
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the
Table Tennis Playing Skills
Eneng Fitri Amalia, Herman Subarjah, and Indra Safari
PPs Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
fitriyuniar120@gmail.com
Keywords: Skills, Motivational Exercises, Motor Skills.
Abstract: This study aims to determine the effect of exercise motivation and motor skills on table tennis playing skills
at junior athletes PTMSI Cianjur regency of West Java, and to know the difference of influence between them
to the skills of playing table tennis. The method used in this research is ex post facto. To obtain the data in
the field, this research uses exercise motivation scale and motor ability test, and test of table tennis ability is
arranged based on indicator. The data needed in this research are exercise motivation data (X1), motor skills
(X2), and table tennis skills (Y). Based on the results of processing and data analysis obtained conclusion as
follows; 1) There is a positive effect of exercise motivation on the skills of playing table tennis. 2) There is
an influence of motor skills on the skills of playing table tennis. And 3) There is a difference in the effect of
exercise motivation and motor skills on table tennis skills in junior athletes PTMSI Cianjur regency of West
Java, where sports motivation contribute more to the skills of playing table tennis when compared with motor
skills. Motivation exercises play a very important role in improving the quality of the exercise process in table
tennis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sports coaching among the community is aimed at
stimulating and growing the motivation and
participation of the community to exercise actively
and purposefully so that everyone will accept and
exercise as an integral part of their life. Sport
coaching is done well and boils down to the increase
in achievement. Especially if done gradually, tiered
and continuously through search and monitoring,
breeding and filing and education based on science
and technology effectively and efficiently. This fact
shows that sports coaching is essential to
achievement, which in turn can bring the name of the
nation and the country on the international stage.
A fact that can be observed in the sports world
shows the tendency of a rapid increase in sport
performance from time to time. This can be seen from
the continuous record-breaking of certain sports, and
the appearance of more effective and efficient
movement techniques supported by excellent
physical and psychological conditions. Given the
increasing trend of achievement, to participate and
compete with other players in the sport of
achievement, it must develop the physical quality,
technique, and tactics demanded by certain
sports. For that required a program of guidance of
achievement that are planned, directed, implemented,
and executed systematically. Many factors must be
taken into account in developing a sports performance
improvement program, including clear coaching
objectives, appropriate training materials and
methods, and evaluations that can measure the
success of the coaching process itself. Besides, it is
also necessary to consider the characteristics of
athletes who are nurtured both physically and
technically, tactically, the ability of trainers, facilities
and facilities, as well as environmental conditions of
coaching. Therefore, coaching and development of
sporting achievements especially at an early age
should be handled more seriously and become a
complex national program, as it demands
fundamental and comprehensive conceptual thinking
as well as ongoing implementation from early age to
golden age.
One group of people who became the object of
fostering and socializing the sport is a young age
group in schools and sports clubs. As one of the
targeted groups, this group is a group that should get
attention, because this group enables the possibility
of emergence of athletes achievement. In these times
physical activity in the form of a game is the activity
Amalia, E., Subarjah, H. and Safari, I.
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the Table Tennis Playing Skills.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 295-304
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
295

most interested by children. Sports coaching among
children is mainly to facilitate the physical,
psychological, environmental and social
development of children through playing and
training, with pleasant physical activity. To socialize
sports among children, a few things need to be taken
into consideration, among them are the sports should
be interesting, easy to play, fun and the availability of
tools and facilities and coaches or coaches. These
criteria have been owned by several sports including
table tennis.
Indonesia‘s national tennis coaching pattern is
implemented in stages. To achieve high achievement,
a tennis athlete first learns and practices starting from
an early age in clubs, and subsequently fostered in
centralizing the region. Today, Indonesia is one of the
countries that has many table tennis players. Several
local, national and international events are mostly
conducted. However, recently with the increasingly
tight competition in the world table tennis, felt the
stagnation of the development of table tennis
performance in Indonesia, Some table tennis players
are not able to speak much. Forget about winning the
world championship, we cannot even stand out much
in the Southeast Asia championship. It has been
difficult for Indonesian table tennis players to win
official championship events. Even today it can be
said that Indonesian tennis players become athletes
who are ranked below and not counted well for Asian
championships. As a result, it must be anticipated and
resolved, the tennis community through the Parent of
the national sports organization should set up and
develop a coaching system to boost the achievement
of tennis at the International championships. The All
Indonesia Tennis Association should seek to evaluate
carefully and improve existing coaching patterns, and
develop them towards a better, more effective and
efficient. One of them is by examining aspects of
physical and technical aspects of psychology in
several societies of tennis in Indonesia.
The coaching of the table tennis sport at a young
age is a starting point for coaching, with planned,
regular, programmed, systematic, and continuous,
expected, time-consuming, “Golden Age“ exercises
expected athletes to achieve optimal
performance. For that it should not only fix the
athletes‘ achievement right now, but no less
important is to foster and develop buds of talented
athlete as early as possible so that at “golden age“ the
athlete is able to excel as much as possible.
Athlete coaching on individual game sports like
table tennis requires careful handling and coaching on
an individual basis. To achieve the achievement of
the optimal table tennis, athlete is required the process
of learning and training which are done carefully,
continuous starting from junior, systematically, tiered
and continuous. For that we need an in-depth study of
how to improve the skills of playing table tennis to
achieve optimal performance. The author tries to
examine and analyze from the physical and
psychological aspects as well as his influence on the
skills of playing table tennis.
As for the authors of the study, among others,
about exercise motivation and athletic motor skills,
which allegedly can affect the skills of playing table
tennis. For that need to be studied in depth through
this research.
Based on the background, problem identification
and problem restrictions that have been proposed, it
can be formulated problems in this study, as follows:
1. Can exercise motivation affect the learning
outcomes of playing tennis skills in junior
athletes?
2. Will motor ability affect the learning outcomes
of playing tennis skills in junior athlete's son?
3. Is there any difference in the effect of
motivation of exercise with motor ablity, to
the learning outcomes of playing tennis skill in
male junior athlete?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theoretical Review
Before describing the results of learning the skills of
playing table tennis, first described about learning
motion skills. Because the skills of playing table
tennis can only be controlled after going through the
learning process and one type of learning that is
closely related to the mastery of such skills is learning
motion skills.
Understanding the learning of motion skills in this
study is assumed to be commensurate with motor
learning, because learning motion as a process that
leads to the effort to acquire changes in motion
behavior is closely related to the term skill, this is due
to changes in behavior expected from motion study in
the form of motion skills in the sense broad, therefore
skill is a manifestation of the result of motion
learning. Although there is a diversity of opinion of
experts on the notion of learning, but generally in
some basic matters. They agree that learning includes
at least three basic characteristics: (1) learning is
characterized by behavioral change, (2) change is
relatively permanent, (3) change is obtained through
training or experience. Further Burden and Byrd cite
Bloom's view of the domain of learning goals stating
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
296

that; Changes in learning behavior include three
categories of domains: (1) cognitive behavior, (2)
affective behavior, and (3) motor behavior.
Changes in cognitive behavior in the form of
intellectual thinking skills, affective behavior is
characterized by the response attitude, feelings,
emotions, and motivation of athletes to learning,
while motor behavior in the form of motion of the
limbs under the control of the nervous system. These
three domains serve as the criteria of change that must
be attained by athletes, and the degree of mastery of
the athlete against the learning objectives is called
learning outcomes.
Based on the description it can be argued that
learning is a process that leads to behavioral changes
(either cognitive, affective, or psychomotor) that is
relatively settled as a result of the exercise process or
experience and not because of the influence of
temporary body conditions such as those caused by
pain, fatigue or drugs, while the learning outcome is
the level of athlete's mastery of the learning
objectives set.
Although the term skill has many meanings, it is
usually used to describe a person's ability to complete
a task. Many experts have tried to give understanding
of skills, interpreting skills as a degree of success in
achieving goals effectively and efficiently. According
to Anderson (2011), the term skill is also defined as
the procedural ability of how to perform a particular
motion task ranging from the simplest to the most
complex. Skill in this sense implicitly refers to a
particular task or action and becomes an indicator of
a level of proficiency in relation to the attainment of
a goal. In its function as an indicator of a level of
proficiency, a skill is conceived as a competence
exhibited by a person in performing a task related to
the achievement of a goal.
The higher a person's ability to achieve the
expected goals, the more skilled the person is. A
skilled tennis player performs a smash hit with a high
percentage of speed, precision, and precision. The hit
ball falls in the opponent‘s game area very quickly,
meticulous, hard, and high accuracy making it very
difficult to return by the opponent. Unlike the
beginner players, his movements are usually less
flexible and his punch results are slow, weak, and less
accurate. A tennis player like Anton Suseno for
example, capable of top spin quickly, hard, and
accurately is a skill created not by chance, but
because of the ability of mastery of effective and
efficient techniques. So, on most new players, it’s still
difficult to just crossing the ball into the field of
opponent game, let alone do the top spin like that
done by Anton Suseno.
As mentioned earlier, learning motion skills is
part of learning, therefore the notion of learning
motion skills is basically not dissimilar to the notion
of learning in general. The difference is linked to the
emphasis of the material being studied, the processes
and conditions of learning, the intensity of the
involvement of each domain element, and the
learning outcomes.
Many experts have described the study of motion
skills, such as Schmidt, Fichman and Oxendine. His
view of the study of motion skills has been widely
used as a reference by other experts mainly because it
has a conceptual representation. According to
Schmidt, learning motion skills is a series of
processes that influence the exercise or experience
that leads to relatively permanent changes in a
person‘s ability to display skilled
movements. According to Schmidt's opinion,
Fischman and Oxendine cited by Williams assert that,
learning motion as an internal process that occurs in
the brain‘s memory system and can not be directly
observed, they therefore describe learning motion
skills as a set of internal processes that influence
exercise or experiences that result in relatively
permanent behavioral changes in the form of skilled
behavior.
Based on these two views, there are at least three
basic characteristics for understanding the learning of
motion skills, namely: First, learning motion skills is
a set of internal processes that influence the activity
of giving practice or experience. The process of
learning or experience is a deliberately created
process with the aim of mastering new knowledge
and skills. The process is developed based on
experiences experienced by athletes. Second, because
of its internal nature, learning motion skills is not
directly observable. As the process progresses, the
memory system of the brain receives a number of
inputs in the form of motion capabilities and
experience, the input is processed, organized, and
transformed into a motion pattern of muscles and all
processes of change take place without being directly
observable, changes that occur through the
performance of motion. That‘s why the learning
process that happens is internal. Third, the behavior
changes that occur relatively permanent. Athletes are
considered to learn if the changes they experienced
are relatively permanent, meaning that the results
obtained can survive relatively long. Conversely, it is
not considered learning if the changes they
experienced are temporary and arise due to the
process of physical maturity, fatigue factors, illness,
drugs, and others. It is only through practice or
experience that a relatively permanent change is
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the Table Tennis Playing Skills
297

achieved, therefore practice or experience becomes
very important in the effort to achieve the desired
result.
Based on several definitions that have been
expressed, the learning of motion skills can be
understood as a set of internal processes that lead to
behavioral changes, especially relatively permanent
motion behavior as a result of the exercise process or
experience and not due to the temporal influence of
body condition such as sickness, fatigue, because of
drugs or physical maturation process.
Referring to this definition, the learning outcomes
in the context of learning motion skills can be
interpreted as the level of mastery of skills to the
purpose of learning motion skills. This level of
mastery is measured through a specific test. With
other sentences it can be stated that the result of the
learning of motion skills is the level of performance
of motion skills acquired through the process of
measurement according to the type of motion of the
learned skill. More specifically in relation to his
tennis playing skills, learning outcomes are defined
as the level of performance or the level of athlete‘s
mastery of the goal of learning the skills to play table
tennis.
2.2 The table tennis game
Table tennis is a very unique and creative game, so
table tennis is much loved by most of Indonesian
society such as kids, teenagers and adults. A table
tennis game is a game using table and equipment
facilities as well as rackets and balls as a tool. the
game begins with the opening blow (servise), the ball
is reflected on the table itself and then over the net
and then bounces at the opposing table, then the ball
is hit at the top of the net must bounce to the opposing
table until the opponent‘s table can not return
perfectly. The player tries to turn off the opponent‘s
blow to get the number from his blow. From this
understanding it can be concluded that table tennis is
a game that uses a table to reflect a ball being beaten
by a player by using a small ball that must be able to
pass or cross the ball and return the ball to the
opposing area after bouncing in its own game
area. As a result of this, good and correct basic skills
are required in addition to being supported by other
factors. Table tennis skills include: (a) even around
the world. This game uses a racket as a bat and the
ball as a hit object, can be played on a closed or open
field. The game field is made of rectangular wooden
material marked with lines, and is limited by the net
to separate between the game area itself and the
opposing game area. This game is individual, can be
played one person way against one person or two
against two people. Can be played by the male, male,
even can also be played by a mixed pair of males and
males.
Skill is the ability to produce some results to the
maximum with little energy or time and energy. Skills
in the sport is the ability to perform the necessary
movements and techniques in the sport one is playing
and is the basic movement needed in a particular
sport. Next According to Lutan; skill is the ability to
use one or several techniques appropriately, both in
terms of time and situation. According to Saidel,
skills is a necessity of motion experience in time-
place position change as a result of the development
of a person‘s energy powers that are expended during
interaction with the environment. Furthermore
Bompa, explains that, techniques cover the overall
technical structure and parts of carefully joined and
efficient movements of an athlete in his quest to do
the sporting task.
The basic skills needed in the game of tennis
are: holding a bet, also advanced techniques such as
hitting the ball, receiving and doing smash.
“Basically playing table tennis is the ability to
apply various skills and technical, physical, and
psychic skills in a table tennis game“. From this point
of view, it can be argued that playing tennis is the
ability to perform moves with one or several
techniques in the game of tennis exactly, both in
terms of time and situation. The basic skills of tennis
games that need to be studied in general can be
grouped into sections namely; how to hold the racket,
stand up, foot movements, and hit the ball. Here are
some basic techniques and skills in playing tennis.
2.3 The Nature of Motivation Exercise
In general, the term motivation refers to factors and
processes intended to encourage people to act or to
not act in situations. Motivation comes from the Latin
word ‘movere‘which means to move. Before
referring to the notion of motivation, we first examine
the identification of the word motive and
motivation. Motive is the driving force in a person to
perform certain activities, in order to achieve certain
goals. Thus, motivation is the impetus in a person to
try to make changes in behavior better in meeting
their needs.
Sudirman explained that motivation comes from
the word ‘motive‘which is defined as the power of
effort that encourages someone to do something. So
motivation can be interpreted as a driving force that
has become active at certain moments, especially in
the need to achieve a very urgent goal. While
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
298

Alderman (1974) in Monti P. Satiadarma defines
motivation as a tendency to behave selectively to a
certain direction controlled by the existence of certain
consequences, and that behavior will persist until the
goal of behavior can be achieved. The selective
nature of behavior means the behavioral individual
makes a decision to choose his actions. The specific
direction of the behavior means that the action
performed has a purpose in accordance with the
wishes. As for the consequence is a negative
condition that is obtained by an individual if he does
not perform his behavior. In Monti P, Satiadarma
more simply suggests that motivation is the direction
and intensity of one‘s business. What is meant by the
direction of the business is an interesting and
intriguing situation so that there is an effort for the
person to do so.
The term motivation (motivation) comes from the
Latin, which is moveré which means to move (to
move). Based on the above definition that motivation
is a boost from within the self to increase self-
actualization. To reach the desired destination or to
meet the necessities of life. Furthermore, The context
of motivation represents the psychological process
leading to the emergence of direction, motivation and
persistence of voluntary activities directed towards
the achievement of certain goals.
Motivation is a behavioral change process that has
been strengthened in the past in the face of failure and
trying to improve it. Reveals that motivation is the
result of a number of processes that are internal or
external to an individual, which leads to an attitude of
enthusiasm and presistence in terms of carrying out
certain activities. The motivation of the exercise is
not in the form of economic necessities that are
material, for example in the form of money, but can
also be tangible respect and appreciation of the
environment, and social status which are all forms of
social rewards that are immaterial. One‘s desired
motivation to meet the needs of his life through
achievement, talent and itelektual that support the
success. The motion (motivating) can be defined as a
whole process of motivation of training to
subordinates in such a way that humans are willing to
practice sincerely in order to achieve organizational
goals efficiently. Motivation contains three main
components of moving, directing and supporting
one‘s behavior. Moving means generating power to
the individual and leading a person to act in a certain
way.
Motivation is the desire of someone to achieve
something desired, the need for security is required
when carrying out the coach, a social needs is a
requirement that is shaped into clothing, food and
boards, self-esteem needs a sense of recognition of
the exercise environment and society, and self-
actualization in improving self potential owned and
maximum self-development. Motivation is the
encouragement of exercise that arise in a person to
behave in reaching expected goals. Motivation is a
human impulse that causes acting, speaking and
thinking in a certain way, and the behavior that exists
in the individual. Exercise motivation is something
that raises the spirit or encouragement of a strong
exercise and weak motivation of one's exercise to
determine the size of achievement.
Basically, according to Singgih motivation comes
because there are stimuli from outside the person
(extrinsic) and stimuli that arises from within a person
(intrinsic). Extrinsic motivation works because there
is stimulation from outside a person. For example,
someone is encouraged for an appearance
goal. Someone feels embarrassed to people because
of his body shape that is overweight so they cannot
stand the circumstances that he obsessed to lose
weight. While intrinsic motivation works because of
the encouragement that comes from his own
individual, and the training is only as a self-
satisfaction. He does not care whether he will get
results, praise or not, and the success or failure of the
goal for him is not a problem.
With practice there are many kinds of
encouragement to do the best that is part of the drive
to develop oneself. Sudibyo Setyobroto argues that
the motivation of training varies between individuals
with each other because of differences in needs and
interests, both due to different levels of development
of age, interests, coaches and other
needs. Motivational exercises for children, teenagers,
and parents who are not preparing for the match but
for other purposes include: (1) To be able to have fun
and get excited. (2) To release psychic tension. (3) To
gain an aesthetic experience. (4) To be able to
influence with others (make friends). (5) For the
benefit of group pride. (6) To maintain a healthy
body. (7) For the purposes of practical needs
according to his coach. Carl Heyel (in Susilo
Martoyo) states, motivation essentially explains that
the degree of willingness of an organism to realize its
intended purpose. The degree of willingness will then
determine the achievement of the goal.
Taking into account the above description, that the
need for motivation in various fields of activity is
considered very dominant. Similarly, in the field of
sports, motivation plays a very important
role. However, in the case of providing motivation to
the members (members) should pay attention to
timing and, the trainer must really understand the
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the Table Tennis Playing Skills
299

forms of the motivation. Thus expected members
(members) are really motivated effectively so there is
a willingness to exercise.
Motivation exercises in this study is focused on
motivation that encourages a person in the exercise to
achieve the needs of practical needs and to maintain
a healthy body that is to control and reduce the
percentage of body fat. Because excess fat in the body
is identical to obesity and can automatically interfere
with one‘s health. The theory of necessity
conceptualizes that everyone has the motive of
exercise or motive away from exercise. The strength
of the two motives is not the same in each member
(member) because everyone has different experiences
in achieving his goals. A strong / high exercise
motive will lead people to approach a situation
related to success and vice versa for low / low training
will keep the offender on success.
Motivation is an organizational behavior that can
not be separated from the need for achievement
(needs for achievement), the need for power (needs
for power), and the need for affiliation (needs for
affillation). Needs of exercise will encourage one to
achieve excellence and achieve the achievement of
success, the need for power provide direction to the
desired goals of individuals, and the need of affiliated
interpersonal will effect one to interact friendly to
another.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs (2002), suggests the
existence of eight levels of basic human needs. To the
eight levels of basic needs is then made into
understanding in studying human motivation. As for
the eight levels of basic needs are as follows: 1)
Physiological needs (physiological needs) this
requirement is a basic need that is primary and vital
related to basic biological functions of human
organisms such as food needs, clothing, boards,
physical health, and so on. 2) The need for safety and
security needs such as security, protected from danger
and disease threat, war, poverty, hunger, unfair
treatment, and so forth. 3) Social needs
(belongingness and loves needs) include the needs of
being loved, calculated as personal, recognized as a
member of the group, a sense of loyal friends,
cooperation and so on. 4) Esteem needs include the
need to be rewarded for achievement, ability, position
or status, rank and so forth. 5) The need to understand
and develop themselves (need to know and
understand) intellectually as the need to enhance the
potential possessed, maximum self-development,
creativity and self-expression. 6) The need for
enjoyment and aesthetic needs such as order and
balance. 7) the need for self actualization, such as the
need to enhance the potential possessed, maximum
self-development, creativity and self-expression. 8)
The need for human existence in influence with God
(transcendence needs). Based on the description, it
can be concluded that the motivation of the exercise
is is a soul impulse that makes a person moved
to perform productive actions, both oriented
exercises to make money or not. The indicators are as
follows: 1) the desire for practice, 2) the growth of the
exercise, 3) the creation of conducive conditions and
conditions, 4) the availability of rewards, 5)
recognition, 6) the need for power, 7) the need to be
affiliated, and 8 ) innovative and creative.
2.4 The reality of Motor Ability
Basically everyone has a motor ability that is different
from each other. According to Wall and Murray,
motor ability is the capacity of one‘s performance in
performing the task of motion. While Oxendine
suggests that motor ability is a description of one of
the skills in performing various basic skills and
physical activity as a whole. Furthermore Seidel
quotes Singer's opinion that motor ability is indicated
as the appearance of a person‘s own ability to exercise
as a basis for performing various motor skills
movements.
It can be argued that motor ability is the capacity
for the performance of a person‘s motion skills to
perform a variety of motor skills and overall physical
activity, or individual capacity that becomes the
determinant of individual performance potential to
display specific skills. Therefore, motor ability in this
context can be understood as an ability that is
specifically related to the appearance of a motion
skill. More specific motor abilities are a number of
abilities that underlie learning motion skills and
performance success.
Revealed from these, several views about the
influence of biological factors as the main force
supporting the motor ability. The point is, motor
ability is considered as a potential ability that
supports certain skills. Motor ability is then the role
as a foundation for the development of skills and in
turn play a role in implementing various sports
skills. In other words, motor ability is an innate ability
that is different in each person, not easily changed
through practice and experience, develops relatively
automatically in the process of growth and maturity,
is relatively lasting, and underlies the formation of
skills.
Magill further quotes Fleishman‘s opinion that
suggests, motor ability is a general capacity to
perform various tasks of motion, or a description of
one of the skills in performing various basic skills and
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
300

activities as a whole. This capacity is a combination
of biological and environmental factors. Nevertheless
biological factors are considered as the main
supporters of motion. Aspects of motor abilities
possessed by a person is very diverse and different
potential of each person. Therefore, experts have
attempted to categorize aspects of these
aspects. Among them, Clarke & Clarke mentions that
there are eight aspects of motor abilities are; muscle
strength, muscle and cardiovascular endurance,
speed, agility, balance, muscle power, eye-hand and
foot coordination. Singer further mentioned, there are
four components that directly affect motor ability and
ability of the ability of coordination, balance,
velocity, and kinestetik.
In regards to the categorization above, Magill
argues that there are two hypotheses developed about
the influence between aspects of motor ability, which
are: motor ability hypothesis in general and motot
ability special. The first hypothesis considers the
motor ability aspect as a whole. Each aspect relates to
one another to influence the success of learning or the
performance of motion. This hypothesis predicts that
if one is good in one motor skill, then he or she is
potentially to be good at all motion skills. In contrast
to a special motor ability hypothesis, every aspect of
motor ability with each other is independent or
independent. That is, if a person is good in the aspect
of balance ability, then it is unpredictable that the
person will be good also in the ability of the reaction
time.
Considering some of these categorizations, the
authors assume, there are five aspects of motor
abilities that underlie all aspects of motor ability of
the individual, especially in relation to his playing
skills of tennis. These five aspects are coordination,
agility, balance, speed, and reaction time.
Furthermore, to know athletes‘ motor ability, then
do the measurement. In accordance with the
characteristics of research subjects, the type of
test used is a motor ability test for elementary school
age children developed by Arnheim and
Sinclair. This test is intended to measure the ability of
athletes to display motor abilities and overall physical
activity gained from the experience of motion in
childhood.
The following is the type of motor ability test for
children, consisting of seven items:
(a) Throw on target or target (target throwing);
(b) Backgroup and backstrength (back and
hamstring stretch);
(c) Skip forward without prefix (standing long
jump);
(d) Face down to standing;
(e) Push-up on chair (chair push-up)
(f) Status balance (static balance)
(g) Agility run (agility run).
3 METHODS
The general objective of this research is to know the
effect of exercise motivation and motor ability on the
learning achievement of tennis skill in male junior
athletes conducted at Family Club Tennis Club of
PTMSI member of Cianjur regency.
The variables in this study are two independent
variables that become the scope of research subjects,
in which are exercise motivation variables and motor
ablity, while the dependent variable used in this study
is the skills of playing table tennis. Specifically the
purpose of this study as follows: 1) To find out how
the influence of motivation of exercise on the results
of playing skills at the junior athletes Cianjur. 2) To
know how motor ability influence to learning result
of playing skill of tennis to male junior athletes. 3) To
know the difference of influence between motivation
of exercise, and motor ablity to the result of learning
skill of playing tennis on male junior athletes.
This research was conducted at tennis club Family
Cianjur member PTMSI Kabupaten Cianjur. The
research period lasted for five months with activities
including testing of research instruments, initial data
collection for grouping samples, and final data
retrieval, data processing, and reporting.
3.1 Research method
Research method used in this research is expost facto
method with correlational techniques.
Kerlinger (1993) in Sugiyono (2004) defines ex
post facto research as an empirical finding that is done
systematically, the researcher does not control the
independent variables because the manifestation has
occurred or the variables are inherently
unmanipulated. To obtain the desired data in the field,
this study uses questionnaires prepared based on
indicators. The data needed in this research is data
about exercise motivation (X1), motor skills (X2),
and table tennis (Y) skills.
The author uses research design by grouping
research variables as follows:
a. Independent variable (X1) exercise motivation
b. Independent variables (X2) motor ability
c. Dependent variable (Y) Skill of playing table
tennis
Constellation Relationship between Independent
Variables, X1 and X2 with Dependent Variables, Y
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the Table Tennis Playing Skills
301
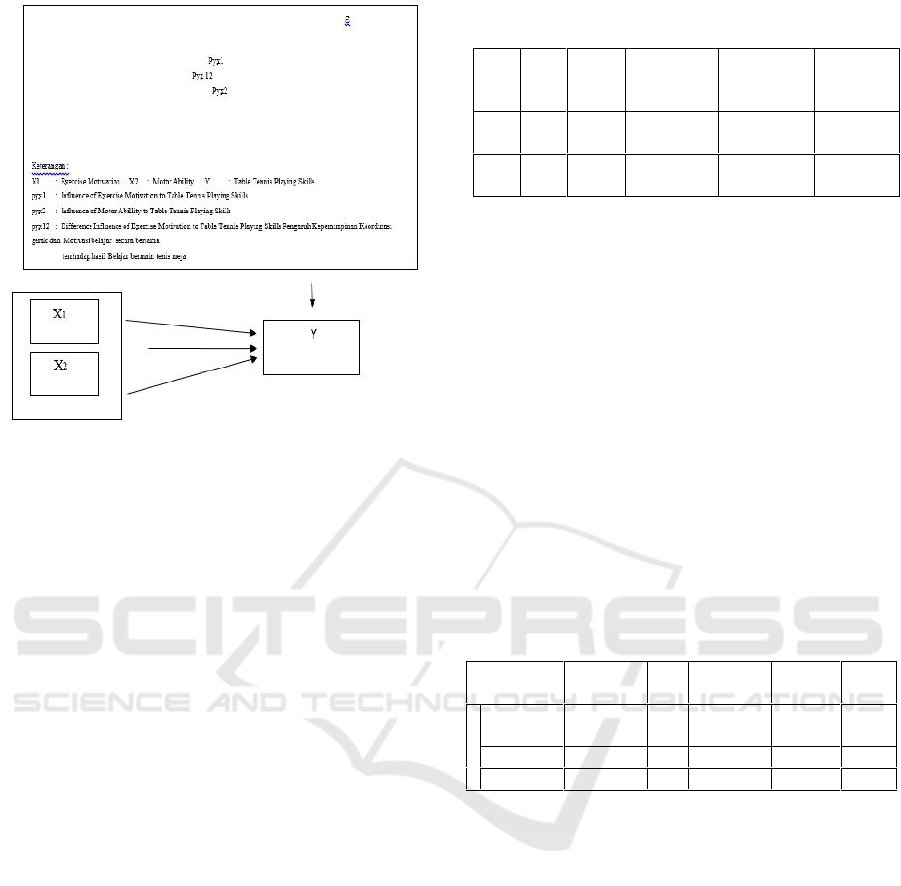
Figure 1: Research Design.
3.2 Data Analysis Technique
The data obtained in this study will be processed and
analyzed using variance analysis technique
(ANAVA) followed by using lisrel (path
analysis). And testing is done at the level of
significance = 0.05.
The measuring instrument used in this study is a
questionnaire to determine the level of athletes‘
motivation and motor skills test. Meanwhile, to
measure the results of the playing skills of table tennis
can be seen from the raw value obtained by athletes
during the test of table tennis skills.
After the preparation of questionnaire motivation
exercise, then tested to respondents who have the
same characteristics with the sample to be
studied. Data from the test results, then processed
and analyzed to determine the degree of validity and
reliability
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Processing Results and Hypothesis
Testing
The data needed for testing the research hypothesis is
as follows:
Result of Calculation of Correlation Coefficiency
Significance
Referring to the result of calculating the
significance of the correlation coefficient as shown in
the table, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. The Effect of Motivation Exercise on table
tennis skills.
From the data it can be concluded that there is a
significant influence Motivation exercise on
table tennis skills, contributed 39.6%.
2. Influence motor ability against table tennis skill.
Furthermore, from the data obtained
information that the motor abilities contribute to
table tennis skills of 52.4
Table 2: Calculation Result of Significance of Coefficient
X1, X2 on Y.
Referring to the result of counting the
significance of double correlation coefficient as
shown in the table, the following conclusions
can be drawn:
3. The same effect between exercise motivation
and motor ability against table tennis skills.
Ho: There is no significant influence between
exercise motivation and motor ability together
with table tennis skills.
H1: There is a significant influence of exercise
motivation and motor ablity together with motor
ability against table tennis skill.
The level of significance = 0.05, and the criteria
of significance testing are:
If Fcount Ftable, then Ho is accepted and other
things are rejected. It turns out that 9.55> 3.44
Table 1: Model Summary
b
Mod
el
R
R
Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error
of the
Estimate
Durbin-
Watson
1
.629
a
.396
.362
5.28528
1.818
2
.724
a
.524
.498
4.69076
2.141
a. Predictors: (Constant), X1
b. Predictors: (Constant), X2
c. Dependent Variable: y
ANOVA
a
Model
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
Regressio
n
440.270
2
220.135
9.548
.002
b
Residual
391.930
17
23.055
Total
832.200
19
a. Dependent Variable: y
b. Predictors: (Constant), X2, X1
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
302

then Fcount> Ftable so Ho is rejected or H1 is
accepted (correlation significant).
In conclusion: There is a significant influence of
exercise motivation and motor ablity together
with Table Tennis Skills.
Table 3: Model Summary
b
Mo
del
R
R
Squar
e
Adjus
ted R
Squar
e
Std. Error
of the
Estimate
Durbin-Watson
1
.7
27
a
.529
.474
4.80153
2.172
a. Predictors: (Constant), X2, X1
b. Dependent Variable: y
Furthermore, the results of this study obtained the
contribution of the motivation of exercise and motor
ablity is as much as 52.9% together with the table
tennis skills.
4.2 Discussion on Findings
After analysis with data obtained through statistical
approach, it can be obtained picture as follows:
a. The influence of exercise motivation on table
tennis skill.
Based on the results of data processing and score
analysis between the motivation of exercise on
table tennis skill, the results obtained that there
is a real correlation of 0.47, is evidenced by the
results of the scale of motivation of youth athlete
training PTM Family to table tennis skills of
0.39.
b. Ability to table tennis
From the processing and analysis of motor
ability data with table tennis skills, obtained the
result that there is a correlation of 0,52. It turns
out that the motor ability level provides a
significant correlation or positive support for
table tennis skills. This is in line with previous
theories, that table tennis skills are better when
supported by a high level of motor ability.
c. The influence of exercise motivation and motor
ability against table tennis skill.
Based on the results of data processing and score
analysis between exercise motivation and motor
ability to table tennis skill, the results obtained that
there is a real correlation of 0.53, is evidenced by the
results of exercise motivation scale and motor ability
junior athlete PTM Family against table tennis skills
tend to be high. This is in line with the theory that
explains that: “the results of the exercise will be
optimal, if there is motivation. The more appropriate
the motivation is, the more likely it is to
succeed“. Similarly, the motor ability, it turns out the
level of motor ability to provide positive support for
table tennis skills. This is in line with previous
theories, that table tennis skills are better when
supported by a high level of motor ability
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the data processing and discussion can be
obtained the following conclusions:
1. There is a significant effect of exercise
motivation on table tennis skill on junior
athletes of PTM Family Cianjur.
2. There is a significant influence motor ability on
table tennis skill on junior athletes of PTM
Family Cianjur.
3. There is a significant influence of exercise
motivation and motor ablity together with table
tennis skill at junior athletes of PTM Family
Cianjur
As a result of the research that the author did,
the authors want to put forward the following
suggestions:
1. For athletes, in order to keep trying to improve
the motivation of exercise so that the
achievement of the results of exercise and table
tennis skills better can be realized, especially if
supported by motor ability with a diligent
practice so that the achievement of results
towards a better can be achieved.
2. For the coach, if he wants his athlete to get good
table tennis skills, to always provide training
materials to pay more attention to his training
motivation and give encouragement to athletes
for more vigorous exercise.
3. For future researchers, it is expected to continue
the research with a wider coverage again
because the authors feel there are still many
shortcomings in this study.
REFERENCES
Arikunto. Suharsimi, 2008, Prosedur Penelitian, Suatu
Pendekatan Praktek, Yogyakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Bompa, Tudor O. 2000. Theory and Methodology of
Training, Dubuque, Iowa: Hunt Publishing Company.
Bowers.
Borg, Walter R., Meredith D. Gall, 2003, Education
Research: an Introduction, New York, Longman, Inc.,
The Influence of Exercise Motivation and Motor Ability towards the Table Tennis Playing Skills
303

Brian J. Sharkey. 2003, Kebugaran dan Kesehatan, Jakarta:
PT. Raja grafindo Persada.
Dinata, Marta. A9 2004, Pedoman Pelatihan Fitness
Center, Jakarta: CERDAS JAYA.
Don R. Kirkendall, Joseph J. Gruber, dan Robert E. Johnso
n, (2010) Measurement and Evaluation for Physical Ed
ucator, Dubuque Iowa: Wim C.Brown Company Publis
her
Elizabeth B. Hurlok, (2007) Psikologi Perkembangan, Sua
tu Pendekatan Rentang Kehidupan terjemahan Istimiw
idayanti dan Soedjarwo, Jakarta: Erlangga, .
Fank M. Verducci, Measurement (1980), Concepts in
Physical Education, St.Louis Missouri: Mosby Compa
ny.
Gelder, Nanny Van & Sherly Marks, (2009), Aerobic
Dance-Exercise Instructor Manual, San Diego
California: IDEA Foundation.
Giriwijoyo. Santoso, 2015, Olahraga, Budaya, dan
Rekayasa, CV. Bintang Warli Artika, Bandung.
Gunarsa, Singgih dkk. Psikologi Olahraga; Teori dan
Praktik, Jakarta: gunung Mulia, 1996.
Hamalik. Oemar, 1994, Pengembangan Kurikulum Dan
Pemlatihanan, Bandung: Trigenda Karya.
Harre D. 1982. Principle of Sports Training: Introduction
to The Theory and Methods of Training. Berlin:
Sportverlag. Increasing Motivation.
(http://www.mental help.
net/psychelp/chap14/chap14.htm.28-02-02.
Harsono, 1988. Ilmu Coaching, Jakarta: Pusat Ilmu
Olahraga, KONI Pusat, 1988.
Huitt, W. (2011). Motivation to learn: An overview.
Educational Psychology Interactive.
Irianto. D Pekik, 2004, Pedoman Praktis Berolahraga
untuk Kebugaran&Kesehatan, Yogyakarta: Andi.
Kepelatihan, Terjemahan, Kasiyo Dwijowinoto. Semarang:
IKIP.
Lefton, Lester A. 1997. Psychology. Boston: Allyn and
Bacon.
Magill A. Richard. 1982. Motor Learning Concepts and
Applications. Dubuque, Iowa: WM. C. Brown
Publishers.
Merriam-Webster. 2015. Learning. Available:
http://www.merriam-webster.com/
dictionary/learning. Last accessed 02/03/15.
Nana, Sudjana,. 2010. Penilaian Hasil Proses Latihan
Mengajar. Cetakan ke XV. Bandung: PT. Ramaja
Rosdakarya.
Nawawi. Hadari, 2007, Metode Penelitian Bidang Sosial,
Yogyakarta: Gadjah Mada University Press.
Nurhasan, 2002, Pengembangan Sistem Pemlatihanan
Modul Mata Kuliah Statistik, FPOK UPI Bandung.
Nurhasan, 2002, Tes Dan Pengukuran Pendidikan
Olahraga, FPOK UPI Bandung
Oxford Dictionary. (2015). learning. Available:
http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/l
earning. Last accessed 02/03/15.
Pate, Russell R., Bruce Mc. Clenaghan, dan Robert
Rottella. 1993. Dasar-dasar Ilmiah
Purwanto. Ngalim, 1990, Psikologi Pendidikan, Bandung:
PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Richard W., and Edward L. Fox. 1992. Sport Physiology,
Dubuque: W.C. Brown.
Rusyan. Tabrani, 1990, Penuntun Latihan Yang Sukses,
Jakarta: Nine Karya Jaya.
Sardiman, 2004, Interaksi&Motivasi Latihan Mengajar,
Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada.
Schmidt A. Richard. 1986. Motor Skill. New York:
Harper & Row Publisher.
School Children. New York: Macmillan Publishing
Company.
Setyobroto, Sudibyo. 2001. Psikologi Olahraga Suatu
Pengantar. Jakarta: P.Solo
Sugihartono, dkk. 2007. Psikologi Pendidikan. Yogyakarta:
UNY Press.
Sugiono, 2005, Metode Penelitian Administrasi, Bandung:
CV. ALFABETA.
Sutopo, Arie & Alma Permana Lestari, Buku Penuntun
Praktikum Ilmu Faal Dasar, Jakarta: Universitas Negeri
Jakarta, 2001.
Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University. Retrieved from
http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/topics/motivation/m
otivate.html
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
304
