
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using
Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case
Study on Baitul Mal
Anwar
Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Malikussaleh, Lhokseumawe, Indonesia
Keywords: Importance Performance Analysis (IPA), Mustahiq Satisfaction, Service Quality, Kano Model.
Abstract: Baitul Mal is a social institution, which is engaged in charity of zakat fund raising for the sake of socially
patterned and sustainable. In its service Baitul Mal must be prosecuted to prioritize satisfaction of mustahiq,
so that progress in the quality of service and able to improve the mustahiq economy and also giving a positive
impact on the survival of Baitul Mal.For the purpose ofresearcher, this paper on the service quality will be
observed by using the method of Importance PerformanceAnalysis (IPA) and Kano model. This method is
used in order to know the attributes that should be upgraded in accordance with the wishes of mustahiq.The
result indicates that, these methods allow us to know the priority attributes that must be improved its
performance by the Baitul Mal it is the Amil of Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe act based on islamic morality,
Amil Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe solve themustahiqproblem related to zakat program on time, Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe always serve mustahiq effectively, Amil Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe has knowledge
about zakat, the Zakat given by Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe has fulfilled the necessity of mustahiq, Zakat
given by Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe can improve the prosperity of mustahiq and Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe do not distinguish between mustahiq one and others.
1 INTRODUCTION
Baitul Mal is a social institution in charity zakat fund
raising. The service in the Baitul Mal is a very
important thing tobe underscored. The creation of
service quality will certainly create satisfaction with
mustahiq. In fulfilling the mustahiq satisfaction
required the quality of service as well as possible and
high commitment from the amil, because mustahiq is
the main target in the distribution of zakat and able to
prosper the life of the mustahiq to be better.
Therefore, it is necessary to conduct research on
Baitul Mal regarding the quality of services provided.
It is because the quality of service will have so many
positive impacts for the survival of Baitul Mal.
2 RESEARCH PURPOSE
The purpose of this research is as follows:
To know what is the main priority attributes in
service quality of Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe. To
find out what is categories of Kano attribute as the
main priority in service quality of Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe. To know the integration of
Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) method and
Kano model in Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe.
3 RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION
The contribution in this research which can be obtain
as follow:
1. It able to assist in improving the quality of
services that have been applied previously.
2. It is providing insight or information about
the condition of satisfaction mustahiq on
service quality.
4 LITERATURE REVIEW
4.1 Definition of Zakat
In terms of language, zakat has several meanings,
namely al-barakatu (blessing), al-nama (growth and
48
Anwar, .
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case Study on Baitul Mal.
DOI: 10.5220/0010037800480056
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 48-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

development), al-tharatu (purity) and al-salahu
(goodness) .
On the behalf of jurisprudence, zakat is a number
of property that is obligated by Allah to be handed
over to the rightful. Zakat is part of the property with
certain conditions required by Allah SWT, to be
shared to the rightful to receive it, with certain
conditions.
Zakat is māliyah ijtimā'iyyah service that has an
important, strategic and decisive position, from the
point of doctrine and the development of the welfare
of the people. Zakat is included in the pillars of Islam,
so it is considered ma'lum minad-din bi al-darurah
(known automatically) and is an absolute part of one's
religion. Even in the Qur'an there are also verses that
equate the level of prayer and the obligation of zakat.
There is al-Qura'an's verse of zakat in different
terms. It has been mentioned by ma'rifah (zakat
treasure) as much as 30 times and it is 8 times of
which are in the surah makkiyyah and 22 times in
madaniyyah. Then 28 verses related to the obligation
to perform the prayer. This makes the position of
zakat high enough and important in the Islamic
Shari'ah. Zakat can also cultivate mustahiq and
muzakki relationships, enhancing ukhuwah
islamiyyah and reducing poverty.
The Qur'an also states that Zakat is the main indicator
of one's obedience to the teachings of Islam, which
will gain the happiness of life, gain the grace and help
of Allah SWT. A person who fulfills the obligatory
obligation is one who wishes to cleanse oneself and
his soul from various bad qualities, such as
selfishness, greed and at the same time desire to
always cleanse, purify and develop his possessions.
The people who are entitled to receive zakat
consist of eight groups, namely:
1. Fakir, ie people who do not have anything or
can not meet half of the needs.
2. Poor, that people can meet half the needs.
3. Amil, the person appointed to take care of
zakat.
4. Muallaf, the new convert to Islam while his
faith is strong.
5. Slave, the servant who has been promised
his master that he may redeem himself with
money or other property.
6. Gharimin, the people who have debts, the
people who bear the burden of debt to
improve human relations or to meet their
personal needs both rich and poor.
7. Fisabilillah, it is jihad and everything needed
with jihad activities, such as recruitment of
war troops, the establishment of factories
and the arms industry and so on.
8. Ibn Sabil, it is all those who run out of life
stock on the way and can not bring his needs
from his village, although he is a treasure in
his village.
4.2 Definition of Service Quality
The service quality is how far the difference between
the reality and expectations of the mustahiq for the
service they receive. The quality of service can be
identified by comparing the mustahiq perceptions of
the services they actually receive.
4.3 Importance Performance Analysis
(IPA)
The Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) method
was first introduced by Martilla and James (1977)
with the aim of measuring the relationship between
the perception of mustahiq and the priority of
product/service quality improvement, also known as
quadrant analysis. Importance Performance Analysis
(IPA) has been generally accepted and used in various
fields of study because of its ease of application and
display of analytical results that facilitate
performance improvement proposals.
Y
X
Main Priority Maintain Achievement
I II
Y
X
Low Priority Excessive
III IV
Figure 1. Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) diagram
Figure1 is IPA matrix which has four quadrants to
analyze the performance of interests. There are th
explanation for each quadrant [9].
1. Quadrant I (Main Priority)
The first quadrant symbolized as the region
that contains the factors that are considered
important by the customer but the level of
satisfaction obtained is still low.
2. Quadrant II (Maintain Achievement)
In the second quadrant this is the area that
contains the factors that are considered
important by the customer and the factors
that are felt relatively high.
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case Study on Baitul
Mal
49

3. Quadrant III (Low Priority)
In this third quadrant is the area that contains
the factors that are considered less important
by the customer and in fact the performance
is not too special. It is because the benefits
are very small customers.
4. Quadrant IV (Excessive)
In this quadrant the area contains the factors
that are considered less important by the
customers and felt too excessive. Then, itis
belong to this quadrant can be reduced in
order to the company can save cost.
The model of Importance Performance
Analysis (IPA) can be seen as follow:
a. Determining the level of conformity
100%x
i
H
i
K
i
Tk
(1)
b. Calculates the average for each attribute
n
i
X
i
X
(2)
n
i
Y
i
Y
(3)
c. Calculates the average of all attributes of
interest
Y
and performance
X
levels that
limit the Cartesian diagram.
k
i
X
X
(4)
k
i
Y
Y
(5)
d. Mapping into Cartesian diagram.
4.4 Kano Model
Kano model developed by Noriaki Kano (1984)
which aims to categorize the attributes of products
and services based on how well the product is able to
satisfy the needs mustahiq.
Service attributes can be divided into several, as
follow[9]:
1. Must beorbasic needs (M)
Mustahiq considers that the attributes
present in this category are a necessity in the
product. Mustahiq will not be satisfied if the
attributes that exist in this category are not
met.
2. One dimensionalorperformance needs (O)
Mustahiq satisfaction will increase if the
attributes that exist in this category are
given, but mustahiq also will not be satisfied
if the attributes that exist in this category
does not exist.
3. Attractive(A)
Mustahiq will feel satisfied if the attributes
that exist in this category are given, but
mustahiq will not be disappointed if the
attributes in this category are not given.
4. Indifferent (I)
Mustahiq does not care about the attributes
offered so that the presence or absence of
these attributes will not affect the increase or
decrease in the level of satisfaction
mustahiq.
5. Questionable (Q)
Sometimes mustahiq is satisfied or absent
with the presence of attributes in this
category, so it is not clear whether the
attributes in this category are expected or not
expected by mustahiq or in other words a
denial in the mustahiq answer to the given
question.
6. Reverse (R)
Mustahiq not satisfied if there are attributes
in this category, but mustahiq will be
satisfied if the attribute in this category does
not exist.
1. Specify the Kano category by using Blauth's
formula [5]:
- If the values of (O + A + M)> the sum
of values (I + R + Q), then the
determination of the Kano category is
obtained from the largest value of (O,
A, M).
- If the values of (O + A + M) <number
of values (I + R + Q), then the
determination of the Kano category is
obtained from the greatest value of (I,
R, Q).
- If the sum of values (O + A + M) = the
sum of values (I + R + Q), the Kano
category is obtained from the greatest
value among all Canoe categories (O,
A, M, I, R, Q).
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
50
2. Calculating coefficient Satisfaction
Mustahiq (CSC) so that the level of
satisfaction mustahiq can be known by the
formula If Better Than (IBT) and If Worse
Than (IWT):
IMOA
OA
IBT
(6)
IMOA
OM
IWT
(7)
5 METHOD
The method used in this research is taken with case
study method through interview to mustahiq which
become respondent by using questioner. Sampling is
done by non-random sampling technique that is
procedure of selecting sample based on consideration
certain characteristic which suitable and needed to
answer the research questionas. The characteristics of
sample taken in this research isfakir that is as much
as 87 respondents. The sampling selection using
Slovin formula where 90% confidence level and error
term around 10%.
6 RESEARCH RESULT
The study was conducted at Baitul Mal in Kota
Lhokseumawe. From the results of the research, the
distribution of questionnaires with the number of
respondents based on slovin method formula where
the 90% confidence level and error rate of 10% test
Validity and Reliability performed, known all the
attributes declared valid and reliable so that data can
be used as research instrument. For the average level
of performance and importance of each attribute can
be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Calculation Result of Suitability Level
Attrib
ute
Perform
ance
Score
(K
i
)
Inter
est
Score
(H
i
)
Level of
Perform
ance
Level
of
Inter
est
TAN1 345 349 3,97 4,01
TAN2 362 345 4,16 3,97
TAN3 349 360 4,01 4,14
TAN4 334 362 3,84 4,16
TAN5 350 359 4,02 4,13
TAN6 355 372 4,08 4,28
REL7 312 352 3,59 4,05
REL8 354 337 4,07 3,87
REL9 353 332 4,06 3,82
REL10 351 352 4,03 4,05
REL11 360 346 4,14 3,98
REL12 307 343 3,53 3,94
REL13 290 344 3,33 3,95
ASS14 282 345 3,24 3,97
ASS15 329 356 3,78 4,09
ASS16 322 352 3,70 4,05
ASS17 355 355 4,08 4,08
ASS18 289 348 3,32 4,00
ASS19 291 353 3,34 4,06
EMP2
0 313 347 3,60 3,99
EMP2
1 350 349 4,02 4,01
EMP2
2 335 334 3,85 3,84
EMP2
3 307 332 3,53 3,82
EMP2
4 304 323 3,49 3,71
Average 3,8 4,0
6.1 Importance Performance Analysis
(IPA) Method
For the Cartesian diagram of Importance
Performance Analysis (IPA) can be seen in Figure 2.
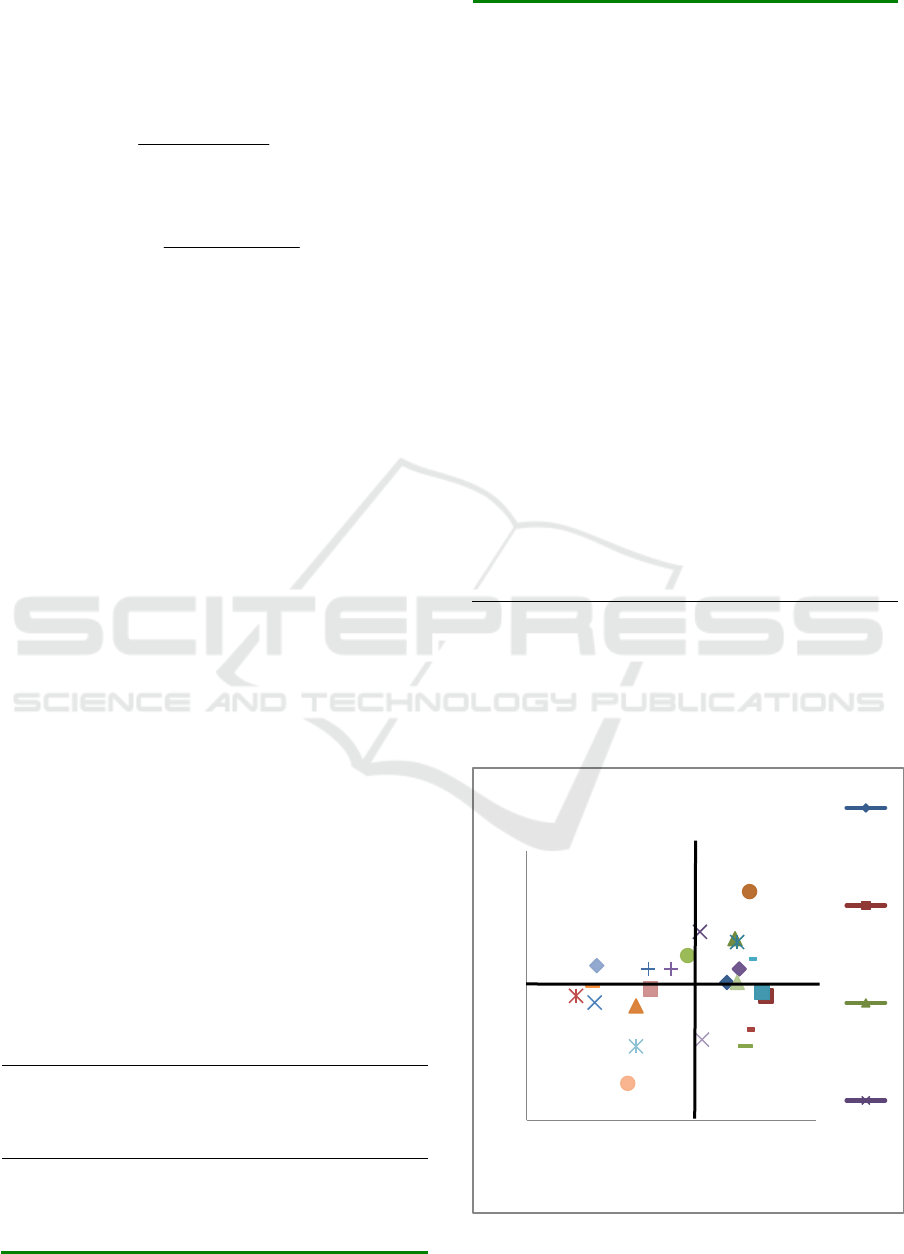
Figure 2: Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) Diagram
3,6
3,7
3,8
3,9
4
4,1
4,2
4,3
4,4
3 3,2 3,4 3,6 3,8 4 4,2 4,4
Importance
Performance
Importance Performance
Analysis (IPA)
T
A
N
1
T
A
N
2
T
A
N
3
T
A
N
4
Main
Priority
Maintain
Achieve
ment
Low
Priority
Exc
essi
ve
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case Study on Baitul
Mal
51

Attributes that are included in the quadrant of the
main priority are attributes that are considered
important but their performance is still considered
less that can be seen in Table 2.
Table 2: Service attributes which included inmain priority
Dimension
Attribute
Code
Questions
Reliability
REL7
Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe solve
the mustahiq problem
related to zakat
p
ro
g
ram on time
ASS15
Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe can
explain the
information to the
mustahiq clearl
y
Assurance
ASS16
Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
knowled
g
e of zaka
t
ASS18
Zakat given Baitul
Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
fulfilled the necessity
of mustahi
q
ASS19
Zakat given Baitul
Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe can
improve the welfare
of mustahi
q
The attributes of Baitul Mal service which are
included in the category of preserving the
performance and must be maintained in accordance
with the wishes mustahiqthat can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Service attributes which included inmaintain
achievement
Dimension
Attribute
Code
Questions
Tangible
TAN1
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
adequate buildin
g
TAN3
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
a clean buildin
g
TAN4
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
shows Islamic
morals
TAN5
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
a neat buildin
g
TAN6
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
a service room in
accordance with its
function
Responsivness RES10
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
always serve
mustahiq quickl
y
Assurance ASS17
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has
enough amil, so
there is always a
substitute if anyone
is unable to atten
d
Emphaty EMP21
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
does not
distinguish
between mustahiq
with one anothe
r
.
The attributes of Baitul Mal service included in
low priority category with low importance level and
in fact the performance is not very special with low
satisfaction level that is seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Service attributes which included in low priority
Dimension
Attribute
Code
Questions
Responsivness
RES12
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe is
always willing to
help the mustahiq
who are in trouble
RES13
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
always listen to
complaints
mustahi
q
Assurance ASS14
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe can
explain the
information to the
mustahiq in detail
Emphaty EMP20
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
52

Lhokseumawe is
always willing to
provide latest
information to
mustahi
q
EMP23
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
always
understands what
the mustahiq
complained abou
t
EMP24
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
always
understands what
the mustahiq wants
The attributes of Baitul Mal service included in
the category of excessive with low importance level
and felt mustahiq too excessive that can be seen in
Table 5.
Table 5: Service attributes which included in Excessive
Dimension
Attribute
Code
Questions
Tangible TAN2
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has a
comfortable buildin
g
Reliability
REL8
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe
is always in the office
during working
hours
REL9
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has an
easy registration
procedure to become
mustahi
q
REL11
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe
can answer the
questions posed by
mustahi
q
Emphaty EMP22
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe
is always willing to
help the mustahiq
who are in trouble
6.2 Kano Model
To calculate the value of the mustahiq satisfaction
coefficient with If Better Than (IBT) and If Worse
Than (IWT), as follows:
Table 6: The mustahiq satisfaction coefficient using Kano
Attribute A M O R Q I IBT IWT
TAN1
0 10 77 0 0 0 0,89 -1,00
TAN2
0 11 76 0 0 0 0,87 -1,00
TAN3
0 13 74 0 0 0 0,85 -1,00
TAN4
2 57 27 0 0 1 0,33 -0,97
TAN5
0 13 74 0 0 0 0,85 -1,00
TAN6
0 19 68 0 0 0 0,78 -1,00
REL7
1 63 23 0 0 0 0,28 -0,99
REL8
0 16 71 0 0 0 0,82 -1,00
REL9
1 21 64 0 0 1 0,75 -0,98
REL10
5 45 37 0 0 0 0,48 -0,94
REL11
50 21 10 0 0 6 0,69 -0,36
REL12
33 17 24 0 0 13 0,66 -0,47
REL13
35 13 24 0 0 15 0,68 -0,43
ASS14
24 25 21 0 0 17 0,52 -0,53
ASS15
18 31 31 0 0 7 0,56 -0,71
ASS16
0 58 29 0 0 0 0,33 -1,00
ASS17
3 21 61 0 0 2 0,74 -0,94
ASS18 3 68 16 0 0 0 0,22 -0,97
ASS19 3 69 15 0 0 0 0,21 -0,97
EMP20 10 20 41 0 0 16 0,59 -0,70
EMP21 8 59 18 0 0 2 0,30 -0,89
EMP22 22 18 26 0 0 21 0,55 -0,51
EMP23 30 32 20 0 0 5 0,57 -0,60
EMP24 16 40 23 0 0 8 0,45 -0,72
Total 13,95 19,66
Average 0,6 -0,8
Based on the results of the calculation of the
mustahiq satisfaction coefficient, the results obtained
If Better Than (IBT) and If Worse Than (IWT), for
each attribute. Then the graph of Kano's mustahiq
satisfaction coefficient can be seen in Figure 3.
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case Study on Baitul
Mal
53
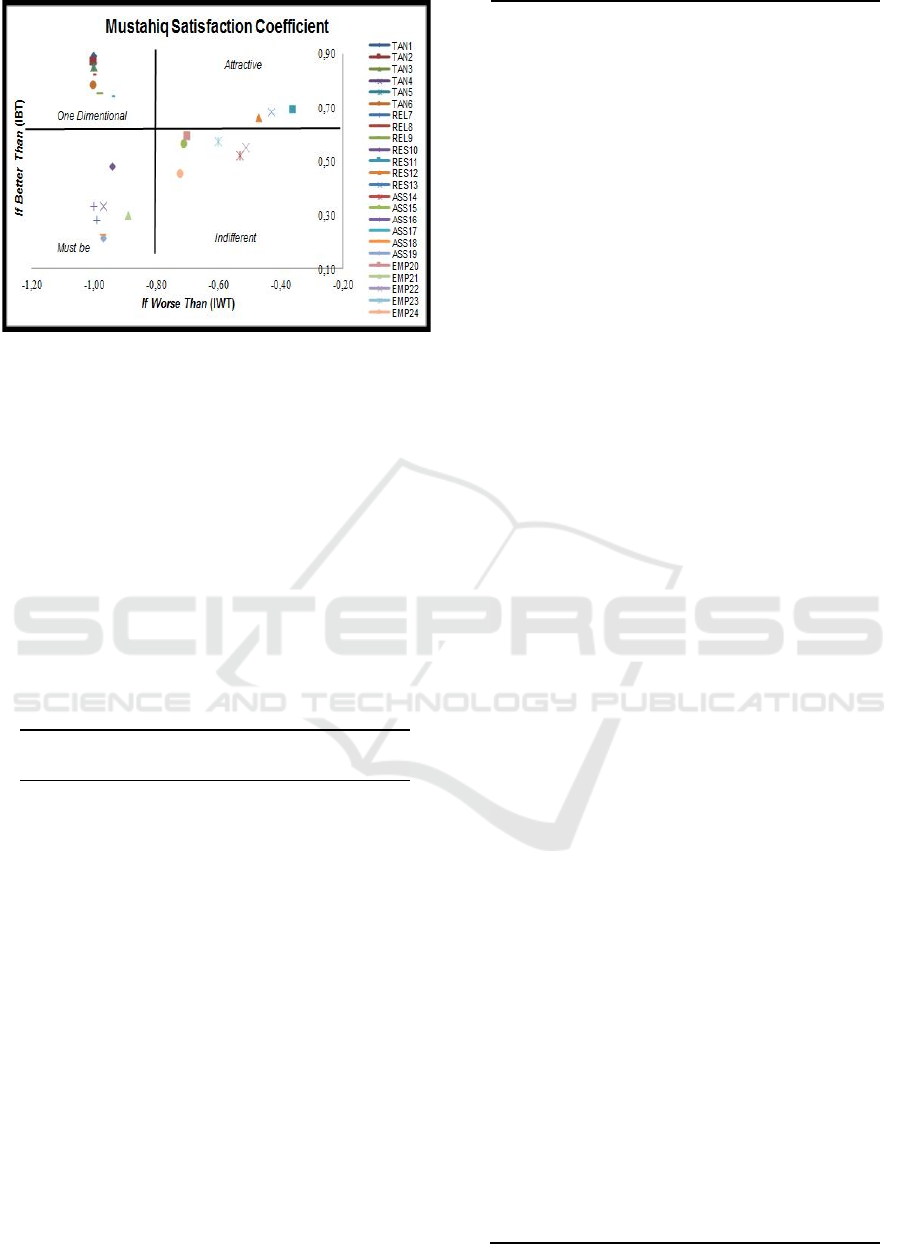
Figure 3: The Diagram of mustahiq satisfaction
Based on the above mustahiq satisfaction
coefficient diagram, the attributes of Baitul Mal
service can be grouped in each dimension. The
attributes are included in one dimentional there are 8
attributes, attributes are included in the category of
attractive there are 3 attributes, attributes included in
the category must be there are 7 attributes, attributes
belonging to the category of indifferent there are 6
attributes.
Integration of attributes on Importance
Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano model can be
seen in Table 7
Table 7: Integration of Importance Performance Analysis
(IPA) and Kano Model
Attrib
ute
Code
Services
IPA
Categories
Kano
Categ
ories
Impr
ovem
ent
REL7
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
solve the
mustahiq
problem related
to zakat program
on time
Main
Priority
M
Enhanci
ng
ASS1
5
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
can explain the
information to
the mustahiq
clearl
y
Main
Priority
I
Enhanci
ng
ASS1
6
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
has knowledge
of zakat
Main
Priority
M
Enhanci
ng
ASS1
8
Zakat given
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has fulfilled the
necessity of
mustahi
q
Main
Priority
M
Enhanci
ng
ASS1
9
Zakat given
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
Main
Priority
M
Enhanci
ng
can improve the
welfare of
mustahi
q
TAN1
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has adequate
b
uildin
g
Maintain
Achievemen
t
O
Maintai
n
TAN3
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has a clean
b
uilding
Maintain
Achievemen
t
O
Maintai
n
TAN4
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
shows Islamic
morals
Maintain
Achievemen
t
M
Maintai
n
TAN5
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has a neat
b
uildin
g
Maintain
Achievemen
t
O
Maintai
n
TAN6
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has a service
room in
accordance with
its function
Maintain
Achievemen
t
O
Maintai
n
RES1
0
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
always serve
mustahiq
quickly
Maintain
Achievemen
t
M
Maintai
n
ASS1
7
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has enough amil,
so there is
always a
substitute if
anyone is unable
to atten
d
Maintain
Achievemen
t
O
Maintai
n
EMP2
1
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
does not
distinguish
between
mustahiq with
one anothe
r
Maintain
Achievemen
t
M
Maintai
n
RES1
2
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe is
always willing to
help the
mustahiq who
are in trouble
Low Priority A
Reducin
g
RES1
3
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
always listen to
complaints
mustahi
q
Low Priority A
Reducin
g
ASS1
4
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
can explain the
information to
the mustahiq in
detail
Low Priority I
Reducin
g
EMP2
0
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe is
always willing to
provide latest
information to
mustahi
q
Low Priority I
Reducin
g
EMP2
3
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
Low Priority I
Reducin
g
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
54

always
understands
what the
mustahiq
complained
about
EMP2
4
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
always
understands
what the
mustahi
q
wants
Low Priority I
Reducin
g
TAN2
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has a
comfortable
b
uilding
Excessive O
Reducin
g
REL8
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe is
always in the
office during
working hours
Excessive O
Reducin
g
REL9
Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe
has an easy
registration
procedure to
become
mustahi
q
Excessive O
Reducin
g
RES1
1
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe
can answer the
questions posed
b
y mustahi
q
Excessive O
Reducin
g
EMP2
2
Amil Baitul Mal
Kota
Lhokseumawe is
always willing to
help the
mustahiq who
are in trouble
Excessive I
Reducin
g
Based on the mapping of Importance Performance
Analysis (IPA) and Kano model, there are 5 attributes
that must be improved by attribute code REL7,
ASS15, ASS16, ASS18, and ASS19. 8 service
attributes retained by the attributes of the TAN1,
TAN3, TAN4, TAN5, TAN6, RES10, ASS17, and
EMP21.11 service attributes that must be reduced to
satisfy the mustahiq satisfaction based on the results
obtained with attribute codes TAN2, REL8, REL9,
RES11 , RES12, RES13, ASS14, EMP20, EMP22,
EMP23, and EMP24.
7 CONCLUSION
Based on the results and discussion that has been
done, it can be concluded:
1. For the Importance Performance Analysis
(IPA) method of service attributes in the
main priority which is considered important
but the performance is still less satisfactory
for the recipient of zakat (mustahiq) is Amil
Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe solve the
mustahiq problem related to zakat program
on time (REL7), Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe can explain information to
mustahiq clearly (ASS15), Amil Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe has knowledge about
zakat (ASS16), Zakat given Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe has fulfilled the necessity of
mustahiq (ASS18), and Zakat given Baitul
Mal Kota Lhokseumawe is capable of
improving the mustahiq's welfare (ASS19).
2. Service attributes in the main priorities
based on Kano category include Amil Baitul
Mal Kota Lhokseumawe solve the mustahiq
problem related to zakat program on time
(Must be), Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe can explain information to
mustahiq clearly (Indifferent), Amil Baitul
Mal Kota Lhokseumawe has knowledge of
zakat (Must be), Zakat given Baitul Mal
Kota Lhokseumawe has fulfilled the
mustahiq (Must be), and Zakat given by
Baitul Mal of Lhokseumawe can improve
the mustahiq welfare (Must be).
3. Based on the results of integration of
Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and
Kano Model, there are 5 attributes that must
be improved in Baitul Mal such as Amil
Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe solve the
mustahiq problem related to zakat program
on time (REL7), Amil Baitul Mal Kota
Lhokseumawe can explain information to
the mustahiq clearly (ASS15), Amil Baitul
Mal Kota Lhokseumawe has knowledge
about zakat (ASS16), Zakat given Baitul
Mal Kota Lhokseumawe has fulfilled the
necessity of mustahiq (ASS18), and Zakat
given Baitul Mal Kota Lhokseumawe can
improve prosperity mustahiq (ASS19).
RECOMMENDATION
Based on the research that has been done, the authors
provide the following suggestions:
1. It is expected that the Amil Baitul Mal can
improve its service attribute performance
based on expectations from Mustahiq.
2. This research can be continued by analyzing
the factors causing the low performance of
some important service attributes, so that the
improvement of Baitul Mal service quality
can be put forward as public sector.
Analysis of Service Quality on Mustahiq Satisfaction using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Kano Model: Case Study on Baitul
Mal
55

REFERENCES
Majma Lughah al-‘Arabiyyah (1972). al-Mu’jām al-Wasīṭ.
Misr: Dār al-Ma’ārif. juz 1 h. 396.
Mulyani, 2008. Analisis Sistem Laporan dana ZIS Pada
Baitul Maal Muamalat (BMM) Jogjakarta. Jurnal
Dinamika Ekonomi & Bisnis Vol 5 No 2.
Yūsuf Qaraḍāwī (1993). Al-‘Ibādah Fī al-Islām.Bayrut:
Muassasah al-Risālah. h. 235.
Ali Yafie (1994). Menggagas Fiqh Sosial.Bandung: Mizan,
h. 231.
Sayyid Sabiq (1968). op.cit., h. 5. Lihat juga Yūsuf
Qaraḍāwī (1985).op.cit., h. 44. Hasbi As-Siddiqy
(2006), op.cit., h. 4-5.
QS. al-Tawbah: 73 dan QS. al-Hajj: 40-41
QS. al-Tawbah: 103 dan QS. al-Rūm: 39. Baca Al-Qurṭubī
(1993), al-Jāmi’ li Aḥkām al-Qurān, Bayrut: Dār al-
Kutūb al-‘Ilmiyyah, h.156.
Tjiptono, F. 2001. Strategi Pemasaran. Andi Offset.
Yogyakarta.
Supranto, J. 2006. Pengukuran tingkat kepuasan
pelanggan.Cetakan ketiga. PT. RIN CIPTA. Jakarta.
Hanoum, S. 2009. Prioritizing Healthcare Service
Attributes. Comparing Importance Performance
Analysis and Kano model. Tugas Akhir. Program
Teknik Industri. Institut Teknologi Surabaya (ITS).
Walden, 1993. Kano’s Methods for Understanding
Customer Defined Quality.Center for Quality of
Management Journal.Vol 2.
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
56
