
Critical Thinking Skill based on IQ and Gender in High School
Diah Mulhayatiah, Endah Kurnia Yuningsih, Siti Eriska Awalyah, Herni Yuniarti Suhendi, and
Sulasman Sulasman
UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, Jl. A H Nasution 105 Bandung, West Java, Indonesia
{diahmulhayatiah, endahkurnia, herni.suhendi}@uinsgd.ac.id, sitieriska70@gmail.com
Keywords: Worksheet, HOT, intelligence.
Abstract: Critical thinking skills are one of the necessary skills in learning so that students can become independent
learners. The research method used is quasi experiment with pretest - posttest experiment and control group
in MAN 1 Bandung with a sample is class XI, uses 8 questions essay test for critical thinking and 30 questions
multiple choices for IQ. The result based ANOVA with SPSS program, average score on each level of IQ and
gender group student is homogeneous. In experimental class, IQ influencing critical thinking skill, gender
influencing critical thinking skills, critical thinking skills due to gender influence depending on IQ, it shows
by the value of sig. in high, average, and low IQ more than 0.05. In the control class IQ influencing critical
thinking skills, gender influencing critical thinking skills, and critical thinking skills due to IQ influence is
independent of IQ. This research can provide information that students' critical thinking skills do not always
depend on the level of IQ and gender, but are dependent on the treatment provided. By knowing the influence
of IQ level and gender on critical thinking skill, it can be seen the right type of worksheet used in learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education in general aims to give each learner with
the ability to be able to adapt to his environment to
become an independent person and have the skills to
be able to solve any problems that arise. This is in line
with that stated by (Demirhan and Köklükaya, 2014)
which states it is very important every individual
develop habits of independent and critical thinking
skill. One of basic aims of education is to educate
every individual who are able to have critical thinking
skill. These critical thinking skills can be processed
through a learning process that can engage learners
with real problems and applications in everyday life.
Critical thinking skill can help individual more
adaptable and flexible to get information with the
rapid development (Dwyer et al., 2014)
The thinking skills of each learner will differ
depending on the characteristics of each individual.
The characteristics of this individual that can cause a
person's intelligence is different, so that this can then
distinguish the thinking patterns of students in solving
any problems that arise. (Stanovich and West, 2014)
says every individual differences in IQ test
performance usually thought to reflect variation in
ability for complex cognition. Such ability is itself
thought to differentiate as a kind of cognitive energy,
capacity, or “strength” variable. The result of research
(Westbrook and Sellers, 1967) there is a relationship
between critical thinking skill with intelligence.
The relationship between critical thinking based
on IQ and gender can happened. (Korkmaz, 2012)
said that multiple intelligence and critical thinking
dispositions and level increase, the skill and
performance students parallel increase too. That’s
why on intelligence sex different in human adults
impact to degree of self-reported liberalism in their
life (Woodley, 2010)
This difference in characteristics, intelligence,
and capabilities leads to the need for learning
facilities in the form of student worksheets required.
Student worksheets can assist students in
understanding the problem, trying to find the right
solution for problem solving, proving the solution,
and being able to deduce the results obtained through
the solution. Intelligence can involve creative and
critical thinking skill to evaluating if the idea was
good or not (Sternberg, 2015). Worksheets are
defined as important tools including the steps of this
process specified what the students should do next,
210
Mulhayatiah, D., Yuningsih, E., Awalyah, S., Suhendi, H. and Sulasman, S.
Critical Thinking Skill based on IQ and Gender in High School.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 210-214
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

help the students themselves set up their information
in their own minds and at the same time provide the
whole class to participate in the given activity
(Celikler and Aksan, 2012).
It is referred that worksheets make the students
active in learning environment showing the way of
getting the findings in a controlled way by making
observation, forming hypothesis and doing
experiments around the specific topic (Pablo
Fernández-Berrocal, 2012).
Strengthening the knowledge aspects for learners
in the learning process, the need for a learning
strategy that can build the knowledge of learners in a
self-directed manner. Building knowledge in-depth
can improve the thinking skills and scientific attitudes
of learners. This can start from a problem that is
closely related to the phenomenon of everyday life.
This learning strategy is called problem-based
learning
Problem-based learning guides learners to useful
facts and concepts that would not otherwise have
been encountered. Finally, problem-based learning
helps cultivate strategic learners and problem solvers
who can work with the local community as innovators
and embracers of productive, progressive education
(Etherington, 2011).The findings of the study
indicated that PBL is just as efficient as the
conventional teaching strategy in enhancing Form
Four students’ mathematics performance (Abdullah
et al., 2010).
Students' thinking ability has always been likened
to, but in reality there are often different values. As a
results teachers held a remedial so that students come
to the standard value that must be achieved. The
process of finding out why there are remedial and
student characteristics such as what typically often
experience remedial it can usually be analyzed based
on IQ (Intelligence Quotients). This is in accordance
with that proposed by (Elliott and Resing, 2015) that
the original function of IQ testing was to ascertain
whether a child was capable of profiting from
schooling, there are many who now claim that
cognitive assessment offers a range of diagnostic and
prescriptive functions which can help teachers in
delivering effective educational programs.
High order thinking can help students to get a
solution to solve the problem in their life. Creative
and critical thinking skill are two of high order
thinking. (Russo, 2004) based on his research said
that there has a significant interaction between
student performance with IQ overtime with verbal,
and there was an increase for average student in IQ
on their performance.
This study aims to determine the effect of
problem-based learning student worksheet on
students' thinking ability on dynamic fluid material
reviewed based on IQ classification and gender so
that it will be seen whether there is influence of IQ
and gender in critical thinking skill and determining
the most dominant student of learning by using this
worksheet will be at a certain IQ level and gender.
2 METODOLOGY
The method used in this research is a quasi-
experimental method with static group comparison
design (Fraenkel and Wallen, 2003). The number of
students in the control class is 28 and the
experimental class is 30 in this design. The
experimental group and the control group are not
randomly selected. Data obtained from this research
is in the form of post test data obtained from critical
thinking skill test using written test with 8 problem
description which have been taken from 16 problems
made and have the best feasibility. IQ determination
using multiple choice questions as many as 30
questions.
The learning process uses a Student Worksheet
containing worksheets based on Problem Based
Learning model, with Dynamic Fluid material.
All data were tested for normality and
homogeneity then calculated its effect with two path
ANOVA test using SPSS program.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of this study using ANOVA test, which
previously tested the normality and homogeneity of
data both for the control class and experimental class.
Table 1 presents the results of normality calculations
for the experimental class.
Table 1: Tests of Normality experiment class.
IQ
Shapiro-Wilk
Stat.
df
Sig.
High
.959
5
.803
Average
.951
21
.353
Low
.945
4
.683
The significance value for the three experimental
grade IQ levels shows a value greater than 0.05 so that
the experiment class data is normally distributed. The
Critical Thinking Skill based on IQ and Gender in High School
211
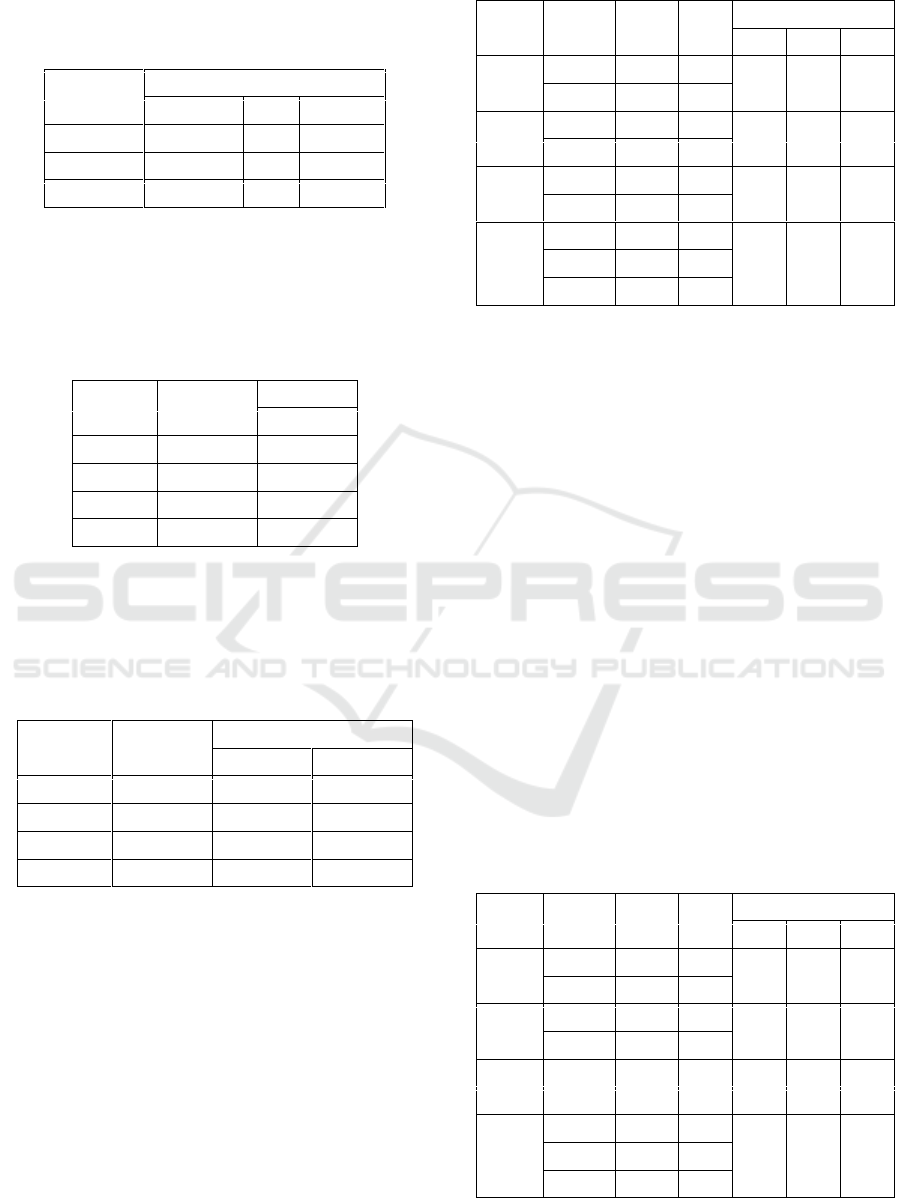
results of control class normality are presented in
Table 2.
Table 2: Tests of Normality control class.
IQ
Shapiro-Wilk
Stat.
df
Sig.
High
.907
3
.407
Average
.904
22
.136
Low
.923
3
.464
Table 2 presents the significance for all three
levels of control class IQ showing values greater than
0.05 so that control class data are also normally
distributed.
Table 3: Tukey HSD Homogeneus Experiment Class.
IQ
N
Subset
1
Low
4
71.8775
Average
21
76.5976
High
5
79.2120
Sig.
.051
Table 3 show homogeneity results for the
experimental and control classes, whose significance
value is greater than 0.05 so that the data is
homogeneous.
Table 4: Tukey HSD Homogeneus Control Class.
IQ
N
Subset
1
2
Low
3
61.4600
Average
22
68.8945
68.8945
High
3
80.2100
Sig.
.581
.296
Table 4 show homogeneity results for the control
classes, whose significance value is greater than 0.05
so that the data is homogeneous.
Next analysis is the value of ANOVA for IQ and
gender impact on critical thinking skills in the
experimental class. To see the affect of gender and IQ
to critical thinking skill there is three partition, gender
affect to critical thinking skill, IQ affect to critical
thinking skill and due IQ and gender affect to critical
thinking skill.
Table 5: ANOVA Experiment Class.
Variable
Gender
Mean
SD
Significance
High
Avg
Low
High IQ
Boy-1
71.06
5.10
0.567
0.103
Girl-4
81.25
6.34
Average
IQ
Boy-6
76.42
4.06
0.567
0.228
Girl-15
76.47
5.65
Low IQ
Boy-1
71.88
3.13
0.103
0.228
Girl-3
71.88
2.55
Total
Boy-8
75.18
4.13
Girl-22
76.85
5.76
Total-30
76.40
5.36
Table 5. shows that the value of gender, IQ, and
gender with IQ greater than 0.05. Sig. High IQ to
average and lower is more than 0.05, sig. average IQ
to high and lower is more than 0.05 and sig lower IQ
to high and average is more than 0.05. It is means that
critical thinking skills are influenced by IQ and
gender. IQ and gender both influence each other in
determining students' critical thinking skills through
the use of worksheet based problem based learning.
This research can provide information that students
'critical thinking skills can depend on IQ and are
influenced by gender, so IQ can influence students'
critical thinking skills, as explained by (Kafadar et al.,
2015) The statistical analyses demonstrated that the
IQ Up Cognitive Training Program affects the
cognitive development of children positively. Lower
and higher IQ associated with level offending
thinking, so the result is have a relationship with
curve linier (Mears and Cochran, 2013) . (Chandra,
2013) based on their research said that IQ influenced
to academic performance but not gender not
influenced.
Table 6: ANOVA Control Class.
Variable
Gender
Mean
SD
Significance
High
Avg
Low
High IQ
Boy-2
71.87
4.42
0.222
0.104
Girl-1
96.88
14.77
Average
IQ
Boy-4
82.35
12.85
0.222
0.508
Girl-18
65.97
10.98
Low IQ
Boy-3
61.46
6.50
0.104
0.508
Girl-3
61.46
6.50
Total
Boy-6
78.65
11.43
Girl-22
66.76
12.22
Total-28
69.31
12.84
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
212

The significance value of IQ and gender influence
to students 'critical thinking skill in the control class
is greater than 0.05, it shows by table 6. It is means
that IQ and gender influence to students' critical
thinking skills, whereas critical thinking skills due to
IQ influence are independent of gender and critical
thinking skills because gender influence is
independent of IQ.
However, the overall use of problem-based
learning worksheets in learning can provide an
improvement in the critical thinking skills of students
both influenced by IQ, gender, or both. This is in
accordance with what is said by (Bakırcı et al., 2011)
Considering the analysis results, it was concluded that
use of worksheets and simulation technique together
has positive effects on students’ hypothetical,
correlation and combinational thinking skills.
4 CONCLUSIONS
IQ and gender influence students' critical thinking
skills through using worksheet based problem-based
learning. IQ and gender affect to increase critical
thinking skill but indirect. The impact of this research
is even critical thinking skill affected both by IQ and
gender but we must separately the individual
differences in performance cognitive so does the
critical thinking because the conceptual and
empirically different. Why, because does not high IQ
have a good on performance critical thinking but
majority was good. It is like (Cho, 2010) said that
high IQ not always predict high performance and
selection good strategy. So we can development the
right worksheet to use in learning.
Suggest for next research is see intelligence based on
multiple intelligence because it more various
intelligence.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks to Lembaga Pusat Penelitian dan
Pengembangan (LP2M) UIN Sunan Gunung Djati
Bandung who has provide funds for the realizations
this paper.
REFERENCES
abdullah, N. I., Tarmizi, R. A., Abu, R. 2010. The Effects
of Problem Based Learning on Mathematics
Performance and Affective Attributes in Learning
Statistics at Form Four Secondary Level. Procedia -
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 8, 370-376.
Bakırcı, H., Bilgin, A. K., Simsek, A. 2011. The effects of
simulation technique and worksheets on formal
operational stage in science and technology lessons.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 15, 1462-
1469.
Celikler, D., Aksan, Z. 2012. The Effect of the Use of
Worksheets About Aqueous Solution Reactions on Pre-
service Elementary Science Teachers’ Academic
Success. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences,
46, 4611-4614.
Chandra, R. 2013. Influence of Intelligence and Gender on
Academic Achievement of Secondary School Students
of Lucknow City.
Cho, S. 2010. The role of IQ in the use of cognitive
strategies to learn information from a map. Learning
and Individual Differences, 20, 694-698.
Demirhan, E., Köklükaya, A. N. 2014. The Critical
Thinking Dispositions of Prospective Science
Teachers. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences,
116, 1551-1555.
Dwyer, C. P., Hogan, M. J., Stewart, I. 2014. An integrated
critical thinking framework for the 21st century.
Thinking Skills and Creativity, 12, 43-52.
Elliott, J., Resing, W. 2015. Can Intelligence Testing
Inform Educational Intervention for Children with
Reading Disability? Journal of Intelligence, 3, 137.
Etherington, M. B. 2011. Investigative Primary Science: A
Problem-based Learning Approach. Australian Journal
of Teacher Education, 36, 53-74.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E. 2003. How to design and
evaluate research in education, McGraw-Hill Higher
Education.
Kafadar, H., Akıncı, Z., Çakır, B. 2015. Effects of the IQ
up Cognitive Development Method on the Cognitive
Development of 10- to 12-Year-old Children. Procedia
- Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 3243-3253.
Korkmaz, Ö. 2012. The Impact of Critical Thinking and
Logico-Mathematical Intelligence on Algorithmic
Design Skills. Journal of Educational Computing
Research, 46, 173-193.
Mears, D. P., Cochran, J. C. 2013. What is the effect of IQ
on offending? Criminal Justice and Behavior, 40, 1280-
1300.
Pablo Fernández-Berrocal, R. C., Ruth Castillo., Natalio
Extremera 2012. Gender Differences In Emotional
Intelligence: The Mediating Effect Of Age. Behavioral
Psychology / Psicología Conductual, 20, 77-89.
Russo, C. F. 2004. A Comparative Study of Creativity and
Cognitive Problem-Solving Strategies of High-IQ and
Average Students. Gifted Child Quarterly, 48, 179-190.
Critical Thinking Skill based on IQ and Gender in High School
213

Stanovich, K. E., West, R. F. 2014. The Assessment of
Rational Thinking. Teaching of Psychology, 41, 265-
271.
Sternberg, R. J. 2015. Successful intelligence: A model for
testing intelligence beyond IQ tests. European Journal
of Education and Psychology, 8, 76-84.
Westbrook, B. W., Sellers, J. R. 1967. Critical Thinking,
Intelligence, and Vocabulary. Educational and
Psychological Measurement, 27, 443-446.
Woodley, M. A. 2010. Are high-IQ individuals deficient in
common sense? A critical examination of the ‘clever
sillies’ hypothesis. Intelligence, 38, 471-480.
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
214
