
Learning Styles and Academic Achievement Among University
Students
Norazlan bin Anual
1
, Muhammad Faizal bin Samat
1
, Zatul Himmah bte Abd. Karim
1
and Norhafiza
Hashim
2
1
Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Kelantan, Kelantan, Malaysia
2
Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Kedah, Kedah, Malaysia
azlananual@kelantan.uitm.edu.my
Keywords: Learning Styles, Academic Achievement, Field of Study, Gender.
Abstract: A student’s learning style preference refers to the way they respond to stimuli in a learning context, and to
their characteristics way of acquiring and using information. Each student has his/her own specific learning
styles that may influence his academic achievements and students in any course will place a variety of
different interpretations onto their lessons. This study aimed to find out the relationship between learning
styles and academic performance; to identify the significant influence between learning styles and academic
performance; and to determine the mean difference between male and female learning preferences. This study
was carried out in UiTM Cawangan Kelantan, UiTM Cawangan Terengganu and UiTM Cawangan Pahang
(East Zone of Malaysia) respectively where a total of 400 first year’s students from the Faculty of Business
and Management, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM) were randomly selected as sample of this study. The
result of analyses of variance shows that there is a statistically significant difference in the academic
achievement of these students that correspond to the four learning styles developed by David Kolbs. It was
found and concluded that converging learning style scored the highest percentage among the respondents
towards their academic performance. There was a relationship between students’ learning styles that relate to
all four learning styles with academic performance. However, converging and accommodating learning styles
have moderate relationships with academic performance. In the meantime, the study hypothesized that
assimilating and diverging learning styles have weak relationships with academic performance. The result
also showed that there was no significant difference between gender and academic performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Learning styles according to Reid (1995) refers to an
individual’s natural, habitual and preferred way of
absorbing, processing and retaining new information
and skills. Students in any course will place a variety
of different interpretations onto their lessons (Bailey
and Garratt, 2002). According to Keefe and Ferrell
(1990), learning problems are frequently not related
to the difficulty of the subject matter but rather to the
type of learning.
Chuah Chong-Cheng (1988) discussed the
importance of learning styles as being not only
necessary, but also important where each style of
learning contributes to the success in retaining what
they learnt and Dun (1983) found that dramatic
improvement in students’ achievement in cases where
learning styles have been taken into account.
There have been many efforts in identifying the
problem of low academic performance and some
factors have been identified in explaining academic
achievement. Among the numerous variables
researched include intelligence (Deary, Strand, Smith
and Fernandes, 2007), attitudes (Erdogan, Bayram,
and Deniz, 2008), behavioral characteristics (Ergul,
2004; Lane, Barton-Arwoo, Nelsonz and Wehby,
2008), self-esteem (Bankston and Zhou, 2002).
Learners’ styles were found to affect learners’
learning behaviors and different learning style
preferences (Junko, 1988) and therefore it is
important for teachers to examine the variations in
their students on their learning styles (Felder &
Spurlin, 2005).
520
Annual, N., Samat, M., Karim, Z. and Hashim, N.
Learning Styles and Academic Achievement Among University Students.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 520-526
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

A compatible learning style with a strong teaching
style of a program instructor will enable the students
to retain information much longer than their
counterparts who experience mismatch learning and
teaching styles (Fedler, 1993). In other words,
understanding learning styles will help increase
learning benefits especially for low and moderate
achieving students (Zin, Zaman Noah, 2002). At
least, this helps as the first step in ensuring students’
achievement. It is believed that when teachers are
able to analyze the differences and needs of their
students, the educational process is likely to become
optimized for both students and teachers (Fairhurst &
Fairhurst, 1995).
This study, therefore, aimed at depicting the
different types of learning styles, the relationship of
learners’ learning styles preference and the overall
academic performance of students from the Faculty
of Business and Management of Universiti Teknologi
MARA branches, so as the information about
learner’s preference can help teachers become more
sensitive to the differences students bring to the
classroom.
1.1 Objectives of the Study
This study aimed to find out the relationship between
learning styles and academic performance; to identify
the significant influence between learning styles and
academic performance; and to determine the mean
difference between male and female learning
preferences.
In addition, the research questions for this study
included what were the types of learning styles
among the Faculty of Business and Management’s
students; what was the relationship between students’
learning styles and academic performance; and was
there a difference between learning styles among
male and female students toward academic
performance.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Holley and Jenkins (1993) have found that there was
a significant difference in learning style. They
claimed that students with different learning style
perform differently depending on the examination
format. There are also a number of studies that have
examined the relationship between learning style and
academic performance in various disciplines. While
some studies indicated the relationship between
performance scores and the converging learning
styles (Rutz, 2003), others explain the learning styles
differences in student performance as the function of
the chosen assessment technique. Based on the
previous study, has leaded the researchers’ interest to
identify the relationship among students’ learning
style and academic performance of UiTM students of
East Zone of Malaysia.
Cornett (1983) sees it as “a consistent pattern of
behavior but with a certain range of individual
variability,” where students learn differently and thus
different learning styles exist (Entwistle, 1981;
Honey and Mumford, 1992; Kolb, 1976; Schmeck,
1988). Grasha (1990) defined it as “the preferences
student has for thinking, relating to others, and
particular types of classroom environments and
experiences”. According to Kolb (1984),
psychological attributes, resulted from individual
differences, determine the particular strategies a
person chooses while learning. Kolb (1984) and
Honey and Mumford (1992) described learning style
as an individual preferred or habitual ways of
processing and transforming knowledge.
Honey and Mumford (1992) stated that learning
exists when someone can do something that he could
not do previously. Among the various learning style
theories, Kolb’s (1984) ELT that defines learning as
“the process whereby knowledge is created through
the transformation of experience. Different individual
uses different learning style and the effectiveness of
the learning style also varies among individuals.
Learning style has been defined by various
researchers mostly as an indication for individual
differences. These differences may noticeable itself
in ‘life styles’ and even in personality types (Zhang
& Sternberg, 2005). Stemberg (1997) stated and
proposed that styles are at least in part socialized,
suggesting that they can, to some extent, be modified.
Hence, by being aware of learning styles of his
students with their academic achievement, educators
and teachers may get huge advantages in managing
them.
2.1 Learning Styles of Kolb
Learning Style Inventory (LSI) by Kolb (1976) as
cited by Zanich (1991) stated that an effective learner
relies on four different learning modes, which include
concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract
conceptualization and active experimentation, and
later, Kolb (1976) further classifies learning style into
four types, i.e. accommodator, diverger, assimilator
and converger.
Learning Styles and Academic Achievement Among University Students
521
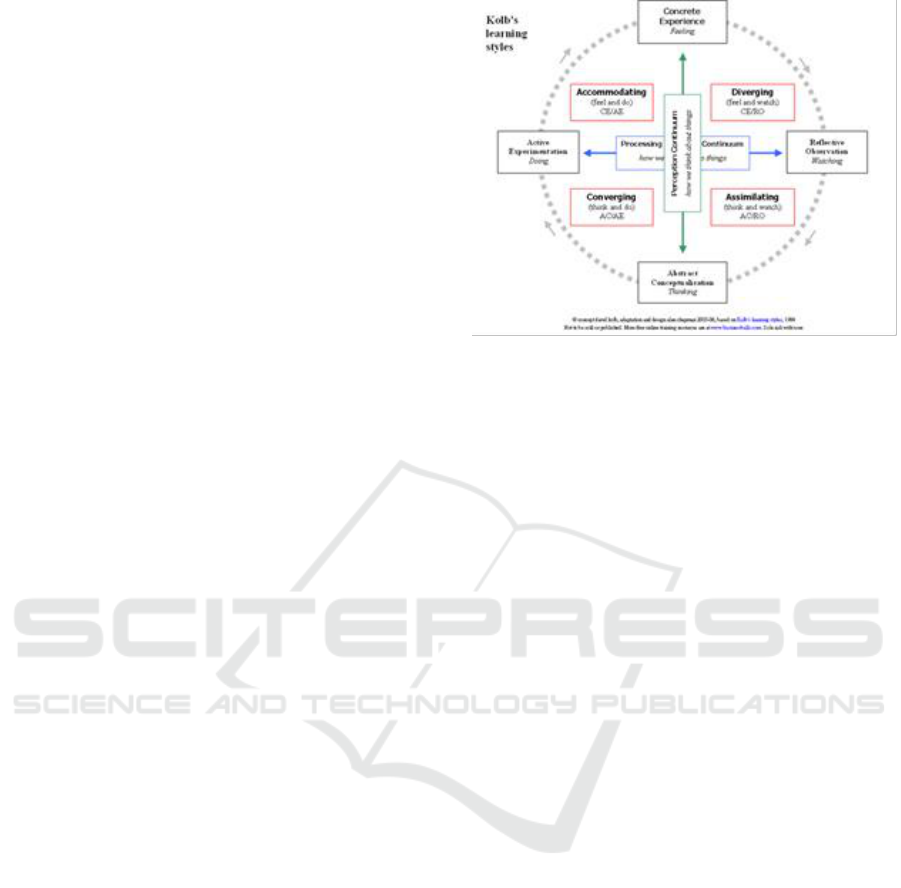
2.1.1 Assimilating
Assimilating learners perceive through active
conceptualization (AC) and process by reflective
observation (RO) where they experience their world
symbolically and transform information through their
imagination (Demirbas & Demirkan, 2003). They are
more concerned with the abstract concepts rather than
practical applications (Kolb & Kolb, 2005).
2.1.2 Converging
Converging learners perceive through active
conceptualization (AC) and process by active
experimentation (AE), bring logical, pragmatic and
unemotional perspective to the problem solving
process (Hsu, 1999). Their knowledge is organized
and they do hypothetical-deductive reasoning while
focusing on a specific problem and they are
unemotional (Smith & Kolb, 1996).
2.1.3 Accommodating
Accommodating learners perceive through concrete
experience (CE) and process by active
experimentation (AE). This is where accommodating
learners are most interested in doing things. They feel
their environment concretely through their feelings
and utilize actions to transform information (Hsu,
1999). They are risk takers and hence, enjoy finding
out new experiences. They also solve problems using
a trial-and-error method instead of using analytical
abilities. In addition, they prefer to work, set goals,
do field work and test various approaches with others
(Kolb & Kolb, 2005).
2.1.4 Diverging
Diverging learners perceive through concrete
experience (CE) and process by reflective
observation (RO). These learners are imaginative and
emotional at the same time (Smith & Kolb, 1996).
They have the ability to synthesize and/or assimilate
various observations for new idea generation (Hsu,
1999). They are less concerned with theorisms and
generalizations. Their approach to problem solving
is not systematic, but is more creative as compared to
the other learning styles. These learners listen to the
suggestions of others and accept critiques from his
group (Kolb & Kolb, 2005).
Figure 1: The diagram of Kolb’s learning styles.
2.2 Academic Performance
Cano and Justicia (1993), stressed that students with
better academic achievement scored higher in
Concrete Experience, Abstract Conceptualization and
Reflective Observation than those with poorer
academic achievement. This result is further
substantiated by Cano-Garcia and Hughes (2000)
who also demonstrated that students with better
academic achievement scored higher in Concrete
Experience.
However, empirical research indicates
inconclusive association between reflective thinking
and the academic performance in different discipline.
For instance, Phan (2007) demonstrates that
understanding (being part of reflective thinking)
is related negatively with academic performance
for students of educational psychology, whereas,
critical thinking (part of reflective thinking) is
positively associated with academic performance for
students in the mathematics discipline.
Felder (1995) stressed that students learn more
when information is obtainable in a variety of
approaches than when only a single approach is
applied. Much experiential research indicates that
learning styles can either hamper or increase
academic performance in several aspects even though
not much research has been conducted on the
relationship between instructional design of learning
materials and learning styles (Riding & Cheema
1991). Therefore, it can be hypothesized as:
H1: There is a significant relationship between
assimilating style and academic
performance.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
522
H2: There is a significant relationship between
converging style and academic
performance.
H3: There is a significant relationship between
accommodating style and academic
performance.
H4: There is a significant relationship between
diverging style and academic performance.
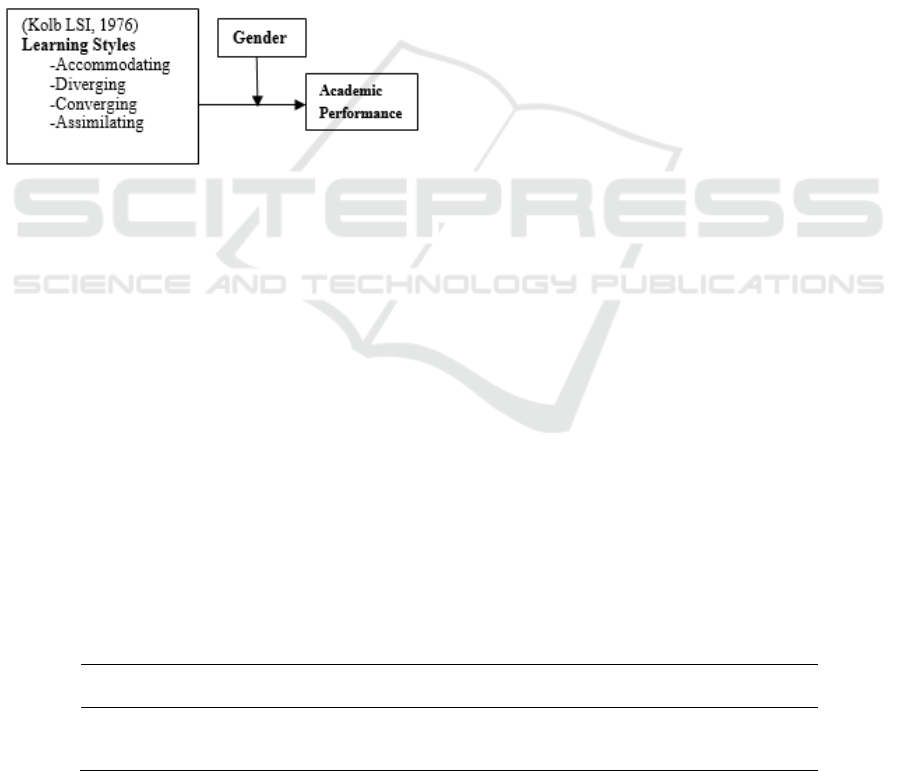
The conceptual framework for this study has been
adapted on the diagrams of Kolb’s Learning Styles.
The independent variables for this study were
Learning Styles which include four types of
learning styles which are accommodating,
diverging, converging and assimilating. The
academic performance is the dependent variable for
this study. This study focused on the relationship
among student learning style and academic
performance and the differences between genders.
Figure 2: Conceptual framework: Students’ learning style
and academic performance.
3 METHODS
This research is important to identify the types of
learning styles among students and their relationship
towards academic performance. According to
Schroeder (1993), when the learning styles were
considered in the teaching-learning process, student
achievement will be enhancing.
The instrument used for this study to generate data
was the survey questionnaire. The questionnaire
consisted of three sections; Section A of
demographic information; Section B of questions that
relate to student learning styles and Section C of
questions that relate to students’ academic
performance according to their course grade.
The research design for this study was a
correlational. Correlational research is a method of
research used to determine relationship between two
or more variables. This type of research describes the
linear relationship between two or more variables
without any hint of attributing the effect of one
variable on another. If they do, the two are correlates
with one another (Salkind, 2006).
This study was carried out in UiTM Cawangan
Kelantan, UiTM Cawangan Terengganu and UiTM
Cawangan Pahang (East Zone of Malaysia)
respectively. The total population of the first year
students of the Faculty of Business and Management
from these three branches were 1000 students.
According to Krejcie and Morgan (1970), when the
population is 1000, the required sample size is 278.
As to get 278 respondents, a total of questionnaire
distributed was 400 from the first year’s students
from the Faculty of Business and Management, were
randomly selected. The questionnaires were
distributed and collected personally and the
respondents were given one week to answer the
questionnaires.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
All data were analysed using the Statistical Package
in the Social Science Software (SPSS) version 22.0.
The data were analyzed for normality, correlation,
descriptive statistics, frequencies, multiple regression
and a T-Test after the entire questionnaire had been
collected from the respondents. 280 questionnaires
were returned. However, only 196 questionnaires
were usable for further analysis.
4.1 Normality
Normality test was conducted and measured using
skewness and kurtosis. Normality test are used to
determine if a data significantly deviate from a
normal distribution.
Table 1: Normality result.
Academic
Performance
Assimilating
Converging
Accommodating
Diverging
Skewness
Kurtosis
-0.399
2.365
0.230
1.251
0.219
0.771
-0.389
-0.419
0.106
0.618
Learning Styles and Academic Achievement Among University Students
523

Based on the above table, the result of normality
test range from -0.419 to 2.365, considered that all
value is acceptable. According to Doane and Tracy
(2001), the value between -3 and +3 are acceptable
and consider as a normal. It means that all variables
that used in this study are normal. Hence, the
researcher can proceed for further analysis.
4.2 Demographic Profile
Table 2: Demographic profile.
Gender
Frequency
Percentage
(%)
Male
35
17.9
Female
161
82.1
Total
196
100.0
Age
Frequency
Percentage
(%)
18-20
190
96.9
21-25
6
3.1
Total
196
100.0
Education
Frequency
Percentage
(%)
SPM
135
68.9
Diploma
61
31.1
Total
196
100.0
Female contributed 161 respondents out of 196
from the total of respondents that involved in this
study with 82.1 percent. While the male respondents
involved were 17.9 percent of the frequency of
respondents i.e. 35 respondents out of 196. The
majority of respondents are between ages of 18 to 20
years old with 190 respondents (96.9 percent). While
6 respondents come from the age of 21 to 25 years old
which indicated 3.1 percent. In addition, 38.8 percent
or 76 respondents obtained a CGPA in between 3.00
to 3.49 followed by 25.5 percent or 50 respondents
scored in between 2.50 to 2.99. 21.4 percent or 42
respondents obtained a CGPA in between 3.50 to
4.00, while 12.2 percent or 24 respondents received n
between 2.00 to 2.49. Lastly, only 2.0 percent or 4
respondents scored below than 2.00 for their CGPA.
4.3 Pearson Correlation Analysis
Pearson Correlation analysis is a statistical analysis
that summarizing the strength of association between
two metric variables (Malhotra, 2010). The
correlation is a technique on how strongly pairs of
variables are correlated.
Table 3: Correlation coefficient.
Variables
AP
Ass
Con
Acc
Div
Academic
Performance
1
Assimilating
0.398**
1
Converging
0.480**
0.569**
1
Accommodating
0.401**
0.344**
0.414**
1
Diverging
0.396**
0.274**
0.095
0.036
1
** Correlation is significant at the level 0.01 level (2 tailed)
* Correlation is significant at the level 0.05 level (2 tailed)
The relationship between assimilating,
converging, accommodating and diverging with
academic performance has been tested. Assimilating
(r value = 0.398, p-value < 0.01), indicate that
positive relationship between assimilating with
academic performance and has a weak strength of
association with academic performance. Then,
converging (r value = 0.480, p-value < 0.01) showed
there is a positive relationship and has a moderate
strength of association between converging with
academic performance. Furthermore, for
accommodating (r value is 0.401, p-value < 0.05),
indicate there is a positive relationship with academic
performance by signifying a moderate strength of
association with academic performance. Lastly,
diverging (r value = 0.396, p-value < 0.01), indicate
that positive relationship between diverging with
academic performance with a weak strength of
association with academic performance.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
524

Table 4: Result of hypotheses testing.
Hypotheses
t-value
Sig
Result
H1: There is a significant
relationship between
assimilating style and
academic performance.
0.469
0.000
Supported
H2: There is a significant
relationship between
converging style and
academic performance.
4.636
0.000
Supported
H3: There is a significant
relationship between
accomodating style and
academic performance.
3.888
0.000
Supported
H4: There is a significant
relationship between
diverging style and
academic performance.
5.949
0.000
Supported
The study hypothesized that assimilating has a
significant relationship with academic performance (t-value
= 0.469, p-value = 0.000). Thus, the result of H1 is
supported. Besides that, the study revealed that converging
has a significant relationship with academic performance (t-
value= 4.636, p-value = 0.000), hence, the result of H2 is
also supported. In the meantime, accommodating has a
significant relationship with academic performance (t-value
= 3.888 and p-value = 0.000). Thus, the result of H3 is
supported. Finally, diverging has a significant relationship
with academic performance (t-value = 5.949, p-value =
0.000) and therefore, the result of H4 is supported.
4.4 T-Test Result for Gender
Differences
Table 5 showed the result of independent sample test
between two groups; gender and academic
performance. Sig. (2-tailed) from the table below was
.201. As referred to Julie Pallant (2005), if the value
in the Sig (2-tailed) column is equal or less than .05,
then there is a significant difference in the mean score
on the dependent variable for each of the two groups.
If the value is above .05, there is no significant
difference between the two groups. Therefore, the
result showed that there was no significant difference
between gender and academic performance.
Table 5: Independent sample t- test.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From this study, it can be concluded that converging
learning styles scored the highest percentage among
the respondents towards their academic performance.
People learn in different styles but some may adapt
their learning styles according to tasks (Pask, 1976).
The convergent learning style relies primarily on the
dominant learning abilities of abstract
conceptualization and active experimentation. The
greatest strength of this approach lies in problem
solving, decision-making, and the practical
application on ideas (Kolb, 1984). In addition,
accommodating learning style scored the least
percentage among the respondents towards their
academic performance.
It can also be concluded that assimilating has a
significant relationship with academic performance,
where the result of H1 is supported. In addition, the
study revealed that converging and accommodating
also have significant relationships with academic
Variables
t
Df
Sig.
(2-tailed)
Learning
Styles
Equal
variances
assumed
-1.283
264
.201
Equal
variances not
assumed
-1.706
136.416
.090
Learning Styles and Academic Achievement Among University Students
525

performance but they are moderate relationships and
thus, the result of H2 andH3 are also supported.
Finally, it is also concluded that diverging has a weak
significant relationship with academic performance
and therefore, the result of H4 is supported as well.
The result also showed that there was no
difference between gender and academic
performance. This is align with Othman and Othman
(2004) who found that there are no differences in
learning styles between males and females and Wei
(2009) also found there are no significant differences
in learning styles Selmes 1987 based on gender, the
result of this study is somehow different.
Awareness of student learning style could provide
a basis for educators to optimize teaching methods for
diverse students’ populations. Learning style
diversity, when properly understood by both students
and educators can be converted into appropriate
teaching and learning methods that enable more
students to attain success.
REFERENCES
Bailey, P.D., Garratt, J., 2002. Chemical Education: Theory
and Practice. University Chemistry Education, 6, 39-57.
Cano, J., 1999. The relationship between learning style,
academic major, and academic performance of college
students. Journal of Agricultural Education, 40(1), 30-
37.
Chuah Chong-Cheng. 1988. Sinar Cendekia. Malaysia,
Penang: Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM).
Cornett, C.E., 1983. What you should know about teaching
and learning styles. Bloomington: Phi Delta Kappa
Educational Foundation.
Dunn, R., 1983. Learning style and its relation to
exceptionally at both ends of the spectrum.
Fairhurst, A. M., Fairhurst, L. L. 1995. Effective teaching,
effective learning. California: Davies-Black Publishing.
Felder, R.M., Spurlin, J. E., 2005. Application, reliability,
and validity of the index of learning styles. Intl. J.
Engr. Education, 21(1), 103-112.
Ferrell, B. G., 1983. A factor analytic comparison of four
learning styles instruments. Journal of Educational
Psychology, 75(1): 33-39.
Grasha, A. F., 1996. Teaching with style: A practical guide
to enhancing learning by understanding teaching and
learning styles, Pittsburgh, PA: Alliance Publishers.
Holley, J. H., Jenkins, E. K., 1993. The relationship
between student learning style and performance on
various test question formats. Journal of Education for
Business, 68, 301 308.
Honey, P., Mumford, A. 1992. The manual of learning
styles. Maidenhead: Peter Honey.
Hyland, K., 1993. Culture and Learning: A study of the
learning style preferences of Japanese students. RELC
Journal, 24(2), 69-91.
Honey, P., Mumford, A., 2000. The learning styles helper's
guide. Maidenhead: Peter Honey Publications Ltd.
Junko. 1998. Learning styles and error correction: How do
learning styles affect students' perceptions towards
error correction in a foreign language classroom?
Keefe, J. W., Ferrel, B., 1990. Developing a defensible
learning style paradigm. Educational Leadership, 10,
57-61.
Kolb, A. Y., Kolb, D. A., 2005. Learning styles and learning
spaces: enhancing experiential learning in higher
education. Academy of Management Learning and
Education, 4, 193e212.
Kolb, D. A., 1984. Experiential learning: Experience as a
source of learning and development, Englewood Cliffs,
NJ: Prentice Hall.
Kolb, D.A., 1993. Learning-style inventory (LSA-IIa): Self-
scoring inventory and interpretation booklet. Boston
M.A.: McBer.
Kolb, D.A., Boyatzis, R.E., Mainemelis, C., 1999.
Experiential learning:
L.F. (Eds). 2000. Perspectives on cognition, learning and
thinking Learning and Education, 4, 193e212.
Reid, J. M., 1995. Learning styles in the ESL/EFL
classroom. U.S.A: Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
Salkind, N.J., 2006, “Exploring Research (6th e.d) New
Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Schmeck, R.R., ed. 1988. Learning Strategies and Learning
Styles. New York: Plenum Press.
Smith, D.M., Kolb, D.A., 1986. Users guide for the
learning style inventory: A manual for teachers and
trainers. Boston: McBer. South African Association
for Psychological
Type (SAAPT). (1998). A Compilation of Myers-Briggs
Type indicator research report. Sandton, South Africa.
Smith, D. M., Kolb, D. A., 1996. User’s guide for the
learning-style. Boston: McBer and Company.
Schroeder, C. C., 1993. New students - new learning styles.
Change. 2 l-26.
Torres, R. M., Cano, J., 1994. Learning styles of students in
a college of agriculture. Journal of Agriculture
Education, 3 5 (4):6 1-66.
Zhang, L. F., 2004. Predicting cognitive development,
intellectual styles, and personality traits from self-rated
abilities. Learning and Individual Differences, 15: 67–
88.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
526
