
Sustainable Regional Expansion Model in Order to Increase the
Regional Potency: Case Study in Indonesia
Sri Winarsi, Wilda Prihatiningtyas and Zuhda Mila Fitriana
Universitas Airlangga, Jalan Dharmawangsa Dalam Selatan Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Local Government, Unitary States, Regional Expansion.
Abstract: As the consequences of applying decentralization system, Indonesia –as a unitary state-, gives bigger authority
for autonomous region is the government obligation to fullfill public demands over public services
improvement and as the implementation of democratic local government. On the other hand, regional
autonomy generates new demands for the government to shorten the relation between the government and its
people. From geographical aspect, the condition of local government is far from the central government
control, thus regional expansion can give contribution in acceleration over public services. In fact, regional
autonmy causes other demands, such as the autonomous region formation request which is known as regional
expansion. Refering to the Data from Ministry of Foreign Affairs, during the period of 1999 to 2009, there
are 205 new regions which consist of 7 provinces, 164 regencied, and 34 municipalities. And the government
needed to spend 300 billion for each region. The Government needs to take serious measure over regional
expansion request increments. This paper is intended to analyze and formulate sustainable regional expansion
in order to increase region’s potential.
1 INTRODUCTION
Regional expansion in the context of regional
autonomy is considerable, since regional expansion is
potentially able lead one state to maximize regional
development equity. The paradigm of regional
development needs to be well directed in order to
accelerate the development, facilitate public service
for society and finally accelerate public welfare. In
post reform regime, there was opportunity for region
to propose state to form new autonomous region in
Indonesia, this chance was given through Law
Number 23 Year 2014 regarding Local Government.
Through this regulation, it is expected that regional
expansion should be more attentive to the law process
which is fairer for the society.
This research is based on 2 main legal issues, first,
ratio legis of regional expansion arrangement under
Indonesian law and regulation. Second, legal
consequence of regional expansion in regard with
regional potential enhancement. Based on those legal
issues, it is expected that sustainable regional
expansion model can be obtained in order to increase
region potential.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This research is based upon 2 approaches, both are
statute approach, and conceptual approach. On the
one hand, Statute approach examines laws and
regulations which are related with the discussed issue.
On the other hand, Conceptual approach is based on
doctrines and point of views which develop within
legal study.
In addition, legal materials which are becoming
the ground of this research are divided into; Primary
legal materials that consist of related laws and
regulations, and secondary legal materials which
consist of literature studies to find concept, theory,
legal opinion or legal discoveries that are relevant to
prescribed legal issue. Not only legal materials, non-
legal sources added in this research are interview and
FGD’s result regarding stakeholders’ perception
related to the religion expansion law and regulation
and the implementation of it.
Winarsi, S., Prihatiningtyas, W. and Fitriana, Z.
Sustainable Regional Expansion Model in Order to Increase the Regional Potency: Case Study in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010049201790186
In Proceedings of the International Law Conference (iN-LAC 2018) - Law, Technology and the Imperative of Change in the 21st Century, pages 179-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-482-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
179

3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Regional Expansion in the Context
of Republic of Indonesia as Unitary
State
Unitary state has different diametrical basic
assumption with federal state. The formation of
unitary state was declared on Independence Day by
Indonesia’s founding father by claiming that the
entire territory as part of this country. There is no
approval from local authorities or states, because it
was assumed that all of region at its territory are not
independent region. Thus, State form regions which
afterwards were given authority by central
government to manage society needs and interest. It
can be assumed that state is the source of it’s authority
(Al Chaidar, 2000).
Pursuant to Article 1(1) The 1945 Constitution of
The Republic of Indonesia, it is mentioned clearly
that Indonesia is a unitary state in the form of
Republic. Consequently, Central Government is the
holder of supreme power over entire state affairs
without any delegation of authority to the Local
Government (Lubis, 1983). In unitary state,
theoretically speaking, there is principle that prohibits
the distribution of power related to the management
of state affairs between Central and Regional
Government, thus state affairs in the concept of
unitary state remain eenheid and the holder of
supreme power in state is The Central Government.
In unitary state, also, Central Government is still
responsible for the governmental affairs. However,
following Indonesia use the principle of decentralized
unitary state model, there are several matters which
can be managed by regional government. This
decision will create reciprocal relation which causes
legal relation between authority and supervision
function.
Moreover, Unitary state concept becomes the
limitation ground of autonomy fundamental
understanding. Based upon that limitation, a ruling
mechanism in which resembles a balance level
between unitary and autonomous region demands.
Both demands, thus, may be able causing a situation
from which “tugging” be created (Manan, 1993).
Despite the situation of tugging create a new stage, it
is common to face this stage, however. Further
observing, this stage is naturally experienced in
countries’ administration matters. In other words,
constitutional and administrative cycle of a state are
connected automatically with its people, either its
citizens or residents.
Every unitary state (eenheidsstaat) can be
arranged based on centralization principle, it can be
conducted wholly-by and from single centralized
government or by central altogether with its organ
which are distributed in regions. Centralization which
is accompanied with distributed who carry out central
government authority partially is called as de-
concentration (centralisatie men deconsentmtie).
Decentralization can be obtained if the authority to
manage state affairs are not solely conducted by
central government, but it is also conducted by lower
independent government entities (zelftanding), which
is autonomous both territorial or functional (Manan,
1994).
On the other hand, the relationship model between
Central Government and regional government is not
only limited on autonomy and federation model.
According to Ismail Suny, there are 5 levels of
relation between Central and Regional Government.
First, unitary state with limited autonomy. Through
Law Number 5 Year 1974 concerning Principle
Government in Region (hereinafter referred as Law
5/1974), Indonesia is one of the example of a state
that use limited autonomy concept. In other words,
theoretically speaking, during the process of regional
autonomy delegating stage, only specific authorities
will be distributed (Hoessein, 1993). Consequently,
itremains giving huge authority for central
government in numerous aspects of state
administrative.
Second, Unitary state with broad autonomy.
Based on economic point of view, this autonomy
should be supported by wealth and good finance
condition. Also, financial balance between Central
and Regional Government is needed. Financial
balance is not conducted solely to give Central
Government authority to manage regional wealth and
financial matter.
Third, Quasi Federal State that equipped with
province which based on central government
“Kindness”. The characteristic of this state is the
authority of central government to decide whether
regional decision is valid or not. This kind of state is
called as quasi federal.
Fourth, Federal State with federal government,
such as the USA, Australia Canada, Switzerland, are
states that
Fifth, Confederation State. At the most extreme
stage, a country can be classified as a Confederation
State model if Central Government has fully trusted
over members of confederation state or
commonwealth member state’s goodwill.
According to that complexity, there are several
criteria that must be applied to measure the
iN-LAC 2018 - International Law Conference 2018
180

decentralization efficacy in a country. These criteria
measure how far does decentralization implemented
within state (Nellis, 1986):
1. Giving contribution to the political
achievement
2. Increase administrative or
governmental effectivity
3. Increase economical and managerial
efficiency
4. Increase government sensibility
towards different needs and demands.
5. Increasing confidence among region’s
groups and organization which
represent legitimate political interest
6. Develops appropriate ways to plan and
implement regional development
program and project
Goebler postulated that from the implementation
of governmental function, decentralization or
autonomy, it is showed that (Goebler, 1993):
1. Decentralization (autonomy) units are
more flexible in coping with various
change that occurred rapidly.
2. The decentralization units can conduct
their affairs effectively and more
efficient.
3. The decentralization units are more
innovative.
4. The Decentralization units encouraging
moral enhancement, higher
commitment and create more
productive units.
However, under decentralization and autonomy
development process, there are at least two criteria
that need to be considered. First, decentralization
units are given authority to make decision regarding
their region’s matters. Second, decentralization units
are given freedom to control and divert various
potential sources in their region. From those criteria,
the first criterion is mostly followed by countries.
Meanwhile, the second criterion starts to be left
behind. It is impossible to implement the second
criterion fully in Indonesia since equity principle over
condition, potential and natural resources which are
different to each region, reaching balanced regional
growth and archipelago insight are fundamental
things that need to be satisfied in order to achieve the
purpose of autonomy which are granted to the head of
region, which is in line with Indonesian principle as
unitary state. Thus, most of financial sources which
come from region centrally collected by central
government, after that it will be returned to region
partially. Broad autonomy was used to be considered
as a threaten of our nation integration, however we
believe that autonomy can strengthen integration to
date. There is no single state that destroyed because
of the application of regional autonomy, on the one
hand. On the other hand, the downfall of state mostly
happens because the state is using centralism
governmental model (Kaunda, 1999).
Even if the valuation of decentralization showing
good side, the government need to be cautious when
they aim to implement broader decentralization or
when they want to delegate the implementation of
regional development. There is no passive result from
the assessment over decentralization; however, the
conditions that affect the implementation of
decentralization program can be certainly discovered.
The condition that affect decentralization
implementation are (Nellis, 1986, p. 21): (i) some of
central government and central bureaucracy officials
support decentralization and support organs which
are given responsibility to do decentralization; (ii) to
what extent do the dominant act, behavior and culture
supporting decision making of decentralization; (iii)
to what extent do the policies and programs are
designated and implemented appropriately in order to
increase decentralization of decision making and
management; (iv) to what extent do financial, human
and physically sources that are available for the
organization which were given responsibility to
conduct decentralization.
In the context of unitary state, the regional
expansion during regional autonomy era is urgently
needed. The regional expansion is not conducted in
order to be separated from the main state but it is
conducted to reach effectivity and efficiency of
society development in region. This is in line with
philosophical point of view of regional expansion
which is conducted in order to fulfill people
prosperity. The regional expansion will shorten
control range between state and its people especially
for some regions which has not received facilities
properly. It is also conducted in order to create equal
development among its regions. Natural resources
might be transferred to the underdeveloped region.
3.2 The Ratio Legis of Regional
Expansion Arrangement under
Indonesian Law and regulation
In the history of regional government implementation
in Indonesia, the regional expansion regulation was
started since the promulgation of Law No. 22 Year
1999 regarding Regional government (Law No.
22/1999) jo Government Regulation No 129 Year
2000 regarding the requirement and the criteria of
regional formation and expansion, abolition of region
Sustainable Regional Expansion Model in Order to Increase the Regional Potency: Case Study in Indonesia
181
and regional unification (PP No. 129/2000). Before
this law was enacted, it doesn’t mean that there is no
regional expansion in Indonesia. Referring to data
compiled by Ministry of Internal Affairs, there was
fact that there was regional expansion during old
regime in Indonesia. The regional expansion
happened mostly outside The Java Island. Regional
expansions were considered to be conducted in
Sumatera, Kalimantan and Sulawesi since those
islands have larger geographical area.
The data of regional expansion which are
happened during Indonesian old regime can be seen
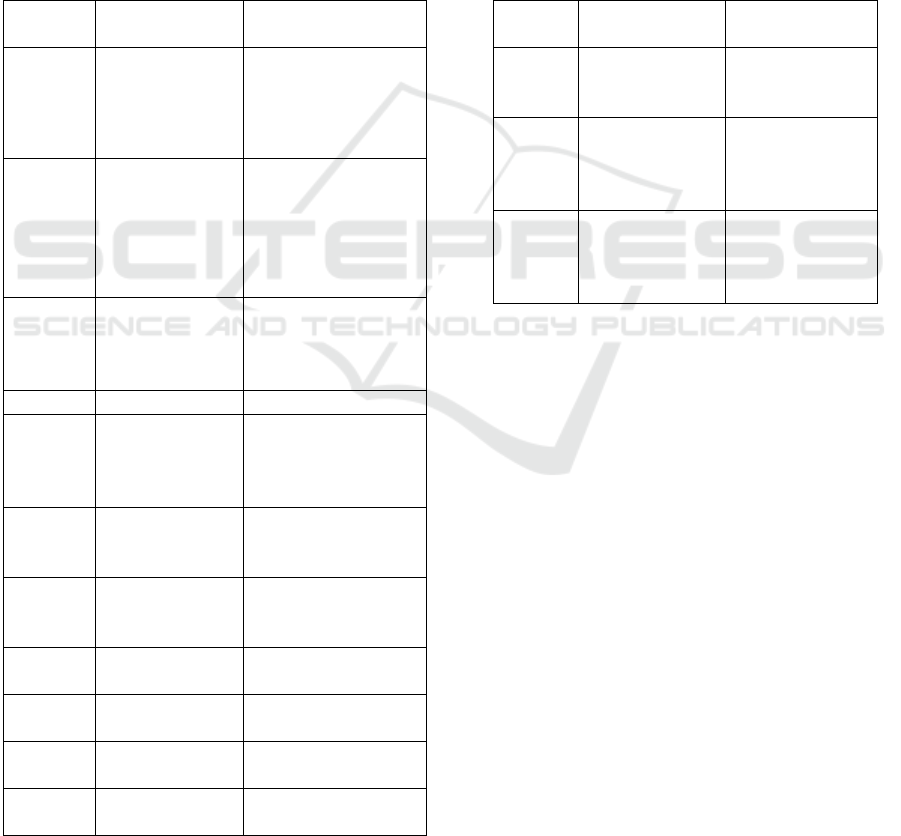
on this table (Herawati, 2011) :
Table 1: Regional Expansion Data of Indonesia: Old
Regime.
Year Main Region New Expanded
Region
1950 Sumatera
Province
N
orth Su
m
atera
Province (including
Aceh), Central
Sumatera, South
Sumatera
1956 Kalimantan
Province
West Kalimantan
Province, South
Kalimantan
province and East
Kalimantan
province.
1957 Center
Sumatera
Jambi Province,
Riau Province,
West Sumatera
province
North Sumatera Aceh Province
1959 Sunda Kecil
(Lesser Sunda
Islands)
Bali Province, West
Nusa Tenggara
Province, East Nusa
Tenggara Province
South
Kalimantan
Province
Central Kalimantan
province
1960 Sulawesi North Sulawesi
Province, South
Sulawesi province
1963 West Irian joined
Indonesia
1964 South Sumatera
Province
Lampung Province
North Sulawesi
Province
Central Sulawesi
Province
South Sulawesi
Province
South East Sulawesi
Province
In the following new order, regional expansions
were also happened even if the total expansion were
not big. The regional expansions that were happened
during this era is the formation of 3 new provinces.
The formation of region was mainly conducted in the
form of formatting municipalities as a result of rural
urbanization. This process were started by the
formation of administrative city as administrative
region, which later on formatted to be municipality as
autonomy region. The regional expansions were Top
Down and dominated by technocratic administration.
Here is the data of regional expansion during new
order era (Herawati, 2011):
Table 2: Regional Expansion Data of Indonesia: New
Regime.
Year Main Region New Expanded
Region
1967 South
Sumatera
Province
Bengkulu
Province
1969 West Irian
become 26
th
province of
Indonesia
-
1976 East Timor
become 27
th
province of
Indonesia
East Timor
conducted
separation in
1999
According to Article 5 paragraph (1) Law No.
22/1999, it mentioned that “Region is formatted
based on the economic ability, region’s potential,
socio-culture, socio-politic, total of population, how
big the area is and other consideration which make
regional autonomy can be conducted”. It is explained
further under article 6 paragraph (1) and paragraph
(2) Law No. 22/1999 which regulates that every
region can be omitted or merged with other region,
and autonomous region can be expanded to be more
than 1 region based on the development of the region
itself. This law gives highest chance for the formation
of new autonomous region. This law is supported by
Government Regulation No. 129/2000 which is
delegated legislation from Law No. 22/1999.
From normative point of view, regional expansion
according to article 16 of Government Regulation No.
129/2000 consists of these actions:
1. There is political willingness from
regional government and its people
2. Regional formation should be supported
by initial research which is conducted
regional government
iN-LAC 2018 - International Law Conference 2018
182

3. The suggestion to form municipality or
regency is conveyed to the Government
cq Minister of Internal Affairs and
Regional Autonomy through Governor,
which is completed by an attachment of
regional research result and approval
from municipality or regency house of
representative which is stated under
Provincial House of Representative’s
Decision.
4. Minister of Internal Affairs and
Regional Autonomy doing further
process and assigning unit to observe
the region, the result of this observation
will be a recommendation for Regional
Autonomy Advisory Council.
5. Regional Autonomy Advisory Council
assigning Regional Autonomy
Advisory Council’s secretarial
technique team to do further research
6. If the Regional Autonomy Advisory
Council meeting result agree upon
regional formation suggestion, Minister
of Internal Affairs and Regional
Autonomy as the head of Regional
Autonomy Advisory Council proposing
the regional formation suggestion and
proposing the Regional Formation Law
Draft to the President.
7. If the President agrees on that
suggestion, the Regional Formation
Law Draft will be conveyed to The
House of Representative in order to get
an approval.
Referring to those normative regulations, it seems
very easy for the region to propose regional
expansion, since it basically only needs the approval
from Regional House of Representative and they
don’t need the approval from the society. The ratio
legis of those regulations is encouraging the
formation of new regions, thus the regional potential
can be maximized. Furthermore by the existence of
regional expansion, regional formation, abolition of
region and merger between region, it is expected that
it can increase people’s prosperity through: a.
Improvement of public service; b. acceleration on
development of democracy; c. acceleration on
regional financial development; d. acceleration on
region’s potential management; e. improvement on
public security and order; f. improvement of
harmonious relation between central and regional
government.(Article 2 Government Regulation No.
129/2000)
Regional Expansion according to Law No.
22/1999 jo Government Regulation No. 129/2000 is
no longer applicable since there is new regulation, it
is Law No 32 Year 2004 regarding Regional
Government (Law No. 32/2004) jo Government
Regulation No 78 Year 2007 concerning the
Procedure of Formation, Abolition, and Regional
Merger (Government Regulation No. 78/2007).
Under Law No. 32 /2004, Government regulates strict
and firm regulation over regional expansion. This can
be seen from the provisions regarding regional
merger that have been expanded if it cannot meet the
minimum standard of work’s result that should be
conducted. Even if it has been regulated under formal
juridical form, there is no regional merger which is
conducted by central government. The addition of
autonomy region is the only thing that has been
implemented as the result of certain region
separation.
Government Regulation No. 78/2007 is stricter
compared to Government Regulation No. 129/2000.
Government Regulation No. 129/2000 is less strict
thus it is easier for region to purpose regional
expansion. For instance, under Government
Regulation No. 78/2007 it is regulated that the
province that would be expanded need to be
minimum 10 years old, meanwhile the municipality
or regency that want to be expanded need to fulfill 7
years of requirement. This provision is different
compared to Government Regulation No. 129/2000
which regulates that the expanded region can directly
be expanded if it is needed. The other significant
chance under this regulation is the minimum amount
of municipalities or regencies that cam be
transformed as New Province and the minimum
amount of districts that can be transformed as new
municipality or regency. Referring to Government
Regulation No. 129/2000, to form new province it is
needed at least 4 municipalities or regencies,
meanwhile under Government Regulation No.
78/2007 it is needed at least 5 municipalities or
regencies. Under Government Regulation No.
129/2000, in order to form new regencies, it is needed
at least 4 districts, meanwhile Government
Regulation No. 78/2007 require at least 5 districts. In
order to form new municipalities, it is needed at least
3 districts, meanwhile Government Regulation No.
78/2007 requires at least 4 districts. Government
Regulation No. 78/2007 has provided legal basis to
merge new region which is a result from separation or
unification of region that is considered unable to
govern its autonomy privilege. It means that if the
expanded region could not maximize its potential, it
would be evaluated by central, thus it is expected that
Sustainable Regional Expansion Model in Order to Increase the Regional Potency: Case Study in Indonesia
183
the region expansion would not cause economic,
socio and political excesses in that region.
By the promulgation of Government Regulation
No. 78/2007, the Government wants to suppress
regional expansion suggestion. Therefore, it would
not be as easy as when Government Regulation No.
129/2000 was applied. Up to 2008, however, regional
expanding remained experienced in a lessen number
compared to previous years, mentioned in data table
below (Agency, 2017) :
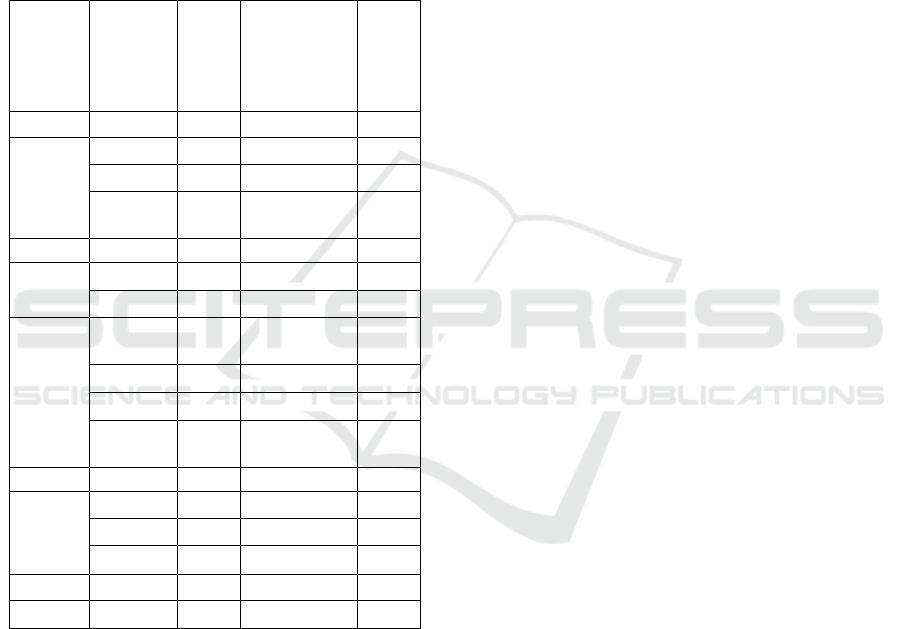
Table 3: Regional Expansion Data in Indonesia:
Reformation era to 2008.
Year Month New
Provi
nces
New
Autonomous
Cities/
Municipalitie
s
Total
1999 October - 27 27
2000 June 2 - 2
October 1 - 1
Decem
ber
2 1 3
2001 June - 12 12
2002 April - 22 22
October 1 - 1
2003 Februar
y
- 12 12
April - 17 17
May - 12 12
Decem
ber
- 23 23
2004 October 1 - 1
2007 January - 16 16
March - 1 1
August - 8 8
2008 January - 6 6
TOTAL
7 157 164
Furthermore, during the period of 2010 – 2025
Ministry of Home Affairs along with House of
Representative do moratorium by designing of new
autonomous region arrangement by limiting the total
of province and municipalities or regencies into
maximum 44 Provinces and 546 municipalities or
regencies. It means the chance to do regional
expansion during this period will be limited to 11 new
provinces and 54 new municipalities or regencies
which can be approved by Central Government.
3.3 The Legal Consequences of
Regional Expansion in Relation to
the Enhancement of Region’s
Potential
Aforementioned under article Article 2 Government
Regulation No. 129/2000, the regional expansion
intends to give prosperity for its people. Up to 2017,
the latest data collected by the National Law
Development Agency (BPHN, hereinafter), this
regional expansion is becoming more favourable
solution overcoming public matters under local
democracy and impacting national democracy
circumstances (Agency, 2017). By enhancing local
democracy, particularly for the sake of new expanded
region, it can create the development of equality,
liberty, and local responsiveness. In other words,
local’s responsiveness towards national legal reform
thus supports national legal enforcement, at least
aiming it towards. For example, local people may be
able to supervise and control policies and other legal
products from which national level regulation will be
affected, vice versa. Ideally speaking, moreover,
under Central Government’s perspective, the regional
expansion policy becomes a good solution to
encourage economics activities and accelerate
economics development around national border
region. Not only supporting economics development,
three other aspects are possibly enhanced, such as: 1)
National Identity, and 2) the Defense Mechanism of
Outer National Border Region (Agency, 2017).
To add, practically speaking, there are several
impacts (advantages and disadvantages) of regional
expansion mentioned as follows (Pratikno, 2008):
1. Socio - politic aspect.
Refering to this aspect regional expansion can
lead into egosentrism for the region which
further can cause horizontal or vertical
conflict. The regional expansion creates
several new regions which means that the
government will face inefficiency in managing
regional governments
2. Socio – economic aspect
The expanded region is expected to contribute
more for the development of state however on
certain point the expanded region is tend to
rely on central government, thus it is giving
more burden for state economic condition.
3. Socio-cultural
On certain point it can create cohesiveness
among its people, but from external point of
view it can be seen as regional egosentrism
4. Increase public service quality
5. Economic development
iN-LAC 2018 - International Law Conference 2018
184
Poverty area is given chance to get more
subsidy from the government which can
improve their percapita income (PCI)
6. Regional expansion can be seen as one of the
cause of the separation which likely happens
within the unitary state. It also can be seen as a
threat for state to form federal state.
In the regional expansion practice field, the logic
consequences that happened are there will be change
in governmental structure, regional budget, region’s
border will be decreased and region’s name will be
changed, and distribution of regional revenue
resources should be conducted (Muqoyyidin, 2013).
According to further studies, the ideal goals’
achievement of regional expansion is threatened by
several factors, such as:1) Performance of Local
Public Servants, 2) the Duration of Regional
Expanding, 3) the Loophole under Local Government
Regulations in Indonesia, and 4) Miss-conceptional
understanding of Local People towards Regional
Expansion Aims (Rebellious Action upon Main
Region inability to provide equality) (Sabarno, 2008,
p. 117)
From the research that has been conducted in
several expanded regions, it is found that the new
region which is a result of regional expansion has no
better economic condition compared to the main
region. The economic development on those new
regions are more fluctuate compared to the main
region. Even if the poverty is successfully reduced in
the main region, the expanded region is not merely
affected.
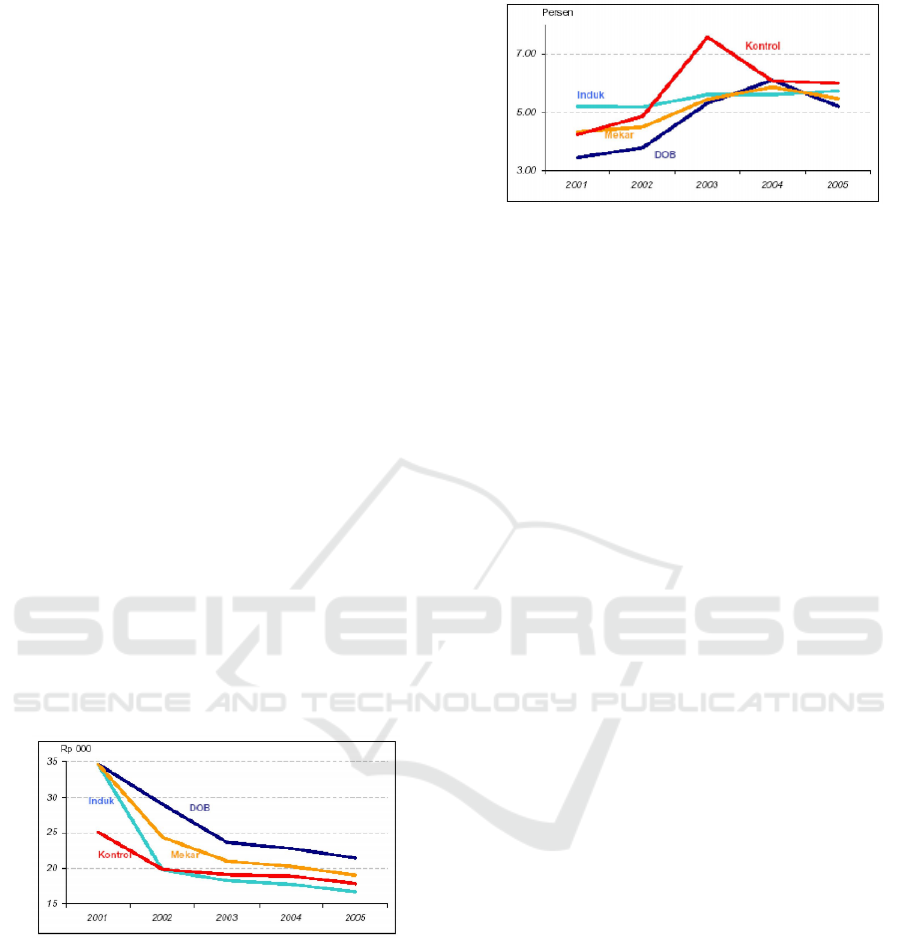
Figure 1. Poverty Level: Home Affairs Department Data
2008.
By 2008, generally speaking, main region
economic development remained stable at 5-6% per
year, whilst new expanded region seemed more
fluctuative depending on natural resources ownership
and management (Affairs, 2008).
Figure 2. Economic Development: Home Affairs
Department 2008.
Following Sabarno, the factual situation is
grounded in those threats of new expanded region
governing ability. Moreover, unstable of economic
development was also triggered by the fact many
local people who experienced economic level
disparity tent to move out from New Expanded
Region to Main Region. For instance, local people of
Bengkayang Municipality moved out towards
Singkawang City. This migration is also experienced
in North Aceh Municipality from which lowers its
Regional-Owned Source Revenues (Ratnawati, 2009)
& (Affairs, 2008).
It is expected that the regional expansion will be
leading the development, increasing economic level,
shortening the relation between the government and
its people within the particular region. In contrast,
factually speaking, it can be shown that the expanded
region tends to have lower economic level and slower
development in several aspects due to the lack of
comprehensive consideration in terms of planning.
This issue may be solved if the planning of expanding
region has been thoughtfully considered by
authorised bodies.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The spirit of regional expansions which is regulated
under Law No.22/1999 jo Government Regulation
No. 129/2000 which is replaced with Law No.
32/2004 regarding Regional Government jo
Government Regulation No. 78/2007 concerning the
Procedure of Formation, Abolition, and Regional
Merger are to bring prosperity for their people. The
regional expansion is intended to improve public
service, accelerate the development of democracy,
financial development, region’s potential
management, improve public security and order and
improve the harmonious relation between central and
regional government. However, in fact, the expanded
region remains placed on lower level of development
Sustainable Regional Expansion Model in Order to Increase the Regional Potency: Case Study in Indonesia
185

both in economic and services compared to the main
region. Thus, the regional expansion should be
planned wisely and there should be fair distribution
of financial sources between the regions in order to
create sustainable regional expansion.
REFERENCES
Affairs, D. o. H., 2008. Media Litbang, s.l.: Department of
Home Affairs.
Agency, t. N. L. D., 2017. www.bphn.go.id. [Online]
Available at:
https://www.bphn.go.id/data/documents/pkj_pemekara
n.pdf [Accessed 10 January 2019].
Al Chaidar, Z. S. H. S., 2000. Federasi atau Disintegrasi,
Telaah Awal Wawancara Unitaria Versus Federalis
dalam Perspektif Islam, Nasionalisme, dan Sosial
Demokrasi. Jakarta: Madani Press.
Al Chaidar, Z. S. H. S. F. a. D. A. W. U. V. F. d. P. I. N. d.
S. D. M. P. J. 2. h. 2.-2., n.d. s.l.:s.n.
Goebler, D. O.-T., 1993. Reinventing Government. New
York: A Plume Book.
Hoessein, B., 1993. Berbagai Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Besarnya Otonomi Daerah di Tingkat II Suatu Kajian
Desentralisasi dan Otonomi Daerah dari Segi Ilmu
Administrasi Negara. Dissertation ed. Jakarta: PPS-UI.
Kaunda, J. M., 1999. State decentralization and the
declining of local government in Malawi. International
Review of Administrative Sciences, Vol. 65(SAGE
Publications), pp. 579-595.
Lubis, M. S., 1983. Pergeseran Garis Politik dan
Perundang-undangan Mengenai Pemerintah Daerah.
Bandung: Alumni.
Manan, B., 1993. Perjalanan Historis Pasal 18 UUD 1945.
Jakarta: UNISKA.
Manan, B., 1994. Hubungan Antara Pusat dan Daerah
Menurut UUD 1945. Jakarta: Sinar Harapan.
Nellis, R. d., 1986. Assessing Decentralization Politics in
Developing Countries: The Case for Cautious
Optimism in Development. Vol. 4 ed. London: Sage
Publication.
Pratikno, 2008. Usulan Perubahan Kebiajakan Penataaan
Daerah : Pemekaran dan Penggabungan Daerah,
Jakarta: USAID.
Ratnawati, T., 2009. Pemekaran Daerah, Politik Lokal dan
Beberapa Isu Terseleksi. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Sabarno, H., 2008. Memandu Otonomi Daerah Menjaga
Kesatuan Bangsa. - ed. Jakarta: Sinar Grafika.
iN-LAC 2018 - International Law Conference 2018
186
