
Haemoglobin Glycosilate as a Glycemic Control at Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus Patients
Rusdiana
1 *
, Maya Savira
2
, Sry Suryani Widjaja
1
1
Departement of Biochemistry, Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansur, Universitas Sumatera
Utara, Medan, 20155
2
Departement of Physiology, Medical Faculty of Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansur, Universitas Sumatera Utara,
Medan, 20155
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, Fasting Blood Sugar, Haemoglobin Glycosylate.
Abstract: Chronic disease that characterized by blood glucose levels that exceed normal values is Diabetes Mellitus.
The patient of type 2 diabetes mellitus must controlled their bood sugar level and the most accurate way to
determine blood sugar levels over the past to three months by Hba1c measurement.This study was to
determine the levels of blood sugar and Hba1c in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Johor Primary
Health Care (PHC) in Medan of Sumatera Utara, Indonesia. This study used cross-sectional design conducted
in Johor PHC, Medan of Sumatera Utara, 40 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. All the samples of fasting
blood sugar and HbA1c were recorded for each patient who attend to the PHC . We collected the primary data
through interviews, physical examination and laboratory test. More than half of the samples of this study
have bad Hba1c levels (>8% ) cause of many patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus lack of knowledge about
the correct management of diabetes mellitus.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the public health problem and a major clinical
is Diabetes mellitus, taht requires continuing medical
care and ingoing patient management education and
support to prevent acute complication and to reduce
the risk long-term complication. All over the world
the precalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus id rapidly
increasing. In 2011, the global prevalence of diabetes
was 366 million and caused 4.6 million deaths (IDF).
This figure is expected to rise to 522 million by 2030
and will be 7th leading cause of death in 2030 (IDF
2012, WHO 2011). Indonesia is the world’s fourth
most populated country, has the seventh largest
number of diabetic patients(7.6 million), despite
relatively low prevalence (4,8% including both
diabetes type 1 and 2 in individuals aged 20-79 years)
in 2012 (IDF, 2012). Because of its high morbidity
and mortality diabetes mellitus is an important health
problem (King H et al, 1998), Indonesia is the country
with the largest numbers of people with diabetes
(Shaw JE,2010, Wild et al, 2004). In urban Indonesia
of the prevalence of diabetes mellitus is 5.7%
(Mihardja L et al, 2009), and a younger age of the
incidence of diabetes mellitus is starting to rise (Chan
JC et al, 2009).
According American Diabetis Association(ADA)
glycemic control as one of the important strategies for
the management of DM and glycosylated
haemoglobin (Hbalc) is the best measure of glycemic
level over the previous 3 months. Hbalc is udes to
monitor diabetic treatment each 3 months once
because of the erythrocyte haemoglobinglycation
since erythrocytes have about 120 days life span, and
reflects overall blood glucose levels over a period 2-
3 months and further, in the achievement of the best
possible glycemic control it has been recognized that
hbalc as an essential adjunct to regular self-blood
glucose measurement assisting (Saudek CD et al,
2009). The health of individuals and communities
depended many factors which was influenced. The
low education level is one of these factors which is
linked poor health, more stress and lower self-
confidence. This aim of study to determine the levels
of Hbalc in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in
Johor PHC in Medan of North Sumatera, Indonesia.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
Patients were recruited from Medan Johor Primary
Health Care (PHC),North Sumatera, Indonesia.This
Rusdiana, ., Savira, M. and Widjaja, S.
Haemoglobin Glycosilate as a Glycemic Control at Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0010067604070409
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches (ICOSTEERR 2018) - Research in Industry 4.0, pages
407-409
ISBN: 978-989-758-449-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
407
was conducted from April to June 2018. We take 40
samples from this PHC. In appropriate with the
inclusion criteria which are both of sex (female,male),
aged > 40 years old, cooperative and gave the
signature for will join this research and exclusion
criteria which are, have the ability to read. All
participants gave written, informed concent to
participate in the study. This research was approved
by Health Research Ethical Committee, Medical
Faculty of University Sumatera Utara /H.Adam Malik
General Hospital by number 591/TGL/KEPK FK
USU-RSUP HAM /2017. Before starting education
activities, each sample we examine weight, height,
waist size, blood pressure, and laboratory tests such
as fasting blood sugar levels (FBS) and Hba1c.
Fasting blood sugar of samples we examined by using
portable measuring instrument (Gluco DR). Blood
samples were collected (using syringe) twice before
and after intervention by education and transferred to
Pramita clinic laboratory immediately to be
conducted glycosilated haemoglobin test by HPLC
method.
According to the American Diabetes
Association (ADA), a diagnosis of diabetes can be
estabilished in the presence of any of the following
(two tests are required) : 1) fasting plasma glucose
levels of ≥ 126 mg/dL ; 2) random plasma glucose ≥
200mg/dL in a patients with classic symptoms of
hyperglycemia ; 3) 2-h plasma glucose level ≥ 200
mg/dL during a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test; 4)
Hba1c level of ≥ 6.5% (Diabetes Care.2015).
The participants completed a general
information from included question on age, marital
status,family history of the disease,duration of the
disease, clinical characteristics, awareness of diabetic
complications, taking oral diabetic or insulin
injection, smoking, following any diet, daily activity,
education level and job.
3 RESULTS
The number of the samples from the Johor PHC were
comprised of female were people (30) and men were
people (10). Mean age of the samples were
62.53±7.809 years old. Hba1c value of the samples
>8% were 67.5% (27) people and Hba1c value 6-8%
were 32.5% (13) people of the samples.The
demographic data; gender, age-group, education
level, family history and type of treatment . See the
table 1 on the bellow.
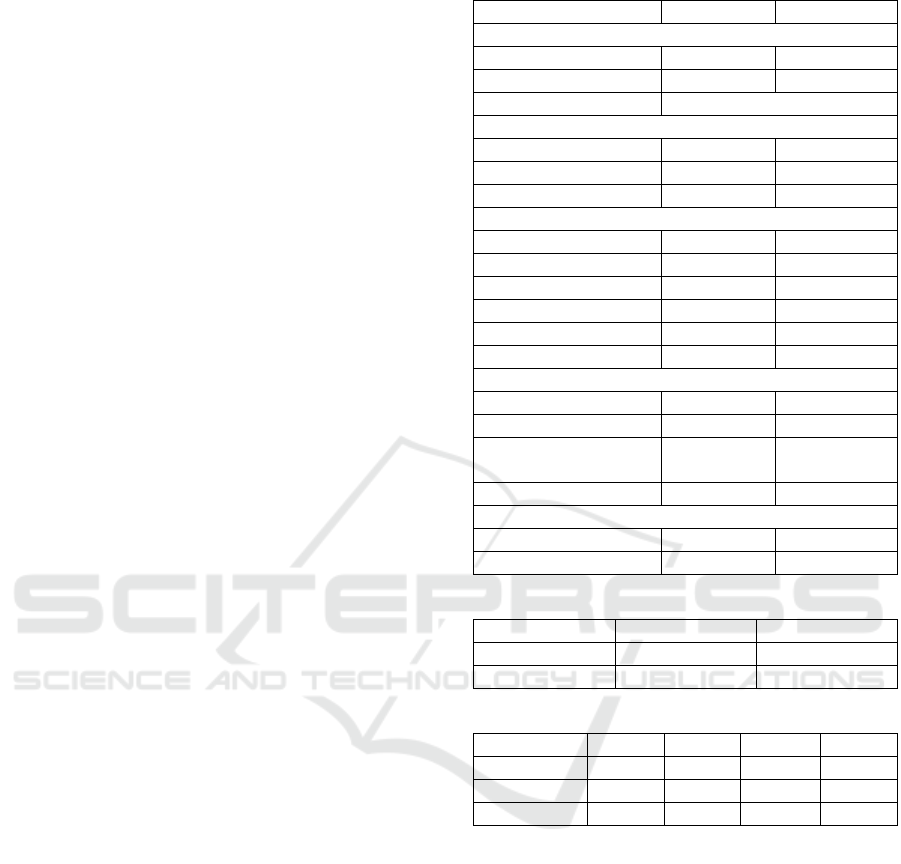
Table 1: Charactheristic of the Participants.
Characteristic N %
Gender
Male 10 25%
Female 30 75%
Mean Age 62.53±7.809
Education Level
Junior High School 10 9%
Senior High School 23 20.7%
Academy/University 10 6.3%
Physical activity
insufficient 28 70%
sufficient 12 30%
Duration of disease
<3 years 18 45%
3-6 years 3 7.5%
>6 years 3 7.5%
Familial History
Mathernal 8 20%
Fathernal 3 7.5%
Mahernal and
Fathernal
4 10%
none 25 62.5%
Medications
OAD 34 85%
OAD+insulin 6 15%
Table 2: Hbalc Value.
Hbalc(%) Frequency Percentace(%)
6.5-8 17 42.5
>8 23 57.5
Table 3: BMI FBS and Hbalc result.
Min Max Mean SD
BMI(kg/m
2
) 18.57 32.46 25.54 3.39
FBS(mg/dL) 143 500 202.20 81.68
Hbalc(%) 6.1 14 8.65 1.75
Among study (n=40)
4 DISCUSSION
The result of this study from the 40 respondents
among the type 2 diabetes mellitus patients showed
that more than half of the samples Hbac1 value > 8%,
it means more than half of the samples were
cathegoryzed as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
patients. Rusdiana et al published at Advanced
Science Letter 2017 showed that most of the type 2
DM patients in PHC in Binjai Hba1c value >8% at
type 2 diabetes mellitus. And research by Rusdiana et
al published at OAMJM showed that by education
management for three months can reduced Hba1c
value, it means for the type 2 diabetes mellitus needed
to increasing their knowledge for diabetes mellitus.
The other research by Rina Amelia about analysis of
ICOSTEERR 2018 - International Conference of Science, Technology, Engineering, Environmental and Ramification Researches
408

factors affecting the self-care behaviors of diabetes
mellitus type 2 patients in Binjai, North Sumatera –
Indonesia showed that self-care behaviors of type 2
diabetes mellitus in Binjai are significantly
influenced by motivation, self – efficacy,
communication,knowledge, and attitude.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Because of more than half of this samples Hba1c
value >8% so this samples needed education about
the management of diabetes mellitus in order the type
2 diabetes mellitus get the a good understanding
about diabetes mellitus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic of
Indonesia. The support is under the research grant
BP-PTN USU of Year 2018 Contract Number:
176/UN5.2.3.2.1/PPM 2018.
REFERENCES
Amelia R,Lelo A, Lindanto D. Analysis of factors affecting
the self-care behaviors of diabetes mellitus type 2
patients in Binjai, North Sumatera – Indonesia Asian
Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and
Environmental Science, 2018;20:2:361-367.
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al. Diabetes in Asia :
Epidemioogy, risk factor, and pathophysiology. JAMA
2009; 41: 169-174.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes
Care.2015;38 (Suppl):S8-S16.
Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010.
Geneva : World Health organization 2011.
International diabetes federation (IDF) atlas 5th edition.
Available from:
http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/the-global-burden.
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH, Global burden of
diabetes,1995-2025 :prevalence, numerical estmates,
and projections. Diabetes Care 1998; 21:1414-1431.
Mihardja L, Delima T, Siswoyo H, et al. Prevalence and
determinants of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose
tolerance in Indonesia. Acta Med Indones 2009;
41:169-174.
Rusdiana, Maya Savira, Rina Amelia. The Effect of
Diabetes Self Management Education on Hba1c Level
and Fasting Blood Sugar in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patients in Primary Health Care in Binjai City of North
Sumatera, Indonesia.Open Access Macedonian Journal
of Medical Science ,Vol 6,No.4 (2018).DOI
:http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2018.169.
Rusdiana, Maya Savira, Rina Amelia. Characteristics of
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Based on Blood
Sugar Level and Hba1c in Binjai Public Health Centres.
Advanced Science Letters, Vol.23, No.4 pp. 3599-
3601,2017. DOI:101166/asl.2017.9190.
Saudek CD, Kalyani RR, Derr RL. 2005 Assessment of
Glycemia in Diabetes Mellitus: HemoglobinA1c.J
Assoc Physicians India.53:299–304.
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the
prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract 2010; 87: 4-14.
Website of the International Diabetes Federation: IDF
Diabetes Atlas Update
2012.[http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/previousedition
], Accessed 28.11.2012
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, et al. Global prevalence of
diabetes . Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1047-1053
Haemoglobin Glycosilate as a Glycemic Control at Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
409
