
Comparison of Extensive and Extensive Interval Exercises in Futsal
VO2max Player Upgrades
Kartono Pramdhan and Dedi Supriadi
Sekolah Tinggi Keguruan Ilmu dan Pendidikan Pasundan Kota Cimahi
kartonopramdhan@yahoo.com
Keywords: Extensive Internal Exercises, Intensive Internal Exercises, VO2Max upgrades.
Abstract: During the game, a futsal player needs a very fast recovery capability, this requires a good capacity of
VO2max. In increasing endurance or VO2Max there are several training methods, one of them with interval
training. The purpose of this study is to know the comparison of extensive and intensive interval training
methods to increase VO2Max in students attending futsal extracurricular in High School Bandung. The
method used in this research is the experimental method. The population of 20 people using sampling
technique is total sampling. The measuring instruments are test bleep and table form calculation. Based on
the results of the research that the authors do as well as the calculation and data analysis of the measurement
results, the conclusion of the results of this study is extensive interval training methods provide a more
significant impact on the increase in VO2Max students attending futsal extracurricular in Bandung High
School.
1 INTRODUCTION
During a futsal game, players perform various
moves such as running, kicking, jumping, and others
and requiring repetition of movements in turns with
short recovery periods. The intensity and duration
may change at any time according to the demands of
the game. Futsal is an intermittent team sport that is
characterized by activity with high intensity action,
interspersed with short recovery period during
game. Futsal is an intermittent sport that makes high
physical, technical, and tactical demands on players
(Soto, 2008). With a dimension of 40 x 20 m field
size, unlimited and frequent attacking and defensive
turnover, futsal players are required to perform high
intensity locomotor activities such as sprints,
acceleration, decelerations and high-demand
alterations placed in aerobic and anaerobic
metabolism systems. Thus, in addition to other
physical qualities of strength and speed, as well as
cardiorespiratory fitness and repeated sprint ability
have been considered as important factors that
determine success in futsal (Teixeira et al., 2017).
A previous study with heart rate analysis (HR)
reported that players maintained HR at the
maximum 85% HR level (HRmax). In addition, a
study reported that futsal players should be able to
alter locomotor activity (eg, run to run, run straight
to the side or run back) every 8-9 seconds. Thus,
futsal can be regarded as a high-intensity game with
important demands that the player needs by having a
good aerobic and anaerobic energetic capacity
(Pedro et al., 2013).
The performance of futsal games also depends
on the player's aerobic capacity. Helgerud et
al. found that improvements in maximum oxygen
uptake (VO2max) lead to improved performance in
futsal playing, evidenced by distance traveled,
intensity of work, and number of sprints during the
match. Thus, improving the fitness of futsal players
through training is a complex process that requires
improvement in both aerobic and anaerobic (Dupont,
Akakpo, And Berthoin 2010). VO2max is one of the
major determinants of aerobic endurance
performance (Helgerud et al., 2007). A significant
correlation between maximum oxygen uptake
(VO2max) and distance traveled during football
matches. In addition, the finding that the top four
ranks of the best teams in Hungary's football
division is equal to the rank among the average
VO2max, thus strengthening the correlation between
VO2max and performance. (Helgerud et al., 2001).
Just as football futsal players need good physical
skills, the performance of players also depends on
aerobic capacity. Helgerud et al. found that high
168
Pramdhan, K. and Supr iadi, D.
Comparison of Extensive and Extensive Interval Exercises in Futsal VO2max Player Upgrades.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 168-173
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Volume Maximum Oxygen (VO2max) players lead
to improved performance in matches, proven
mileage, intensity of work, and number of sprints
during the game. Thus, improving the fitness of
players through training is a complex process that
requires improvement in both aerobic and anaerobic
qualities (Dupont, Akakpo and Berthoin, 2004)
Resistant Power Exercises involving
manipulation of exercise intensity, duration, and
frequency, with implicit goals to maximize
performance, minimize the risk of negative training
outcomes, and determine the fitness time and peak
performance to be achieved are essential (Seiler
2010).
It is important to know the determination of the
intensity of a different sport training activity as it
may affect the adaptation of physiological
parameters, accuracy in choosing the optimal
training method for specific sports or to improve
fitness in the general public. Cardiorespiratory
endurance has long been recognized as one of the
fundamental components of physical fitness. Since
the accumulation of lactic acid is associated with
muscle fatigue, anaerobic metabolism contributes to
a quantitatively significant level of energy released
(Helgerud et al., 2007).
In increasing endurance or VO2Max, there are
several training methods used. One of them with
interval training. Interval training improves fitness
and decreases health risks (Astorino et al.,
2012). According Harsono (1988: 156) „Interval
training is a system of exercise interspersed by
intervals in the form of periods of rest. So, exercise
(eg run) - rest - exercise - rest - exercise and so
on“. Interval training is an important exercise that is
included in the whole exercise program. Interval
training is highly recommended by renowned
coaches because the results are very positive for the
development of endurance and stamina
athletes. Interval training method is the method of
exercise that distance, time, rest and repetition have
been determined, or also called the exercise
variables that have been determined. Recent interval
training has been used as an alternative method of
endurance training to alter cardiorespiratory fitness,
as demonstrated by Maximum Oxygen Volume
(VO2Max) and muscle metabolism (Astorino et.al.
2012). Interval training is a kind of realistic exercise
that can be done by elite athletes and untrained
individuals. Interval training, revealing sports
potential with Intensity to stimulate adaptation of
skeletal muscle in improving performance and
having implications for improving health (Talanian
et al.).
In the interval training there are several methods
such as intensive interval training methods and
extensive interval training methods that each has
different characteristics, as Schmolinsky (1983: 66)
notes that “the total load result froam a great volume
of work in time and space, we speak of extensive
interval work; the intensive interval work is
characterized by greater application of power and
reduced volume in one unit of time“. The statement
indicates that the total load is a form of the volume
of work in time and space, hereinafter referred to as
the extensive work interval, while the intensive work
interval is characterized by the use of greater power
and the decrease in volume in a single unit.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the
comparison of extensive interval training methods
and intensive interval training methods on the
improvement of VO2Max.
2 METHODS
This method is used on the basis of the consideration
that the nature of this study is to compare the
differences as well as the effect of extensive interval
training methods and intensive interval training
methods on improving VO2Max in students
attending futsal extracurricular in Bandung High
School. Both groups then undergo the training
process in accordance with the exercise program that
has been prepared by the author. The sample used in
this study is high school students in Bandung who
are active in futsal extracurricular, as many as 20
students. The instruments used in this research data
retrieval using a multi-stage test (bleep test) where
the author took from the book Nurhasan (2013: 120).
Comparison of Extensive and Extensive Interval Exercises in Futsal VO2max Player Upgrades
169
2.1 Statistic analysis
2.1.1 Average Calculation and Standard
Deviation
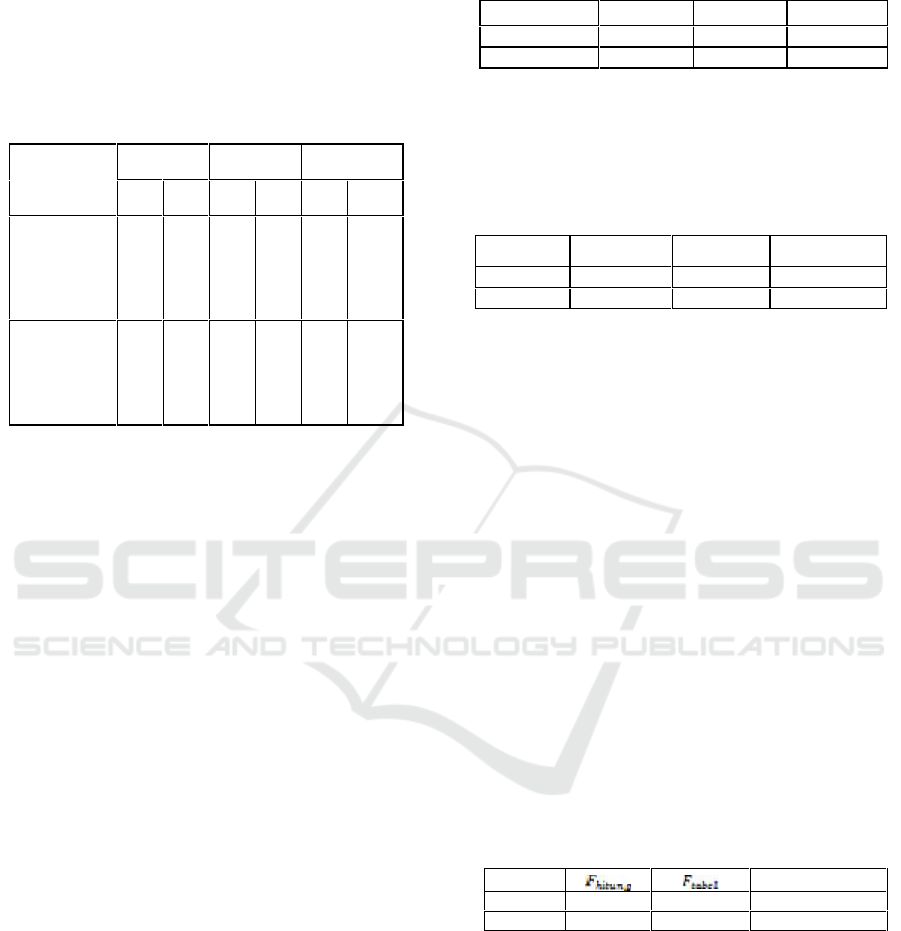
Table 1: Results Calculation of Average Score and
Standard deviation Test of Futsal Extracurricular
Members’ VO2Max SMA YWKA Bandung.
GROUP
EARLY
TEST
END TEST
GAIN
S
S
S
Exercise
VO2max with
Extensive
Interval
Training
Methods
2.67
4.95
6.22
5.07
3.55
0.32
Exercise
VO2max with
Intensive
interval
training
Methods
2.26
5.02
4.83
4.83
2.57
0.302
The data in Table 1 shows that the average of
group A tests (VO2Max improvement exercise with
extensive interval training method) is 42.67 and for
group B (VO2Max improvement exercise with
intensive interval training method) of 42.26. The
standard deviation for group A was 4.95 and
standard deviation of group B was 5.02. The mean
and standard deviation values of the two groups'
initial tests were almost identical due to the pre-
exercise sample division into two groups with
similar abilities. While for the final test the average
of group A was 46.22 with standard deviation of
5.07 while the final test group B had an average of
44.83 with standard deviation of 4.83.
Table 4.1 also shows that the gain or gap from
the initial and final test of the two groups, ie group
gain A gain (VO2Max increase in training with
extensive interval training method) is 3.55 with
standard deviation 0.32 is greater than the mean -
average group gain B (VO2Max exercise with
intensive interval training method) of 2.57 and
standard deviation of 0.302.
2.1.2 Normality Testing
The next step is to test the normality by using the
liliefors normality test. From the results of this test
will determine which approach will be used in data
analysis, whether using parametic statistical
approach or parametric statistics. The normality test
results can be seen in the table below:
Table 2. Test Result of Normality Test of Both Group
Before Experiment.
Group
Conclusion
Group A
0.2315
0.258
Normal
Group B
0.2257
0.258
Normal
Then, calculated the normality of both groups
after the experiment was done. The result of the
calculation can be seen in table 3.
Table 3: Calculation Result of Normality Test of the
Second Group After Experiment.
Group
Conclusion
Group A
0.2238
0.258
Normal
Group B
0.2324
0.258
Normal
The test criteria for liliefors normality test are:
1. The hypothesis is rejected if L_o > L_(t-) the
conclusion is an abnormally distributed
population
2. The hypothesis is rejected if L_o < L_(t-) the
conclusion is that the population is normally
distributed
Based on table 4.2 and table 4.3 above it can be
seen that all the highest absolute value (L_o) value is
less than the value of value (L_ (t-)) is 0.258, then
the conclusion is that all populations are normally
distributed.
2.1.3 Homogeneity Testing
After the measurement of the average values and
standard deviation and the normality test results
from both groups of samples, for the next step to test
the homogeneity of the data by using the two
variance equality test. The results of the test can be
seen in table 4 below:
Table 4: Homogeneity test results of two variance of both
groups.
Groups
Conclusions
F initial
1,028
3,18
Homogeneous
F final
1,12
3,18
Homogeneous
On the basis of the results of testing the
similarity of two variance in table 4.2 above, kindly
note that the result F_hitung initial test = 1.028 and
final test = 1.12 smaller than F_tabel = 3.18 at dk
(9.9) with a real level = 0.05. The conclusion of the
two variance equality test results is that both groups
are homogeneous.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
170

2.1.4 Second Significance Test Forms of
Exercise
The next step is to test the results of the test data
from the two test results to the sample (this test and
analysis to find out whether there is a significant
increase of exercise results from both groups of
samples). The results of statistical analysis can be
seen in table 5 below:
Table 5. Significant Test Results From Both Forms of
Exercise.
Sample group
Information
Group A
28.85
2,262
Significant
Group B
26.91
2,262
Significant
The calculation and the significant test of the
increase of training result form is done by using two
significant test of two parties ie t test. From the
results of the test that is in table 4.5 obtained that:
1. For the form of group A exercise (VO2Max
improvement exercise with extensive interval
training method) obtained t count (28,25)> t table
(2,262) at level of trust / s ignifle α = 0,05 with
dk (9,9). The test criterion is, accept if -t1- ½ α
<t_count <-t1- ½ α. In this other case tcount is in
the rejection area of Ho, meaning Ho is rejected.
The conclusion is that there is a significant
influence from the extensive lati han interval
form to the increase of VO2max in the futsal
extracurricular students in Bandung High School.
2. For the form of group B exercise (VO2Max
improvement exercise with intensive interval
training method) obtained t count (26,91)> t table
(2,262) at level of trust / significant α = 0,05 with
dk (9,9). The test criterion is, accept if -t1- ½ α
<t_count <-t1- ½ α. In this other case t_count is
in the rejection area of Ho, meaning Ho is
rejected. The conclusion is that there is a
significant influence from intensive interval
training form to the improvement of VO2max in
futsal extracurricular students in Bandung High
School.
2.1.5 Two-level Significance Test (One
Party) Both Groups
The next step is to calculate and analyze the
differences in the influence of both forms of exercise
on the improvement of VO2Max in futsal
extracurricular students in Bandung High School.
For that required data in the form of the difference
of the initial test results and the final test of each
group of exercises as data increase exercise results.
The data of the difference calculation can be seen in
table 6 below:
Table 6. Significance Test Result of Two-Average (One
Party) Both Group Exercises Difference.
Group
Information
Group A-B
7,54
1,734
Significant
From the test results obtained that t_count of
7.54 is larger than 〖 t ₁ 〗 _ (- α) (1,734). The test
criterion accepts Ho if t ≤ t ₁ _ (- α) at the real level
α = 0.05 with dk = 18. In this case t_ (ˉcount) is in
the rejection region Ho, so Ho is rejected which
means there is a difference from both forms of the
method of training .
The conclusion is that there are significant
differences in impact between extensive interval
training methods and intensive interval training
methods on increasing VO2Max in futsal
extracurricular students in Bandung High School.
This means that the extensive interval training
method impacts better than extensive training
methods on increasing VO2Max in futsal
extracurricular students in Bandung High School.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Extensive interval training methods have a
significant effect on VO2Max improvement, while
intensive training methods, although they have an
effect on the increase in VO2Max, but the difference
in the increase gives a real indication that there are
factors that can affect the achievement of a person's
maximum ability. Strong evidence supports the
upgrading of aerobic and VO2max via the Sprint
Interval Training (SIT), which coincides with
muscle adaptation (Sloth et.al 2013). Endurance
exercise with high aerobic intensity through interval
methods showed significantly more effective than
medium and low intensity training to improve
VO2max (Helgerud et al., 2007).
Endurance Training and Exercise Interval both
improve aerobic fitness and thus have a connection
in risk of cardiovascular factors, fitness and all
causes of death. Several studies have suggested that
interval training leads to improvements in both
aerobic and anaerobic fitness as well as improving
endurance performance to a higher level. For
example, Daussin et al. found Increased Maximum
Oxygen Volume (VO2max) increased higher for
trained men and women who participated in an
Interval training program for 8 weeks (Milanović,
Sporiš and Weston, 2015). Many studies have shown
that a sufficient high intensity interval (HIT),
conducted at least 6 weeks, increases the peak
Comparison of Extensive and Extensive Interval Exercises in Futsal VO2max Player Upgrades
171

oxygen capacity (VO2max) (Gibala and Mcgee,
2008).
Physiologically, the closer a person‘s ability to
his or her maximum ability (the higher one's ability),
the more difficult it is to improve it. However, many
factors may influence both externally and internally.
For example, one‘s physical fitness and one‘s level
of motivation to improve the ability of physical
condition. These factors may be one of the many
obstacles that could inhibit VO2Max increase.
Interval training shows that the maximum aerobic
velocity is increased. This study shows that physical
quality improvement can be performed during the
in-season period (Dupont, Akakpo and Berthoin,
2004).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study are extensive interval
training methods giving a more significant impact on
the increase of VO2Max extracurricular futsal
members in high school. Extensive interval training
methods have significantly impacted VO2Max
increase in futsal extracurricular members of high
school. That is the average gain or difference
between the initial test and the final test of 3.55 with
standard deviation 0.32. the test t-test is worth
t_count (28,25)> t_table (2,262). Intensive interval
training methods have a significant impact on the
VO2Max increase in extracurricular members of
high school futsal. That is the average gain or
difference between the initial test and the final test
of 2.57 with standard deviation 0.302. tested t-test is
t_count (26,91)> t_tabel (2,262). There are
significant differences in impact between extensive
interval training methods and intensive interval
training methods on VO2Max increase in
extracurricular members of high school futsal.
Compared to the fact that extensive interval training
methods have a more significant impact on the
increase in VO2Max extracurricular futsal members
of Senior High School. This can be seen from the
results of the practice with extensive interval
training methods obtain an average increase of 3.55
more than in the practice with intensive interval
training methods that obtain an average increase of
2.57.
REFERENCES
Astorino, T. A. et al. 2012. ‘Effect of high-intensity
interval training on cardiovascular function, VO2max,
and muscular force.’, Journal of strength and
conditioning research, 26(1), pp. 138–145. doi:
10.1519/JSC.0b013e318218dd77.
Dupont, G., Akakpo, K. and Berthoin, S. 2004. ‘The effect
of in-season, high-intensity interval training in soccer
players.’, Journal of strength and conditioning
research, 18(3), pp. 584–589. doi: 10.1519/1533-
4287(2004)18<584:TEOIHI>2.0.CO;2.
Gaiga, M.C., And D. Docherty. 1995. The Effect Of An
Aerobic Interval Training Program On Intermittent
Anaerobic Performance. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 20:452–
464.
Gibala, M. J., Mcgee, S. L. 2008. Metabolic Adaptations
to Short-term High-Intensity Interval Training : A
Little Pain for a Lot of Gain ?, 2.
Helgerud, J. et al. 2001. ‘Aerobic endurance training
improves soccer performance’, Medicine & Science in
Sports & Exercise, 33(13), pp. 1925–1931. doi:
10.1097/00005768-200111000-00019.
Harsono. 1988. Coaching dan Aspek – Aspek Psikologis
Dalam Coaching. Bandung: Tambak Kusuma CV
Helgerud, J. et al. 2007. ‘Aerobic high-intensity intervals
improve V?? O2max more than moderate training’,
Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 39(4),
pp. 665–671. doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e3180304570.
Milanović, Z., Sporiš, G. and Weston, M. 2015.
‘Effectiveness of High-Intensity Interval Training
(HIT) and Continuous Endurance Training for
VO2max Improvements: A Systematic Review and
Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials’, Sports Medicine,
45(10), pp. 1469–1481. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-
0365-0.
Nurhasan. 2013. Tes dan pengukuran pendidikan olahraga
dan kesehatan. Cimahi: STKIP Pasundan Cimahi.
Pedro, R. E. et al. 2013. ‘Running Speeds at Ventilatory
Threshold and Maximal Oxygen Consumption
Discriminate Futsal Competitive Level’, Journal of
Strength and Conditioning Research, 27(2), pp. 514–
518. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182542661.
Schmolinsky, Gerhardt. 1983. Track and Field. German:
DVL Sport Verlag.
Seiler, Stephen. 2010. What is Best Practice for Training
Intensity and Duration Distribution in Endurance
Athletes?.. International JOURNALS Of Sports
Physiology and Performance. Volume 3 issue 3
Sloth, M, Sloth, D, Overgaard, K, Dalgas, U. 2013. Effects
of sprint interval training on VO2max and aerobic
exercise performance: A systematic review and meta-
analysis. Scandanavian Journals Medicine Science
Sports. doi: 10.1111/sms.12092
Soto, V. M. 2008. ‘Match analysis and heart rate of futsal
players during competition’, (January 2013), pp. 37–
41. doi: 10.1080/02640410701287289.
Talanian, JL, Galloway, SD, Heigenhauser, GJF, Bonen,
A, and Spriet, LL. 2007. Two weeks of high-intensity
aerobic interval training increase the capacity for fat
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
172

oxidation during exercise in women. J Appl Physiol
102: 1439–1447, 2007.
Teixeira, A. S. et al. 2017. Comparative effects of two
interval shuttle-run training modes on physiological
and performance adaptations in female professional
futsal players, Journal of Strength and Conditioning
Research. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002186.
Comparison of Extensive and Extensive Interval Exercises in Futsal VO2max Player Upgrades
173
