
A Development of Moodle based Test Simulation for ZIDS-Exam
Pepen Permana, Irma Permatawati and Ending Khoerudin
Department of German Language Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Setiabudhi 229, Bandung, Indonesia
{pepen, irma.permatawati, ending.khoerudin}@upi.edu
Keywords: ZIDS, language exam, German, Moodle.
Abstract: The certificate for Indonesian German students (ZIDS) has to be acquired by the German students at some
universities in Indonesia. This test is carried out once a year in Department of German Language Educations.
The participants of this test are German students in the 4th semester. Within the scope of the ZIDS test, the
Department of German Language Education of the Faculty of Languages and Literature of the Pedagogical
University of Indonesia (FPBS UPI) has offered an intensive one-month preparatory program. Based on their
average score, which is 60-70%, the students show no excellent performance. Since the Curriculum 2013 of
the UPI comes into force, this preparation program is being carried out regularly in a semester. As the present
preparation program is less intensive than before, an innovation is needed to improve the performance of the
students in the ZIDS test. The intended innovation is the development of the online ZIDS test simulation
based on the LMS Moodle, which allows students to prepare themselves for the test alone or outside the
classroom. The results of the study demonstrate that the ZIDS test stimulation has contributed to the
performance improvement of the students in the ZIDS test.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since 2003, German language education departments
in some universities in Indonesia have obligated their
students to take the national German language
examination, namely ZIDS (Zertifikat für
indonesische Deutschstudierende). The acquisition of
this certificate entails that the students are able to
express themselves in German about everyday topics
orally as well as written.
The test can be taken by German students at 10
universities, namely Universitas Pattimura Ambon,
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Universitas Negeri
Jakarta, Universitas Negeri Malang, Universitas
Negeri Manado, Universitas Negeri Medan,
Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Universitas Negeri
Makassar, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, and
Universitas Nommensen Pematang Siantar. This
examination is carried out once a year at the end of
the 4th semester. At the German Department of
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia (UPI), the
examination is carried out every year in June. To
complete their studies, the German students must
prove that they have earned the certificate of the ZIDS
examination.
The program for the preparation of the ZIDS at the
German Language Department of the FPBS UPI was
carried out intensively, but it was not yet an
outstanding achievement. This can be seen from the
annual result of the average grade of the students at
ZIDS exam, which is 60-70 percent from the desired
maximum marks. Even 10-20 percent of the students
did not pass the ZIDS exam.
Compared to the old preparation program the
quantity of the teaching sequence in the subject ZIDS
preparation is less than before. Previously the
students had 20 learning sequences within a month,
but now only 14 to 16 learning sequences within a
semester. This gives us cause for concern that in the
future the performance of the students might be lower
in ZIDS exam.
In order to overcome the concern, an innovation
is needed to improve the result quality of the subject
ZIDS-Prüfungsvorbereitung and to increase student
performance during the ZIDS exam. The intended
innovation is the optimal use of the internet, by
creating an online test simulation to prepare the
student facing the ZIDS exam. With this online
program, the students are able to prepare themselves
for the ZIDS exam without time and space
limitations, so the problem about smaller quantity of
the learning sequence would be solved.
Nowadays there are many available possibilities,
whereby the optimization of the role of the internet in
548
Permana, P., Permatawati, I. and Khoerudin, E.
A Development of Moodle based Test Simulation for ZIDS-Exam.
DOI: 10.5220/0007170705480553
In Proceedings of the Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference
on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education (CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017) - Literacy, Culture, and Technology in Language Pedagogy and Use, pages 548-553
ISBN: 978-989-758-332-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

lessons can be carried out. One of them is the use of
the online learning application “Learning
Management System” (LMS). LMS is an application
with the purpose of managing, tracking, and reporting
a series of online learning programs and activities
(Ellis, 2009). This LMS allows users to create virtual
learning environment and have access to the learning
content and their administration actively and
interactively.
One of the most frequently used platforms LMS is
Moodle (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic
learning). Moodle is an open source product,
developed by a broad community and constantly
improved. These include developers, education
experts, translators, and many more. There are
numerous ways to join the community. Moodle offers
different types of online learning modules in a way
that can be easily adapted by the teachers in order to
achieve the learning objectives. Because of its many
learning modules, Moodle is recommended for Web-
based teaching, according to Kaya (2012, p. 680).
Sahin-Kizil (2014, p. 184) also notes that most
learners reacted positively to the use of Moodle in the
classroom, where they are more engaged in language
learning.
In its official website (http://docs.moodle.org),
it’s stated that the design and the development of
Moodle is guided by a “social constructionist
pedagogy”. This concept is largely motivated by
constructivism theory. A key point of constructivism
is that meaning is actively constructed by learners and
learning and development socially situated activities
that are enhanced in the meaningful contexts
(Kargiban and Kaffash, 2011).
This means its goal is to provide a set of tools that
support an inquiry and discovery-based approach to
online learning. Furthermore, it purports to create an
environment that allows for collaborative interaction
among students as a standalone or in addition to
conventional classroom instruction (Kotzer and
Elran, 2012).
Moodle has pedagogical advantages since it was
built in accordance with the teaching approach which
emphasizes the construction of knowledge through
active and interactive learning and learning multi-
sensory experience through multimedia (Kotzer and
Elran, 2012).
With its numerous features, Moodle enables
instructors to create test kits, that is secure and easy
to set up. There are over 20 highly configurable
activities available - for example, forums, glossaries,
wikis, tasks, tests, databases and more. Interesting in
this activity-oriented approach is the possibility to
freely configure these activities regarding to the
combination and the sequence. Thus, the learners'
learning path can be designed freely based on the
learning objectives. Also, the results of the previous
activities can be used for the next activities.
In addition to the standard modules of Moodle,
there are also hundreds of third-party modules and
plug-ins that can be installed according to the needs
of learning. From a technical point of view, Moodle
can run well with at least the Apache web server, PHP
and MySQL Database or PostgreSQL. Moodle also
supports multiple languages as the system language,
including Indonesian and also German.
Another important feature of Moodle was the
feedback capability. Students who participate in E-
Learning environments often complain about the lack
of feedback that is available in conventional
classroom settings (Kotzer and Elran, 2012). In
Moodle, almost all modules are designed to allow
teachers or course participants to provide feedback in
qualitative or quantitative form.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research conducted the Research and
Development (R&D) approach with the steps define,
design, develop, and disseminate (Borg and Gall,
1979). This research method aims to produce a
product and to test its effectiveness (Sugiyono, 2011,
p. 297). The product of this study is an online ZIDS
exam simulation based on LMS-Moodle.
According to Sugiyono (2011, p. 289), the R&D
research method comprises the following steps: (1)
analysing potentials and problems; (2) gathering
information; (3) designing the product; (4) validating
the design; (5) revising the design; (7) conducting
limited trial; (8) revising the product; (9) conducting
larger trial; (10) revising the product; and (10)
preparing the final product.
The research was carried out in two years and
mainly took place at the German Department FPBS
UPI. In the first year (2016) the research was focussed
with the development of the product and consisted of
field observations in order to analyse the problems
and the existing potentials. The information used for
the research was then collected. The simulation
program was then developed and then validated
according to the expert evaluation. After revision of
the product, the limited trial was performed, the
subjects of which were only UPI students. In the
second year (2017) the research has focused on
revising the product based on the results of the first
/limited trial. At the end, the large sample was
A Development of Moodle based Test Simulation for ZIDS-Exam
549
conducted, the subjects of which were the UPI and
UNJ students.
As already mentioned, the subject of this research
were the German students of FPBS UPI and FBS
UNJ, who participated in the ZIDS exam 2017. In
total, they were 82 persons and have belonged to the
sample group. The control group of this research was
83 German students of the FBS Unesa and FS UM.
Only the students from the sample group practiced
with the online simulation program which they could
use several times according to their wishes. They also
completed a questionnaire for the assessment of
simulation program.
The students from the control group are
considered as a comparison group. Their results of in
the ZIDS exam 2017 were taken and statistically
compared with the results of the sample group. These
data were analysed by t-test to find out whether there
is a significant difference between the results of the
two groups. This difference could help to find the
effectiveness of the simulation program for ZIDS
exam.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The main goal of this research is to develop an online
ZIDS exam simulation based on Moodle. The ZIDS
exam itself consists of five parts, namely reading
comprehension (LV = Leseverstehen), grammar and
vocabulary (SB = Sprachbausteine), listening
comprehension (HV = Hörverstehen), written
expression (SA = schriftlicher Ausdruck), and oral
expression (MA = mundlicher Ausdruck). The
examination parts developed in the simulation are
only the written parts because it is technically not
possible yet for us to carry out the oral exam online.
The development of this online ZIDS-exam
simulation program fully utilizes the Quiz module
provided by Moodle. The questions presented in this
program are in the form of objective questions, that
are made using the type of embedded answer (cloze)
feature. These questions consist of a passage of text
in Moodle format that has various answers embedded
within it, including multiple choice, short answers
and numerical answers.
The online ZIDS exam simulation is available at
http://jerman.upi.edu/zids. Because it is based on
Moodle, only the registered students or users can log
in to the site. After confirmation, the students can
simulate the ZIDS exam. There is a time limit of 150
minutes. However, the allowed attempt of the
simulation is unlimited. This means that the students
can use this ZIDS exam simulator as many times they
want.
Overall, this ZIDS exam simulation consists of 10
pages: a homepage, a results page, and eight test
pages. There are hints for the simulation on the start
page. Clicking the "attempt quiz now" button will
bring the students to the exam page after confirming.
Thus, the time of the simulation starts to run. The
"submit" button is available on each page. This means
that when the students click the button, their entries
are temporarily stored on the page. At the end of the
exam page, there is also the "submit all and finish"
button, which means students can stop their attempts
and they can no longer edit their answers. Then the
results page appears and shows the students where
they can improve their performance. The site
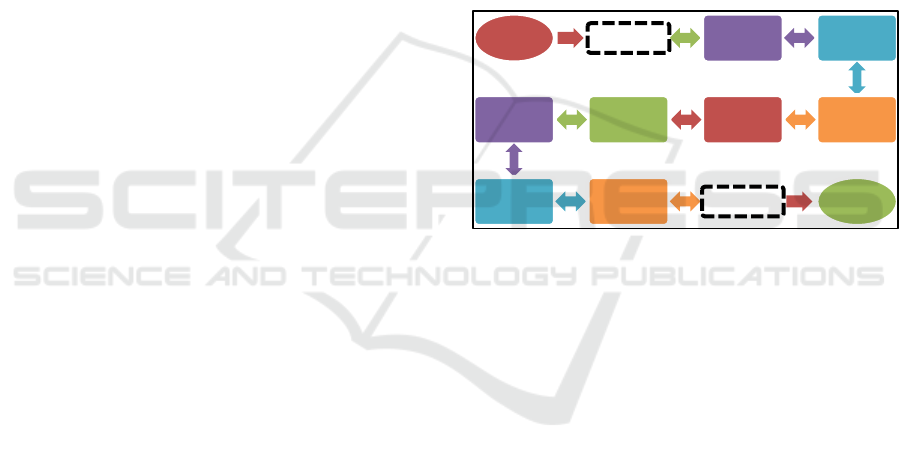
navigation of the ZIDS exam simulation is shown in
figure 1.
Figure 1: The flow chart of the navigation of ZIDS exam
simulation.
As long as the simulation test time is still running,
the students can navigate from one page to another
page. This is useful when students want to check their
answer. When the time has elapsed, the system closes
automatically and any open attempts are submitted.
The system then shows the results page.
The tasks in the ZIDS exam simulation come from
several exam preparation books and web pages. A
number of tasks have also been modified and / or
reworded to suit the design of the ZIDS exam and the
students' language level. Currently, there are more
than four test sets for each test piece in the simulation
program for ZIDS exam.
Because there are more than one sets for each test,
it allows the question to be randomized for each
students. It is also to be expected that each student
gets different test sets. They could also have a
different test set on the next attempt. Nevertheless, it
might also be possible for students to answer the same
questions. In order to get a better online test
simulation, it is therefore necessary to add more test
sets to the task collection.
START confirmation LV part 1 LV part 2
LV part 3SB part 1SB part 2HV part 1
HV part 2 SA
confirmation FINISH
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
550
3.1 Statistical Analyse of Attempts
Made in ZIDS Exam Simulation
Moodle provides the reporting function of statistical
analysis of all attempts made by the students. This
report provides a statistical evaluation of the test, and
the questions within it. With this statistical analyse,
one can determine whether the questions in the test
are suitable or not. Table 1 provides general statistical
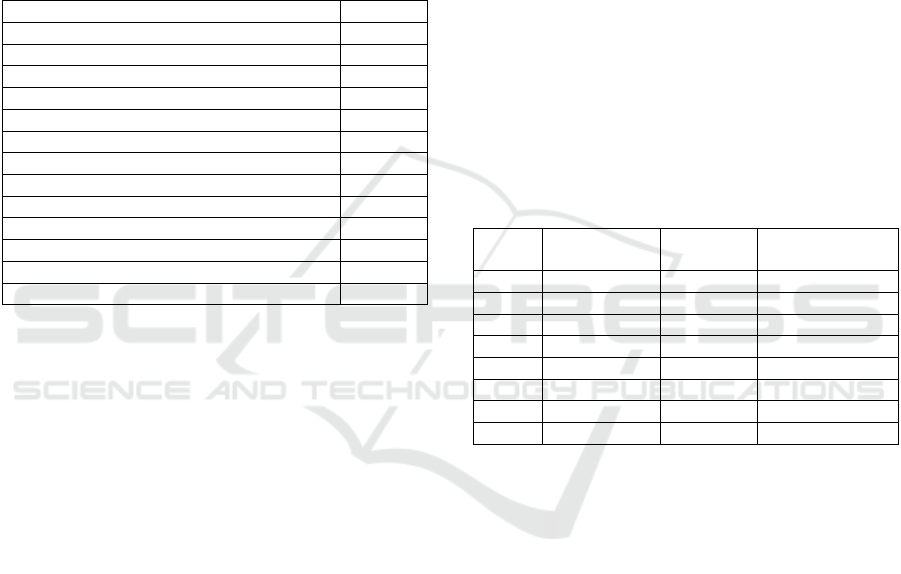
information about the online ZIDS exam simulation.
Table 1: Basic statistical information about ZIDS exam
simulation as a whole.
Statistical Information
Result
Number of complete graded first attempts
82
Total number of complete graded attempts
223
Average grade of first attempts
75,71%
Average grade of all attempts
76,26%
Average grade of last attempts
79,80%
Average grade of best attempts
83,09%
Median
77,50%
Standard deviation
13,60%
Score distribution skewness
-0,3701
Score distribution kurtosis
-0,4967
Coefficient of internal consistency
60,51%
Error ratio
62,84%
Standard error
8,55%
The table 1 indicates that the number of first attempts
is 82, that means all the students in the sample group
have engaged with the simulation program. They
have even worked with this program more than once;
it could be two or three times. This can be seen in the
total number of all attempts, which show the number
223.
The average grade of the students in the first
attempt is 75.71 and the last attempt is 79.8. From this
grade difference, it can be seen that the students have
received better grades in the last attempt. The above
table also shows that the average grade of all attempts
is 76.26 and the average grade of the best test is 83.09.
The grades show that the students were able to cope
well with the tasks of the simulation program.
The score of the coefficient of internal
consistency is 60.51%. This coefficient, which is also
called Cronbach Alpha, is a measure of whether all
the items in the test are testing basically the same
thing. It measures the consistency of the text, which
is a lower bound for the validity. Higher numbers are
better here. The points 60.51% are interpreted as
"questionable". This means that the test in this online
ZIDS exam simulation is not acceptable yet, but it is
also not bad.
The error ratio shows the relationship between
random differences and performance-related
differences in the grading. The smaller the error ratio,
the less the random difference and thus the better the
test reflects the actual knowledge. The error ratio for
this online ZIDS exam simulation is 62.84% and is
unfortunately not low enough. This means that in this
ZIDS exam simulation there are still many random
differences in grading.
The standard error is a parameter derived from the
error ratio, and is a measure of how much random
variation there is in the test grade. The standard error
of this test simulation is 8.5%. That is, if a student has
reached 70% in the exam simulation, the student's
actual ability is probably between 78.5% and 61.5%.
In addition to the general statistical information,
statistical analysis of the individual test questions is
also available. The result of this analysis also serves
as a measure of whether a questions can be posed. The
statistical analyse of the individual test questions is
shown in the table 2.
Table 2: Test structure analysis.
Test
Name
Facility
index
Standard
deviation
Discrimination
index
LV1
81.79%
20.28%
19.31%
LV2
71.93%
26.90%
31.04%
LV3
77.98%
19.31%
35.12%
SB1
66.46%
28.56%
43.90%
SB2
77.26%
22.16%
43.63%
HV1
72.02%
29.27%
42.46%
HV2
79.55%
20.48%
38.36%
LV1
81.79%
20.28%
19.31%
Table 2 shows that facility index shows the
percentage of students that answered the question
correctly. This number shows the difficulty level of
the task in the test. The table above shows that the
general facility index of this ZIDS exam simulation
program is between 60% and 80%. Based on the
interpretation table of the possibility index (see
http://docs.moodle.org/dev/Quiz_report_statistics),
this option index belongs to the category "fairly
easy".
The standard deviation shows us how large the
deviation of the individual scores from the average
score was. The lower the standard deviation, the
smaller is the deviation of the individual scores from
the average score. Low standard deviation shows that
the abilities of the sample group are diverse. The
smallest possible value for the standard deviation is
0, and this occurs only in staged situations where each
individual number in the record is exactly the same,
that is, there is no deviation. In the table above, it can
A Development of Moodle based Test Simulation for ZIDS-Exam
551

be seen that the value of the standard deviation from
this simulation program is rather low. It is less than
30%. This means that students' ability to perform in
this ZIDS exam simulation was rather homogeneous.
The discrimination index is a parameter for the
correlation between the achieved score for the
question and the score achieved in the test as a whole.
In the case of a "good" question, the participants who
achieved a high score in this question should also
have achieved a high score in the test. Here, it is
expected that the score of the discrimination index is
large. It can be seen in the table that the
discrimination index of all tests in this simulation
program is less than 50%. This means that the
questions of the tests do not have so strong
discrimination index. Thus, the questions could not
distinguish the abilities of the students. This means
that the questions research must be revised.
3.2 The Result of the Experiment
To find out the effectiveness of the online ZIDS exam
simulation program, the statistical assessment of the
grades of the two groups in ZIDS exam 2017 was
required. The t-test was used to see if the mean scores
of the sample group and the control group had a
significant difference. Before the t-test, the normal
distribution test and the variance equality test were
performed. The tests resulted that the distribution to
be tested has normal distribution; and that the equal
variances are assumed.
After conducting the above tests, which serve as
the prerequisite test for data analysis, the
independent-sample T-test was carried out. The
leading point for interpretation of the t-test is if the
significance value is lower than 0.05, then there is a
significant difference on the 5% significance level.
The result of the t-test showed the significance value
of 0.048. This value is lower than 0.05, so it can be
said that the average scores of the two groups have a
significant difference.
Because there is a significant difference between
the scores from the sample group and the control
group, the effectiveness of the online ZIDS exam
simulation program can be found by comparing the
average scores of the two groups. The average scores
on scale 100 from both groups are as shown in table
3.
Table 3: The average score of the two groups in ZIDS exam
2017.
Group
Average
Std. Deviation
Sample
61.72
8.28
Control
60
7.77
From table 3 it can be seen that the two groups
have received almost the same average score, which
is 60% - 70%. According to the grading criteria of
Nurgiyantoro (2009, p. 399), these grades belong to
the "sufficient" category. Nevertheless, the mean
score of the sample group was higher than the control
group. This shows that the online ZIDS exam
simulation was effective. The effectiveness was also
confirmed by the correlation test which measured the
relationship between the scores of the sample group
during the simulation and the test. The correlation test
has shown that there is a relationship between the
simulation score and the test results that is at the
significance level of 0.005 with the correlation
coefficient 0.46. Based on the interpretation criteria
of the correlation coefficient according to Sugiyono
(2011, p. 183), this correlation is one of the middle
category.
The survey among students from the trial group
showed that 46% of the students felt that the questions
in the ZIDS exam simulation program matched their
abilities. 44% of students have hesitated, whether the
questions were according to their abilities. This can
be seen in the answer to the question of the degree of
difficulty of the tasks. 70% of the students have
confirmed that the tasks have moderate difficulty.
16% of whom said the tasks were difficult, and 14%
felt that the tasks were too simple.
The results of the survey also show that most
students (73.4%) find that this simulation program
has helped them prepare the ZIDS exam. They used
this program by practicing for the exam and
familiarizing themselves with the design of the ZIDS
exam. Although most students (66%) had no previous
experience with online learning, 73% of them have
confirmed that dealing with this simulation program
has not caused any difficulties.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The online ZIDS exam simulation, available at
http://jerman.upi.edu/zids, could bring benefits to the
learner, namely: (1) they can familiarize themselves
with the exam format; (2) the assessment is close to
the result of a real ZIDS exam, so they can be realistic
in assessing their preparation level; (3) the results
page shows them where they can improve their
CONAPLIN and ICOLLITE 2017 - Tenth Conference on Applied Linguistics and the Second English Language Teaching and Technology
Conference in collaboration with the First International Conference on Language, Literature, Culture, and Education
552

performance; (4) they can practice again and again
and improve themselves. As it is online, the students
would have more possibilities to access the ZIDS
exam simulator without time and space barriers.
The result of the statistical evaluation has pointed
out, however, that this online ZIDS exam simulation
still contains some questions with unsuitable
difficulty level. But on the basis of the results of the
experiment it was shown that the online ZIDS test
stimulation contributed to the improvement in student
performance during the ZIDS examination and that
there was a moderate correlation between the
simulation score and the grade of the ZIDS exam. At
this point, further research is recommended that
involves a larger sample and more questions so that
the questions available in the online ZIDS exam
simulation might have higher validity and reliability.
REFERENCES
Borg, W.R. and Gall, M.D., 1979. Educational Research:
An introduction. New York & London: Longman.
Ellis, R., 2009. A Field Guide to Learning Management
Systems. Learning Circuit.
Kargiban, Z.A. and Kaffash, H.R., 2011. The effect of e-
learning on foreign language students using the
student’s attitude. Middle-East Journal of Scientific
Research, 10(3), pp.398-402.
Kaya, M., 2012. Distance education systems used in
universities of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 31, pp.676-680.
Kotzer S., and Elran Y., 2012. Learning and teaching with
Moodle-based E-learning environments, combining
learning skills and content in the fields of Math and
Science & Technology. Paper presented in the 1st
Moodle Research Conference, Heraklion – Greece.
Nurgiyantoro, B., 2009. Penilaian dalam Pengajaran
Bahasa dan Sastra (3
rd
ed.). Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Sahin-Kizil, A., 2014. Blended instruction for EFL
learners: Engagement, learning and course satisfaction.
Jalt Call Journal, 10(3), pp.175-188.
Sugiyono, 2011. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan. Bandung:
ALFABETA.
A Development of Moodle based Test Simulation for ZIDS-Exam
553
