
Influence of Interest Rate of Commercial Conventional Banks and
Levels for Results on the Impact of the Number of Deposits in
Sharia Banks of 2010-2015
Meta Arief, Asep Kurniawan and F.M. Nugraha
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Keywords: Interest Rate, Profit Sharing Rate and Mudharabah Deposit.
Abstract: This study aims to determine the effect of conventional bank interest rates and the level of profit sharing on
the increase in the number of deposits in Sharia Commercial Banks. The research method used is descriptive
analytic and verifikatif. Data collection technique used is documentation method. This study uses secondary
data collected from the website of financial statements and annual reports of sharia banking that started from
2010-2015. The sampling technique is based on purposive sampling so that the sample of 11 sharia banks is
obtained. Hypothesis testing in this study used multiple linear regression analysis using EViews computer
pro-gram. The results showed that simultaneously conventional commercial bank interest rates and profit
sharing rates significantly influence the increase in the number of deposits in Sharia Commercial Banks.
Partially, the significant interest rate has a negative effect on the amount of deposits in the Sharia Commercial
Bank and the significant profit sharing rate has a positive effect on the amount of deposits in the Sharia
Commercial.
1 INTRODUCTION
Banks in Indonesia use dual system banking, namely
conventional and syariah systems. Currently
registered in January 2016 there are 34 units, namely
12 sharia commercial banks and 22 units of sharia
business. Meanwhile, the number of syariah-based
lending banks increased to 164 units (Sharia Banking
Statistics, January 2016). Sharia banking began to be
known in 1992 after the enactment of Law No.7 of
1992 which enables sharia banking to run its
operational activities based on the principle of profit
sharing. Fundamental be-tween sharia and
conventional banks lies in the principles in
operational activities. Husni (2009) said that "one of
the principles in sharia banking operations is profit
and loss sharing, this principle does not apply in
conventional banking that implements the interest
system." The existence of such operational
differences makes people in Indonesia can choose to
invest in both types of banking, namely sharia or
convention. The rational society of society that
determines choice based on profit not based on
religious beliefs, will certainly determine & nbsp;
Option based on the level of profit offered by both
types of banking. Society invests to improve its
welfare and one of human nature who always wants
to secure his property. One of the investment
instruments that can be done by the public is by
depositing funds in banking fundraising products. On
the one hand, one of the main interests of the bank is
to collect public funds. The new bank can operate if
the funds al-ready exist. One source of bank funds is
Third Party Fund (DPK). DPK is funds in rupiah or
foreign currency owned by a third party (the public)
consisting of demand deposits, savings and time
deposits or deposits. In addition to raising public
funds, banks should be able to return the funds along
with the return or return in accordance with the
agreement. In the banking world there is often a
competition to gain customer trust in order to keep the
funds in the Bank concerned. Competition between
these banks can occur between Banks adhering to the
Sharia system with Conventional Bank due to the
existence of floating market segment. This Customer
may make withdrawal of funds or placement of funds
from one Bank to another Bank causing a decrease or
increase of DPK in the Bank. Floating market
Arief, M., Kurniawan, A. and Nugraha, F.
Influence of Interest Rate of Commercial Conventional Banks and Levels for Results on the Impact of the Number of Deposits in Sharia Banks of 2010-2015.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 441-446
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
441
segment, has more characteristic shows the financial
benefit aspect compared with the aspect of sharia. The
existence of the floating market segment triggered the
Bank Syariah to provide services and benefits as
optimal as possible so that the community of money
owners interested to save funds in the bank concerned
DPK is used as one of the factors that can be used to
assess the Bank's success rate. There are several
parties related to the large number of DPK in the
Sharia Bank, the bank itself, the management and the
bank as a company. The Bank expects the increasing
DPK, to maximize funding and financing, the
management is concerned with the size of DPK in
relation to the assessment of managerial performance,
while the bank as a company expects high DPK for
the optimization of corporate profits. The following
is comparative data on the composition of
Conventional Commercial Banks' Deposits (BUK)
and Sharia (BUS) Commercial Banks in 2006-2015.
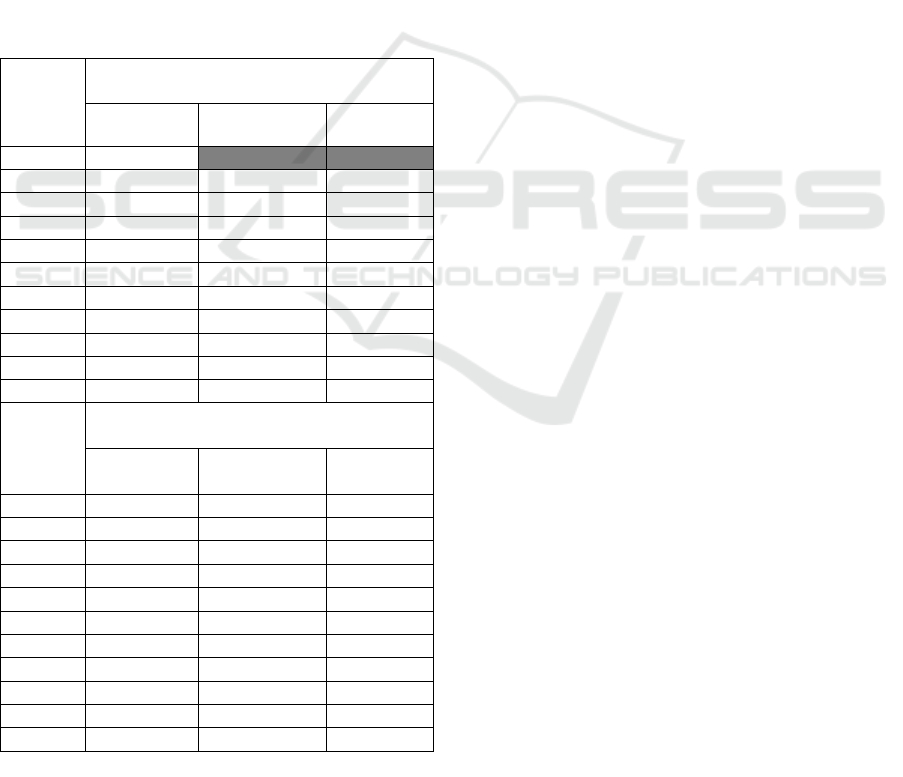
Table 1: Comparison of DPK BUK and BUS composition.
Years
Composition of DPK of Sharia
(billion rupiah)
Total DPK
Total Growth
of DPK
(%)
2006
20.708
2007
28.001
7.293
35,22%
2008
36.852
8.851
31,61%
2009
52.271
15.419
41,84%
2010
76.036
23.765
45,46%
2011
115.415
39.379
51,79%
2012
147.512
32.097
27,81%
2013
183.535
36.023
24,42%
2014
217.922
34.387
18,74%
2015
231.175
13.253
6,08%
Average
110.942,7
21.046,7
31,44%
Years
Composition of Conventional Commercial
Bank DPK (billion Rupiah)
Total DPK
Total Growth
of DPK
(%)
2006
1.287.102
2007
1.510.833
223.731
17,38%
2008
1.753.291
242.458
16,05%
2009
1.950.712
197.421
11,26%
2010
2.338.823
388.111
19,90%
2011
2.784.912
446.089
19,07%
2012
3.225.198
440.286
15,81%
2013
3.663.978
438.780
13,60%
2014
4.114.423
450.445
12,29%
2015
4.413.056
298.633
7,26%
Average
2.704.232,8
312.595,4
14,74%
Source: Indonesian Banking Statistics.
From the above table it can be seen that in terms
of total accounts both in sharia and conventional
banking continues to increase, but the percentage of
growth conditions total account of the year 2006-
2011 for the conventional bank looks volatile. while
the islamic banking showed relatively increased, but
in the last four years there was a decrease in total
growth of both conventional banking accounts and
sharia banking. Where the portion of the decline in
total growth of islamic banking accounts is greater
than conventional banking. The lowest decrease of
sharia banking occurred in 2015, which dropped to
6.08%, in the previous year was at 18.74%, ie
decreased by 12.66%, even in 2015 the decline in the
number of islamic banking DPK is under the banking
conventional in the figure of 7.26%. This is certainly
a problem that needs to be resolved. The DPK
function is vital in banking, the increase in deposits
will encourage the development of sharia banks, so
that banking management continues to strive to
increase the DPK (Piliyanti, 2014). There are some
impacts if the bank decreases the number of depositor
funds. the decline in the number of deposits allows
the public's trust in the bank to decline. According to
Hasibuan (2007: 71) "confidence means savers
believe that the money and interest on his savings can
be withdrawn from the bank in accordance with the
agreement." In addition, the decreasing dpk will
disrupt credit activities and bank operations are
disrupted so that banks are no longer rendebel. based
on the composition of deposits, the portion of deposits
always occupy the most amount of funds raised by
banks. Thus, deposits have a substantial share in
increasing or decreasing deposits. judging from the
type of fund raising facility offered by the bank, the
deposit includes an investment account, which is an
investment vehicle located in the bank. There are
several factors affecting dpk. according to husnan
(2006: 29) that customers who act as investors in the
bank will consider the level of risk and expected
profit levels of investment instruments. Based on
research conducted by nelwani (2013), there are
several factors that influence the deposit in sharia
commercial bank (bus), namely: inflation rate,
interest rate, promotion fee, office network amount,
profit sharing rate and rupiah exchange
rate.preferences, symbols and units.
Based on Adiwarman Karim and Adi Zakaria
Affif from Karim Business Consulting, the seg-
mentation of sharia banking customers in Indone-sia
is divided into three segments, namely shariah
loyalist, floating market and conventional loyalist
market. The floating market segment will keep its
money in the bank more due to economic ra-tionale
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
442

such as profit rate and quality of service offered. As
stated by Karim (in Nurlaeli, 2007) This market
segment will transact with the Sharia Bank if the
Sharia Bank provides the same mini-mum profit
service or more as compared to the Conventional
Bank. Vice versa with Convention-al Banking,
savings interest rate is an important variable to attract
debtor customers. The public interest in saving is
influenced by the interest rate. If interest rates
increase, allowing people who have already adopted
a Sharia Bank to move im-mediately to a
Conventional Bank. Based on the above description
can be concluded that one of the main differences
between conventional and syariah is the interest rate
in conventional banking and profit sharing in sharia
banking to describe the rate of return given to both
types of banks. In-terest rate movements and profit
sharing rates will attract rational customers to deposit
or withdraw funds at the Bank.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Bank Syariah Deposits Syariah deposits are de-posits
that are based on sharia principles (Karim, 2008:
303). The National Sharia Council of the MUI has
issued a fatwa stating that a justified de-posit is a
deposit based on mudaraba principles. Mudharabah is
a profit sharing agreement between the owner of the
fund (shahibul maal) that provides 100% capital to
the fund manager, in this case is the Bank that acts as
the fund manager (mudharib). This product is
intended as an investment tool for customers. Interest
Rate According to Kasmir, (2012: 133) Bank interest
can be interpreted as a fraction of the services
provided by the bank based on conventional
principles to customers who buy or sell their products.
Bank interest in this case can be interpreted as the
price to be paid bank to customers who have deposits.
The interest rate here is peroxide as an alternative
choice for floating market customers who save their
funds in sharia banking. Profit Sharing Rate the
profit-sharing agreement in principle, is a transaction
that seeks an added value of a cooperation between
parties in producing goods and services (Ascarya,
2008: 214). According to Agustianto (2013: 56),
profit sharing is a profit or a result obtained from the
management of both investment funds and buying
and selling transactions provided to customers. In
simple terms, profit sharing is the return or profit that
will be obtained by the parties who contribute to
provide funds for business activities.
3 METHODS
The method used is descriptive analytic and
verification methods. The independent variables of
this research are conventional bank interest rate and
profit sharing rate. Dependent variable of de-posit
amount in sharia commercial bank. The population in
this study is all Sharia Commercial Banks in
Indonesia. In sampling, the technique used is
Purposive Sampling, so that obtained 11 Sharia
Commercial Banks used in this study during the
period 2010-2015, i.e. six years.
Table 2: List of sample Bank Syariah.
No.
Name of Bank Sharia
1
PT. Bank Muamalat Indonesia
2
PT. Bank Victoria Syariah
3
PT. Bank BRI Syariah
4
PT. Bank Jabar Banten Syariah
5
PT. Bank BNI Syariah
6
PT. Bank Syariah Mandiri
7
PT. Bank Mega Syariah
8
PT. Bank Panin Syariah
9
PT. Bank Syariah Bukopin
10
PT. Bank BCA Syariah
11
PT. Maybank Syariah Indonesia
Source: Statistics of Sharia Banking
3.1 Classic Assumption Test
Before performing the regression test, a classical
assumption test is performed first. For multiple linear
regression test the assumptions used are as follows:
JB value counted 24,746, while Chi Square with
dk = (n-1) = 66-1 = 65, at alpha; = 5% is 84.82,
then. Data is normally distributed.
VIF value of 1.647 means VIF < 10. There is no
multicollinearity problem.
The White test value can be calculated with a W
result of 25.94 which means W < 84.82 (chi
square value) with dk = (n-1) = 66-1 = 65 and &
alpha; = 5%. There is no heteroscedasticity
problem.
The Durbin-Watson count is 1.6316. Value du
and dL in DW table with & alpha; = 5%, dk = 2,
n = 66 is du at 1.5395 and dL 1.6640, thus
1.5395 ≤; 1.6316 ≤; 2.3360 (4 - 1.6640), that
there is no autocorrelation.
3.2 Panel Data Regression
Test Panel data is a combination of cross-section data
(cross) with time-series data (time series). Panel data
processing can be done with several models, namely:
Influence of Interest Rate of Commercial Conventional Banks and Levels for Results on the Impact of the Number of Deposits in Sharia
Banks of 2010-2015
443

Common Effect Model, Model Fixed Effect and
Model Random Effect. The steps to determine the
model in regression with panel data are as follows:
3.2.1 Chow Test
The Chow test model is used to find out whether the
panel data regression technique with fixed effect is
better than the common effect regression model. In
Chow test can be made hypothesis as follows:
Ho: Model follows PLS / common effect
H1: The model follows fixed
The scoring criteria are the results indicating that
F-test and Chi-square if p-value; 5% then H0 is
accepted, and if p-value & lt; 5% then H0 is rejected
(Rohmana, 2010: 242).
The chow test results show that the F-test and Chi-
square are significant (p-value is not more than 5%)
so that Ho is rejected, the more appropriate fixed
effect model is used compared to the PLS model.
3.2.2 Hausman Test
The hausman test is performed to determine whether
the fixed effect model is better than the REM model.
In the Hausman test, the proposed hypothesis is as
follows:
Ho: using the Random Effect model
H1: using Fixed Effect model
With assessment criteria, if p-value & gt; 5%,
then received, if p-value & le; 5%, then rejected.
The hausman test results show that p-value is
greater than 5% so Ho is accepted. Then a more
appropriate random effect model is used than the
fixed effect model. Based on chow test and hausman
test that has been done, then the most appropriate
model used in this research is random effect model.
3.2.3 Test of Simultaneous Regression
Coefficient (Test F)
This test is to determine whether all the independent
variables included in the model of interest rate and
profit sharing rate have simultaneous effect on the
amount of deposit in sharia bank as dependent
variable. Hypothesis in this research:
BUK interest rate and profit sharing rate do not
affect the increase of deposit amount in Sharia
Commercial Bank.
BUK interest rate and profit sharing rate
influence the increase of deposit amount in
Sharia Commercial Bank.
3.2.4 Partial Regression Coefficient Test (t
test)
Hypothesis testing partially with t-test aims to
determine the influence of each independent variable
to the dependent variable. Assuming other
independent variables are fixed. Hypothesis in this
research are:
Hypothesis of variable X1 to Y:
The interest rate of BUK does not affect the
increase of deposit amount in Sharia
Commercial Bank, The interest rate of BUK
affects the increase in the number of deposits in
Sharia Commercial Banks
Hypothesis of variable X2 to Y:
The profit-sharing rate does not affect the in-
crease in the number of deposits in Sharia
Commercial Banks, The profit sharing rate has
an effect on the increase of deposit amount in
Sharia Commercial Bank.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Interest Rate
The interest rate of the bank determines how much
the remuneration is provided by a bank based on the
conventional principle to the depositary customer.
One of the existing types of interest is the
conventional deposit interest rate, which means the
customer will get a fee of interest provided by the
bank after the maturity date.
Interest rates in the 2010-2015 period tend to
fluctuate with the trend having an average in-crease
of 1.13%. In the period 2010-2015 the average
interest rate set by banks was in the range of 7.42%.
The highest interest rates occur in 2014 (amounting
to 8.92%) and the lowest interest rates occur in 2012
(amounting to 5.90%).
The increase and decrease in interest rates is
caused by several reasons, such as the economic and
financial situation faced in foreign countries overseas
and monetary policy set by Bank Indonesia.
Generally, Bank Indonesia will raise the BI Rate if
inflation is expected to exceed the set target.
Banking with a flower system will certainly raise
public funds with the lure of interest rates that tower.
This is in line with Karnaen (2011: 24) "A savings
interest rate would be interesting if: higher than the
inflation rate, higher than the real interest rate abroad,
and more competitive in the country".
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
444

4.2 Profit Sharing Rate
The profit-sharing rate determines how much of the
services provided by the banks with the principles of
sharia to depositors. The profit-sharing principle is
only granted to customers who deposit funds on the
principle of mudaraba.
The description of profit sharing rate at Syariah
Public Bank in 2010-2015 is getting an average value
of 6.74%. Overall, the average Shariah-compliant
bank's share rate appears to be fluctuating every year,
but has declined by an average of 0.82%. The highest
share rate of Sharia Commercial Banks occurred in
2010 (7.32%) and the lowest average share-sharing
rate in 2013 (6.33%). The increase and decrease in
profit-sharing rate is strongly influenced by the ratio
provided and the financing activities performed by
the Sharia Bank.
4.3 Deposit of Sharia Commercial
Bank
As a financial intermediary institution, banking
activities cannot be separated from collecting funds
from the community and channelling the funds back
to the community. The portion of de-posits always
occupies the most number in third party collections.
The nominal amount of deposits of Sharia Banks
collected during the period 2010-2015 has increased.
In the period 2010-2015, the average amount of
mudharabah deposits of Sharia Commercial Bank as
a whole amounted to 74,692,000,000,000 rupiah.
Growth, however, the trend of mudharabah deposits
for six years (2010-2015) decreased by 11%.
Seeing the increase and decrease in deposits in
Islamic banking is influenced by several things, such
as factors of public confidence and public
understanding of sharia banking. These community
clusters will not pay attention to the level of revenue
share and the rate of interest that decreases or rises.
People will also see the quality of services provided
and benefits. Product products is-sued and
promotions made by sharia banks also become an
important role of banks to attract customers in raising.
4.4 Regression Coefficient Test
Simultaneously
This study used panel data, which is a combination of
cross-section data and time-series data. From research
procedure to panel data obtained result that this
research better use Random Effect model. The
applicable regression model is DM = 5616136 -
1486139 TSB + 1493060 TBH. Where the interest
rate variable has a negative influence on the number
of mudharabah deposits and the variable of profit
sharing rate has a positive influence on the number of
mudharabah deposits.
The result of regression significance test
simultaneously through F-test shows that the interest
rate of conventional commercial bank and profit
sharing rate influence the number of deposits in
Sharia Commercial Bank in 2010-2015. This is
evidenced by the value of F arithmetic of 20.37 is
greater than F table 3.14.
R square result shows that 0,393 means 39, 3%
variation of conventional bank interest rate variable
and profit sharing rate influence deposit amount in
Syariah Bank 2010-2015. While the remaining 60.7%
(100% -39.3%) is influenced by other factors outside
the interest rate and the level of profit sharing.
4.5 Effect of Interest Rates on Deposits
in Sharia Commercial Banks
Partial test for profit sharing through t-test is obtained
result that at 5% significance level, th > tta that is
4,76 1,67 with a significance value of 0.0000 then
H0 is rejected and H1 accepted which means there is
influence between the level of prof-it sharing and the
amount of deposits in Islamic banks.
Regression coefficient value of 1.493.060 which
means any increase of 1% profit sharing rate will
increase the number of Islamic banking mudharabah
deposits of 1.493.060 million rupiah. This result is in
accordance with the theory that the in-crease in profit
sharing will affect the amount of third party funds,
where one of the largest contributor of third party
fund sources is deposits. Banking customers in
Indonesia are divided into three layers, namely;
Conventional market, floating market, and sharia
loyalist market. As stated by Karim (in Nurlaeli,
2007: 65), "The factor that attracts a floating market
customer is transacting with a Sharia Bank if a Sharia
Bank provides a profit service of at least the same or
more than that of a Conventional Bank".
It means that some customers make the choice to
place funds in sharia banking is very dependent on the
yield obtained. With a high profit sharing rate will
increase the interest of the community, especially the
floating market segment to save funds in Islamic
banks. Therefore, when the profit sharing rate is high,
there is an increase in the number of syariah banking
deposits. For that Islamic banks need to keep in order
to still be able to provide attractive revenue sharing to
its customers.
From the research conducted, confirmed that the
preference of Indonesian people, especially the
floating market segment in saving the funds in
banking will see the benefits offered. This means that
Influence of Interest Rate of Commercial Conventional Banks and Levels for Results on the Impact of the Number of Deposits in Sharia
Banks of 2010-2015
445

customers consider the choice to place funds in either
sharia or conventional banking is very de-pendent on
the level of returns to be obtained. So by using only
sharia principles, it is not the primary value to acquire
customers, although some Indonesians are Muslim.
The results of this study support the results of
research conducted by Nurika (2014), Suratman
(2011), Reswari (2010) and Nurlaeli (2007)
concluded that the profit sharing effect on mudhara-
bah deposits due to some customers who put their
funds in Islamic banks are still influenced by the
motive Looking for profit.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In 2010-2015 conventional bank interest rates ranged
from 5.90% - 8.92%, while the profit sharing rate
ranged from 6.33% - 7.32%. The nominal amount of
Sharia Commercial Bank deposits has increased, but
the growth of total deposits in Sharia Commercial
Banks in 2010-2015 percentage decreased by an
average of 11% per year. The interest rate of
conventional banking and the level of profit sharing
simultaneously have a significant effect on the growth
of deposit amount in Sharia Commercial Bank. The
conventional bank interest rate has a significant
negative effect on the amount of deposits in Sharia
Commercial Banks, while the profit sharing rate
significantly affects the amount of deposits in Sharia
Commercial Banks.
REFERENCES
Agustianto. 2013. Determination of Profit Sharing of
Mudharabah Deposit at Bank Syariah. [On line].
Available: Brawijaya. http://www.iaei-pusat.net [12
Juni 2016].
Ascaraya. 2008. Akad & Bank Syariah Products. Jakarta:
Raja Grafindo Persada.
Azmansyah, Ahmad, Z. 2012. Comparative Analysis of
Profit Sharing and Interest and Its Influence on
Community Funds Collection (Case Study at Riaukepri
Syariah Bank Pekanbaru). Journal of Economics,
Management and Accounting. Vol.18 No. 1, p.1-25
Bank Indonesia. 2006-2015. Indonesian Banking Statistics.
Jakarta: Bank Indonesia
Hasibuan. 2007. Fundamentals of Banking. Jakarta: PT
Bumi Aksara.
Husnan. 2006. Fundamentals of Financial
Management.Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPM.
Husni, A. 2009. Factors Affecting Third-Party Funds
Growth in Syariah Banking in Indonesia Period:
January 2006-December 2007.
Karim, A.A. 2008. Islamic Bank Fiqh and Financial
Analysis. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada.
Karim, A., Affif, A. Z. Islamic Banking Consumer
Behavior in Indonesia, a Qualitative Approach.
[Online]. Tersedia:
http://www.kantakji.com/media/163564/file515.pdf.[2
5 Juni 2016]
Kasmir. 2012. Dasar-Dasar Perbankan. Jakarta: Rajawali
Pers.
Karnaen, A., 2011. Bank Syariah Theory, Practice and
Role. Jakarta: Celestial Publishing.
Nelwani, C.Y., 2013. Factors Affecting Mudharabah
Deposits in Sharia (BUS) Banks Period 2009-2012.
Essay. Yogyakarta: Department of Islamic Economics
UIN Sunan Kalijaga
Nurika. 2014. Analysis of Profit Sharing Factor and
Interest Rate to Third Party Fund at Bank Muamalat
Indonesia with Variation Moderation of Financial
Crisis of 2008. Thesis. Bandung: M2B Department
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
Nurlaeli, L., 2007. The Effect of Profit Sharing and Interest
Rate on Total Mudharabah Deposits at PT Bank
Muamalat Indonesia Tbk. Thesis. Bandung:
Department of Economic Education UPI.
Financial Services Authority. 2016. Statistics of Sharia
Banking.Jakarta: Bank Indonesia
Reswari, Y.A., Abdurahim, A. 2010. Influence of Interest
Rate, Profit Sharing and LQ 45 on Mudharabah
Deposit at Indonesian Sharia Bank. Journal of
Accounting and Investment.Vol. 11 No.1, p.30-141
Rohmana, Y. 2010. Econometrics (Theory and
Applications with Eviews). Bandung: Economic and
Cooperative Lab.
Suratman. 2013) Effect of Mudharabah Deposit Amount,
SBIS Reward Rate, 1 Month Deposit Interest Rate, and
Inflation Rate on Mudharabah Deposit (Case Study of
PT Bank Syariah Mandiri Tahun 2007-2011 Thesis,
Jakarta: Department of Management UIN Syarif
Hidayatullah.
Wulansari, D. I., 2015. The Effect of Profit Sharing and
Interest Rate on the Number of Mudharabah Deposits
(Case Study of Sharia Banking Year 2009-2013). Essay.
Malang: Department of Economic Universitas
Brawijaya.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
446
