
Factors Affecting the Quality of Audit
Case Study at Inspectorate Central Lombok Regency
Vera Baiq Febrina Angri, Ni Ketut Surasni and Hamdani Husnan
Master of Accounting Economics and the Business University of Mataram, Mataram, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Keywords: Due Professional Care, Independence, Characteristics auditee, Quality Audit.
Abstract: This paper aims to examine and obtain empirical evidence about whether due professional care, independence
of the auditor and auditee characteristics affect the audit quality at Inspectorate of Central Lombok regency.
This paper refers to the results of previous research. This is an explanatory research with purposive sampling
method of interpretation. The questionnaires were distributed to 45 respondent. The data was tested by
analysis tools SmartPLS 3.0. Based on the field test results found that due professional care auditor has
positive and significant effect on audit quality, while Independence and characteristics of auditee did not
significantly effect on audit quality. The results of this test further will be retested on the next research by the
number of samples and a wider factors affecting the quality of audit.
1 INTRODUCTION
Undang – Undang no 32 tahun 2004 on Regional
Government said that the area has the authority to
regulate and manage their own affairs and interests of
local communities in accordance with the legislation.
It requires regions to make up various aspects of
governance including institutional and financial
problems apply in areas of accountability and
transparency to achieve good governance, There are
three main aspects that support the creation of good
governance (good governance), namely monitoring,
control and inspection (Mardiasmo, 2005).
Quality Audit is very important because of the
audit results public as stakeholders can determine
whether the government has used the funds in
accordance with procedures and standards applicable
(Rai 2008 ; 32), For local government, the quality of
auditing are expected to reduce the findings of a loss
of area and improve the performance of Unit (SKPD),
while for the auditee in this regard SKPD, quality
auditing are expected to improve the value for money
(economy, efficiency, and effectiveness). However,
the fact that the findings of the area loss are never
decreased significantly and the type of findings
Inspectorate against SKPD as auditee recur-ring
annually that indicate SKPD cannot apply the concept
of value for money.
The findings were always appearing in any Audit
Reports are incomplete document, the mark up price,
payment of goods / services which exceed the market
price, and fictitious service trips (LHP Central
Lombok District Inspectorate, 2017).
In some studies that have been done about the
quality of audits states that audit quality is determined
by two things: the competence and independence
(Christiawan 2002Alim et al 2007). DeAngelo (1981)
defines the quality of audits as the probability that the
auditor will find and report violations to the client's
accounting system. It is strengthened with the opinion
of Donald R. Deis and Giroux (1992), which explains
that the probability of finding a violation depends on
the technical ability of auditors (competence) and the
probability of reporting a violation depends on
auditor independence.
In research Singgih & Bawono (2010) and
Febriyanti (2014) says that due professional care
positive effect on audit quality, while Saripudin,
Netty and Rahayu (2012) in his research indicates that
due professional care does not affect the quality of the
audit. Not only is it as contained in the study
Setyaningum (2012) quality audit cannot be separated
from the object of the audit itself or commonly called
the auditee,
This test combines the variables used by previous
researchers to analyze the impact on audit quality
improvement. This study was done considering the
number of cases is now questioning the quality of the
audit.
Angri, V., Surasni, N. and Husnan, H.
Factors Affecting the Quality of Audit - Case Study at Inspectorate Central Lombok Regency.
In Proceedings of the 2nd Inter national Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 745-750
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
745
Based on the explanation of the problem in the
quality of audits and previous research studies so that
this test will examine and provide empirical evidence
the independence of auditors, auditors and due
professional care, the characteristics of the auditee
effect on audit quality, this test analyzed by the
Agency Theory approach. The results of this test will
be used as the basis for a retest in thesis research with
larger samples and improve other variables that affect
the quality of the audit.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theoretical Basis
Agency theory developed by Jensen and Meckling
(1976) in Elfarini (2007: 15) tried to ex-plain the
conflict of interest between the management agent
and the owner as well as the other entities in the
contract (e.g. creditors) as the principal.
Viewed from the standpoint of agency theory
above. The relationship between the community and
the government is like the relationship between prin-
cipal and agent. Society is the principal and the gov-
ernment is the agents. Principal authorizes the setting
to the agent and providing resources to the agent (in
the form of taxes and others). As a form of account-
ability for the authority given, agents provide
accountability reports to the principal. Because it
does not know what is actually done by the agent (the
case of information asymmetry), the principal needs
a third party that is able to convince the principal that
what is reported by the agent is true. In the position
as a third party is actually the auditor is expected to
play a major role. Given that some (or even most)
report given by the government is a form of financial
information. Auditors have an important position on
the grounds that; (1) have access to financial
information, (2) have access to information
management, (3) independent, (4) have received
professional training, and (5) can be obtained (No)
(Jones, 1990).
In this test, the author will provide empirical
evidence of the factors that affect audit quality as a
third-party auditor to analyze the variables
independence and due professional care on the
auditor and auditee characteristics (agent) striving to
audit quality produced by the auditors in the form of
audit reports where the purpose of the audit is to
reduce the agency conflict between agent and
principal (society).Based on the theoretical study and
previous studies, the research model developed by the
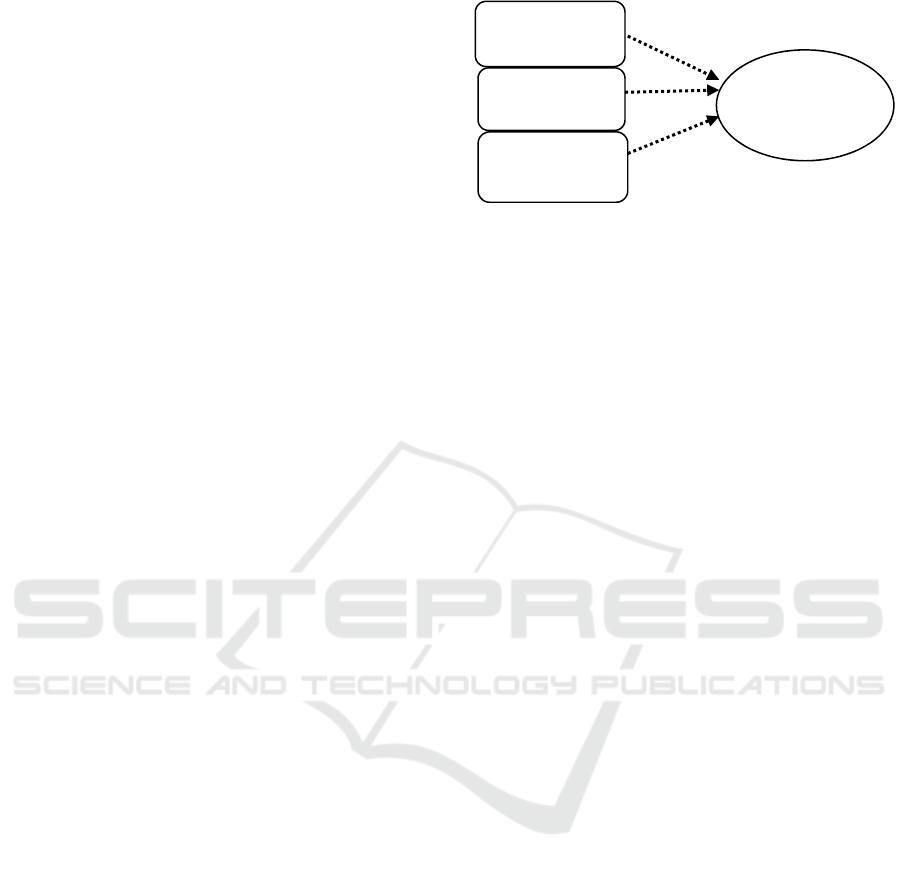
authors can be seen from Figure 1 below:
Figure 1: Research model.
2.2 The Research Hypothesis
Formulation
Mardiasmo (2005) suggested that the examination
(audit) is an activity undertaken by the party that has
the competence and independence to examine
whether the results of the government's performance
in accordance with established standards. The
auditor's professional proficiency to perform
demanding professional scepticism in auditing
activities (Rai, 2008: 51).
Several studies on the quality of audits that have
been done to conclude the different findings about
factors that affect audit quality. Research conducted
by Singgih and Bawono (2010) concluded that the
independence, due professional care and
accountability, both simultaneously and partially
influence on audit quality. Setyaningrum (2012) in
his research concluded that the characteristics of
auditors consisting of educational background,
professional skills, and continuing professional
education are partially not affect the quality of the
audit. While the characteristics of the auditee only the
size of the local government which proved negative
effect on the quality of the audit, the auditee
characteristics that form the complexity of local
government is not proven effect on audit quality.
Zawitri (2009) found that due care Professional
Skeptical negatively associated significant and
positive attitude is not significantly associated with
perceived audit quality. Ardini study (2010)
concluded that the competence, independence,
accountability and motivation together have a
significant effect on audit quality. Then partially
accountability has a positive and significant impact
on audit quality.
The independence is often also referred to as a
mental attitude that is free from influence, not control
and is not dependent on the other party. In-
dependence high attitude will produce quality audit
reports and accountable. Based on these explanations,
the first hypothesis in this test are:
Independence
Due
Professional
Characteristics
auditee
Quality
Audit
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
746

H1: Independence of the positive effect to audit
quality
Due Professional Care the other is absolute
attitude that must be owned by an auditor. This means
that an auditor must have a careful attitude and
earnest in their profession as an auditor in order to
produce quality audit reports. Accuracy and precision
requires the auditor to exercise professional
scepticism, which is an attitude that requires the
auditor to think critically about the audit evidence that
is by always questioning and evaluating audit
evidence that, be careful in the task, and not careless
in conducting examination and have perseverance in
carrying out the responsibility. Based on the
explanation, the second hypothesis in this test are:
H2: Due care professional’s positive effect on
audit quality
Accountability indicates Characteristics auditee
public sector can be seen from SKPD size and
complexity of the organization. SKPD size refers to
the number of managed funds, the greater the funds
managed by the greater demand for transparency
(Setyaningrum, 2012). While the complexity of the
organization includes a number of fields or echelon
III who served. The more complex an organizational
structure, the more comprehensive SKPD duties and
authority owned. Often auditors become more alert
and apply the high scepticism attitude toward auditees
have a big budget and a complex organizational
structure. Based on the explanation, the third
hypothesis in this test are:
H3: Characteristics auditee take effect positive the
quality audit
3 METHODS
3.1 Population and Sample
This test is used to experiments in central Lombok
regency government because it has the largest
population among the other districts in the island of
Lombok.
Sample interpretation technique in this test
method with probability sampling technique was
giving the same opportunity or chance for every
element of population being a member (Creswell:
220) such was the case in thi test using 45 respondents
i.e. Functional official auditor and functional P2UPD.
3.2 Method of Data Collection
Data collection was done with questionnaire survey
based development from previous risets roommates
strongly correlated with variables in this test.
Questionnaire is a set of questions arranged
systematically so that the same questions can be
submitted to every respondent. The questioner is an
effective instrument of the data collection can be
gotten standards because the data can be ac-counted
for analysis needs comprehensively re-searched
about a population characteristic (Suprinto, 2000). In
a test pilot, questioners are transferred directly to a
Functional official auditor and functional P2UPD
Becomes roommates sample of this research.
3.3 Method of Data Analysis
The data gotten from the result questioners was
managed with using SmartPLS 3.0. SmartPLS was
chosen because it was Able to help the writer to get
scores of latent variables for prediction. Chin and
Newsted (1999 in Ghozali and Latan) explained that
the formal model of latent variables in PLS De-
scribed explicitly with the aggregate linear variable
from its observation or indicators. Weight estimation
to create a component of the latent variable score was
gotten from inner and outer of the model specifically.
The result was the residual variance from the
endogenous variable minimized.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Test of Outer Model (Evaluation of
Measurement Model)
Evaluation of the model or the outer measurement
models used to score the construct validity and
reliability. To measure the convergent validity can be
seen from loading factor for every construct factor. In
hair and friends (2013), he said that scores of loading
factor of 0.7 must be more than minimally because
latent variables can explain 50% variants for every
indicator. Loading factor in this test can be seen at the
picture below:
Factors Affecting the Quality of Audit - Case Study at Inspectorate Central Lombok Regency
747
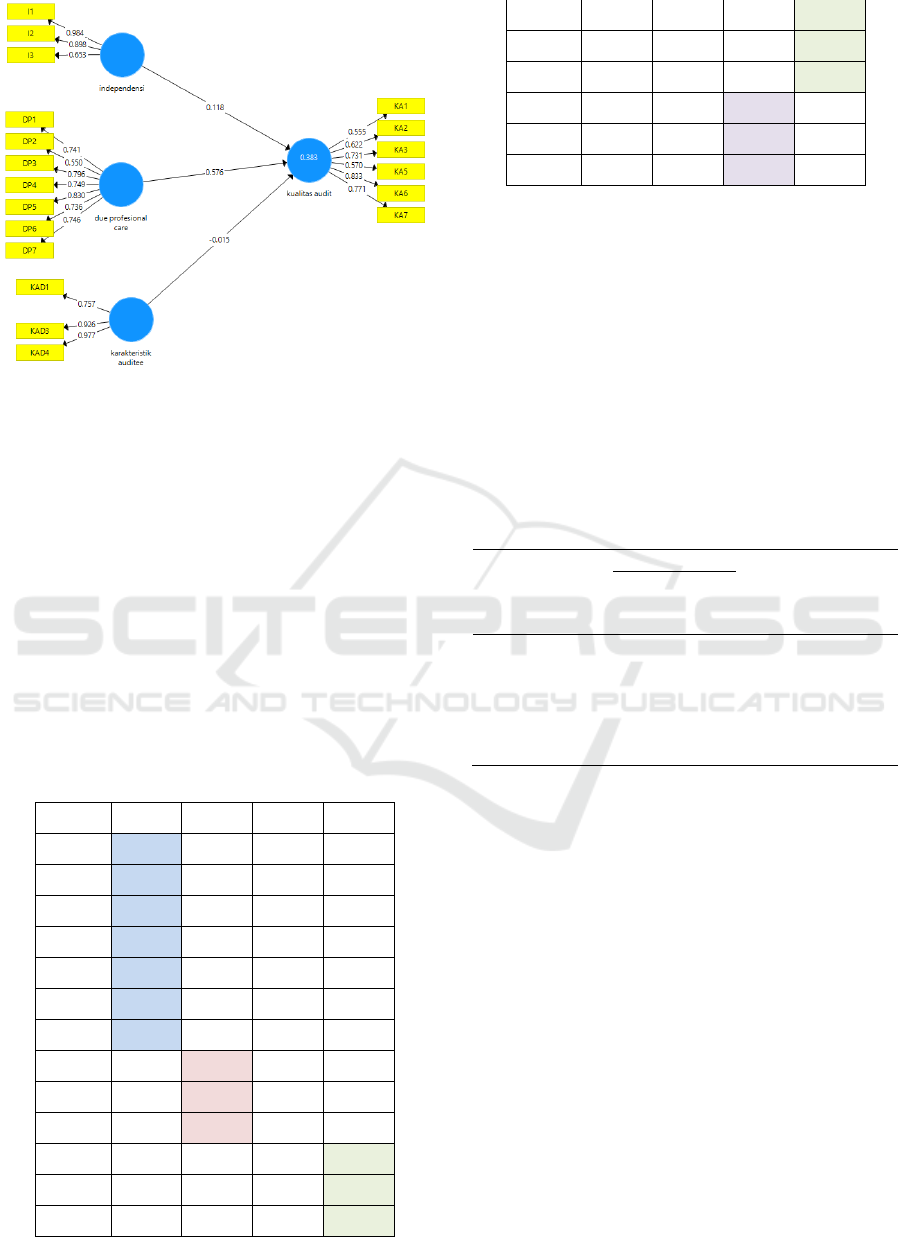
Figure 2: Load factor.
Based on the loading factor of the above, it can be
seen that there is the indicator value is less than 0, 70.
This is because of the indicator on low or indicator
data variation with nearly the same value. In Hair and
friends said that loading must be from 0.40 to 0.70
among Considered to be defended. Therefore
indicators of independence of auditors, auditors and
due professional care, the characteristics of the
auditee because convergent validity have fulfilled all
loading factors were upper than 0.50.
Next from the test of discriminate validity can be
seen at the cross loading with comparing the
correlation between its indicator construct
correlations and the other indicators such as at table
1. Be-low:
Table 1: Cross loading.
DP I KAD KA
DP1 .748 0.259 -0.149 .448
DP2 .773 0.345 -0.172 0,384
DP3 .789 0,312 0.061 0.554
DP4 0.739 0.345 -0.033 0,509
DP5 0.822 .193 -0.137 0.512
DP6 0,745 0.184 -0.135 0.376
DP7 0.754 0.256 -0.204 .449
I1 0.319 .917 -0.140 .309
I2 .220 .820 -0.083 0.126
I3 0,004 .636 0,040 -0.041
KA1 0.338 0.164 -0.492 0.611
KA2 0.594 .329 -0.271 .649
KA3 0.277 .220 0,032 .690
KA4 0,270 0.102 0,002 0.537
KA5 .409 0.354 -0.019 .807
KA6 0.411 .181 -0.194 0.754
KAD1 0,139 -0.057 -0.532 0,072
KAD2 0.204 0.135 -0.896 .178
KAD3 .220 0.167 -0.913 0.192
Source: PLS outputs; 2017
From this table, we can see that the construct
correlation of due professional care with its indicators
has higher correlation score Compared with the
indicator of the quality of the audit with the other
constructs. This Showed that reflective indicator has
fulfilled discriminant validity.
While the reliability test aims to prove the ac-
curacy, consistency, accuracy in measuring
instruments build. To measure the reliability can be
done with composite reliability with a score of more
than 0.7 for confirmation study. Results of reliability
can be seen in the table below:
Table 2: Results of validit
y
and reliabilit
y
test.
No. variable
reliabilit
y
Explanation
composit
e reliability
(0.60 to 0.70)
1
DP
0.909
Valid and Reliable
2
I
0.726 Valid and Reliable
3
KAD
.654 Valid and Reliable
4
KA
.787 Valid and Reliable
Source: PLS outputs; 2017
From the table above, this can be explained that
the construct variable of due professional care,
independence, the characteristics of the auditee and
audit quality have more than fulfilled the reliability
score of 0.70 for every variable (Ghozali & Latan:
77).
4.2 Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis test results can be seen in Table 3 below
where the results obtained from the bootstrap test
with SmartPLS 3.0 software to see the support of the
hypothesis.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
748
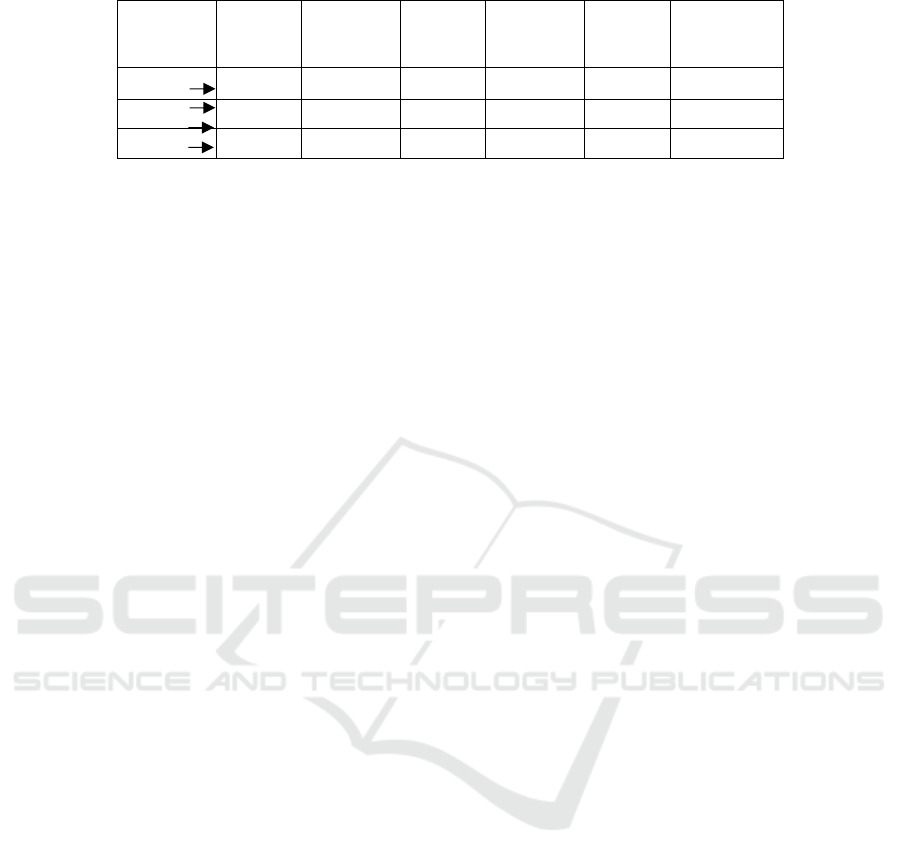
Table 3: Land coefficient.
Original
Sample
(O)
Samples
Mean (M)
Error
standard
T
Statistics
value P Conclusion
I KA 0111 0113 0172 0642 0521 rejected
DP KA 0579 0553 0117 4953 0000 be accepted
KA KAD -0016 0005 0211 0077 0939 rejected
Source: Output PLS 2017
Result of the first hypothesis test Showed that
independency did not influenced of quality audit, this
can be seen from Table 3 in the t-statistic was 0.642
less than 1.64 t-table this can therefore be concluded
that the first hypothesis was rejected. P-value was
0.521 more than 5% alpha means that significant.
Result of the second hypothesis test Showed that
positively influenced due professional care to-ward
the management of audit quality in the which T-
Statistic score of due professional care was
4.953more than T-Table 1.64 this can therefore be
concluded that the second hypothesis was accepted.
P-value of 0.000 was smaller than 5% alpha means
that significant.
Result of the third hypothesis test Showed that the
auditee characteristic did not influence quality of
audits in the t-statistic was 0.077 less than 1.64 t-table
this can therefore be concluded that the third
hypothesis was rejected. P-value of 0.939 was smaller
than 5% alpha means that significant.
4.3 Effect of Independence the Quality
Audit
The auditor's independence is one of the important
factors to produce high-quality audit. The in-
dependence by Halim (2003: 46) is a mental attitude
that is owned by the auditor to be impartial in con-
ducting the audit. Research conducted by Alim et al.
(2007) showed that the competence and
independence of a significant effect on audit quality,
but it is not the same as the results of the statistical
analysis in this study is that independence has no
significant effect on audit quality.
According Widhiarso (2011) there are seven
reasons why the test was not significant statistically,
namely: 1) the presence of outliers; 2) a model that
does not fit; 3) the small sample size; 4) the effect of
intervening variables; 5) pre-requisite analysis are not
obeyed; 6) differing contexts; 7) measuring devices
that are less valid and reliable.
4.4 Effect of Due Professional Care the
Quality Audit
Based on statistical analysis in this study it was found
that the second hypothesis (H2) due care
professionals have a significant positive influence
quality of the audit. In other words, the auditor should
implement professional scepticism in auditing
activities, which the auditor is always questioning and
critically evaluating audit evidence the results of
audits of quality expected. (Rai, 2008: 51), the results
of this study are supported by research con-ducted
Singgih & Bawono (2010) and Febriyanti (2014) says
that due professional care positive effect on audit
quality.
4.5 The Influence of the Characteristics
of the Auditee the Quality Audit
Results of the analysis showed that characteristics of
the auditee have no significant effect on audit quality.
This contrasts with research conducted by
Setyaningrum (2012) in "Analysis of the factors that
affect the quality of BPK-RI audit" to see that not
only the factor of the auditors that affect audit quality,
but from the auditee is also believed to affect the
quality of the audit. The results showed that the
characteristics of the auditor and auditee
characteristics together affect audit quality.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the testing results of data analysis shows
that due professional care positive effect on audit
quality, so as to obtain results of quality audit reports
required accuracy and prudence - carefulness auditor.
Whereas the independence and the characteristics of
the auditee has no significant effect on audit quality
inspectorate central Lombok district.
The results of these tests are expected to be a
reference to the author of the thesis by adding more
variables and samples and improve analysis of the
Factors Affecting the Quality of Audit - Case Study at Inspectorate Central Lombok Regency
749

data is higher (Ghozali & Latan) to obtain better
results and improve other factors in that.
Although the implications of these tests may be
suggestions for local governments in central Lombok
in Indonesia in particular and government in general
to improve the quality of audits in order to achieve
good governance.
Restrictiveness from this test will give direction
for next Researchers in thesis research to be Able to
test the implication from quality audits.
REFERENCES
Alim, M. N., Hapsari, T., Purwanti, L., 2007. “Pengaruh
Kompetensi dan Independensi terhadap Kualitas Audit
dengan Etika Auditor sebagai Variabel Moderasi”.
SNA X Makassar.
Anderson, J. C. et al., 1997. “The Mitigation of Hindsight
Bias in Judges’ Evaluation of Auditor Decisions.
Auditing”. A Journal of Practice and Theory, 16 (2),
20-39.
Christiawan, Y. J., 2002. “Kompetensi dan Independensi
Akuntan Publik: Refleksi Hasil Penelitian Empiris”.
Jurnal Akuntansi dan Keuangan. (4)2. 79-92.
Creswell W. J., 2010. Research Design of qualitative and
quantitative approach and mixed. Yogyakarta; Pustaka
Pelajar.
Ghozali Imam, Latan Hengky. 2014. Partial Least Square:
concepts, technique and application of Smart PLS 3.0.
Semarang; Diponegoro University
Harhinto, T., 2004. Pengaruh Keahlian dan Independensi
Terhadap Kualitas Audit (Studi Empiris pada KAP di
Jawa Timur). Tesis Maksi Universitas Diponegoro
Semarang.
Hussey, R., George Lan. 2001. “An Examination of Auditor
Independence Issues from the Perspectives of U.K.
Finance Directors”. Journal of Business Ethics, (32)2,
169-178.
Ikatan Akuntan Indonesia-Kompartemen Akuntan Publik
(IAI-KAP). 2001. Standar Profesional Akuntan Publik.
Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Indriantoro, N., Supomo, B., 2002. Metodologi Penelitian
Bisnis untuk Akuntansi dan Manajemen. Yogyakarta:
BPFE.
Kadous, K., 2000. “The Effects of Audit Quality and
Consequence Severity on Juror Evaluations of Auditor
Responsibility for Plaintiff Losses”. The Accounting
Review. (75)3,327-341.
Louwers, T. et al. 2008. “Deficiencies in Auditing Related-
Party Transactions: Insights from AAERs”. Current
Issues in Auditing, (2)2, A10–A16.
Mansur, T., 2007. “Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Kualitas Audit Ditinjau dari Persepsi Auditor atas
Pelatihan dan Keahlian, Independensi dan
Penggunaan Kemahiran Profesional”. Tesis Program
Studi Magister Sains Akuntansi Universitas Gadjah
Mada (Tidak Dipublikasikan).
Mardisar, D., Sari, R. N., 2007. “Pengaruh Akuntabilitas
dan Pengetahuan terhadap Kualitas Hasil Kerja
Auditor”. SNA X Makassar.
Mautz, R. K., Sharaf, H. A., 1980. The Philosophy of
Auditing. Florida: American Accounting Association.
Safitri dkk (2014). Analisis Faktor-Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Kualitas Audit Dengan Reward
Sebagai Variabel Pemoderasi (Studi Pada Aparat
Pengawas Internal Pemerintah Di Inspektorat Daerah
Kabupaten Se Eks Karesidenan Banyumas. Fakultas
Ekonomi Universitas Jenderal Soedirman
Saripudin, N., Rahayu. 2012. Pengaruh Independensi,
Pengalaman, Due Professional Care dan Akuntabilitas
terhadap Kualitas Audit. E-Jurnal Binar Akuntansi.
Vol. 1 No. 1 September.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
750
