
Investigating the Relationship between Information System Usage
and Employee Job Performance Among Staff at a Local Government
Office in Malaysia
Mimi Zazira Hashim, Wan Nor Hazimah Wan Azib, Farah Ahlami Mansor, Norrini Muhammad and
Nur Hezrina Estiar
Faculty of Business and Management, Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Kelantan
mimiz949@kelantan.uitm.edu.my, wanno358@kelantan.uitm.edu.my, farah865@kelantan.uitm.edu.my,
norri5282@kelantan.uitm.edu.my, hezrinaestiar@gmail.com
Keywords: Information System, System Quality, Information Quality, Employee Job Performance.
Abstract: Employee job performance is part of crucial elements to increase company performance. Thus, this paper
investigates the relationship between information system usage and employee job performance among staff
at a local government office in Malaysia. Information system usage is measure for two elements; Information
quality and System quality. Four elements were used to measure system quality namely integration,
correctness, response time and reliability. Information quality was measured in term of accessibility,
completeness, timeliness, relevant and accuracy. Meanwhile, seven elements for employee job performance
were tested including productivity, timely, quantity, quality, efficiency, creativity and creating new ideas. By
using stratified random sampling technique, a survey was conducted among 181 staff through the use of self-
administered questionnaires. The data was analyzed by using statistical method Smart PLS. The result
indicates that there was a significant relationship between information system usage and employee job
performance. Hence, a company need to focus on information and system quality to ensure the employee’s
job performance increase and contribute to the survival of company in competitive environment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Evaluating employee job performance from
information system usage has been an ongoing
activity in information system research. Yaser, Alina
and Nor (2014) has categorized seven elements of
information system; people as IS user, the use of
software and hardware, the communications tools,
types of networks, the data resources, and existing
policies and procedures that process the information
in an organization. Information system is described
as a knowledge intensive setting where IS
professionals involved in frequent knowledge sharing
activities with collegues, and discussion of
information, knowledge and solution in a timely
manner (Deng and Chi, 2015). According to Imran
(2014), employee work behavior and performance is
closely related to the use of technology-based
systems. Employees who find information that
relates to the job and use information system to
complete their task effectively will have a better
performance.
Past research on this topics revealed different
results that identify various and unique relationship
between IS and employee job performance range
from positive to non-significant, to even a negative
relationship. Goodhue and Thompson (1995) found a
positive relationship between information system and
individual job performance. Conversely, Pentland
(1989) found a negative relationship. Meanwhile,
Lucas and Spitler (1999) found that information
system has no impact on individual job performance.
Having better productivity contribute a lot of
benefits, either for the country, organization or
individual through higher revenues or incomes,
enhanced reputations and less wastage of resources.
However, Malaysia Productivity Corporation (2016)
currently claimed that labor productivity level was
still at low rate compared to global frontier (USA).
Hence, this research was conducted to investigate the
relationship between information system and
employee job performance at one of the local
government office in Malaysia.
Hashim, M., Azib, W., Mansor, F., Muhammad, N. and Estiar, N.
Investigating the Relationship between Information System Usage and Employee Job Performance Among Staff at a Local Government Office in Malaysia.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 447-451
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
447
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Previous literatures look into how information
systems influence on the employee job performance
and productivity. This topic had become one of the
great interest to many researchers to study types of
relationship existed between these three variables. As
a lot of works nowadays depend on the usage of
information system, the information system
availability and reliability is crucial to ensure the
employee may perform their job well. User
satisfaction is highly depends on the system quality
leading to positive impacts on individual
productivity or performance (Delone & Mclean,
2003). System quality is measure in terms of
integration, correctness, response time and reliability.
Meanwhile, information quality is measure in term of
accessability, completeness, timeliness, relevant and
accuracy (Delone & McLean, 2003).
Besides that, others researchers also discussed on
the impacts of information systems on individual job
performance. A theoretical model has been
introduced by Stone et. al. (2006) shows an
interrelationship between the quality of information,
system and organizational performance with system
ease of use and lead into increase or decrease
individual job performance. Meanwhile, Bejjar &
Younes (2013) found that the measures of the
quality of information and system affect the tasks
performed by the user. They study the relationships
between information system and user performance by
investigating several variables including system use,
system quality, information quality and user
performance. They indicated that the above factors
affect user performance positively and has the
strongest direct effect on individual job performance.
The use of information system will affect the
employee when performing their task, and these
individual impacts cooperatively result in
organizational impact (Mclean, 2003). Information
system has given the employee a better
understanding of their task, coordination between co-
worker and the decision making, improved in
productivity, and change user’s perception of the
information system usage has importance influence
on employee job performance. Direct positive result
on individual performance was identified as
perceived impact of computer system usage on
decision making quality, performance, productivity,
and effectiveness of the job (Hou C.K., 2012).
According to Ajoye & Nwagwu (2014), two
factors that indirectly influence were by human and
organizational factors. Therefore, measurement of
information system impact and it success is a tough
processes. System quality significantly related to
user satisfaction of a management information
system. The influence of system quality on user
satisfaction was very strong and required a critical
system analysis and proper adjustment to maximize
users experience and satisfaction.
Using DeLone and McLean model refers to the
both quality of data components and software to the
system components that support the end-user and the
way they interact with the system. There is a
positive impact on the system quality with intention
to reuse IS (Zaremohzzabieh, et al., 2016).
Furthermore, according to Al-Mamary, Alina & Nor
(2014), system quality has positive association with
information quality, and information quality is
positively associated with organizational impact that
finally affect employee performance and lead to
organizational impact (employee satisfaction).
Besides, Bharati & Chaudhury (2006) claimed
that system quality and information quality, either
singularly or jointly, impact use and user
satisfaction. Their research model was based on the
information system success model and employs some
of the constructs of that model specifically at the
technical level of system quality and information
quality. This is because; user satisfaction can
influence the intention to use information system that
lead to the employee performance in performing their
work in an organization and can make them do the
right decision making.
According to Bejjar & Younes (2013),
information system quality has direct and indirectly
effect on individual performance with a strong direct
correlation. Integration and system reliability were
the most important elements contribute significantly
to individual performance. Consistent with previous
studies, the result of the study indicates that the
impact of information quality on individual
performance is positive and significant. This study
has shown the importance of these qualities on
individual performance.
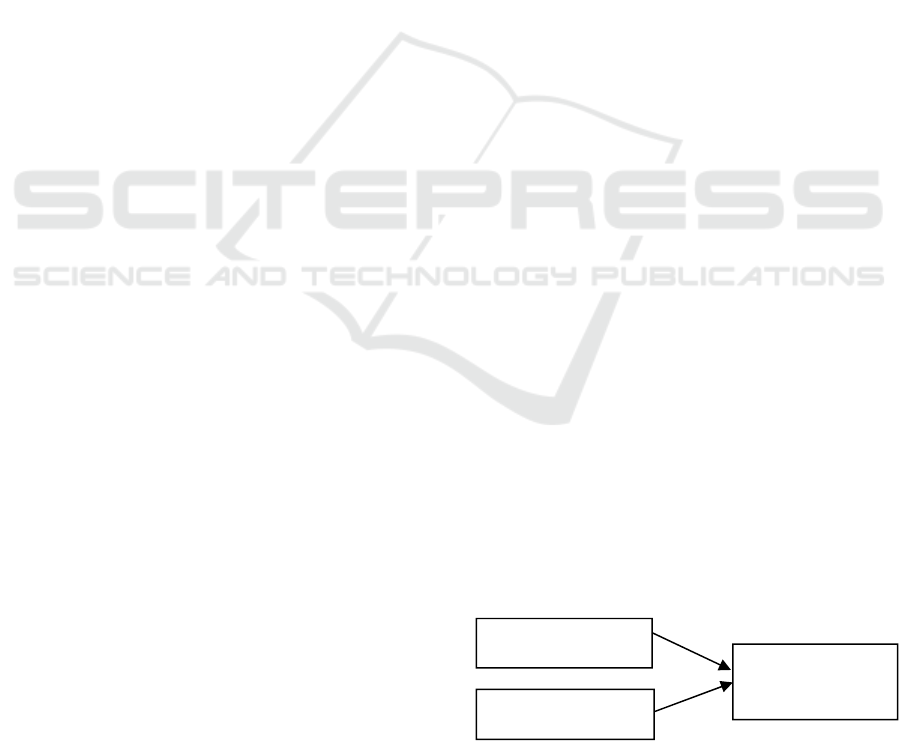
2.1 Research Framework
Figure 1: Information system.
System quality
Employee Job
Performance
Information quality
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
448
Based on literature review and conceptual
framework, hypotheses can be concluded into:
H1 There is a positive relationship between
system quality and employee job
performance.
H2 There is a positive relationship between
information quality and employee job
performance.
3 METHODS
This study was a quantitative research and was
carried out based on correlational research. The unit
of analysis was individual employee that currently
worked at one of local government office in Malaysia.
A total of 181 questionnaires were distributed and
returned using stratified random sampling through
self-administered questionnaire. The measurement
for each independent variable and independent
variable of this study were adapted from previous
studies using Five-Point Likert scale, ranges from
strongly disagree to strongly agree accordingly,
Strongly Disagree=1, Disagree=2, Neutral=3,
Agree=4 and Strongly Agree=5.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Construct Validity
This type of analysis is conducted to measure the
items used in the instrument, whereby the existence
of acceptable level of items used in the model was
equal to construct validity (Hair et al., 2014). The
model validity of the measurement was assessed for
both convergent validity and discriminant validity. If
the indicators of one construct converge or share a
higher proportion of variance refers to convergent
validated and vise versa. The calculation of factors
loadings, average variance extracted (AVE) and
composite reliability (CR) for all items shows validity
in the model.
The quality of the measurement model was
assessed by examining convergent validity includes
factor loading, average variance extracted (AVE),
composite reliability (CR) as well as discriminant
validity which is suggested by Hair, Ringle &
Sarstedt, (2011) as a rule of thumb for model
evaluation. Results show that indicator loadings for
all items exceeded the recommended value of 0.6
(Hair, Black, Babin & Anderson, 2009). AVE were in
the range of 0.535 and 0.639, which is above the
recommended value of 0.5, and CR ranged from
0.850 to 0.925 which exceeded the recommended
value of 0.7 (Hair et al., 2009). The results are shown
in Table 1. Moreover Robustness of the model is
verified through Collinearity statistic (VIF) which is
significant (<5).
Table 1: Result of convergent analysis.
4.2 Discriminant Validity
The discriminant validity of the measurement items
was tested through the criteria suggested by Fornell
and Larcker (1981). Figures highlighted in Table 2
represent diagonal elements displays the correlation
matrix square root of the AVE extracted from the
variables. Findings indicate there is adequate
discriminant validity since the diagonal elements are
significantly greater in rows and columns than the
off-diagonal elements.
Constructs
Items Loadings AVE CR VIF
System
Quality (SQ)
B1 0.775
0.567 0.797 1.244
B2 0.763
B4 0.720
Information
Quality (IQ)
C1 0.645
0.535 0.850 1.244
C4 0.601
C5 0.773
C6 0.826
C8 0.786
Employee
Job
Performance
(JP)
D1 0.762
0.639 0.925
D2 0.920
D3 0.831
D4 0.734
D5 0.865
D6 0.720
D7 0.742
Investigating the Relationship between Information System Usage and Employee Job Performance Among Staff at a Local Government
Office in Malaysia
449
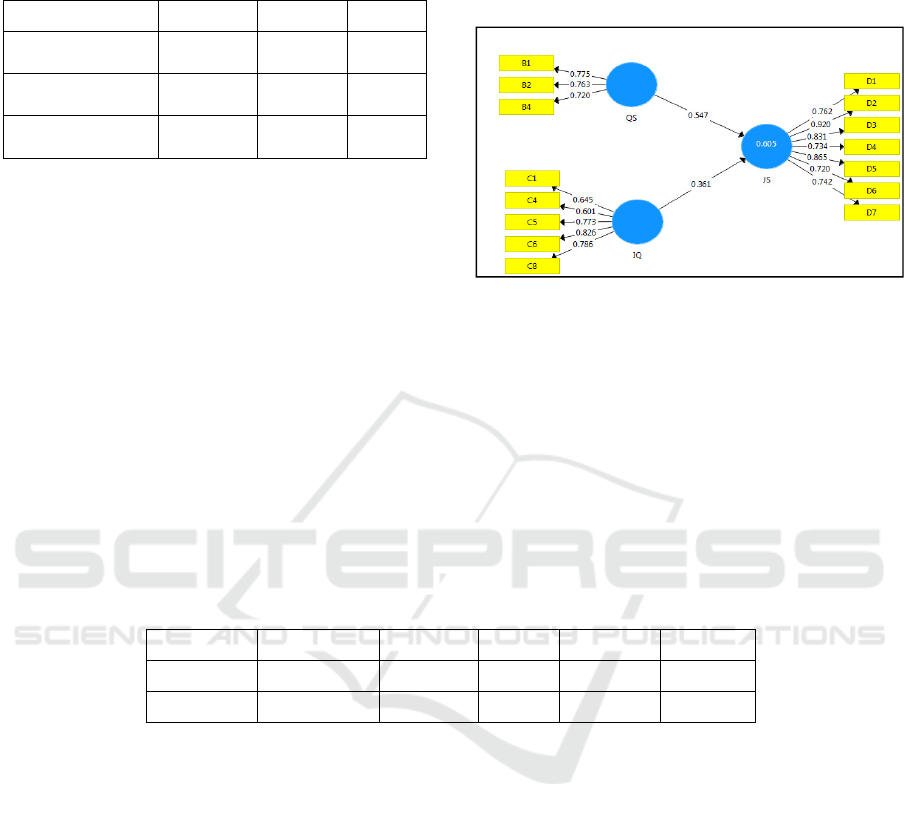
Table 2: Result of discriminant validity.
Construct IQ JP SQ
Information
Quality (IQ)
0.731
Employee Job
Performance (JP)
0.604 0.799
System Quality
(
SQ
)
0.443 0.707 0.753
Note: Values in the diagonal (bold) are square root
of the AVE while the off diagonals are the inter
construct correlation.
4.3 Hypotheses Testing
The hypotheses of this study were tested using
structural equation modelling by examining the path
coefficients to identify the relationships of variables
rather than using traditional regression coefficients
(Gefen, Straub & Boudreau, 2000). Path coefficients
indicate the strengths of the relationships among
variables, while the R² value shows the degree of
predictive power of a model for dependent variable.
Moreover, t-values of the parameter refers the
strength of the relationship; therefore, the higher t-
value equal to stronger relationship (Hair at el., 2014).
Subsequently, the t-values of each coefficient were
obtained by using the bootstrapping resample
technique (Chin, 2010; Efron & Tibshirani, 1993).
Figure 2 represents the results of the analysis.
Figure 2: Structural model.
This study has developed two hypotheses and
tested using path analysis from the research model.
The result for R² is 0.605, indicates 60.5 percent of
the variance can be explained in the extent of
information quality and system quality. Based on path
coefficient and t-value results show that H1 and H2
are both supported which refers to System Quality
and Information Quality were positively influence
Employee Job Performance at significant level of
p<0.05 (See Table 3).
Table 3: Hypotheses testing.
Hypothesis Relationship Std. Error T values P values
Result
H1 SQ -> JP 0.052 10.451** 0.000**
Supporte
d
H2 IQ -> JP 0.038 9.426** 0.000**
Su
pp
orte
d
Note: Significant if the t-value is greater than 1.645 (*p<0.05)
The above table summarizes the results of the
best-fitted model and explains the direct relationship
between exogenous variables and endogenous
variable. Two exogenous variables refers to system
quality and information quality, have a direct
significant effect on employee job performance (JP).
The result indicates that information quality (t-
values=9.426) and system quality (t-values=10.451)
has a significant relationship with employee job
performance. Thus, the H1 and H2 of this study were
supported.
The employee’s job performance will be better if
the system can support employee’s task effectively
and efficiently. Goodhue et al. (2000) also found that
when a system has the features needed to accomplish
a task, better performance is achieved. More
specifically, the study shows that information quality
and system quality have significant impact on their
performance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The result found that there was a significant positive
relationship between Information System and
Employee Job Performance. It also supported by
Abugabah, Sanzogni, & Poropat (2010), the
relationships between Information System and user
performance by investigating several variables
including system use, system quality, information
quality and user performance. They indicated that the
above factor affect user performance positively and
has the strongest direct effect on individual
performance.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
450

The system quality plays an important role in
improving the performance and increase the volume
of users work. Thus, the company need to constantly
update and upgrade their systems to ensure that the
system support the employees to get information
efficiently. The company should also provide
training to employees to equip them with up-to-date
information and can fully utilize company’s
information system. Therefore, the employee may
serve customers better with excellence services.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study is financially supported by ARAS Research
Grant, 600-IRMI/DANA /5/3/ARAS (0148/2016)
Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia.
REFERENCES
Abugabah, A., Sanzogni, L., & Poropat, A. (n.d.). The
impact of information systems on user performance: A
critical review and therotical model.
Ajoye, M. B., & Nwagwu, W. E. (2014).Information
System User Satisfaction: A Survey of the Postgraduate
School Portal, University of Ibadan, Nigeria. Library
Philosophy and practice.
Al-Mamary, H. Y., Alina, S., & Nor, A. (2014). The
Relationship between System Quality, Information
Quality, and Organizational Performance. International
Journal of Knowledge and Research in Management &
E-Commerce.
Bejjar, M. A., & Younes, B. (2013). The Impact of
Information Systems on user Performance: An
Exploratory Study. An Exploratory Study.
Bharati, P., & Chaudhury, A. (2006). Product
Customization on the Web:An Empirical Study of
Factors Impacting Choiceboard User Satisfactioni.
Information Resources Management Journal.
Chin, W.W. (2010). How to write up and report PLS
analyses. In V.E.Vinzi, W.W.Chin, J.Henseler &
H.Wang (Eds). Handbook of partial least squares.
Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Delone, H. W., & McLean, R. E. (2003). The DeLone and
McLean Model of Information System Success: A Ten-
Year Update. Journal of Management Information
System/ Spring, 9-30.
Deng, X., & Chi, L. (2015). Knowledge boundary spanning
and productivity in information systems. Decision
Support Systems 80.
Efron, B. & Tibshirani, R. (1993). An introduction to the
bootstrap. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating Structural
Equations Models with Unobservable Variables and
Measurement Error. Journal of Marketing Research,
18(1), 39-50. Doi: 10.2307/3151312.
Gefen, D., Straub, D.W. & Boudreau, M.C. (2000).
Structural equation modelling and regression:
guidelines for research practice. Communication of the
Association for Information Systems, 4(7), 1-79.
Goodhue, D., & Thompson, R. (1995). Task-Technology
Fit and Individual Performance. Mis Quarterly.
Goodhue, D., Klein, B, and March, S. “User evaluations of
IS as surrogates for objective performance”,
Information & Management, 38, 2000, pp. 87-101.
Hair, J., Hult, T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2014).
A primer on partial least squares structural equation
modelling (PLS-SEM).
Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., & Anderson, R.E
(2009). Multivariate Data Analysis. Seventh Edition.
Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
Hair, J.F., Ringle, C.M & Sarstedt, M (2011), PLS-SEM:
Indeed a Silver Bullet. Journal of Marketing Theory
and Practice, 19(2), 139-152.
Hou, C. K. (2012). Examining the effect of user satisfaction
on system usage and individual performance with
business intelligence systems: An empirical study of
Taiwan's electronic industry. International Journal of
Information Management.
Imran, M. (2014). Impact of Technological Advancement
on Emplyoee Performance in Banking Sector.
International Journal of Human Resource Studies.
Lucas, H. C., & Spitler, V. K. (1999). Technology Use and
Performace: A Field Study of Broker Workstation.
Decision Sciences.
23rd Productivity Report 2015/2016, Malaysia Productivity
Corporation, 2016.
Mclean, W. H. (2003). The DeLone and McLean Model of.
Journal of Management Information Systems , 22.
Pentland, B. T. (1989). Use and productivity in personal
computing: An empirical test. In Tenth international
conference on information systems Boston, MA, (pp.
211–222).
Stone, R., Good, D., & Eveleth, B. (2006). The Impact of
Information Technology on Individual anf Firm
Marketing Performance. Behaviour and Information
Technology. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Yaser, A.-M. H., Alina, S., & Nor, A. (2014). The Role of
Different Types of Information Systems In Business
Organizations : A Review. International Journal of
Research (IJR).
Zaremohzzabieh, Z., Abu Samah, B., Bolong, J.,
Muhammad, M., Abdullah, R., D’Silva, J. L., &
Shaffril, H. A. (2016). A Model of Information Systems
Success for Assessing the Effectiveness of Statistical
Learning Tool on University Students Performance in
Statistics. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences.
Investigating the Relationship between Information System Usage and Employee Job Performance Among Staff at a Local Government
Office in Malaysia
451
