
Evaluation of Blood Glucose Level and Microscopic Pancreatic Islets
of Langerhans Treated with Lawsonia Inermis Linnaeus Leaves
Ethyl Acetate Extract in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rat
Dwi Rita Anggraini
1*
, Tri Widyawati
2
, Siti Syarifah
2
, Arlinda Sari Wahyuni
3
1
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutic, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara,
Medan, 20155, Indonesia
3
Department of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 20155, Indonesia
Keywords: blood glucose level, pancreatic islets of Langerhans, Lawsonia inermis Linnaeus, diabetic rat
Abstract: Lawsonia inermis Linnaeus leaf, is one of alternative medicine that used to treat diabetes mellitus (DM) in
Indonesia. We investigated the effect of ethyl acetate extract of Lawsonia inermis Linnaeus (EAE) on blood
glucose level (BGL) and the histopathological alterations of pancreatic islets of Langerhans (iL) in
streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. A number of 24 rats were divided into 6 groups, Normal control
(NC) was feed ad libitum, while STZ-induced diabetic rats (SDR) groups were treated with normal saline 10
ml/kg (P1), glibencamide 10 mg/kg (P2), EAE 250 (P3), 500 (P4) and 1000 (P5) mg/kgbw, daily orally for
14 days. Data were analyzed using one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett t test. BGL of NC-(79.75 4.95);
P2 (77.5 3.8); P3 (79.56.9); P4 (78.5 4.5); P5 (83.25 4.3) were lower than P1-treated groups (292.5
4.63) mg/dl, significantly (P<0.01). The histopathological evaluation showed that the perimeter of the islets
of Langerhans P1 were shrinked (8.59 1.8)µm, while P2(12.71 5.4); P3 (11.42 2.9); P4 (1679 11;4)
and P5 (14.373.5)µm were larger and closed to NC (19.27 3.5)µm. The present study concluded that EAE
have antihyperglycemic activy and improve the pancreatic islet of Langerhans structure.
1 INTRODUCTION
In spite of knowledge, there are great efforts that have
been made in the understanding and management of
diabetes. Today, disease related complications are
increasing day by day without any reduction in
strength (Tiwari, 2002). In spite of the presence of
known antidiabetic medicine available in the
pharmaceutical market, remedies derived from
medicinal plants are successfully used in the
treatment of this disease (Bhattaram et al., 2002;
Choubey et al., 2010)
However search for new Antidiabetic drugs
continues. The mechanism of most of the herbals used
to treat diabetes has not been defined. It has been
attributed that the antihyperglycemic effect of these
plants is due to their ability to restore the function of
pancreatic tissues by causing an increase in insulin
output or inhibit the intestinal absorption of glucose
or to the facilitation of metabolites in insulin
dependent processes. Hence treatment with herbal
drugs has an effect on protecting â-cells and
smoothing out fluctuation in glucose levels (Jia et al.,
2003; Elder, 2004)
Lawsonia inermis Linn. commonly known as
henna, is a finely ground brown or green powder
originating from dried leaves of the plant Lawsonia
inermis which is grown in dry tropical and subtropical
zones, including North Africa, India, Sri Lanka, and
the Middle East. (Borade et al., 2011).
Lawsonia inermis Linnaeus is one of the plants
commonly used in Indonesian community for the
treatment of different diseases (Widyawati et al,
2016). Previous study has been well investigated
phytochemically by various researchers such as β-
sitosterol, lawsone, esculetin, fraxetin, isoplumbagin,
scopoletin, betulin, betulinic acid, hennadiol, lupeol,
lacoumarin, laxanthone, flavone glycosides, two
pentacytic triterpenes glucoside, flavonoids,
quinoids, naphthalene derivatives, gallic acid,
coumarins, and xanthones (Chaudhary et al., 2010;
Kamal and Jawaid, 2010; Borade et al., 2011; Musa
and Gasmelseed, 2012) in Lawsonia leaves has been
reported. Earlier work establishes the use of henna as
108
Anggraini, D., Widyawati, T., Syarifah, S. and Wahyuni, A.
Evaluation of Blood Glucose Level and Microscopic Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Treated with Lawsonia Inermis Linnaeus Leaves Ethyl Acetate Extract in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic
Rat.
DOI: 10.5220/0010039101080112
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 108-112
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

an alternative vegetable retanning agent (Musa and
Gasmelseed,2012).
Several study showed that effect of Lawsonia
inermis Linn ethanolic extract 500 mg/kg of body
weight was found to be better then Glibenclamide
(10mg/kgbw). These results suggest that the ethanolic
extract possess significant antidiabetic effect
(Choubey et al., 2010). Widyawati et al., 2016
showed that EAE is the most active extract as
antihyperglycemic than with n-hexane (HE),
ethylacetate (EAE), ethanol (EE), water1(WE1) and
water2 (WE2). Hence the aim of the study is to
investigate hypoglycemic effect of ethyl acetate
extract of Lawsonia inermis Linn in streptozotocin
induced diabetic rats and evaluated microscopic
pancreas of islets Langerhans.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Chemical and Reagents
Streotozotocin, formalin buffer 10%, paraffin wax,
TBA reagent, heparin sodium, sodium chloride, cell
lysis buffer, aquabidest, 70% and 80% aqueous
alcohol and 96% absolute alcohol, xylol, glyserin,
Mayer”s haematoxylin, eosin, canada balsem. All
other chemical were of analytic grade.
2.2 Animals
Healthy male Wistar rats (150-200 g) were obtained
from animal house of Universitas Sumatera Utara.
The study was conducted after approved by Animal
Research Ethics Committees (AREEC), Faculty of
Mathematics and Natural Sciences (FMIPA),
Universitas Sumatera Utara (No. EC: 115/KEPH-
FMIPA/2017).
2.3 Plant Material and Preparation of
EAE
Lawsonia inermis Linn leaves were collected from
Titi Kuning, Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia and
was authenticated by Department of Botany,
Universitas Sumatra Utrara. The fresh leaves were
dried under shade and ground into powder. The
powdered leaf then was extracted serially by
maceration in n-hexane and ethyl acetate (EAE).
2.4 Induction of Diabetes
Diabetic rats were obtain by induction STZ (55
mg/kg) intraperitoneally. Diabetic rats with fasting
blood glucose level more than 200 mg/dl were
included to the study. BGL was confirmed using
glucometer (Accu check), after 72 hours of STZ
injection.
2.5 Experimental Design
The animals were divided randomly into six groups
of four rats each and treated as follows:
Group I (NC): Normal control rats (standard
pellets and water ad libitum) for 14 days.
Group II (P1): Diabetic control rats were
administered with STZ, were treated with
normal saline 10 ml/kg
Group III (P2): Diabetic rats were treated with
glibencamide 10 mg/kg
Group IV (P3): Diabetic rats were treated with
EAE 250 mg/kgbw daily orally for 14 days.
Group V (P4): Diabetic rats were treated with
EAE 500 mg/kgbw daily orally for 14 days.
Group VI (P5): Diabetic rats were treated with
EAE 1000 mg/kgbw daily orally for 14 days.
2.6 Preparation Pancreatic for
Histopathological Analysis
At the end of the stipulated 14 days feeds were
withdrawn, the rats were subjected to a 12 hours fast
but had access to water. Sacrificed using chloroform
vapour. Rats were positioned on the surgical board
using pins or pin needles. The surgery started in rat
stomach by using surgical scissors. The pancreas
organ were carefully dissected out, trimmed of all fat
and connective tissue blotted dry to remove any
blood.
Within a 30 minute interval after excision, the
pancreas was immersed in buffered 10%
formaldehyde for 24 hours. The samples were fixed
in buffered 10% formaldehyde for 24 hours, followed
by dehydration
in: 1) 70% alcohol for 60 min, 2) 96% alcohol for 45
min, 3) absolute alcohol for 2 h. The clearing phase
of the samples was made by repeated xylene
immersions, followed by paraffin wax infiltrations.
The samples were automatically processed with
tissue processor Thermo Scientific STP 120-3 and
paraffin embedding was done with modular tissue
embedding center Thermo Scientific Microm EC
350-1. Next,the resulting blocks were cut at 5 μm
using the Leica RM 125RTS microtome and then
carefully placed on the microscope slides. In order to
distinguish between tissue types the sections were
stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining
techniques, after which they were passed through
ascending grade of alcohol, cleared in xylene and
mount in DPX mountant, allowed to dry at room
Evaluation of Blood Glucose Level and Microscopic Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Treated with Lawsonia Inermis Linnaeus Leaves Ethyl
Acetate Extract in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rat
109

temperature and observed histopathologically under
digital light microscope
2.7 Photomicrography
Records of the Histopathological results were
obtained by photomicrography using digital
photomicrographic microscope was made with an
Olympus BX 41 microscope coupled to an Olympus
DP25 video camera at the Anatomic Pathology
Laboratory, Department of Anatomic Pathology,
Universitas Sumatera Utara.
2.8 Image Analysis
Morphometric measurements of the digitalized
images of immunostained sections were carried out
using the Image J IJ 1.46r plus image analyzer
computer system (Wayne Rasband, Maryland, USA).
The average area of the islets was determined by
measuring the area of 3 islets in each section of one
rat, and in total for 12 islets from each group (Ferreira
and Rasband, 2012)
2.9 Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed and presented as means ± SD.
Differences between continuous data were analyzed
using one way Annova followed by Dunnett t test. p <
0.01 was considered significant.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Blood Gucose Level (BGL)
BGL concentration increased following STZ
injection in all groups compared with the diabetic
group during the duration of the experiment. The rats
in group treatment which received glibencamide
10
mg/kg (P2), EAE 250 (P3), 500 (P4) and 1000 (P5)
mg/kgbw
showed a significant decrease (P < 0.01) as
compared with the rats of the untreated diabetic group
(P1) (Table 1).
Table 1: Effect of EAE on blood glucose level in STZ-
induced diabetic rats
Grou
p
Blood Glucose Level (mean SEM)
NC
79.75 4.95***
P1
292.5 4.63
P2
77.5 3.8***
P3
79.5 6.9***
P4
78.5 4.5***
P5
83.25 4.3***
Data was expressed as mean SEM. ***p<0.01
The decrease of BGL in the treatment group with
EAE caused by bioactive compounds of Lawsonia
inermis Linn leaf can prevent the occurrence of
oxidation in pancreatic β cells so the damage can be
reduced. The bioactive compounds contained in
previous study has been well investigated
phytochemically by various researchers such as
polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids and tannins. The
role of polyphenols is thought to be capable of
protecting pancreatic β cells from the effects of free
radical toxicity produced (Chaudhary et al., 2010;
Kamal and Jawaid, 2010; Borade et al., 2011.
In line with previous studies showed the that the
feeding of 0,8mg/kg/bw of Lawsonia inermis Linn
extract ethanol decreased the glucose concentration to
normal condition after the 14th day (Syamsudin et al.,
2008). The study of Choubey et al., showed the effect
of ethanolic extract of Hena 500 mg/kgbw was found
to be better then Glibenclamide (10 mg/kgbw).
(Choubey et al., 2010)
This result so in agreement with Ojewunmi et al.,
showed that
ethanol extract of Lawsonia inermis
leaves was significantly reduced fasting blood
glucose (P<0.001) compared to the untreated diabetic
control. (Ojewunmi et al., 2014). Antika et al.,
showed the group treated ethanol extract of Lawsonia
inermis a dose of 400mg/kgbw had the lowest
decrease blood glucose levels. (Antika et al., 2017)
3.2 Evaluation of the Islets of
Langerhans (iL)
Morphometric measurements showed changes in the
mean values of iL in figure 1. The average area of iL
P1 were shrinked (8.59 1.8)µm
2
, while P2 (12.71
5.4); P3 (11.42 2.9); P4 (1679 11;4) and P5
(14.373.5)µm
2
were larger and closed to NC (19.27
3.5) µm
2
.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
110
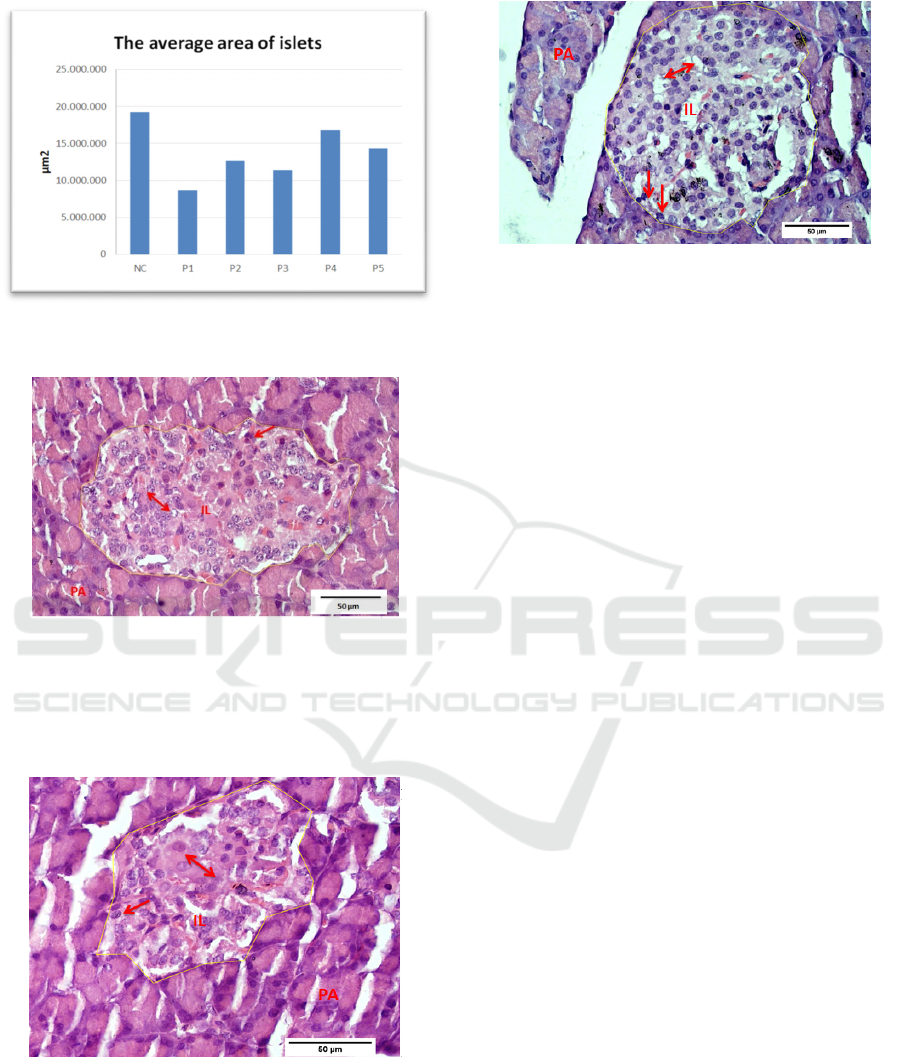
Figure 1: The average area of islets of Langerhans (iL)
Figure 2: Photomicrographs of sections of the pancreas
from control group showing pancreatic acinar (PA) and
islets of Langerhans (IL) with granulated cytoplasm of islet
cells with small, dark nuclei on the periphery (alpha-cells)
(arrow), or with light and large nuclei (beta-cells) (duble
arrow); H&E staining, scale bar = 50 μm
Figure 3: Photomicrographs of sections of the pancreas
from diabetic group showing pancreatic shrinked with
degenarative change in IL espescially in center of islet
(double arrow). Irregular outlining of the islet. H&E
staining, scale bar = 50 μm
Figure 4: Photomicrographs of sections of the pancreas
from EAE group showed the nearly regular outline of islet
with apparently normal appearance of most cell. H&E
staining, scale bar = 50 μm
The examination of H&E stained sections from
the control group showed the pancreas to have a
normal histological structure. The islets of
Langerhans appeared as noncapsulated pale stained
rounded or oval areas inside the pancreatic acinar
lobules, which were formed of groups of cells
arranged in irregular, branching, and anastomosing
cords separated by blood capillaries (Figure 2). In
diabetic group (P1), STZ caused degenerative
changes in the pancreatic islets, mainly at the center
of the islets. An apparent reduction in the size and
number of islets was noticed (Figure 3). Sections
from the iL of group P4 (given 500 mg/kg bw EAE)
showed islets with nearly regular outlines and almost
normal cell morphology (Figure 4).
Streptozotocin (STZ) is an antibiotic produced by
Streptomyces achromogenes. It has been widely used
for inducing experimental diabetes mellitus in a
variety of animals, it stimulates the naturally
occurring metabolic disorder DM by causing
degeneration of pancreatic β cells. (Coskun, 2005).
The selective β cell toxicity of STZ is related to the
glucose moiety in its chemical structure, which
enables STZ to enter the cell via the low affinity
glucose transporter Glut2 in the plasma membrane
which induces an increased release of reactive oxygen
species, subsequently causing DNA damage
(Szkudelski, 2001).
This study indicated that treated of EAE L.
inermis extract caused improved destruction of iL
with increases size and number of islets caused STZ-
induced diabetic rats.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Lawsonia inermis Linn EAE have anti-
hyperglycemia effect and protective microscopic
Evaluation of Blood Glucose Level and Microscopic Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Treated with Lawsonia Inermis Linnaeus Leaves Ethyl
Acetate Extract in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rat
111

changes of islets of Langerhans in STZ-induced
diabetic rats.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of
interest.
REFERENCES
Al-Damegh, M.A., 2014. Evaluation of the antioxidant
activity effect of Henna (Lawsonia inermis linn.) leaves
and or vitamin C in rats. Life Sci J, 11(3):234-241
http://www.lifesciencesite.com
Antika, M.A., Ilyas, S., Sari, M.I., 2017. Effect of Lawsonia
inermis Linn. Ethanol Extracton the Superoxyde
Dismutase Activity in Hyperglicemic Rattus
novergicus. Indonesian Journal of Medicine, 2(2): 79-
85
Bhattaram, V.A, Ceraefe, M., Kohlest, C., Vest, M., and
Deundorf, H., 2002. Pharmacokinetics and
bioavailabitlity of herbal medicinal products.
Phytomed, 9: 1-36.
Choubey, A., Ojha, M., Mishra, A., Mishra, S., and Patil,
U.K., 2010. Hypoglycemic And Antihyperglycemic
Effect Of Ethanolic Extract Of Whole Plant Of
Lawsonia Inermis (Henna) In Streptozotocin Induced
Diabetic Rats IJPSR, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Suppl.): 74-77
Coskun, O., Kanter, M., Korkmaz, A., Oter, S., 2005.
Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and
protects streptozotocin induced oxidative stress and β-
cell damage in rat pancreas. Pharmacol Res,51: 117-
123.
Elder, C., 2004. Ayurveda for diabetes mellitus: a review of
the biomedical literature. Altern Ther Health Med, 10:
44-50.
Ferreira, T., and Rasband, W., 2012. Image J User Guide
ImageJ/Fiji 1.46r. Revised Edition.
http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/docs/guide.
Jia, W., Gao W.Y., and Xiao, P.G., 2003. Antidaibetic
drugs of plant origin used in China: Composition,
pharmacology and hypoglycemic mechanisms.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 28: 108-113.
Ojewunmi, O.O., Oshodi, T., Ogundele, O.I., Micah, C.,
Adenekan, S., 2014. In vitro Antioxidant,
Antihyperglycae-mic and Antihyperlipidaemic Acti-
vities of Ethanol Extract of Lawsonia inermis Leaves.
British Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 4(3): 301-
314
Szkudelski, T., 2001. The mechanism of alloxan and
streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas.
Physiol Res.50:537–546.
Syamsudin, I., and Winarno, H., 2008. The effects of Inai
(Lawsonia inermis) leave extract on blood sugar level:
An Experimental Study. Res. J. Pharmacol. 2(2):20-23.
Tiwari, A.K,. and Rao, J.M., 2002. Diabetes mellitus and
multiple therapeutic approaches of phytochemicals:
Present status and future prospects. Curr Sci, 83: 30-38
Widyawati, T., Pane, Y.S., Hasibuan, S.S., and Satria, D,
2016. Effect of Lawsonia inermis innaeus leaf extracts
on blood glucose level in normal and streptozotocin-
induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes Metab, 7:10 (Suppl)
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
112
