
Comparison of Shooting Accuracy between Dominant and Non-
Dominant Leg among Indonesian Soccer School Players
Saharuddin Ita and Pahala Tua Hutajulu
Department of Physical Education, Health, and Recreation, Cenderawasih University, Abepura, Jayapura, Indonesia
saharuddinita@yahoo.com
Keywords: Shooting, Accuracy, Dominant Leg, Soccer school.
Abstract: In this study, the comparison of shooting accuracy between dominant and non-dominant leg within resting
state and fatigued state among Indonesian soccer school players was examined. Fifteen soccer school
players from the Batik Soccer School, Jayapura, Indonesia, volunteered to participate in this study. The
subjects had a mean age of 16.44 ± 0.86 (years), a mean height of 1.61 ± 0.042 (m) and a mean weight of
58.60 ± 3.81(kg). The comparison research method and shooting target boards were applied. The results
showed that the shooting accuracy score between dominant and non-dominant leg within resting state and
fatigued state were of 3.49:2.26 and 3.36:1.87 respectively (p<0.05). Significant differences between
dominant and non-dominant leg indicated unbalanced muscle strength of both legs. The shooting skill
among Indonesian soccer school players was found at a relatively low level. Furthermore, coaching method
and curriculum in soccer school should be examined comprehensively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Soccer is known as the most popular sport in the
world, including Indonesia. It involves more than
270 million practitioners in more than 200 countries
(FIFA, 2016). This sport is played by both men and
women, age ranging from children to adults, at
various levels of ability. The huge number of
participants led to the growth of soccer clubs at
various levels, both professional and amateur,
together with large numbers of tournaments and
championships. However, the FIFA World Cup
tournament is the highest level of soccer tournament
in the world, and since its formation only listed 43
countries in the quarter finals and 8 countries as
winners, namely Brazil, Germany, Italy, Argentina,
Uruguay, France, England, and Spain (Stokkermans,
2015). The international successes of the former
countries was largely considered due to their
comprehensive talent identification and development
systems, since those factors were regarded as the
breeding ground for the next generation of top-level
athletes (Holt, 2002). Soccer school was known as
an organization or an independent legal entity whose
primary objective is to provide players with long-
term training through the provision of the necessary
training facilities and infrastructure. For this reason,
soccer school, a place where youth talent
identification, coaching, and education begin in
youth players, should be listed as one of the
determining factors in national team achievement. In
Indonesia, soccer school is known well as an
informal education institution, established for more
than 10 years and spread all over the country.
Unfortunately, very limited research has been
conducted related to Indonesian soccer schools.
In soccer games, strategies and techniques must
be developed in order to create an interesting game
and a winning team. Basic techniques of soccer are
divided into two: with and without the ball. Basic
techniques with the ball are: shooting, passing,
receiving, dribbling, keeping, heading, throwing-in,
and some related to goalkeeper techniques. Basic
techniques without the ball are running, jumping,
and feinting (Carr, 2005). Since the main purpose in
soccer games is to score as many goals as possible
against the opposing team, shooting technique
became the main basic technique and the most
important aim of training programs in young
players. These facts lead many researchers focused
on shooting technique (Kellis and Katis, 2007;
Bjelica, Popović, and Petković, 2013; Mohammed
and Kohl, 2016). Shooting quality is determined by
power and accuracy (Shan et al., 2012). Shooting
power is associated with the momentum of the leg
while shooting accuracy means precision of the ball
towards the target point, which is the goal. Accuracy
is the decisive factor in scoring goals; hence
practicing accuracy over power was more
emphasized (Hargreaves and Bate, 2010). Carr
Ita, S. and Hutajulu, P.
Comparison of Shooting Accuracy between Dominant and Non-Dominant Leg among Indonesian Soccer School Players.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 163-167
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
163

(2005) suggests that the best shooting accuracy can
be achieved by using the instep. Instep position is an
area on top of foot or one can say at the braided
shoelaces area.
It has been known the importance of hand and
leg dominance, where the second one has been given
minimal attention (Spry, Zebas, and Visser, 1993).
In the case of hand dominance, while one hand is
being used the other has no significant roles.
Contrarily, the notion of leg dominance should be
viewed in a different perspective considering the
roles of the legs in different tasks such as mobility
and stability. While a leg is being used, such as to
shoot a ball, the other leg has an important role of
postural control and stability (Velotta et al., 2011).
Numbers of research have been conducted on leg
dominance, giving the fact that the characteristics of
the dominant leg and non-dominant leg are generally
different (Rahnama, Lees, and Bambaecichi, 2005;
Spry, Zebas, and Visser , 1993; Velotta et al., 2011;
Witkowski et al., 2011; Bjelica, Popović, and
Petković, 2013). Researchers generally make the
assumption that the dominant leg is the preferred
limb and the non-dominant leg is the non-preferred
limb. In this study the dominant leg is identified as
the preferred leg or the leg frequently used in
shooting the ball (Velotta et al., 2011).
Soccer players, particularly junior players, tend
to use the dominant leg only (Costa Silva et al.,
2015). However, unbalanced use of one leg only
induced asymmetries musculoskeletal (Maupas et
al., 2002). Junior football players under-18 years old
often at times experience muscle asymmetries
(Capranica et al., 1992). For this reason, it is very
important for the junior players to increase muscle
strength balance in both legs. Although many studies
exist with junior league players, limited research has
been conducted with soccer school players. This
study was also conducted in order to review the
coaching method and curriculum in soccer school in
Indonesia.
The aim of this study was to compare accuracy
of shooting between dominant and non-dominant leg
among Indonesian soccer school players. The
comparison method was applied in two states: rest
and fatigued state. This study was conducted as an
evaluation model for the soccer school program. The
question arises: to what degree is the difference of
accuracy shooting between the dominant and non-
dominant leg in soccer school players and how to
enhance the balance performance of both legs?
2 METHODS
2.1 Participants
Fifteen soccer school players from the Batik Soccer
School, Jayapura, Indonesia, volunteered to be
subjects. The criteria for selecting players for the
sample were as follows: being a student of the
soccer school for two years, member of U-18’s
class, and having a good health condition. Research
was conducted at Cigombong Soccer Field,
Jayapura, Papua, Indonesia. Batik soccer school
located in Jayapura city was chosen since Jayapura
is known as one of the cities with a considerable
source of talented players for the Indonesia national
team.
2.2 Procedure
Data collecting procedures to measure the accuracy
of shooting were as follows: warm-up, stretching,
shooting trials, and finally shooting accuracy test.
Each player was asked to shoot on target from the
distance of 20 meters, with both dominant and non-
dominant legs, within two different conditions: rest
and fatigue. At rest condition, players had to shoot
only if their heart rate was under 90 bpm (bit per
minute), while fatigue condition means players had
to complete ten squats before shooting. Those four
variables were outlined in table 1.
Table 1: Shooting Test Variables.
Test Variables
Condition
DR: Shoot with dominant leg
in rest state
NR: Shoot with non-dominant
leg in rest state
Rest state:
player’s heart rate
under 90 bpm
DF: Shoot with dominant leg
in fatigue state
NF: Shoot with non-dominant
leg in fatigue state
Fatigue state:
player complete 10
squats before shoot.
Each player performed a total of ten shoots for
each variable, using a standard soccer ball and a
target board. The target board was adapted from the
one previously developed by University of
Montenegro (Bjelica, Popović, and Petković, 2013)
with simplified scaling system (1 – 10) for easy
scoring. The midpoint of the target board was given
the highest score of 10 and the edge of the target
board was given a score of 1, while every failure to
make contact with the board was given a score of 0.
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
164
2.3 Data Analysis
The obtained data was calculated using descriptive
statistics; proceeded with the independent t-test
calculation to determine whether there were
significant differences of the four variables. The
analysis provided the answers to the question of
whether there were differences between shooting.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
From the descriptive analysis, it is known that the
fifteen players who participated in this study have
the following characteristics: age 16.44 ± 0.86 years,
height 161.13 ± 4.17 cm, and weight 58.60 ± 3.81
kg. Descriptive statistics of the sample profiles and
shooting scores are given in table 2.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics
M
SD
SE
Min
Max
R
Ku
Sk
Age (years)
16.44
0.86
0.22
15.02
17.74
2.72
-1.11
-0.30
Height (cm)
161.13
4.17
1.08
153
166
13
-0.39
-0.80
Weight (kg)
58.6
3.81
0.98
50
65
15
0.59
-0.57
DR
3.49
0.86
0.22
1.7
5
3.3
0.11
-0.14
NR
2.26
0.90
0.23
0.5
3.4
2.9
-0.62
-0.63
DF
3.36
1.11
0.29
1.9
5.8
3.9
0.10
0.80
NF
1.87
0.89
0.23
0.4
3.7
3.3
-0.11
0.02
Legend: M – mean, SD –standard deviations, SE– standard errors, Min–minimum value, Max–maksimum value, R–
range of value, Ku–Kurtosis, dan Sk–Skewness.
The result of independent t-test at a significant
level of p < 0.05 was shown in table 3. It revealed
significant differences of shooting accuracy between
dominant and non-dominant legs both in rest and
fatigued states. The value of this comparison is 7.30.
Table 3: Independent t-test calculation.
DR
NR
DF
NR
*7.30
DF
0.47
*-4.06
NF
*6.56
1.60
*9.94
* p < 0,05
Figure 1 shows the comparison of shooting
accuracy score between dominant and non-dominant
legs in a resting state. The shooting score
comparison of 3.49:2.26 revealed a significant
difference.
Figure 1: Comparison of shooting accuracy score between
dominant and non-dominant leg in a resting state.
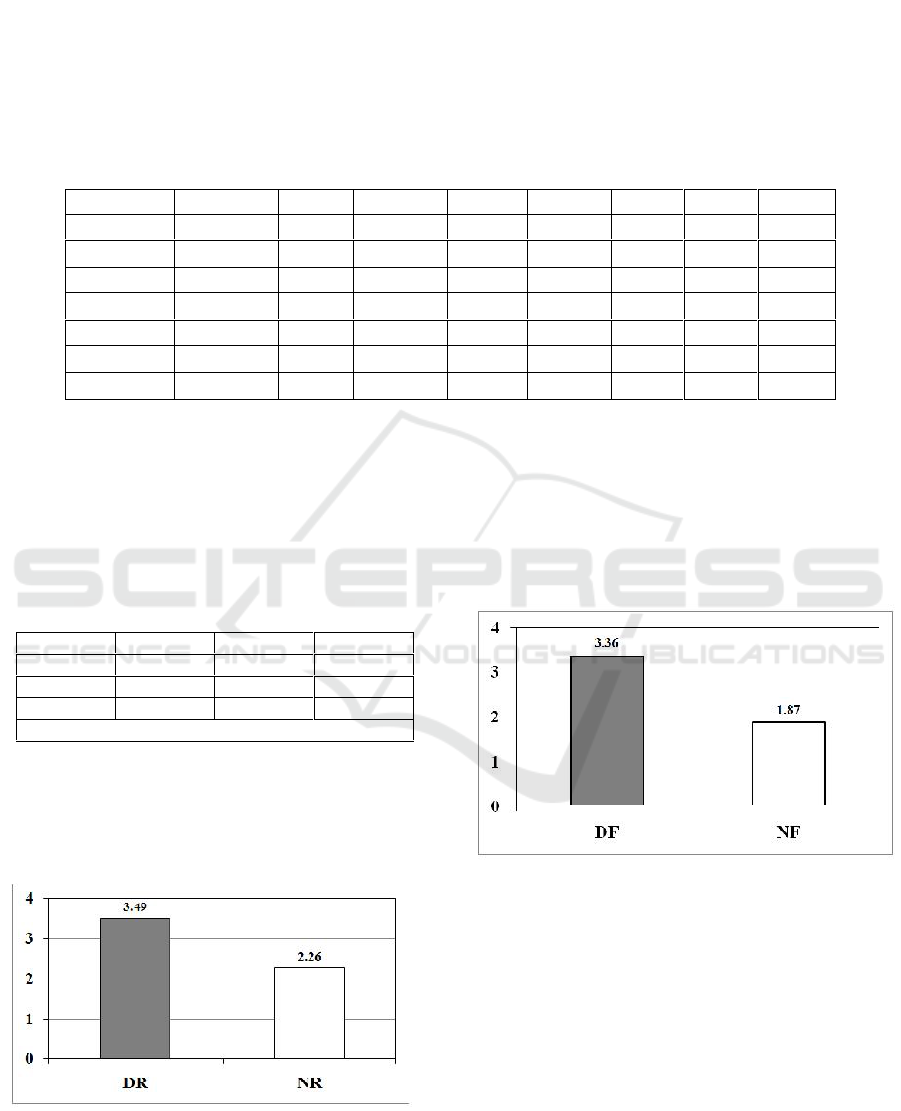
Furthermore, figure 2 shows the comparison of
shooting accuracy score between dominant and non-
dominant legs in a fatigued state. Like in a resting
state, it also shows significant difference between
these two variables. The value of this comparison is
9.94 with shooting score comparison of 3.36:1.87.
Figure 2: Comparison of shooting accuracy score between
dominant and non-dominant leg in a fatigue state.
The previous study from Montenegro junior
premier league revealed that the shooting score
comparison in resting state of 5.86:4.76 and in
fatigued state of 5.58:4.71 (values were normalized
in 0-10 scale). We could notice that shooting quality
of Batik soccer school students was lower than that
of the junior premier league. This affirmed that the
basic techniques learned and applied in the soccer
school were not yet optimum, even though instep
shooting together with dribbling is the most
fundamental stage in the youth coaching curriculum
(National Soccer Coaches Association of America,
Comparison of Shooting Accuracy between Dominant and Non-Dominant Leg among Indonesian Soccer School Players
165

2014). The players volunteering for this study had
not even conducted shooting practice using target
boards before. Wide range of shooting ability,
peculiarly in a fatigue condition, indicated
unbalanced muscle strength of both legs in players.
This is noteworthy since the unbalanced use of one
leg induced asymmetries musculoskeletal and may
cause injury to the players in the future.
Low quality in shooting and unbalanced use of
both legs among Indonesian soccer school soccer
players indicated that the coaching method and
soccer school curriculum should be examined
comprehensively. Scheunemann at al. (2012) stated
in their book about soccer school curriculum, that
one of the most fundamental weaknesses in the
youth player development system in Indonesia was
the lack of focus of the soccer school organization.
Soccer school mostly focuses on reaching the
victory of the club rather than the player’s
competency, which are; technique, tactics, physical
training and character. Cholid (2014) also analyzed
the soccer school system and determined that
generally soccer school in Indonesia still applies an
internal curriculum instead of a national standard
curriculum. All stakeholders in Indonesian soccer
schools need to review the implementation of
coaching standard and education of soccer school, in
order to improve the quality of the youth talent
development system, and eventually improve the
national team performance to higher levels. Batik
soccer school has been informed of the results
revealed in this study and currently they are
reviewing their curriculum.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The comparison of shooting accuracy between
dominant and non-dominant leg within resting state
and fatigued state among Indonesian soccer school
players has been studied. Significant differences
between dominant and non-dominant leg indicated
unbalanced muscle strength of both legs. The
shooting skill among Indonesian soccer school
players was found to be at a relatively low level, and
coaching method and curriculum in soccer school
should be examined comprehensively.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks to all players for their efforts, Batik Soccer
School for the collaboration, and Herman Mayoseph
for his assist in technical preparation and data
collection of this study.
REFERENCES
Bjelica, D., Popović, S., and Petković, J., 2013,
Comparison of Instep Kicking Between Preferred and
Non-Preferred Leg in Young Football Players,
Montenegrin Journal of Sports Science and Medicine,
2(1), 5-10.
Capranica, L., Cama, G., Tessitore, A., and Figure, F.,
1992, Force and power preferred and non-preferred leg
in young soccer players, The Journal of Sports
Medicine and Physical Fitness, 32(4), 358-363.
Carr, T. 2005, How to coach a soccer team: Professional
advice on building a winning team. London: Hamlyn.
Cholid, A., 2014, Evaluasi Pelaksanaan Sekolah
Sepakbola (Pelatih) di Pengprov Persatuan Sepakbola
Seluruh Indonesia (PSSI) Jawa Timur. In Prosiding
Seminar Nasional Olahraga (pp. 286-299). Yogyakarta,
Indonesia: UNY Press.
Costa Silva, J. R. L., Detanico, D., Dal Pupo, J., and
Freitas, C. R. 2005. Bilateral asymmetry of knee and
ankle isokinetic torque in soccer players u20 category.
The Revista Brasileira de Cineantropometria e
Desempenho Humano. 17(2), 195-204.
Fifa Communications Divisions. (2006, 05 31). FIFA Big
Count 2016. Retrieved 04 12, 2015, form FIFA.com:
http://www.fifa.com/mm/document/fifafacts/bcoffsurv/
bigcount.statspackage_7024.pdf
Hargreaves, A. and Bate, R., 2010, Skills and Strategies
for Coaching Soccer, Champaign: Human Kinetic, 2nd
edition.
Holt, L. H., 2002, A comparison of the soccer talent
development systems in England and Canada,
European Physical Education Review, 8(3), 270-285.
Kellis, E., and Katis, A., 2007, Biomechanical
characteristics and determinants of instep soccer kick,
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 6, 154-165.
Maupas, E., Paysant, J., Datie, A. M., Martinet, N., and
André, J. M., 2002, Functional asymmetries of the
lower limbs. A comparison between clinical
assessment of laterality, isokinetic evaluation and
electrogoniometric monitoring of knees during
walking, Gait Posture, 16(3), 304-312.
Mohammed, Z., and Kohl, K., 2016, Which Orthoptic
Visual Approach Evaluates Shooting Skill Accuracy in
Soccer Players? Journal of Physical Education and
Sport, 16(2), 471-475.
National Soccer Coaches Association of America, 2014,
Complete Soccer Coaching Curriculum For 3-18 Year
Old Players. Volume 1. Kansas City: Coaching Media
Group.
Rahnama, N., Lees, A., and Bambaecichi, E., 2005,
Comparison of muscle strength and flexibility between
the preferred and non preferred leg in English soccer
players, Ergonomics, 48(11-14), 1568-1575.
Scheunemann, T., Reyna, C., Perez, J., and Gunadi, P.
2012, Kurikulum dan Pedoman Dasar Sekolah
Sepakbola Indonesia Untuk Usia Dini, Usia Muda dan
Senior, Jakarta: Football Association of Indonesia.
Shan, G., Yuan, J., Hao, W., Gu, M., and Zhang, X., 2012,
Regression equations for estimating the quality of
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
166

maximal instep kick by males and females in soccer,
Kinesiology, 4(2), 139-147
Spry, S., Zebas, C., and Visser, M., 1993, What is Leg
Dominance? In XI Symposium of the International
Society of Biomechanics in Sports (pp. 165-168).
Amherst, Massachusetts: International Society of
Biomechanics in Sports.
Stokkermans, K. (2015, 01 18). World Cup 1930-2018.
Retrieved 04 25, 2015, from The Rec.Sport.Soccer
Statistics Foundation (RSSSF):
http://www.rsssf.com/tablesw/worldcup.html
Velotta, J., Weyer, J., Ramirez, A., Winstead, J., and
Bahamonde, R., 2011, Relationship between leg
dominance test and type of task. PJSS, 11,1035-1038.
Witkowski, Z., Lyakh, V., Gutnik, B., Lipecki, K.,
Rutowicz, B., Penchev, B., and Pencheva, L., 2011,
Corrective effects of different training options on
development and maturation of professional motor
skills from dominant and non-dominant legs of young
soccer players. Journal of Physical Education and
Sport, 11(3), 291 – 299.
Comparison of Shooting Accuracy between Dominant and Non-Dominant Leg among Indonesian Soccer School Players
167
