmonary
Tuberculosis in Indonesia based on data from the
Ministry of Health 2011-2015, the number of new
cases of BTA positive Tuberculosis found in 2011
were 197,797 new cases, 202,301 in 2012, 2013 of
196,310 new cases, 2014 of 176,667 new cases and
2015 as many as 330,910 new cases (Ministry of
Health, 2015).
TB drop out rates are many factors that affect the
recovery of TB patients. Many factors that succeed
in TB programs such as pmo and cadres. The
training model for the development of participatory
training can improve the cadre's competence on TB
(Ariga & Zahara) .
The high rates of pulmonary TB incidence
worldwide are common due to poor patient
adherence (45%) (Viney, et al, 2011). Drug
adherence is one of the important indicators in the
successful treatment of a disease. The average
patient's adherence to long-term treatment of chronic
diseases varies greatly. In developed countries the
percentage of patient adherence to taking medication
is 50% while for developing countries the
percentage is only about 24% (WHO, 2015). Low
patient compliance in taking medication is a serious
health problem and this often occurs when patients
Ariga, R., Nasution, S., Amelia, R. and Nasution, S.
Increase Medicine Adherecence TB Patient with Ners-Short Message Service Intervenstion (N-SMSI).
DOI: 10.5220/0010076905190524
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
519-524
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
519

are confronted with long-term treatment of chronic
illness such as pulmonary TB disease (WHO, 2015).
Low medication adherence in patients with
pulmonary TB will slow the healing process of the
disease, increase the risk of morbidity, mortality,
and drug resistance to either one type of OAT
(mono-resistant), or more than one type of OAT
(poly resistant, multidrug resistant, extenly drug
resistant, or totally drug resistant) (Departement of
Health Indonesiam 2005). Low patient compliance
with OAT also causes patients to be a source of
transmission of resistant bacteria in the community,
which in turn will complicate the eradication of
pulmonary TB disease in Indonesia and exacerbate
the burden of the government (WHO, 2015).
Drug adherence is influenced by several factors
such as knowledge and attitude (Departement of
Health Indonesiam 2005). According to research
Tachfouti et al (2011) there is a real relationship
between knowledge and attitude with adherence to
taking anti-tuberculosis drugs in Morocco, Africa
(BPOM RI, 2006). According to research Avianty
(2005) knowledge and attitudes become factors that
affect the level of adherence of a person in taking
medicine (Widjanarko, Gompelman, Dijkers &
Werf). According to research Luluk at Health Center
Gatak Surakarta (2012) it is said that there is a
significant relationship between the knowledge of
adherence to taking medication of patients with
pulmonary tuberculosis (CAN, 2013).
Based on the above it can be assumed that there
are several factors that influence the level of patient
compliance in the treatment of pulmonary
tuberculosis such as knowledge and attitude of the
patient. Active care management of lung TB patients
at home can be done through telenursing.
Telenursing is defined as a process of providing
management and coordination of care and delivery
of health services through information technology
and telecommunications (Sholikhah, 2012)
According to Wulandari (2012), that the use of
telenursing can improve patient behavior in
prevention of transmission of pulmonary
tuberculosis. However, this method of telenursing is
quite expensive. Therefore, researchers are trying to
develop new, cheaper models through N-SMSI
(Ners-Short Message Services) (Wulandari, 2012).
N-SMSI is one form of community nursing
intervention, where community nurses send SMS to
Pulmonary TB patients. SMS contains reminder
messages of medication and nutrition, sent daily,
with frequency adjusted to the timing schedule for
taking TB lung medication. Website-built SMS,
hosted on an email provider, so this method does not
cost a lot. To overcome this problem, researchers
apply communication technology through
telenursing known as N-SMSI (Ners-Short Message
Service Intervention) by sending short messages to
patients in accordance with the time of taking the
drug. This study aims to increase the rate of healing
of pulmonary TB patients and reduce mortality by
increasing knowledge, making decisions and
improving patient compliance to take medication
independently. This study has the outcomes of
producing appropriate methods in improving the
adherence of taking pulmonary TB patients with N-
SMSI (Ners-Short Message Service Intervention).
2 METHOD
Ners-Short Message Service Intervention (N-SMSI)
study on improving medication adherence of
pulmonary TB patients in Medan using Quasi
Experiment method with pretest-posttest design with
control group, population of 72 people. 36 controls
and 36 intervention groups. Sampling technique
used in this research is non probability sampling
technique with total sampling approach that is
sampling technique by taking the whole sample
amount of research. The inclusion criteria in this
study were the new intensive phase intensive TB
patients expressed by the Johor Field Health Center
and the Medan Amplas Community Health Center,
the patients with tuberculosis aged 21-60 years, the
patients had mobile phones, were willing to be
respondents. Exclusion criteria include Pulmonary
TB patients with accompanying diseases, such as
HIV, cancer, and DM, Pulmonary TB patients who
refuse to be respondents.
This research was conducted for 2 months.
Starting from April to June 2018. The reason for the
study was to select the working area of Medan Johor
Health Center and Puskesmas Medan Amplas as a
research site because this location is a densely
populated location with TB patients and Puskesmas
have TB program. Instrument used in this research is
questionnaire of medication patient compliance level
of Lung TB patient with CVI value. Instruments
have been derived with crobaalfa value. The process
of collecting data is done by 1) the researcher fill out
the format of assessment of respondent
characteristics that include age, sex, occupation, and
education level, and patient's cellular contact
number; 2) The researcher evaluates the patient's
compliance rate before taking N-SMSI (pre-test) on
the first day; 3) Researchers conducted N-SMSI
implementation in coordination with patient and
family for 2 months by sending a short message
containing reminder of taking medicine 15 minutes
before taking medicine. SMS is given in the morning
at 07.00 WIB but pasa when the fasting month is
done 03.00 WIB. Researchers previously gave the
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
520
news at the time to make changes sms at the time of
fasting. SMS contains information on reminders for
taking medication as well as information on
tuberculosis, such as prevention of TB transmission,
drug side effects, cough etiquette and sneezing, the
importance of medication adherence 4) researchers
reevaluate the level of adherence of taking
medication to patients with lung TB (post test) using
questionnaires level of medication adherence of lung
tuberculosis patients. Analysis of this research data
is processed by using SPSS program.
3 RESULT
The result showed that demographic data, the
majority of age <40 years old were 43,1% (31),
66,7% (48) male majority, 54,2% (39) private
employees, the majority of private sector employees
occupy 54.2% (39), the majority of private
employment is 54.2% (39), the majority of private
employment is 54.2% (39), the majority live with
households with the wife as much as 48.6% (35), the
majority of home high humidity home conditions are
38.9% (28), the majority of high school education as
much as 62.5% (45), the majority of respondents had
contact with patients in contact with previous
patients as much as 54.2% (39). Description can be
seen in the table below.
Tabel 1. Characteristic Of Patient Demographic
Karakteristik Demo
g
rafi F %
Age
<40
y
ea
r
31 43.1
40-60
y
ea
r
33 45.8
>60 yea
r
8 11.1
Sex
Female 24 33.3
Male 48 66.7
Profession
Labor 7 9.7
Farmer 1 1.4
Civil Servant 6 8.3
emplo
y
e 39 54.2
Deale
r
19 26.4
Families live at home
Main Family (father,
mother, chidren)
13 18.1
Extended Family
(father, mother, children,
the other family)
10 13.9
House condition
In front of hi
g
htwa
y
17 23.6
N
o window 27 37.5
Stuff
y
house 28 38.9
Education
Elementary school 2
Junior Hi
g
h School 8
Senior Hi
g
h School 45
Diploma 10
Bachelo
r
7
History of contact with
tuberculosis patients
Yes 33
N
o39
Culture
Bata
k
38
Jawa 26
Minan
g
8
Get TB Informa
t
ion
Ya 66
Tida
k
6
Total 72
TB Resource
Television 41
N
ews paper/
ma
g
azine
4
Flip Char
t
22
Total 57
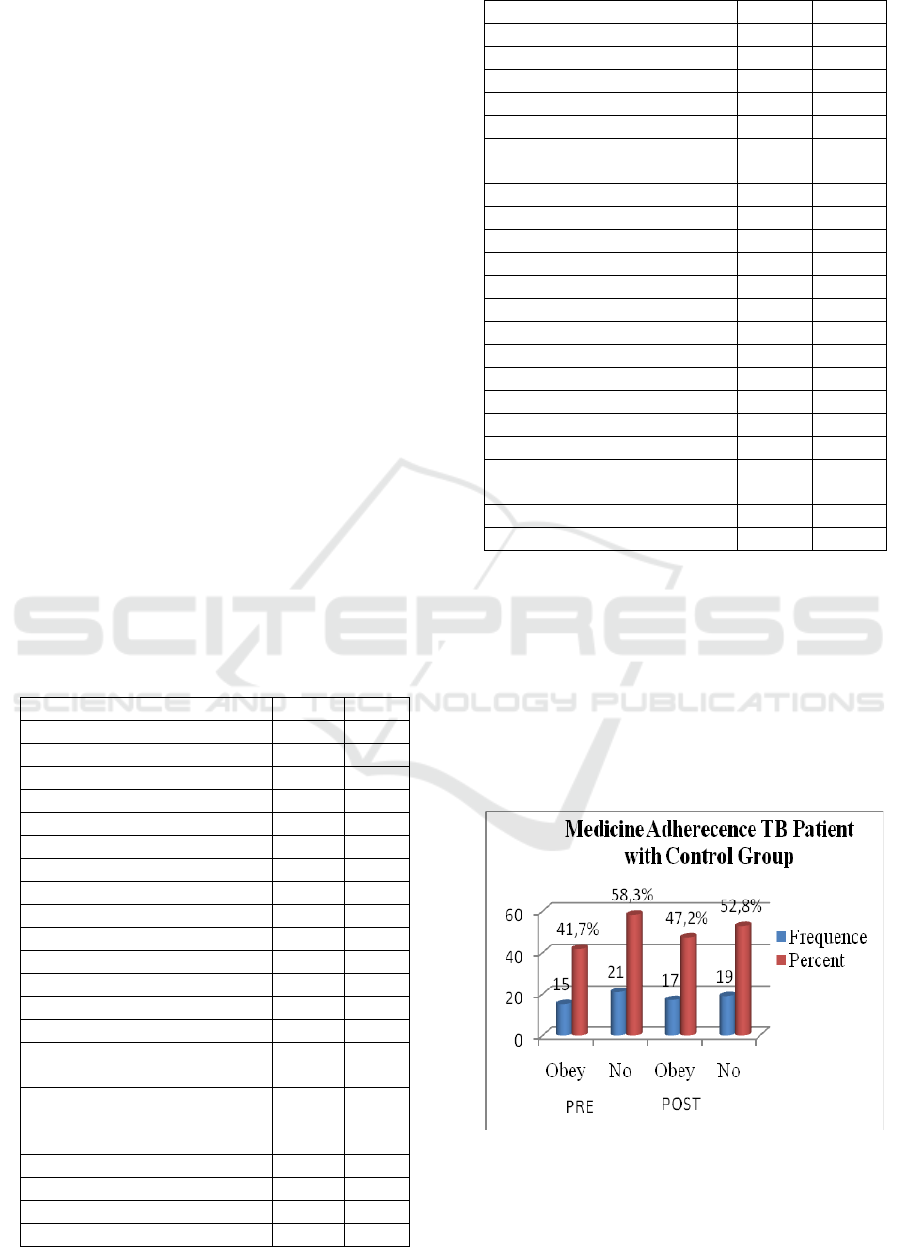
The result of the study showed the
characteristics of medication adherence of TB
patients before and after intervention, ie before the
action in the control group of the majority of the
disobedient patients 58.3% and the intervention
group the majority of the patients did not obey
55.6%. After an action on the control group the
majority of patients did not adhere 52.8% and the
intervention group the majority of patients obedient
80.6%. Description can be seen on the graph below.
Figure 1. Patient medication adherence of Pre-Post TB
patients to Control Group
Increase Medicine Adherecence TB Patient with Ners-Short Message Service Intervenstion (N-SMSI)
521
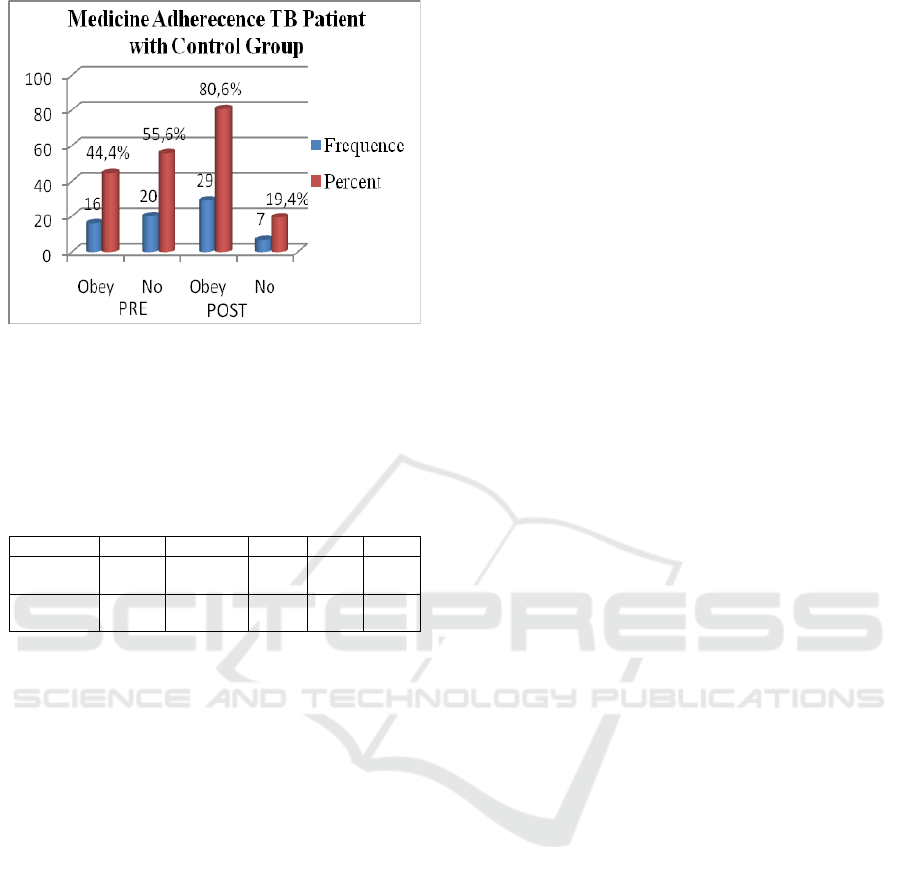
Figure 2. Patient medication adherence of Pre-Post TB
patients to Intervention Group
The results showed that test results using Man
Whitney that there is influence of N-SMSI on
patient compliance in taking medicine p = 0,000
Tabel 2. Different of Patient Obediance Among Control
and Intervention Group
Group Mean Median Min Max P
Control 20,31 0 0 2 0,00
0
Invention 52,69 2 1 6 0,00
0
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Characteristic of Patient
Based on Table 1. The results showed the
demographic data, the majority of age group <40
Years as much as 43.1% who suffer from TB
compared with other age groups. This is supported
by Mahpudin and Mahkota (2007) that the age
group 49 years and under has a higher proportion of
63.2% compared with age group 50 years and over
(Mahpudin & Mahkota, 2007). The age group is a
productive age group. The majority of sexes of
patients with TB are men as much as 66.7%. The
research conducted by Zerbini, Greco, Cisneros,
Colombo, Beltrame, Boncompain and Genero
(2017) that the majority of sex of adult TB patients
in Argentina are men by 65% and men 1.7 times
more at risk suffer from pulmonary tuberculosis
compared to women. Women are usually more
docile than men. This is because majority women
are more concerned with their health than men
(Zerbini, Grec, Estrada, Cisneros, Colombo
Beltrame, Boncompain & Genero, 2017)
The majority of patients' occupations are private
employment of 54.2%. This is because the location
of the patient's residence is an industrial area such as
a factory. Occupational and occupational factors can
also lead to the incidence of TB known as Work-
Dose Disease. The workplace is an environment
with a concentrated population at the same place and
time, so it is one of the potential environments in TB
transmission (Ministry of Health, 2015).
The majority live with households with wives as
much as 48.6%. this is in line with research
conducted by Rukmini and Chatarina (2011) that as
much as 54.4% is the head of the household. The
head of the household can not provide for the child
and his wife, infectious diseases to other family
members, the patient can feel HDR (Low Self-
Esteem) because they can not produce and provide
for their children. Gender is one of the risk factors of
TB. The majority of house high humidity house
condition is 38.9%. The condition of the room is
related to the incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis
where people with unqualified room conditions have
a chance of 1.18 times for contracting pulmonary TB
compared to a house with a qualified room
condition. Condition of the room is eligible if
ventilation is available> 10% floor area, windows
are opened every day, lighting is good enough in the
bedroom, kitchen or living room. Houses with good
lighting and ventilation will complicate the growth
of germs, because ultraviolet light can kill germs and
good ventilation causes air exchange thus reducing
the concentration of germs (Rukmini, 2011)
In fact, people spend more time indoors than
outdoors. The concentration of pollutants in
buildings / rooms can be higher than outdoors,
especially in big cities. This is further exacerbated
by the lack of ventilation in the house building. The
largest sources of air pollution in the room are
cigarette smoke, combustion products (fuel energy),
radon gas (derived from floor cement dust, walls,
etc.), chemical products (hair spray, room cleaners,
paint, and others) and biological pollutants (fungi,
bacteria, animal dander, etc.) (Ministry of Health,
2014). The majority of respondents had contact with
patient contact with previous patient as much as
54.2% (39). The results of Agustina and Wahyuni's
(2017) study that the patient's actions in preventing
the TB exclusion of the members at home-level
family members were 56% (Nurjanah, 2015).
4.2 Obedience before NSMS
Based on the results of the study of TB drug
treatment adherence prior to Ners-Short Message
Service Intervention (N-SMSI) in the control group
it was found that 58.3% were not adherent and in the
intervention group it was found that did not comply
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
522

as much as 55.6%. The patient's compliance can be
affected by several factors, one of which is patient
education. This is because the majority of TB
patients education is high school as much as 62.5%.
Nurjana (2015) study on the risk factors of
pulmonary tuberculosis in productive age in
Indonesia that the most influential factor is
education. This is because education will affect one's
perception and knowledge about pulmonary TB.
With good knowledge, there will be prevention and
treatment efforts if the pulmonary TB. Information
received, role needs to be improved. Role as a
family nurse. Nurse improvement needs to be done
through training. The role of families needs to be
improved through family empowerment of drug
control. With a skilled family, the patient is obedient
in the tuning. The condition of education is one
indicator that is often reviewed in measuring the
level of human development of a country (Nurjanah,
2015). Research Pasek et al (2013), found that in TB
patients with positive perceptions have the
possibility of adherence in the treatment of 21.41
times greater than those having a negative
perception. So it can be concluded that TB patient
compliance is related to behavioral role of illness in
which the role describes behavior that should be
shown by the patient to get healing (Pasek, Suryani
dan Murdani, 2013). Through knowledge, education
contributes to health behavior. Knowledge that is
influenced by the level of education is one of the
predisposing factors that play a role in influencing
one's decision to behave healthy (Departement of
Health Indonesia, 2009)
4.3 Obedience after NSMS
Based on the results of the study of TB patients' drug
adherence before Ners-Short Message Service
Intervention (N-SMSI) in the intervention group
found that obedient as much as 80.6% and in the
control group obedient as much as 47.2%. In this
study there were some non-adherent patients as
much as 19.4% in the intervention group. This is
because the patient does not visit the health center
regularly to take medicine. Patients do not visit the
clinic regularly to take drugs because patients are
busy with rutinasnya, such as patients are more
concerned with their work, the symptoms felt the
patient has been reduced so that the patient felt he
had recovered and ignored taking medicine
according to the rules. This is in line with research
conducted by Munro et al (2007) that patients
prioritize work and take medicine is a choice
between work and adherence, so patients feel
compelled to choose (Munro, Lewis, Smith,
Freitment dan Volmink, 2007). The government
through the program is very good.
Permasalahhannya sekang lies in puskesmas staff,
do or not the program launched by the government.
4.4 Effect NSMS for Obedience Patient
Man Whitney test results obtained values pvalue =
0.000. These results indicate that the pvalue <0.05
indicates that there is a difference between the
control group and NSMS intervention for TB drug
treatment adherence. A person's compliance is the
result of the person's decision-making process, and
will affect people's perceptions and beliefs about
health. In addition, beliefs and cultures also
determine the behavior of compliance. The value of
a person has a belief that health advice is considered
correct then respondents will be obedient to taking
medicine. Patients who received health counseling
from health workers were 4.19 times more likely to
be regular or obedient than those who did not
receive health education. N-SMSI is one form of
community nursing intervention, in which
community nurses send short messages via cell
phone (SMS) to Pulmonary TB patients. SMS
contains reminder messages for medicine and
nutrition, sent daily, with frequency adjusted to the
timing schedule for taking lung tuberculosis patients
and also to provide TB pulmonary information about
prevention of TB transmission, drug side effects,
cough and sneeze ethics, the importance of
medication adherence. The information is given
twice a week every Monday and Wednesday
4 CONCLUSIONS
NSMS (Ners-Short Message Service Intervention) is
a Nerser-Short Message Service Intervention
(NSMS) model of care to improve medication
adherence of Pulmonary TB patients. provide
benefits for patients will be obedient to take
medicine. The action is so important that it is not
just adherence to taking medication, but to the
behavior of patients or TB patients' habits.
Compliance of TB patients in taking medication is
very important. This is because if the patient is not
obedient in taking medicine or medication, then the
patient will repeat the treatment again. If this bears
repeated it will cause the bacteria to become
resistant to the drug. Resistant is a condition where
bacteria can not die with the drug hence intensive
treatment is required to be left higher health services
by referring to the hospital.
Increase Medicine Adherecence TB Patient with Ners-Short Message Service Intervenstion (N-SMSI)
523

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic of
Indonesia. The support is under the research grant
TALENTA USU of Year 2018.
REFERENCES
Agustina S, Wahjuni CU 2017 Jurnal Berkala
Epidemiologi. E-JURNAL UNAIR
Ariga, R. A. dan Siti Z. N. 2016 Procedding PHICO
Universitas Sumatera Utara
Badan Litbangkes Kemenkes RI 2011 Laporan
Akhir Riset Fasilitas Kesehatan tahun
BPOM RI 2006
CNA 2013
Departement of Health Indonesia 2005 Rencana
Strategi Departemen Kesehatan 2005
Departement of Health Indonesia 2009 Profil
Kesehatan Indonesia 2008
Mahpudin, AH, Mahkota, R, 2007 Kesmas Jurnal
Kesehatan Masyarakat Nasional 01 147 – 152
Ministry of Health Indonesia 2014
Ministry of Health Indonesia 2015
Ministry of Health Indonesia 2015
Munro SA, Lewin SA, Smith HJ, Freitheim M,
Volmink J 2007 Plos Med, Adherence to Anti-
TuberculosisTreatment04 1230-1245
Nurjana, MA 2015 Balai Litbang P2B2 Donggala,
Badan Litbang Kesehatan, Kesehatan Republik
Indonesia25 165-170
Pasek MS, Suryani N, Murdani P 2013 Jurnal
Magister Kedokteran Keluarga01 14-23
Rukmini, Chatarina UW 2011 Bulletin system
research Health14 320 – 331
Sholikhah, L F 2012 Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta
Viney, K., et al, 2011 Information Action 11 1-5.
Widjanarko B, Gompelman M, Dijkers M, Werf M
2009 Patient Preference and Adherence03 231 –
238
World Health Organization (WHO) 2015
Switzerland
World Health Organization (WHO) 2015
Switzerland
Wulandari N, 2012 Thesis Universitas Airlangga
Zerbini E, Greco A, Estrada S, Cisneros M,
Colombo C, Beltrame S, Boncompain C, Genero
S 2017Medicina (B Aires)77 267 – 273
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
524
