
The Competency of Pedagogic and Professional Mathematics
Teachers Relevant with Curriculum
Ehda Farlina, Wati Susilawati, Asep Jihad and Rahayu Kariadinata
Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, Jl. AH. Nasution No. 105, Bandung 40614,
Indonesia
{ehda.farlina, rahayu.kariadinata}@uinsgd.ac.id
Keywords: Pedagogic, Curriculum, Competence.
Abstract: The implementation of the curriculum in schools should be supported by teacher competencies. There are
four competencies that must a teacher have, it should be pedagogic, professional, social, and personality. The
purpose of this study is to determine the relevance of pedagogic competence and professional high school
mathematic teachers with curriculum. The method used is a descriptive-qualitative. The random sampling
technique is used to take a sample of 30 High School. The instruments used were questionnaires, interviews,
and observations. The results of data analysis shown that 1) teacher pedagogic competence in planning,
process, and evaluation is not maximal in accordance with the demand of curriculum, 2) professional
competence of teacher in explanation of concept on some high school level material still difficult enough to
be taught and lesson using technology that has not developed optimally. Based on the results of this study it
can be concluded that pedagogic and professional competencies of high school mathematics teachers are not
in accordance with the expectations and objectives of the curriculum. Teacher is a designer in classroom, who
can make an effort for student.
1 INTRODUCTION
Teachers are a major factor in the educational process
(Ibrahim, 2004; Fasli and Dedi, 2001; Syaiful, 2000).
So is the teacher of mathematics, which is the main
factor and the key to success in learning mathematics.
Regulation of the Minister of National Education No.
16 of 2007 states that teachers must have
competencies such as pedagogical, professional,
personality, and social competence. The competence
of a teacher can determine the quality of education
and the characteristics of a teacher can affect student
achievement (Alqiawi and Ezzeldin, 2015; Renol,
2015). One of the primary keys of effective teachers
is knowing the students and how they learn, as well
as knowing the learning materials and how to teach
them (Celik, 2011). Teachers must understand the
content and context of teaching to help successful
students understand contextual learning (Johnson,
2002).
Leinhard and Smith (1984) mentioned that
teachers should understand the classroom
management system and the subject matter. The
classroom management system is similar to
pedagogic competence. Pedagogic competence is the
ability to manage learning that includes
understanding students, planning, implementation
and evaluation of learning and development of
students to apply various potentials (Inám, 2011).
Minister of National Education Regulation No. 70 of
2013 states that pedagogical competence consists of
understanding the characteristics of students,
mastering the theory of learning, developing curricula
relevant to the subjects, utilizing information and
communication technology, facilitating the
development of students’ potentials, being able to
communicate effectively with students, and
evaluation, performing a reflection action. Akhyak
(2013) asserts that pedagogical competence consists
of lesson plans, processes, assessment and evaluation.
Meanwhile, professional competence is the
teacher's knowledge of the subject matter. A teacher
should pay attention and understand the content
(Good and Bropphy, 1987). Professional competence
is the ability to comprehend the content of learning
materials in depth (Akhyak, 2013). Professional
competence includes: a) mastering learning materials
392
Farlina, E., Susilawati, W., Jihad, A. and Kariadinata, R.
The Competency of Pedagogic and Professional Mathematics Teachers Relevant with Curriculum.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 1 , pages 392-394
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and scientific methodology; b) mastering the
structure and curriculum of learning materials; c)
mastering and utilizing information technology to
improve the quality of learning.
The competencies of a teacher must be in
accordance with the curriculum being used. The
curriculum is a structured sequence to generate
learning outcomes (Johnson, 1969). Law No. 20 of
2003 on the National Education System states that the
curriculum is a set of plans and arrangements
concerning objectives, content, and lesson materials
and ways used as guidelines for the implementation
of learning activities to achieve certain educational
goals.
Based on the above description, a review of the
competence of mathematics teachers especially
pedagogic and professional needs to be studied
whether it is relevant to the curriculum used or not.
2 METHOD
This study used descriptive-qualitative method
involving 30 math teachers from 30 high schools. The
participants were selected using random sampling,
and the instruments were questionnaire, observation
and interview.
There are three pedagogical competency
indicators (Akhyak, 2013) namely planning, process,
and evaluation. Meanwhile, professional competence
is divided into mastery of material, mastery of
structure and material curriculum, and the utilization
of technology.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Pedagogic Competence of
Mathematics Teacher
Based on the results of questionnaires, observations,
and interviews, the pedagogic competence of 30 math
teachers in high schools can be identified as in Table
1.
Table 1: The results of pedagogic competence of
mathematics teacher.
Indicator
Results
Planning
50% of teachers prepare
lesson plans in mid-
semester
80% of teachers apply
lecture and discussion
methods
20% of teachers use
inquiry, problem based
learning, constructivism
Process
40% of teachers use media
or teaching aids in learning
40% of teachers cannot pay
attention to the overall
condition of the students
Evaluation
80% of teachers use
procedural questions in
their tests. The rest uses
contextual questions.
For students who do not
understand, teachers do
repetition of the material by
providing additional
questions.
The latest curriculum used today requires teachers
to use a scientific approach in learning. The scientific
approach has the learning characteristics of the
student-cantered learning, so the students discover
their own concepts and formulas that will be used.
Based on Table 1, teachers have not prepared the
learning tools before the teaching and learning
activities begin. Sumarno (2014) and Partin (2009)
state that the teacher must arrange learning tools well
so that the learning outcomes were in line with the
expected outcomes. However, teachers still do not
understand the learning tools that are suggested in the
curriculum. The method is still teacher-cantered. In
process indicators, teachers have not used learning
aids. This is because high school math materials are
very difficult to use learning aids. In the evaluation
indicator, teachers are still using procedural problems
so that students have not been able to develop math
skills entirely. From these results, it can be argued
that the pedagogical competence of mathematics
teachers has not been fully in accordance with the
demands of the curriculum used.
3.2 Professional Competence
A description of the results of professional
competence of 30 math teachers at senior high
schools can be seen in table 2.
The Competency of Pedagogic and Professional Mathematics Teachers Relevant with Curriculum
393
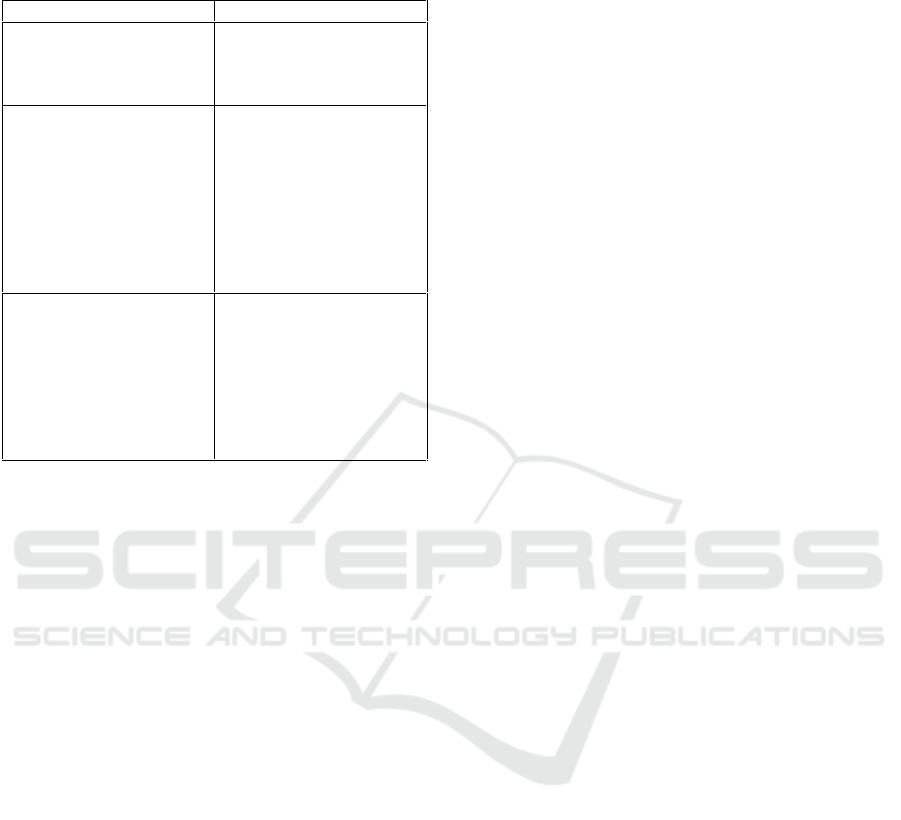
Table 2: The results of professional competence among
mathematics teachers.
Indicator
Results
Mastering learning
materials and scientific
methodology
80% of teachers master
learning materials, but
30% still have difficulty in
delivering them.
Mastering the structure
and curriculum of learning
materials
60% of teachers master the
curriculum used. On the
other hand, teachers have
difficulty in meeting the
administrative demands of
the curriculum and
applying contextual
problems in mathematics
learning.
Mastering and utilizing
information technology to
improve the quality of
learning
80% of teachers know the
application or props used
in learning mathematics
but only 20% of teachers
already use information
technology in learning.
Table 2 shows that high school math teachers still
need additional knowledge of interactive learning
models, the way they make contextual questions and
the use of mathematical applications in learning.
Contextual questions are needed because procedural
questions without concepts are just rules that will
bring misunderstandings and make students dislike
mathematics (Van de Walle, 2007).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Competencies that must be possessed by teachers of
mathematics are pedagogic and professional
competence. The pedagogic competencies of the
teacher must be in accordance with the curriculum
used in the school. Professional teacher competence
shows the teacher's ability to master the material
content to be given. Teachers have a major role in
learning. If the pedagogic and professional
competence of teachers is not maximized, then the
ability of students cannot be developed maximally.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank the Institute of
Research and Community Service (LP2M) UIN
Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung which has provided
financial support to this research.
REFERENCES
Akhyak, I.,Abu Bakar, 2013. Implementation of Teachers
Pedagogy Competence to Optimizing Learners
Development in Public Primary School in Indonesia.
International Journal of Education and Research1 (9).
Alqiawi., Ezzeldin., 2015. A Suggested Model for
Developing and Assessing Competence of
Prospective Teachers in Faculties ofEducation.
World Journal of Education5 (6), 65-73.
Celik, S., 2011. Characteristics and Competencies for
Teacher Educators: Addressing the Need for
Improved Professional Standars in Turkey.
Australian Journal of Teacher Education36 (2), 18-
32.
Good, T.L., Brophy, J.E., 1987.
Looking in Classrooms
.
Harper and Row, Publisher. New York.
Ibrahim B., 2004. Peningkatan Profesionalisme Guru
Sekolah Dasar.BumiAksara. Jakarta.
Johnson, E.B., 2002.
Contextual Teaching and Learning:
What is and why it's here to stay.
Corwin Press.
California.
Leinhardt, G.,Smith, D., 1984. .
Expertise In Mathematic
Instruction: Subject Matter Knowledge
. Eric (ED 247137).
Partin, R., 2009.The Classroom Teacher’s Survival Guide.
JohnWiley and Sons. San Fransisco,3
th
edition.
Permendikbud RI, 2003. Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan
dan kebudayaan (Permendikbud) Republik
Indonesia No 70 Tahun 2013 Tentang Kerangka
Dasar dan Struktur Kurikulum Sekolah Menengah
Kejuruan/Madrasah Aliyah Kejuruan.
Departemen
Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan
. Jakarta.
Permendiknas RI, 2007. Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan
Nasional (Permendiknas) Republik Indonesia No 16
Tahun 2007 Tentang Standar Kualifikasi Akademik
dan Kompetensi Guru.
Departemen Pendidikan
Nasional
. Jakarta.
Renol, S., 2015.Pengaruh kompetensiguru dan motivasi
belajar siswa terhadap prestasi belajar siswa kelas
XI IPS SMA Negeri 17 Medan. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional Pendidikan Ekonomiand Bisnis Fakultas
Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan Universitas Sebelas
Maret Surakarta. Surakarta.
Shulman, L.S., 1986. Those who understand:
knowledge growth in teaching. Educational
Researcher15,4-14.
Shulman, L.S., 1987. Knowledge and teaching:
foundations of the new reform.Harvard Educational
Review57(1),1-22.
Sumarno, W., Dhariva, U., 2014. Pengembangan
Perangkat Pembelajaranpada Materi Pokok Kalkulus
SMA Kelas XI Semester 2.Jurnal Riset Pendidikan
Matematika1(2),257-267.
Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 20 Tahun
2003 Tentang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional. 2003.
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional. Jakarta.
Van de Walle, J., 2007. Elementary and Middle School
Mathematics2nd Edition. Pearson Education. Canada.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
394
