
Effect of Method of Teaching and Learning Motivation toward Skills
Freestyles Swimming 25 meter
Asep Sujana Wahyuri, James Tangkudung, and Sayuti Syahara
Sport Science Faculty, Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia
asepsw.unp@gmail.com
Keywords: Skills Freestyles Swimming, Motivation Learning, Teaching Style.
Abstract: This study of this research is to find out the effect of teaching style toward the ability of the student in of the
freestyles swimming. Experimental method used in this study, while the 2x2 ANOVA to analyze the data
and see the interaction between the two styles of teaching, as well as between the moderator variables.
Based on the sampling technique according to the Verducci samples taken 27% of the highest scores and
27% of the lowest score. The result of this research; The Self Check Teaching Style has better effect than
Command Teaching Styles; There is an interaction between Teaching Styles and Motivation Learning
toward Freestyle Swimming; At high motivation Self Check style gives a better effect than the command of
teaching styles; While in the low motivation, the Command Teaching style provides better effect.
1 INTRODUCTION
The lecturing process at the Faculty of Sport
Sciences at Padang State University is conducted by
the SKS system. Students must complete 144-148
credits divided into a number of courses. One of the
subjects that must be followed by students is
swimming or aquatic courses. This subject becomes
the subject of compulsory subjects at the Faculty of
Sport Sciences State University of Padang because
graduates of the Faculty of sports science later one
of them will work as a physical education teacher.
Physical education teachers are required to teach
swimming subjects / aquatic activities in both
elementary and secondary schools (Bob et al, 1997).
In the swimming / aquatic courses students learn
some swimming styles such as freestyle swimming,
freestyle swimming, backstroke swimming, butterfly
swimming and swimming match systems (Woolfolk,
2016).
The results of observations of researchers in the
field found. There are still many students who score
E or fail in this course. Even in the semester of
January-June 2014 there are 32% of students who
fail in basic swimming. The value of the students
taking the basic swimming courses is still low.
Learning methods of lecturers are not appropriate in
the learning process (Woolfolk, 2009). A
monotonous learning method can make students feel
bored. Incorrect learning method for all student
characteristics can also cause lecture process can not
be followed well (Langendorfer, 2007). Lecturers
give lectures only with one method only, while
students have different karakristik (Becker, 2011).
There are students who need more repetition to
master a skill. The number of students who follow
the basic swimmingof one section of the course
subjects an average of 35-40 students. The large
number of students has heterogeneous
characteristics. Therefore lecturers can not correct
carefully one by one technical error by the students.
For that we need an appropriate method in teaching
swimming skills. According to Moston there are
several methods that can be applied by lecturers in
learning, such as: Command Style, the practice style,
the reciprocal style, the self-check style, the
inclusion style, the guided discovery style, the
divergent style, the going beyond style (Robert. J.
David. Yun dai, 2008). In their application each
style has its own characteristics. Lecturers are
expected to be able to choose the right style of
teaching in accordance with the purpose of learning
(Gentile, 1972). In choosing an approach or teaching
style lecturers should pay attention to: the ability of
lecturers, the needs of students, the size of classes,
tools and facilities available, the media, the goals to
be achieved and the material to be studied.
Wahyuri, A., Tangkudung, J. and Syahara, S.
Effect of Method of Teaching and Learning Motivation toward Skills Freestyles Swimming 25 meter.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 255-258
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
255
2 METHODS
The use of methods of teaching command mode is
the application of a teaching style in which the
learning is fully controlled by the educator. The
lecturer prepares all aspects of teaching and he is
fully responsible and initiative towards teaching and
monitoring the great progress of his student
development. Concerning learning in a command
mode is an educator-centered learning, supported by
Alnedral (2015: 36) who argue that command-line
learning is a learning approach that involves the
whole educator to make policies and learners must
follow the policy. From the expert's opinion above,
it can be concluded that the learning by command-
style method is a centered learning to the educator in
making decisions either during the preparation of the
lesson, while the learning takes place and when the
learning should be terminated. According to Trisna
E. (2013: 143) states on the style of commanders
educators have an important role in the learning
process because educators become subjects and
students become the object of learning. Lecturers
determine the form, intensity, assessment and
learning objectives. The role of educators in this
learning is very dominant, namely as decision
makers at all stages, because at the planning stage,
implementation stage and evaluation phase is fully
done by educators, while students / students only
serve as executors who must fully submit to the
direction, and all orders from educators.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The essence of the command mode is the direct and
rapid connection between lecturer stimulus and
student response. Stimulus in the form of sign /
command given by lecturer, will initiate every
movement of student / student in showing movement
according to example from lecturer. Typically, the
style begins with an explanation of the standard
technique, and then the students imitate and do it
repeatedly according to the instructor's instructions.
Mosston (2008: 81) describes the stage of execution
of command styles namely; 1) Preparation before the
meeting is to plan.
Table 1: Summary of Free Style Swimming Skills Data.
In the above table the overall look of the Check-
Out style itself has a higher average result than the
Command Style. Students who have high motivation
to learn more in accordance with the style of
teaching Self Check. While students who have low
Learning Motivation higher the average value with a
style of teaching Command (Schunk, Dale H.
Zimmerman. Barry J, 2009).
3.1 There is a Difference between
Teaching Style Self Check Style and
Command Style to Freestyle
Swimming Skills
Based on the result of variance analysis (ANAVA)
at significant level α = 0,05, obtained Fo = 3,49 and
Ft = 2,92. The summary can be seen in table 18.
Thus Fo> Ft, so there is reason to reject Ho, it can be
concluded that overall, there is a real difference
between Self Check Style and Command Style on
Freestyle Skills.
The result of freestyle swimming skills after
learning by using Self Check Style (= 52,90; SD =
7.46) is better than Command Style (= 47,10; SD =
7.71). This means that the research hypothesis states
that the overall result of freestyle swimming skills
Teaching Style
Learning
Motivation
Self Check Style
Command Style
High
∑X
1
= 695,39
∑X
1
2
= 3358,12
X
1
= 57,95
∑X
2
=
490,47
∑X
2
2
=
1670,53
X
2
=
40.87
Low
∑X
1
= 574,24
∑X
1
2
= 2289,92
X
1
= 47,85
∑X
2
=
639,91
∑X
2
2
=
2843,61
X
2
=
53,33
Total
∑kX
1
=
1269.63
∑ kX
1
2
=
68443,50
∑ k
X
2
=
52,90
∑ kX
2
=
1130,37
∑ kX
2
2
=
54607,41
∑ k
X
2
=
47,10
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
256
using Self Check Style is better than using
Command Style or in other words the use of Self
Check Style is better than Command Style. This is
evident from the results of further tests in the
analysis of variants (ANAVA), the results are as
follows:
Table 2: The Difference between Teaching Style.
Compared
Groups
F
c
F
t
Conclusion
A
1
and A
2
3,49
2,92
Significant
3.2 There is an Interaction between
Teaching Styles and Learning
Motivation of Freestyle Swimming
Skills
Based on the result of variance analysis about the
interaction between teaching style and learning
motivation toward the result of freestyle swimming
skill seen in the table of calculation of anava above,
that the price of Fo interaction (FAB) = 77,42 and F
table = 4.06 shows that Fo> Ft, so there is reason to
reject Ho. The conclusion is that there is an
interaction between the two Teaching Styles with the
Motivation of Learning to Freestyle Skills. In other
words, there is cooperation between Teaching Style
and Learning Motivation to FreeStyle Swimming
Skill.
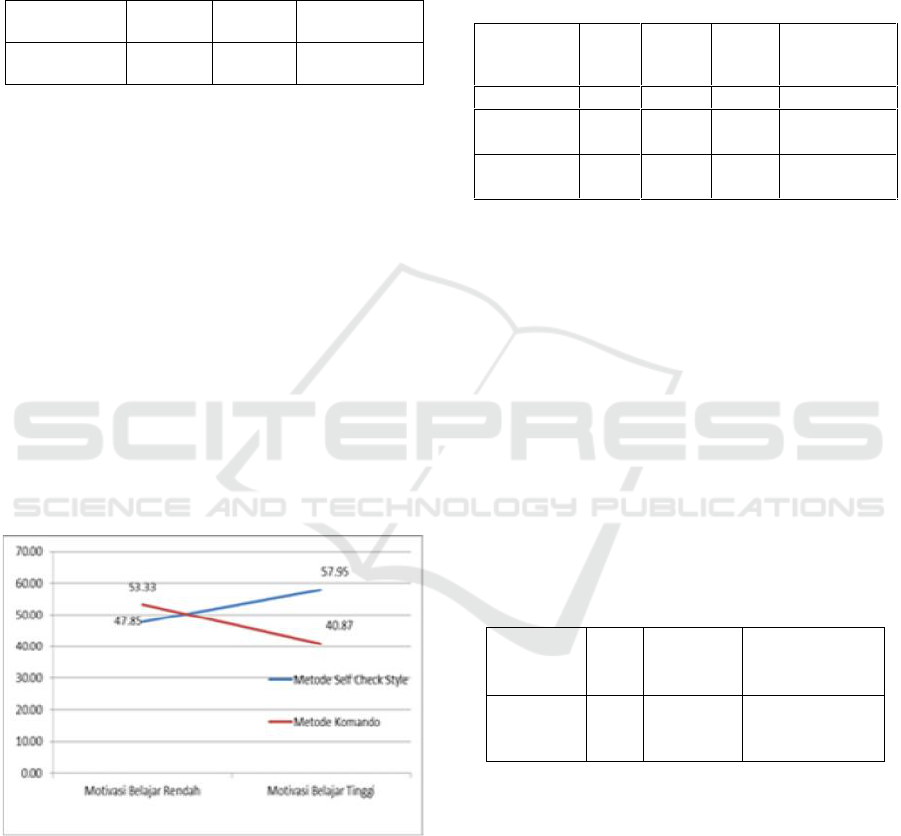
Figure 1: Interaction between Teaching Style and
Learning Motivation of Free Style Swimming Skill.
The Interaction between Teaching Style and
Motivation Learning in its influence on Free Style
Skills can be graphically visualized as shown in
Figure 1.
With terujinya interaction, then further need to
test further. The advanced test is intended to know
about: (1) Differences in the result of Free Style
Skill between Self Check Style and Command Style
in High Learning Motivation group; (2) Different
results of Free Style Style Skill between Self Check
Style and Command Style in Low Learning
Motivation group. The summary of the advanced
test results can be seen in table 3 below:
Table 3. Summary of Tukey Test Calculations.
Compared
Groups
Dk
Q
c
Q
table
(α =
0.05)
Conclusion
A1 and A2
0,90
3,49
2,92
Significant
A1B1 and
A2B1
1,38
12,33
3,77
Significant
A1B2 and
A2B2
1,38
3,95
3,77
Significant
3.3 There is a Difference in Freestyle
Swimming Skills between Student
Groups learning with Self Check
Style) Better than Students studying
with Command Style on Higher
Learning Motivation
Self Check Style gives a better influence on the
results of freestyle swimming skills in groups with
high learning motivation. This is evident from the
results of further tests in the analysis of variants
(ANAVA) by using Tukey test which results as
follows:
Table 4: Differences Group Self CheckStyle and
Command Style on High Learning Motivation.
Compare
d Groups
Q
c
Q
table
(α=0.05)
Conclusion
A
1
B
1
and
A
2
B
1
12,3
3
3,77
Significant
Group of high motivation study with Self Check
Style compared with high learning motivation group
with Command Style, obtained Fh = 12,33 and Ft =
3,77. Thus Fh> Ft, based on the data there is a
reason to reject Ho, so it can be interpreted that there
is a distinct difference in freely styled freestyle skill
between Self Check Style and Command Style, with
high learning motivation level.
Based on the calculation, it is found that average
students who have high learning motivation by using
Self Check Style (= 57,95; SD = 7,46) is better than
Command Style (= 53,33; SD = 7.71) in the results
Effect of Method of Teaching and Learning Motivation toward Skills Freestyles Swimming 25 meter
257

of freestyle swimming skills. Thus the research
hypothesis stated that students with high learning
motivation who learn with Self Check Style, Better
than Command Style.
3.4 There is a Difference of Freestyle
Swimming Skills between Student
Groups who studied with Self Check
Style and Command Style on Low
Learning Motivation.
Command Style Teaching gives an insignificant
effect on the result of freestyle swimming skills in
the group of students with low learning motivation.
This is evident from the results of further tests in the
analysis of variants (ANAVA) by using the Tukey
test, which results as follows:
Table 5: Differences of Self Check Style and Command
Style Groups in Low Learning Motivation.
Compared
Groups
Q
c
Q
table
(α=
0.05)
Conclusion
A
1
B
2
and
A
2
B
2
3,95
3,77
Significant
The low learning motivation group with the Self
Check Style compared with the low learning
motivation group with Command Style obtained Fh
= 3.95 and Ft = 3.77 Thus Fh <Ft, based on the data
there is a reason to accept Ho, so it can be
interpreted that there is a distinct difference in freely
styled freestyle skills in Self Check Style with
Command Style at low motivation level.Based on
the calculation, obtained the average score of
students who have low learning motivation by using
Command Style Style (= 53.33) is better than the
Self Check Style (= 47.85) in the freestyle skill
result. But if empirically tested the average value of
the two teaching style groups shows a significant
difference with Fh> Ft, so Ho is rejected or there is a
significant difference.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on data analysis, the conclusion is (1). Free
Spirit Style Style Skills of Self Check Style students
are better than the Command Style Group. 2). There
is an Interaction between Teaching Style and the
Motivation of Learning to Freestyle Skills. 3). On
Higher Learning Motivation, Student Free Style
Students Free Style Skills, Better Self Check Style,
4). At Low Learning Motivation, Student Style Free
Student Style Skills Outcomes Better than Self
Check Style, to the Results of Free Style Skill 25
meter Students Department of Sport Education FIK
UNP.
REFERENCES
Alnedral, 2015. Strategi Pembelajaran PJOK,
Yogyakarta:Andi, 2015, h.36.
Woolfolk, A. 2009. Educational Psychology Active
Learning. Edisi Kesepuluh Bagian Dua.
Langendorfer, S. J. 2007. Swimming: Steps to Success.
International Journal of Aquatic Research and
Education, 1(4), 9.
Becker, T. J, 2011. Overuse 'Shoulder' Injuries' In
'Swimmers, Journal Swimming Research, Vol.18, h.1.
Bob D. et al. 1997. Physical Education and the Study of
Sport. London: Mosby, an imprint of Times Mirror
International Publisher Ltd.
Trisna E., 2013. Strategi Pembelajaran Pendidikan
Jasmani, Bandung: Alfabeta.
Gentile, A. M. 1972. A working model of skill acquisition
with application to teaching. Quest, 17(1), 3-23.
Mosston M., Sara A. 2008. Teaching Physical Education.
Online Edition.
Robert. J. D., Yun dai. 2008. Motivation, Emotion, and
Cognition.. h.178
Schunk, Dale H. Zimmerman. Barry J. 2009. Motivation
And Self- Regulated Learning: Theory, Research, and
Applications. h.1.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
258
