
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural
Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials
Rahayu Condro Murti and Marsigit Marsigit
Yogyakarta State University, Colombo Street, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
rahayu_cm@uny.ac.id , marsigitina@yahoo.com
Keywords: perspectives on culture, teaching materials, primary mathematics.
Abstract: An integrated concept of culture should be understood by students of primary mathematics teaching education
program before they implement culture-based learning in primary schools. This study aims to recognize and
analyze students’ perspectives on the concept of culture. Both of recognition and analysis are done in order
to determine students’ needs in the framework of developing culture-based teaching materials in the
Department of Primary Teacher Education (PGSD). This study adopts an integrated concept of culture that
contains three aspects, namely values, contexts and artifacts. Data were obtained from 278 PGSD students
(respondents) who have passed the course of primary mathematics education. Date were obtained through
two instruments, questionnaire and lessons’ implementation plans (RPP). Data then analyzed in quantitative
(for questionnaire) and qualitative (Critical Discourse Analysis for the RPPs) modes. Opinions of students
were positive in general towards the need for culture-based teaching materials, where they realize that culture
is a part of real life that mathematics tries to solve its problems. Very few of the students still believe in
separation between culture and mathematics. Results also show that students rarely experience culture-based
learning and rarely get involved in cultural activity during their course.
1 INTRODUCTION
What will be envisioned in our minds when we hear
the word ‘culture’? what will people around us, like
pre-service teacher students, say about it?. As we
were preparing this study, one of our interviewee
said: “the culture has begun to be forgotten, especially
in a modern environment”.
Technological developments in this era of rapid
globalization, not only provide many facilities for
human life, but also a direct or indirect negative
impact for the world of education and exceed it to the
world of citizenship and belonging. In Indonesia
nowadays, 84% of citizens have cell-phones.
Moreover, with the vast presence of smart phones, it
is familiar now to see children, and even babies, play
with gadgets. The more children are exposed to
globalized entertainment floods, with American
settings in general, through TVs and gadgets; the less
they have chances to know about their communities,
environments and actually culture! Culture, in our
point of view, is not limited to traditional things,
culture is that general context of psychological, social
and material surrounding us, yesterday, tomorrow
and of course today.
The abundance of Indonesian children from their
noble culture and their low ability to solve story
problems becomes urgent duty for educators,
especially mathematics educators at the primary
school level. Primary school children who are,
cognitively, in concrete operational phase, should be
able to build new concepts in mathematics that are
learnt meaningfully. Being meaningful means well-
connected to their selves, natural, social and material
environments surroundings them. Being meaningful
may be realized by getting back to know, explore, and
preserve those settings that constitute together
Indonesian culture. Thus, learning mathematics is not
just learning to count, but also conserve the noble
culture of the nation.
Based on the results of discussions the researcher
had with mathematics education specialists from
Michigan State University, learning mathematics in
primary schools should not abandon the existing
culture in the student environment. Culture here, not
only limited to the art, dance or food that is
traditional, but also on the daily events that exist in
the student environment. Mathematics learning that
relates to the problems around students will help the
students in facing the problems they encounter.
210
Murti, R. and Marsigit, M.
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 1, pages 210-217
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved

Students of PGSD (Department of Education for
Primary School Teacher in Yogyakarta State
University, Indonesia), as prospective primary school
teachers, should be empowered to teach mathematics
that pay more attention to the cultural values of the
nation and reconnect students to their environments.
Empowering pre-service teachers to teach such
culture-based mathematics should start with infusing
curricula in PGSD with cultural aspects, especially
the integrated concept of culture. Integrated concept
of culture becomes an urgent need because, as we
were preparing our recent study, most PGSD students
appeared to have partial concepts of it.
2 CULTURE IN MATHEMATICS
EDUCATION
2.1 The Meaning of Culture
Robert Kohls in Wintergerst (2011) states that
"Culture is an integrated system of learned behavior
patterns that are characteristic of any given society.
Culture refers to the total way of life of particular
groups of people. It includes everything that a group
of people thinks, says, does, and makes. Its systems
of attitudes and feeling. Culture is learned and
transmitted from generation to generation”. In this
regard, Wintergerst notices that culture can be seen
from different disciplinary perspectives. For
example, anthropologists view culture as the
perspective of human studies. Sociologists view
culture as social relationships between people and
their groups. Psychologists view culture as a
phenomenon related to mind and behavior.
Meanwhile, linguists focus, primarily, on language
practice. To be briefly stated, “Culture is a universal
fact of human life”.
Saifer (2011), goes in the same current as states
that: “culture can be defined as a way of life that
relates to socially transmitted habits, customs,
traditions, and beliefs that characterize a particular
group of people at a particular time”. Culture
influences the way people learn, solve problems, and
teach”. Therefore, learning mathematics in primary
school, as a learning and teaching activity, cannot be
isolated from the existing culture in the student and
teacher environment. Actually, school math aims to
help students overcome the problems they encounter
in their environment using mathematical methods.
Some of the following figures clarify the cultural
significance of mathematics in primary school.
K.H. Dewantara (2013) states that culture is the
fruit of human civilization or human mind. In Bahasa
Indonesia, the word civilization means ‘peradaban’.
Peradaban comes from the root ‘adab’, which means
‘virtue of total nature of human mind’. The researcher
proposes the phrase ‘total nature of human mind’
because that is the way Malay language represents
‘mind’. Mind in Malay culture is ‘budi’, budi is not
limited to cognitive functions of mind, but exceeds it
to the emotional, wills, and even supernatural
functions. To sum it up, culture in Indonesian
perspective is related to civilization, and total
existence experience of man.
According to Dewantara (2013), “all cultures are
orderly, beautiful, useful, sublime, giving a sense of
peace, happy, happy, and so on. Culture is the result
of the struggle of human life”. Dewantara even tries
to explain culture by dividing it into elements, based
on man’s mind functions. According to Dewantara,
human mind encompasses all the movements of
mind, taste, and will, so that culture can be divided
into entities of thought (e.g. science, education and
teaching, philosophy), entities of feeling (e.g. all
noble character, customs, justice, religion, arts,
temples, batik, wicker, wayang and so on), and
entities of will (e.g. agriculture, shipping, buildings,
etc.). Culture never has an everlasting existence, but
is constantly changing because of the changing nature
and the age. Sometimes culture generally benefits
human civilization. Other times, culture may instead
endanger civilization and even life! Therefore, we
may always sustain a sort of critical thought that
enables us to adapt our culture to the ever-changing
demands of contexts surrounding us.
In line with the opinion of K.H. Dewantara,
Honigmann in Koentjaraningrat (1990) states that
there are three forms of culture, namely ideas,
activities, and artifacts. Following is a brief
explanation of that trilogy of culture.
Culture as ideas, values and norms.
Culture as patterned activities or actions in the
community, also called the social system. This
social system consists of human activities that
interact with each other and are concrete,
happening around us every day, observable,
photographed and documented.
Culture as artifacts, objects of human works.
This type of culture is also called the physical
culture so that the most concrete, can be objects
that can be touched, seen, and photographed.
Another famous author that tries to construct the
concept of culture is Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934), a
Russian psychologist, as he proposes Cognitive-
Construction theory. Theory of cognitive-
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials
211
Construction assumes the active role of learners
(students) in building their own knowledge.
Vygotsky improves Piaget's ideas, as he specifically
looks at how social interactions and collaborations
proceed in learner’s learning. Piaget argues that the
development of one's character has an end point and
consists of four major growth periods. Those periods
are, in order, (1) sensorimotor, (2) preoperational, (3)
concrete operations, and (4) formal operations.
In the contrary, Vygotsky believes that
character’s development is a life-long process that is
too complex to be defined gradually (Driscoll, 1994).
Learning process will occur efficiently and
effectively if learners learn cooperatively with their
friends in a supportive and guided environment,
accompanied by a more capable person or an adult,
such as a teacher. The theory formulated by Vygotsky
includes (1) culture, (2) language, and (3) the zone of
proximal development (ZPD).
Vygotsky argues that the culture and social
environment of a child is paramount in influencing
the formation of their knowledge. Children learn
through songs, languages, arts, and games, as culture
affects the learning process. A person's mind must be
understood from the social and cultural background
and history. Besides, Vygotsky agrees with Piaget as
emphasizing the importance of an individual's active
role in constructing his knowledge. In addition to
culture, language also plays an important role in the
process of cognitive development of children. There
is a clear relationship between language development
and cognitive development of children.
The third component in Vygotsky’s theory is
‘Zone of Proximal Development’ (ZPD). In this
regard, Vygotsky states that “what children can do
with help today will be able to do it on their own
tomorrow” (Vygotsky, p.81, 1978). ZPD implies that
a child learns by building or collecting his own
knowledge, and in the same time affected by social
context around her. This opinion is supported by
Bruner, co-founder of constructivist theory. Bruner's
theoretical framework is based on the theme that
learners build ideas or concepts based on new existing
knowledge. Learning is an active process. Aspects of
the process include selection and transformation of
information, decision making, generate hypotheses,
and the meaning-making of information and
experience.
Bruner postulates three stages of intellectual
development, (1) the enactive stage, (2) the iconic
stage, and (3) the symbolic stage. At an enactive
stage, children learn an active knowledge by using
concrete objects or through real and contextual
situations. In the iconic stage, children learn and gain
knowledge through images or graphs that are images
of the manipulated objects. Children do not directly
interact with real objects as in the enactive stage. At
a symbolic stage, the child learns in the form of
abstract symbols used according to the agreement of
the people in the field concerned, either verbal
symbols (e.g. letters, words, and sentences),
mathematical symbols, or symbols / other abstract
symbols.
The three-stages of learning proposed above by
Bruner are more clarified by four stages of learning
by Fruedenthal. Fruedenthal is the founder of
Realistic Mathematics Education (RME), which
includes concrete mathematics, concrete models,
mathematical models, and formal mathematics. RME
is closely related to culture-based learning, because
it’s philosophical foundation (Freudenthal (2002)),
assumes that Mathematics should be connected to
reality and should be seen as living activity, hence it
relates to cultural elements. As Moritz (2011) argues
that a mathematician must have mastered the
technical framework in which they are placed.
Based on previous opinions of famous researcher
mentioned above, the meaning of culture in learning
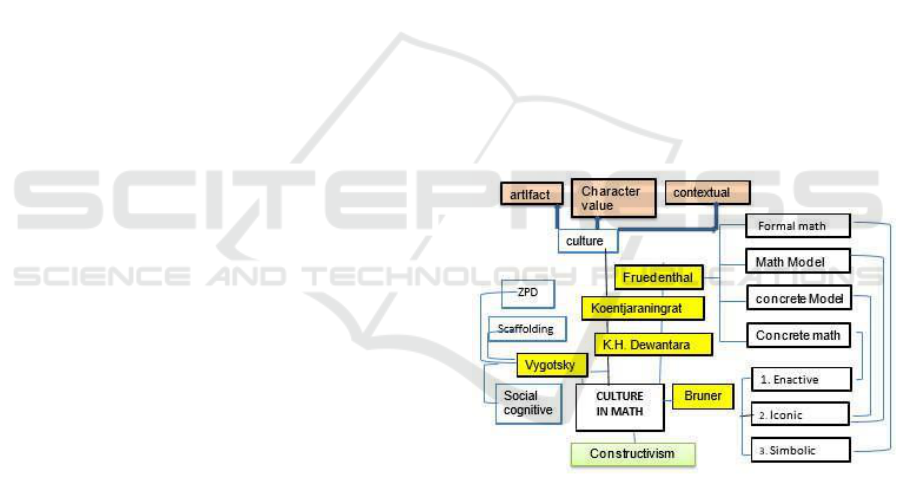
mathematics can be explained as follows in figure 1.
Figure 1: Concept map of culture based mathematics
learning.
2.2 Implementation of Culture-Based
Mathematics Learning
Albanese (2015) found that the potential of working
with ethno mathematical micro projects about other
signs of cultural identity and to begin with, the
curriculum of primary education may be the most
accessible to work with. Cimen (2014) argue that
mathematics can be relative among cultural
perspectives and social groups, so it can be developed
as a result of various activities based on practices and
experiences of these cultural groups. Based on
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
212
previous discussion about the meaning of culture, this
article adopts the point of view that culture-based
mathematics learning is that kind of learning that
links mathematics with the cultural trilogy, namely
value/character, social context, and artifact. Here is
an example of primary mathematics learning based on
that element. In this context, Ghislaine Guedet (2016)
argues that children should learn by applying hands-
on material and concrete activities. In line with this,
Trinick et al (2016) argue that students need to be
involved in critical reflections on the processes by
which practices and knowledge come to be valued.
Therefore, it is important to make the students active
in learning and involve the culture that exists in their
environment.
2.2.1 Values/Character in the Learning of
the Sum of Two Integers
The learning of the summing of two integers using
black and white buttons, where black buttons are
negative and white buttons are positive. If associated
with the culture that exists in Indonesia, then black
(magic) is usually indicates evil, while the white
indicates good character.
Summing operations of integers may be done by
involving white-black or white-red analogues
(metaphors), as teacher shows students concrete
materials that represent each one. Besides, summing
operations of integers may be useful in cultivation of
good values in student personality. Four types of
summations are explained below (table 1) alongside
suggested ways to realize that cultivation.
Table 1: Cultivation values by utilizing four types of
integers’ summation operations.
No.
Type of
summing
integers
Metaphores of
integers in
cultivating values
Examples
1
Summing
two
positive
integers.
Good deed added to
another good deed
result in more good
deeds.
3 + 4 = 7
2
Summing
two
negative
integers
Wrong deed added
to another wrong
deed result in more
wrong deeds.
-3 + (-5) = -8
3
positive
integer
plus
negative
integer
The type of result
(positive or
negative) is
determined by
considering which
actions are more
numerous (if the
wrong deed is
1 + (-3) = -2
7 + (-3) = 4
No.
Type of
summing
integers
Metaphores of
integers in
cultivating values
Examples
bigger, so the result
will be negative and
if the good deed is
bigger, so the result
will be positive).
4
negative
integer
plus
positive
integer
The type of result
(positive or
negative) is
determined by
considering which
actions are more
numerous (if the
good deed is bigger,
so the result will be
positive)
-4 + 6 = 2
Moreover (as in (Rahayu Condro Murti, 2014))
those operations of integers’ summation may be
utilized in cultivation religious values as follows. (1)
two positive integers: as a servant of God, a student
should do good deeds as much as possible, so as to
save as much reward as possible, (2) two negative
integers: a servant of God should not do evil, because
it will always be recorded as a sin that will increase
continuously if added to other evil, (3) and (4)
summing negative and positive integers, gives
meaning that a student, as a human being, may do
good or wrong deeds, but he should always try to do
more (add) good deeds (positive integers), so that
when his deeds are to be weighed in the hereafter,
good deeds will ultimately exceed the wrong ones
(negative integers).
2.2.2 Contextualizing Two Natural Numbers
Multiplication
Students usually face the concept of two natural
numbers multiplication in everyday life. The
following figure 2 is an example of a multiplicity of
two natural numbers. This example in figure 2 is
introducing the concept to second grade students of
primary school.
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials
213

Figure 2: Introducing the concept of two natural numbers
multiplication.
Multiplication of two numbers or other number
operations can also be found in the existing buying
and selling activities in the modern market (mall) and
traditional markets, such as the following floating
markets (figure 3), where floating markets are special
trait of archipelagic nature of Indonesia.
Figure 3: Floating markets in archipelagic Indonesia.
2.2.3 Primary Mathematics at Prambanan
Temple (Artifact)
Learning primary mathematics may carried out in
cultural artifacts context. One of famous Indonesian
culture artifacts is Hindu Temple of Prambanan,
which is located in the heritage city of Yogyakarta.
Within that huge temple complex, many of primary
mathematics may be done. Starting from number
learning to geometry learning, from simple to more
complex forms. For example, students may be asked
to count the number of statues in the entire temple,
the number of stairs in the entire temple, the number
of corners on the entire temple, the number of doors
on the entire temple, the summits of the entire temple,
the number of animals’ figures in the temple relief,
the number of hands’ figures on a certain statue, …
etc.
Moreover, primary mathematics can be done
through the location map of temple, the scale of the
temple size (length and width) or the scale of the
temple distance from a certain place (figure 4). In
Prambanan, there are a lot of shapes, either flat or
space shapes. Students may learn primary geometry
by calculating various dimensions of space shapes
existing in the building, such as the area of the temple,
the width of the stairs, and so on.
Figure 4: Measuring one temple (standard and nonstandard
length unit).
3 PGSD STUDENTS’
PERSPECTIVES ON CULTURE
CONCEPT IN PRIMARY
MATHEMATICS LEARNING
3.1 PGSD Students’ Perspective on
Culture Concept Based on
Questionnaire
This study defines PGSD students’ perspectives as
opinions of PGSD students on ‘culture’ concept
within the process of developing culture-based
primary mathematics learning materials. Those
students are 278 respondents who have passed the
course of mathematics education. Those students
were asked questions around the importance of
learning culture-based primary mathematics.
Researcher distributes questionnaires in the form
of statements related to the development of cultural-
based teaching materials. Applied questionnaire is
based on the trilogy of cultural elements, namely
value / character, social context, and artifacts (each
contains 6 statements). Respondents fill questionnaire
by giving check mark "√" according to their
experience, on score with 4 scales. Here is the result
of data analysis from the questionnaire.
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
214
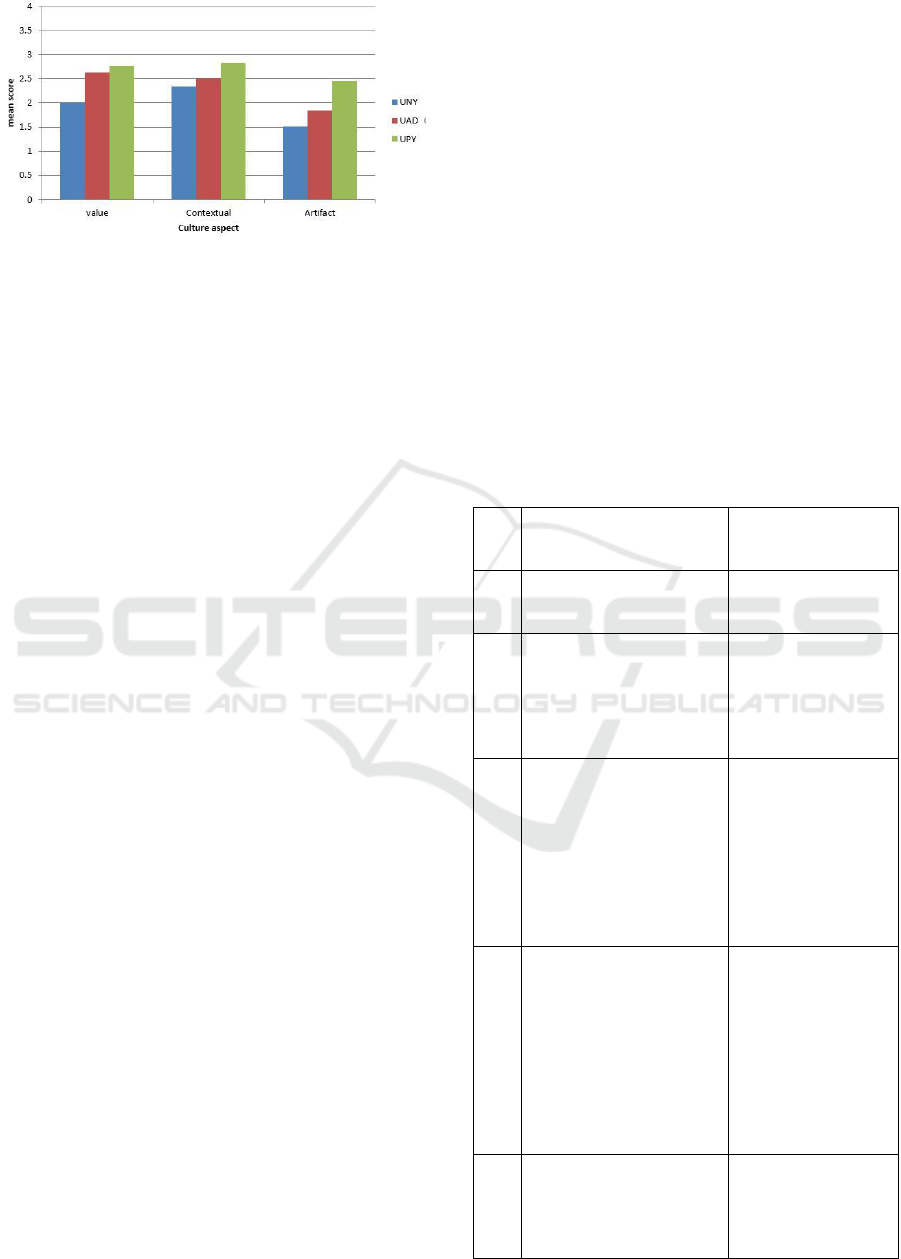
Figure 5: Culture aspect mean score of student.
Based on the figure 5 above, primary mathematics
learning PGSD students experienced fells in the rare
category (score 2). On the "value" aspect, the average
score is 2.266, which means that PGSD students
experience is rarely related to values/character. On
the "contextual" aspect, the average score is 2.559, it
also means that students’ experience is rarely
associated with contextualized mathematics learning.
Nevertheless, this contextual aspect is the highest
score compared to the other two cultural aspects. The
"artifact" mean score is the lowest cultural aspect
(1.938) in the student experience of the primary
school mathematics lectures.
3.2 PGSD Students’ Perspectives on
Culture Concept Based on
Fairclough’s Framework of Critical
Discourse Analysis (CDA)
Fairclough (1995) argues that language analysis can
reveal the structure of relations and ideology that
underlies a discourse. This language analysis can be
done in 3 levels, namely at the level of the text itself,
at the level of discourse practice, and at the socio-
cultural level. In this paper the CDA is conducted
only at the level of the text itself which analyzes the
answers of the students about whether the
development of the primary mathematics teaching
materials needs to be carried out or not. Students were
also asked to mention their opinions backed by
sufficient reasons. Researcher, also, analyzes
students’ opinions as shown from their lessons’
implementation plans (RPP). Following the results of
both analyses in detail. Answers and RPPs are
analyzed to extract students’ representations of the
concept of ‘culture’.
3.2.1 CDA of Students’ Answers
276 students (out of 278) declared the need to develop
cultural-based primary mathematics teaching
materials. Remembering that students’ culture-based
learning experience in PGSD, in the course of
‘Mathematics Education’, is rare, so such finding
does make sense. Such finding also indicates that the
students already have an awareness of the importance
of linking the learning of mathematics with culture.
Ylva Jannok Nutti (2013) found that cultural-based
mathematics learning at Sami's school were mainly
challenged by external obstacles, for example lack of
textbooks that prevented culture-based
implementation. Other researcher, Chahine and
Kinuthia (2013) was successfully used the Zulu
culture called Beadwork and Basketery in developing
mathematical knowledge of students and
disseminating Zulu cultural values to their students.
Therefore, teaching materials that provide examples
of cultural-based mathematics learning in elementary
schools become important to develop Here's the CDA
of 10 students’ opinions on the concept of ‘culture’
(Table 2).
Table 2: CDA of 10 students’ opinions endorsing the
importance of culture-based mathematics teaching
materials.
No
Students’ Answers
Representations of
‘Culture’
1
Yes, so children do not
forget the culture and
history it has
Culture as a
monuments of the
ancestors
2
Yes, because humans
will definitely need a
culture in their life in the
future, and better can be
taught from primary
school
There is separation
between man and
culture, whereas the
existence of culture
because of human
being
3
Yes, culture is a real part
of human life. The
mathematical substance
that students have to
master will become more
plausible and more easily
mastered if they are
integrated with
mathematics learning.
Paying attention to
the contextual
aspect of culture,
and aware that
culture is an integral
part of human life.
4
Yes, cultural-based
mathematics learning is a
form of contextualization
of matter because culture
exists because of human
existence itself.
Paying attention to
the contextual
aspect, also
understands the
integrated nature of
the relation between
human and culture;
culture exists
because of human
existence
5
Yes, because in the
future PGSD graduates
will live in the middle of
a cultured society, if
from the time of
The life of a cultured
society becomes the
spirit of cultural-
based mathematics
learning
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials
215
No
Students’ Answers
Representations of
‘Culture’
education PGSD students
already know the
mathematics based
culture then in the future
PGSD students will have
the ability and skills of
math and supported by a
strong cultural identity.
6
Yes, the cultural aspects
that are integrated in
mathematics learning,
will make the material
more meaningful and
become more easily
understood by the
students
Mathematical
meaning-making
occurs by relating it
to the cultural aspect
7
Yes, if you can do
lessons based on culture,
you may love culture
itself.
Using the
expression ‘love’ of
culture shows
culture as a
traditional entity.
8
Yes, mathematics need to
be associated with
positive values so as to
strengthen the student's
character. Artifacts and
contextual help students
learn mathematics that is
close to everyday life,
This answer shows
understanding
culture as a whole;
values, contextual
and artifacts.
9
Yes, because during this
course learning
mathematics rarely pays
attention to the values of
education, (we are) only
motivated to complete
the achievement of
cognitive competence of
the course
This answer shows
awareness of the
importance of
strengthening
values’ education.
However, it is
limited to value
aspect of culture
concept.
10
Yes, for the
mathematical material to
be closer to the student
environment, the material
is not abstract and easily
understood by the student
Shows culture as a
social context
As for two of the 278 respondents who declared
no need to do the development of teaching materials
of cultural-based mathematics education, their
answers are explained and critically analyzed below
(table 3).
Table 3: CDA of 2 students’ opinions opposing the
importance of culture-based mathematics teaching
materials.
No
Students’ Answers
Representations of
‘Culture’
1
It is not necessary,
because the
mathematical point is
not the focus of
culture
The notion that math is
not the focus of culture,
suggests the separation
between culture and
mathematics, although
mathematics is a
representation of the real
world, where culture
actually exists. This
proves that the student
has not yet understood
the meaning of culture.
He still thinks culture is
only related to historical
or traditional entities.
2
No, because there are
other courses that
cover that area
(cultural values)
Culture is represented as
a course that is just
enough to be introduced
to students, separating
math from culture, and
shows vague conception
of culture.
3.2.2 CDA of Students’ RPPs
Out of 278 respondents, 10 RPPs were taken from
their work while attending lectures on primary
mathematics education. RPP analysis is done by
considering the RPP as a whole and by looking for the
trilogy of culture in it, namely value / character,
contextual, and artifacts. Of the 10 RPPs, only one
RPP raises the trilogy of culture. However, within
that RPP, the aspect of values is not explicit. It is
implicit in apperception, and it has not yet emerged in
the core activities or lessons learned. The contextual
aspect is also implicit within apperception, although
it should arise in the core activities of learning. As
Ernest (2016) argues in a broad sense, mathematics is
always related to human’s life, both individually and
socially. Thus, contextual learning becomes
important. Furthermore, Boris Reliable and Janette
Bobis (2004) stated that teaching mathematics should
relate mathematics to real life situation. Artifacts that
are presented have not involved traditional. The other
Nine RPPs focus more on formal mathematics
learning and learning mathematics using
mathematical symbols. Such an orientation of
focusing in formal mathematics does not match the
characteristics of primary students who are still in
concrete operational stage. Below (table 4) is an
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
216
explanation of the CDA results of the only one RPP
that reflects the trilogy of culture.
Table 4: CDA of the only one student’s rpp that represents
the trilogy of culture (values, contexts and artifacts).
Culture’s
aspect
Analysis of RPP
Value
Value of justice is implied in the story of
sharing that is relevant to the
mathematical material.
Contextual
Apperception given in the form of stories
about the relationship of children with
parents.
Artifacts
Practicing uses star paper to explain the
multiplicity of counting.
Learning mathematics involving culture is not just
clarifying the concept but also can make students more
interested in math. In line with the research results from
Yusuf et al (2010) that this might even encourage our
younger ones who dread mathematics to have more interest
in the subject.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Pre-service primary mathematics teacher students’
opinions on the concept of culture were analyzed in
the framework of preparing culture-based teaching
materials. Generally speaking, students showed
awareness of the need to develop such materials, as
culture is a part of real life that mathematics tries to
solve its problems. Only few students thought that
there is no need for such development. However, in
their experience, students still rarely involve the
trilogy of culture concept (values, contexts and
artifacts) in their on-campus learning. That rareness
was shown with the average score for the value aspect
being 2.466, the contextual aspect 2.559, and the
artefact aspect 1.938. All three scores fall into the
"rare" category. Therefore, it is important for
educators, especially in PGSD to develop their
culture-based lectures.
REFERENCES
Albanese, Veronica, 2015. Enculturation with Ethno
mathematical Micro projects: From Culture to
Mathematics. Journal of Mathematics and Culture Vol.
9 No. 1. p. 1-11.
Chahine, I., Kinuthia, W., 2013. Juxtaposing Form,
Function, and Social Symbolism: An Ethno
mathematical Analysis of Indigenous Technologies in
the Zulu Culture. Journal of Mathematics and Culture.
p. 1558 – 5336
Cimen, O. Arda, 2014. Discussing ethno mathematics: Is
mathematics culturally dependent?. Procedia - Journal
of Social and Behavioral Sciences 152. p523 – 528
Driscoll, M. P.. 1994. Psychology of Learning for
Instruction. Needham, Ma: Allyn and Bacon.
Ernest, P., 2016. The Philosophy of Mathematics
Education. ICME 13. Hamburg: Springer
Epple, M., 2011. Between Timelessness and Historiality on
the Dynamics of the Epistemic Objects of Mathematics.
www.jstor.org. p.481-493
Fairclough, N., 1995. Critical Discourse Analysis; The
Critical Study of Language. London. UK: Longman
Guedet, G., 2016. Transition in Mathematics Education.
ICME 13. Hamburg; Springer. P. 18
Handal, B., Bobis, J., 2004. Teaching Mathematics
thematically; Teachers’ Perspectives. Mathematics
Education Research Journal. Vol. 16. No.1.p3-18.
Ki Hadjar Dewantara. 2013. Pemikiran, Konsepsi,
Keteladanan, Sikap Merdeka, Jilid I Pendidikan.
Yogyakarta: Universitas Sarjanawiyata Tamansiswa
Press.
Koentjaraningrat. 1990. Pengantar Ilmu Antropologi,
Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta, p.186-187
Rahayu Condro Murti. 2014. Membangun Karakter Siswa
Sekolah Dasar Melalui Pembelajaran Penjumlahan
Bilangan Bulat. Kumpulan artikel pada DIES FIP 2014.
UNY Press.
Saifer, S., Edwards, K., 2011. Culturally responsive. USA:
SAGE.
Trinick, Tony et al, 2016. The Relationship between
Language, Culture and Ethno mathematics. Journal of
Mathematics and Culture Vol. 10 No. 2. p 175-191.
Vygotsky, L. S. 1978. Mind and society: The development
of higher mental processes. Cambridge, MA:
Harvard University Press.
Wintergerst, A. C., Mc Viegh, J., 2011. Tips for Teaching
CULTURE. USA: Pearson Longman. p. 1-4.
Ylva Jannok Nutti, 2013. Indigenous teachers’
experiences of the implementation of culture-based
mathematics activities in Sámi School. Mathematics
Education Research Journal, No. 25:57–72.
Yusuf, Muhammed waziri, 2010. Ethno mathematics, A
Mathematical Game in Hausa Culture. International
Journal of Mathematical Science Education. Techno
mathematics Research Foundation Vol. 3, No. 1, p 36 –
42
Primary School Pre-Service Teacher’s Perspectives on Cultural Needs in Developing Culture-Based Mathematics’ Learning Materials
217
