
The Description of Cognitive Function on Dementia Elderly in
Ciparay Tresna Wreda Social Protection Center
Putri Citra Resmi, Lisna Anisa Fitriana and Afianti Sulastri
Faculty of Sport and Health Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jln. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229 Bandung, Indonesia
putriresmi@gmail.com
Keywords: Elderly, Dementia, Cognitive Function.
Abstract: Along with the health and welfare of the population, the number of elderly are increasing. It caused the
number of degenerative diseases getting higher. One of them is dementia. Dementia is a global cognitive
impairment progressive. Impaired cognitive function can be quite serious health problems seriously which
can cause psychological, social and economic such as social isolation, financial difficulties, motor is
retardation, aggravate other symptoms and identify the quality of life of the elderly. The purpose of this
study is a picture on description of cognitive function on elderly dementia at the center of social protection
for elderly in Ciparay Bandung. This study used descriptive quantitative. Design technique purposive
sampling from 40 elderly people with dementia aged > 60 years, they were in health based on nursing
assessment and nine signs checking, results of score the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) < 24. The
research instrument used the Trail Making Test - B (TMT-B) with a frequency distribution analysis data.
The results of this study were found data majority elderly dementia cognitive impairment were less and
elderly dementia cognitive impairment just a little. From this research, it can be concluded that the
description of cognitive function in elderly patients with dementia in the Center of Social Protection for
Elderly in Ciparay majority experienced less cognitive function. Recommendations for the BPSTW Ciparay
is necessary holding of activities of brain for the elderly like play crosswords puzzle, embroider and other
activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on WHO data, in recent years there has been
an increase in the elderly population in Southeast
Asia by 8% or about 142 million people. This
condition is expected to increase threefold by 2050.
Nowadays there are special health challenges with
increasing number of elderly. The emergence of
degenerative and multipathological problems, such
as decreased biological reserves, changes in
symptoms and signs of disease, disruption of
functional status of elderly patients is most notable
is the decline in cognitive function (Tsilimparis et
al., 2013).
A meta-analytic study was conducted to examine
the hypothesis that aerobic fitness training enhances
the cognitive vitality of healthy but sedentary older
adults. Eighteen intervention studies published
between 1966 and 2001 were entered into the
analysis (Colcombe and Kramer, 2003). The
phenomenon of worry is considered to arise from
cognitive processes involved in anxiety, that serve to
maintain high levels of vigilance for personal
danger. Rather than rely on self-report alone, the
research described here draws on information
processing methodology, to investigate this
hypothesized cognitive function (Mathews, 1990).
This individual differences study examined the
separability of three often postulated executive
functions—mental set shifting (“Shifting”),
information updating and monitoring (“Updating”),
and inhibition of prepotent responses
(“Inhibition”)—and their roles in complex “frontal
lobe” or “executive” tasks. One hundred thirty-seven
college students performed a set of relatively simple
experimental tasks that are considered to
predominantly tap each target executive function as
well as a set of frequently used executive tasks: The
Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), Tower of
Hanoi (TOH), random number generation (RNG),
operation span, and dual tasking (Miyake, et al.,
2000).
Cognitive function is part of the lofty cortical
function, where knowledge of noble cognitive
452
Resmi, P., Fitriana, L. and Sulastri, A.
The Description of Cognitive Function on Dementia Elderly in Ciparay Tresna Wreda Social Protection Center.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 452-457
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

functions links human behavior with the nervous
system. Cognitive function consists of the ability of
attention, language, memory, visuospatial and
executive functions. Impaired cognitive function
occurs when one or more cognitive functions are
damaged.
There was evidence of an increase in
responsiveness, strongly in the analogue and less in
the digital simulation, in choice reaction time. This
could be associated with an effect on the angular
gyrus that acts as an interface between the visual and
speech centres and which lies directly under and on
the same side as the antenna. Such an effect could be
consistent with mild localized heating, or possibly a
non-thermal response, which is nevertheless power-
dependent (Preece, 1999).
Dementia is a general term used to describe the
progressive destruction of global cognitive function
and affect normal occupational activity as well as
daily life activities. Diseases that increase the
symptoms of dementia include Alzheimer's disease,
vascular problems such as multi-infarction dementia,
normal pressure hydrocephalus, Parkinson's disease,
chronic alcoholism, picky diseases, Huntington
disease brain progressively), and Acquired Immune
Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). The prevalence of
dementia disorder becomes higher with increasing
human age, the most common form of Alzheimer's
disease in the elderly, followed by multi-infarction
dementia (Folkman et al., 1997).
These results are important in that behavior
analytic methods were shown to have utility for: (1)
assessing the functional relationship between
environmental contingencies and behaviors related
to differential diagnosis; and (2) evaluating the
independent and interactive effects of behavioral and
pharmacologic treatments (Kelly et al., 1989).
The results from Experiment 1 indicate that
measures of working-memory capacity and verbal
information-processing speed correlate with speech
recognition in noise. The pattern of results was
consistent with the idea that when auditory
processing becomes very difficult, because of an
adverse listening situation and a damaged cochlea,
the individual’s cognitive function influences
performance to a high degree (Pichora- Fuller et al.,
1995).
Alzheimer dementia (dementia) is a degenerative
disease in which the decline in brain function that
affects emotion, memory, decision making, behavior
and other brain functions that interfere with daily
activities (Herholz et al., 2002). Alzheimer's disease
is most commonly found in aged parents & gt; 65
years, but can also attack people aged around 40
years.
Previous research was conducted on the
description of cognitive function in elderly in Three
Yayasan Manula in Kecamatan Kawangkoan get
result of research obtained 61 people who meet
inclusion criteria consist of four men and 57 women.
Based on age, and educational level showed the
most decrease in cognitive function was at age 75 -
90 years and last elementary school education
(Shadlen, 2001).
After conducting preliminary study at Tresna
Wredha Ciparay Social Protection Center, there
were 63 dementia population data from 150 elderly
people with initial screening using Mini Mental
State Examination (MMSE). So based on the
background that has been described the researcher
will conduct research on "The Cognitive Function of
Dementia in Elderly Age at Social Protection Center
Tresna Wreda Ciparay Bandung Regency".
2 METHODS
The design used in this study is descriptive
quantitative design that aims to describe (describe)
the image of cognitive function in elderly dementia
at the Center for Social Protection Tresna Wreda
Ciparay Bandung Regency.
The population in this study is all elderly
dementia as much as 63 elderlies. Sampling
technique used is purposive sampling in which the
sample was taken based on some considerations.
Sample size 40 is dementia elderly according to
inclusion criteria 1) Aged more than 60 years, 2)
Healthy by anamnesa and vital signs check 3)
Dementia elderly with MMSE score less than or
equal 24, 4) Understanding research objectives and
research procedures, 5) Willing to complete the
cognitive ability test by signing informed consent.
The instrument is Trail Making Test - B to
examine cognitive function in elderly dementia.
TMT - B is a test that measures the planning,
organizing, and execution skills of a person. The
variable used in this research is cognitive function in
elderly dementia.
3 RESULTS
The following will show the demographic
characteristics of the results of the study of cognitive
The Description of Cognitive Function on Dementia Elderly in Ciparay Tresna Wreda Social Protection Center
453
function in elderly dementia at BPSTW Ciparay
Bandung regency.
Table 1: Frequency distribution of general characteristics
of respondents by sex in BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Gender
Frequency
Percentage
Male
14
35 %
Female
26
65 %
Total
40
100 %
Based on table 1 40 respondents mostly (65%)
are female as 26 people are elderly.
Table 2: Frequency distribution of general characteristics
of respondents by sex in BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Age Characteristics
Frequency
Percentage
60-74 years old
18
45 %
75-90 years old
21
52,5 %
> 90 years old
1
2,5 %
Total
40
100%
Based on table 2, from 40 respondents, most of
them (52.5%) aged 75 - 90 years as many as 21
people elderly.
Table 3: Frequency distribution of general characteristics
of respondents based on educational background at
BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Education
Frequency
Percentage
N/A
10
25 %
Elementary School
16
40 %
Junior High School
9
22,5 %
Senior High School
2
5 %
College
3
7,5 %
Total
40
100 %
Based on table 3 from 40 respondents almost half
(40%) of elementary education background that is as
many as 16 people.
Specific Data
Table 4: Frequency distribution of respondent
characteristics based on cognitive function in BPSTW
Ciparay in May 2017.
Cognitive Function
Frequency
Percentage (%)
Good
3
7,5 %
Bad
37
92,5 %
Total
40
100 %
Based on table 4, Most of the respondents
(92,5%) has low cognitive function as many as 37
people.
Table 5: Frequency distribution of respondent
characteristics based on Gender and cognitive function in
BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Gender
Cognitive Function
Total
Number
Percentage
Good
Percentage
Bad
Percentage
Male
0
14
37,8%
14
(35%)
Female
3
100%
23
62,2%
26
(65%)
Total
3
100%
37
100%
40
(100 %)
Based on table 5 from 40 respondents, most of
them (62.2%) are female as many as 26 people.
Table 6: Frequency distribution of respondent
characteristics based on Gender and cognitive function in
BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Age
Cognitive Function
Total
Number
Percentage
Good
Percentage
Bad
Percentage
60-74
years
old
2
66,7%
16
43,2 %
18
45 %
75-90
years
old
1
33,3 %
20
54,1 %
21
52,5 %
> 90
years
old
0
1
2,7 %
1
2,5 %
Total
3
100 %
37
100%
40
(100%)
Table 6 showed that most of the respondents
(66,7%) age between 60 - 74 years old have good
cognitive function and many of them as many as
54,1% age between 75 -90 have low cognitive
function.
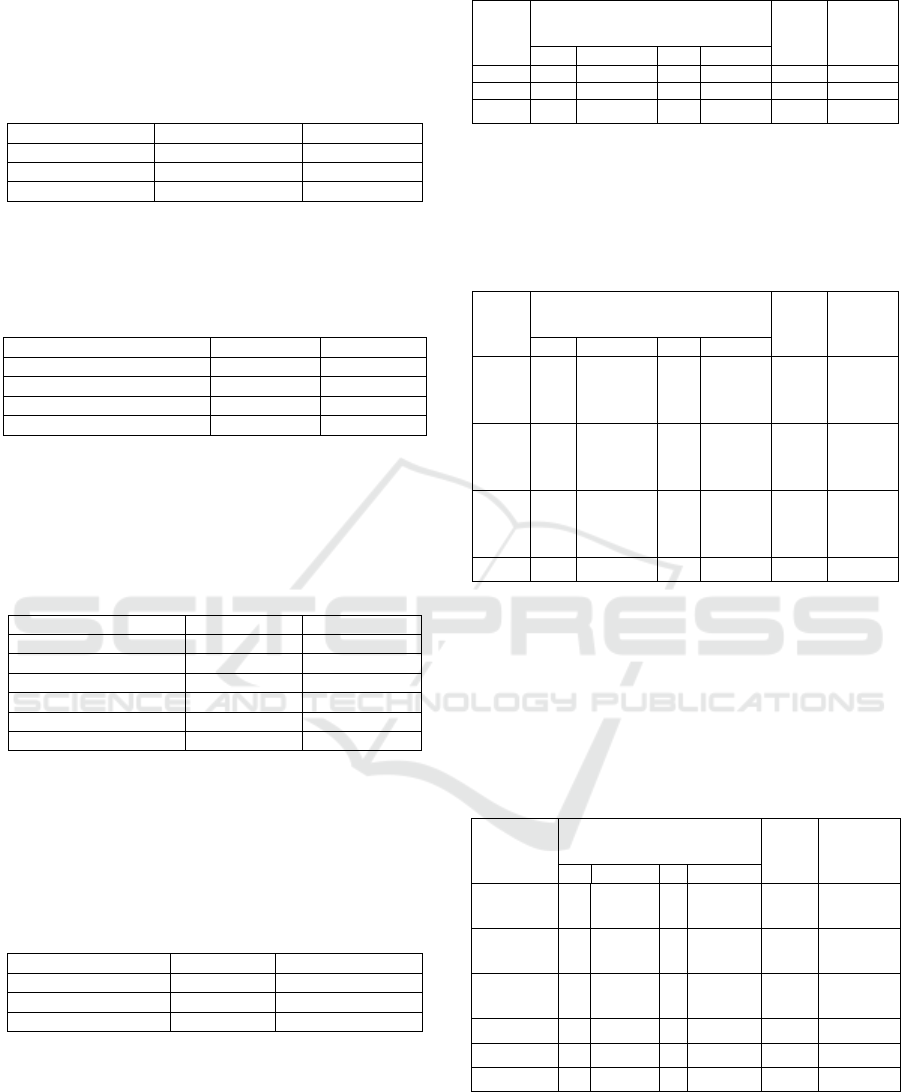
Table 7: Frequency distribution of respondent
characteristics based on Education and cognitive function
in BPSTW Ciparay in May 2017.
Educational
Background
Cognitive Function
Total
Number
Percentage
Good
Percentage
Bad
Percentage
Elementary
School
0
16
43,2%
16
(40%)
Junior High
School
0
9
24,3%
9
(22,5%)
Senior High
School
1
33,3%
1
2,7%
2
(5%)
College
2
66,7%
1
2,7%
3
(7,5%)
N/A
0
10
27,1%
10
(25%)
Total
3
100%
37
100%
40
(100%)
Table 7 showed that as many as 66,7%
respondents with college educational background
have good cognitive function and those who only
attend elementary school and did not attend any
school have low cognitive function.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
454

4 DISCUSSION
4.1 The Description of Cognitive
Function of the Elderly in BPSTW
Ciparay
From 40 respondents, almost all respondents
(92,5%) has low cognitive function as many as 37
people and most of them are women 62,2% with
elementary school educational background. Only 7,5
% have good cognitive function. They are three
female elderlies; one senior high school graduate
and two college graduates. In addition, the three
elderly have daily habits of embroidering, making
accessories and activities to hone other skills (see
tables 4, 5 and 7)
4.2 The Description of Cognitive
Function of the Elderly Based on
Gender in BPSTW Ciparay
Table 5 shows that generally cognitive function is
less experienced mostly by elderly women (62.2%)
while in elderly men as many as 14 people (37.8%).
This is in line with the theory according to Myers
(2008) that women are more at risk of decreased
cognitive function than in men. The theory explains
the role of endogenous sex hormone levels in
changes in cognitive function. Estrogen receptors
have been found in areas of the brain that play a role
in learning and memory functions. Then the decline
in general and verbal cognitive function is associated
with low levels of estradiol in the body. Estradiol is
neuroprotective that can limit damage due to
oxidative stress and as a protector of nerve cells
from amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer's patients.
The results of this study also in accordance with
previous research on the Cognitive Functional View
of the Elderly at UPT Panti Werdha Mojopahit
Mojokerto regency obtained the results of the study
of decreased cognitive function weigh more
experienced by the women than men. In this study,
most data (85.7%) elderly female gender
experienced severe cognitive function change that is
as many as 12 elderly people (Maryani et al., 2013).
4.3 The Description of Cognitive
Function of the Elderly Based on
Age in BPSTW Ciparay
Table 6 showed that most of the respondents
(66,7%) age between 60 - 74 years old have good
cognitive function and many of them as many as
54,1% age between 75 -90 have low cognitive
function. This suggests that age significantly affect
cognitive function. The older someone is, the greater
the chances and the more severe the cognitive
function impairment experienced by the elderly.
This is because age is one of the factors causing the
cognitive impairment.
In the results of this study the average age of
aged between 75-90 years experienced a decline in
cognitive function ability. In Bandiyah (2009), it is
explained that the increasing of one's age hence the
speed of process at nerve center decreasing which
can cause change of cognitive function decline. The
decline of cognitive function before the age of 50 is
abnormal and pathological. Changes in cognitive
function experienced by almost everyone who
reached the age of 70 years. At the age of 65-75
years, there is deterioration in some abilities. Over
the age of 80 years, there is considerable
deterioration.
Previous research was conducted by Ramadian
(2013) on the description of cognitive function in
elderly in Three Yayasan Manula in Kecamatan
Kawangkoan get result of research obtained 61
people who meet inclusion criteria consist of four
men and 57 women. Based on age, and educational
level showed the most decrease in cognitive function
was at age 75 - 90 years and last elementary school
education.
4.4 The Description of Cognitive
Function of the Elderly Based on
Age in BPSTW Ciparay
Table 7 showed that as many as 66,7% respondents
with college educational background have good
cognitive function and those who only attend
elementary school and did not attend any school
have low cognitive function. This suggests that the
higher a person's education level is, the more likely
it is to increase the chances of maintaining his
cognitive function.
This is supported by the explanation in
Bandiyah (2009) that the higher the education of a
person the easier it will be to receive information,
and eventually the more knowledge he has. In this
case it can indirectly improve cognitive function in a
person. Conversely, a person with a low level of
education will inhibit the development of a person's
cognitive function of acceptance, information and
new things received (Bandiyah, 2009).
In addition, the results of this study also in
accordance with previous research by Maryani et al.
(2013) regarding the Cognitive Function of the
The Description of Cognitive Function on Dementia Elderly in Ciparay Tresna Wreda Social Protection Center
455

Elderly at UPT Panti Werdha Mojopahit Mojokerto
regency obtained data mostly (64.3%) who did not
attend school decreased weight cognitive function.
As described above that the results of this study
are the three elderly people who have good cognitive
functions have a daily habit of embroidering,
making accessories and activities to hone other
skills. This is in line with the theory of Exercise
related to the development of cognitive function of
the elderly. The elderly who often train their
memories by performing day-to-day activities
productively and supported by skills has a good
cognitive functioning ability compared to the elderly
who have a habit at home without practicing
cognitive abilities.
These exercises are useful in the attention aspect
which refers to a person's ability to respond to
specific stimuli by ignoring other stimuli outside his
environment. This can help in maintaining good
cognitive function.
Based on the description of the results of this
study note that cognitive function is determined by
various factors. The main and most common factor
in all elderly dementia is the exercise of cognitive
function or activity that can train the brain. By doing
brain training activities such as playing TTS,
embroidering, playing chess and others then
cognitive function can be prevented severity or at
least can maintain the condition of cognitive
function owned by elderly dementia.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research, it can be concluded that:
The results of this study indicate that the
picture of cognitive function in elderly
dementia in BPSTW Ciparay Bandung
Regency almost entirely suffer less cognitive
function and few elderly dementias whose
cognitive function is still good;
The results of this study indicate that the
picture of cognitive function in elderly
dementia based on sex in BPSTW Ciparay
Bandung Regency mostly have less cognitive
function in elderly female dementia;
The results of this study indicate that the
picture of cognitive function in elderly
dementia based on age in BPSTW Ciparay
Bandung Regency is mostly elderly dementia
aged 75 - 90 years have less cognitive
function;
The results of this study indicate that the
picture of cognitive function in elderly
dementia based on educational background in
BPSTW Ciparay Bandung Regency is most of
elderly dementia elementary school have low
cognitive function with the demand of such
raw materials in a certain period. The
company can save a significant inventory cost
by using appropriate technique in inventory
management.
REFERENCES
Bandiyah, S., 2009. Seniors and Nursing Gerontik, Musha
Medika. Yogyakarta.
Colcombe, S., Kramer, A. F., 2003. Fitness effects on the
cognitive function of older adults: a meta-analytic
study. Psychological science. 14(2), pp.125-130.
Folkman, S., Moskowitz, J. T., Ozer, E. M., Park, C. L.,
1997. Positive meaningful events and coping in the
context of HIV/AIDS. Coping with chronic stress (pp.
293-314). Springer, Boston, MA.
Herholz, K., Salmon, E., Perani, D., Baron, J. C., Holthoff,
V., Frölich, L., Schönknecht, P., Ito, K., Mielke, R.,
Kalbe, E., Zündorf, G., 2002. Discrimination between
Alzheimer dementia and controls by automated
analysis of multicenter FDG PET. Neuroimage. 17(1),
pp.302-316.
Kelly, J. A., Lawrence, J. S. S., Hood, H. V., Brasfield, T.
L., 1989. An objective test of AIDS risk behavior
knowledge: Scale development, validation, and norms.
Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental
Psychiatry. 20(3), pp.227-234.
Maryani, S. A. N. M., Putra, E., Artawan, I. W. G.,
Indraguna, P. G. N., 2013. Association Between
Nutritional Status and Intelligence Quotient of Junior
High School Students in Denpasar. Public Health and
Preventive Medicine Archive. 4(1), 35-42.
Mathews, A., 1990. Why worry? The cognitive function of
anxiety. Behaviour research and therapy. 28(6),
pp.455-468.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A.
H., Howerter, A., Wager, T. D., 2000. The unity and
diversity of executive functions and their contributions
to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable
analysis. Cognitive psychology. 41(1), pp.49-100.
Myers, J. S., 2008. Factors associated with changing
cognitive function in older adults: Implications for
nursing rehabilitation. Rehabilitation Nursing. 33(3),
117-123.
Pichora-Fuller, M. K., Schneider, B. A., Daneman, M.,
1995. How young and old adults listen to and
remember speech in noise. Journal of the Acoustical
Society of America. 97(1), 593–608.
Preece, A. W., 1999. Effect of a 915-MHz simulated
mobile phone signal on cognitive function in man.
International journal of radiation biology. 75(4),
pp.447-456.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
456

Ramadian, D. A. (2013). 1 Gambaran Fungsi Kognitif
Pada Lansia di Tiga Yayasan Manula di Kecamatan
Kawangkoan. E-clinic. 1(1).
Shadlen, M. F., 2001. Ethnicity And Cognitive
Performance Among Older African Americans,
Japanese Americans, and Caucasians: The Role Of
Education. Journal of The American Feriatrics
Society.
Tsilimparis, N., Perez, S., Dayama, A., Ricotta, J. J., 2013.
Endovascular repair with fenestrated-branched stent
grafts improves 30-day outcomes for complex aortic
aneurysms compared with open repair. Annals of
vascular surgery. 27(3), pp.267-273.
The Description of Cognitive Function on Dementia Elderly in Ciparay Tresna Wreda Social Protection Center
457
