How Can Population Density Affect Economic Growth?
Lucky Rachmawati
Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: population density, economic growth.
Abstract: Population density is identical with the abundant supply of labor. Abundant labor will contribute to the
production of goods and services, so that economic growth will increase. However, how the effect of
population density on economic growth needs to be further investigated. The aim of this study is to know how
the effect of population density on economic growth. Data analysis technique used is panel regression analysis
method. The data analyzed include population density and economic growth of selected countries in the world
in 2011-2015. The results of the study indicate that population density has significant effect on economic
growth.
1 INTRODUCTION
Economic growth is one indicator of the success of a
country's economic development. Economic growth
illustrates that in an economy experienced an increase
in national income. National income measures the
extent to which a country's economy can produce
goods and services over a period of time. This
increase in the capacity to produce goods and services
can be referred to as economic growth.
Most countries in the world, have a large target of
economic growth to be achieved per year. It is
expected that economic growth will continue to
increase, although the increase is not so great but is
not kept down.
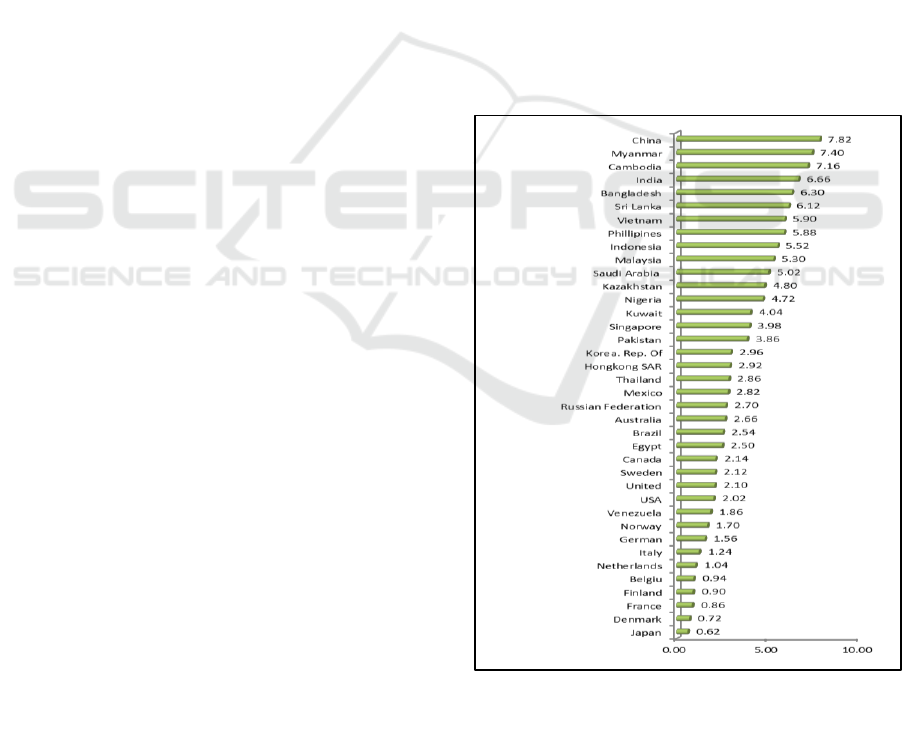
The economic growth conditions of each country
can be seen in Figure 1. Japan has the lowest average
economic growth compared to other countries in the
World, while China is highest. High economic growth
depends on the productivity of a country in producing
goods and services. Each country certainly has
different potential in the availability of production
factors, it can happen because of different natural and
geographic characteristics. Some of the production
factors used for production inputs include: land,
natural resources, labor, capital and entrepreneurship.
Figure 1: Average economic growth rate of selected
countries at constant market price (percent), 2011-2015.
Source: International Monetary Fund (IMF): “World Economic
Outlook, April 2016
Countries
Average Population Density
Rachmawati, L.
How Can Population Density Affect Economic Growth?.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 411-415
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
411
Availability of manpower in a country, is one of
the factors that influence the decision making
company to be located in a country or in other
countries in producing goods and services.
Companies tend to choose production sites in
countries that provide manpower with large quantities
and good quality. It is of course related to the
calculation of the costs to be incurred or the profit that
will be obtained by the company.
Quantity of labor, will affect the amount of goods
and services to be generated. The more manpower
available, the more goods and services will be
generated. This is in line with the production theory
proposed by several economists, including von
Thünen (1826), Turgot (1776), Smith (1776), Steuart
(1767), Malthus (1815) and Ricardo (1817), Cobb-
Douglas (1934) , Arrow et al. (1961), and Leontief
(1966). The large quantity of labor supply will result
in lower wages, thus the company will incur minimal
labor costs (Nicholson and Snyder, 2012: 320).
Good labor quality, will affect the efficiency in
producing goods and services produced. A qualified
workforce will produce goods and services
effectively and efficiently. In accordance with the
theory of production Solow (1957 in Nicholson and
Snyder, 2012: 320) suggests that technical progress /
technology as one of the factors that can increase
output. The efficiency of this workforce will increase
output, so the profit earned by the company will also
increase.
The availability of labor in a country both in terms
of quantity and quality encourages the formation of
an economic concentration in a particular country.
When there is concentration of the economy in a
particular country, in addition to affect the company
will also affect the decision of the workforce.
Employment decisions, related to their choice to
choose where they will work. The workforce in
maximizing its utility will choose a job that gives a
decent life.
Workers do not hesitate to move (migrate) to get
more decent work than they work at home. However,
the workforce must, of course, adjust its
competencies to the qualifications of the requested
workforce. This labor migration, will increase the
population density in a particular country.
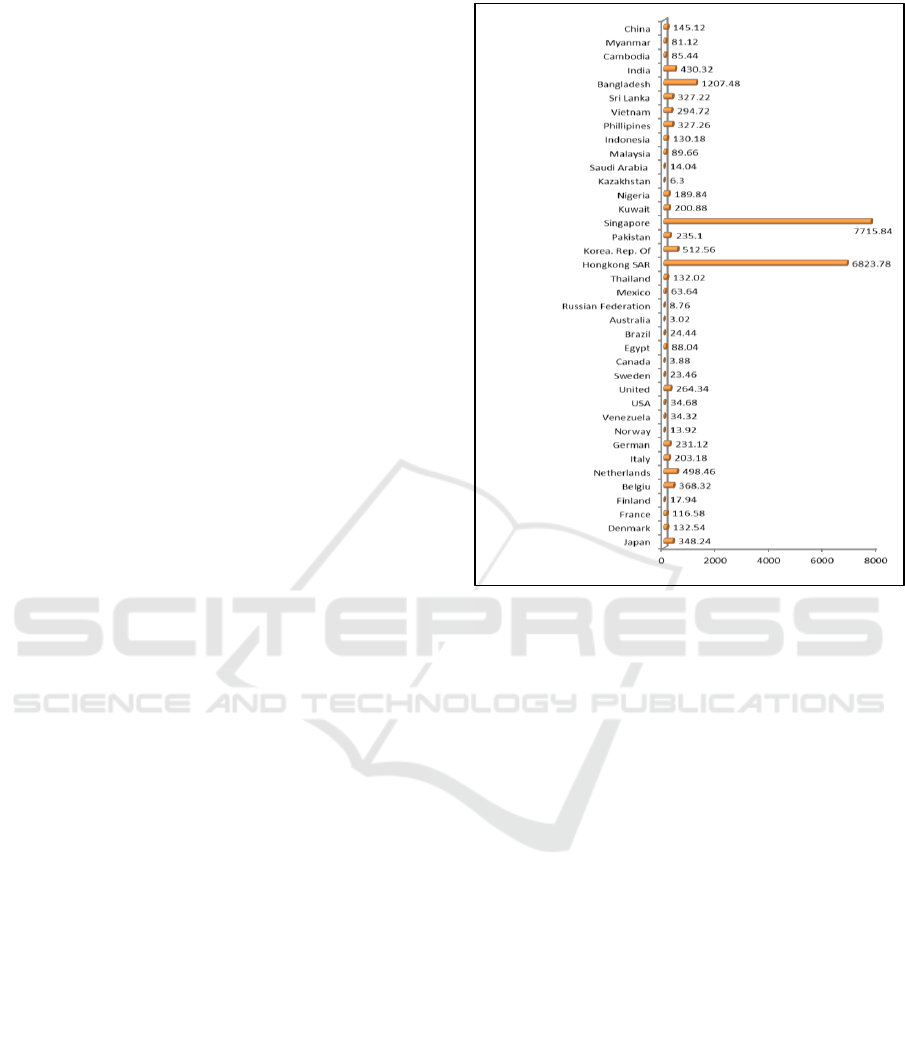
Figure 2: Average population density of selected countries
(people per sq.km), 2011-2015.
Source: United Nations: “World Population Prospects: The
2015 Revision”
Population density in a country, related to labor
demand and supply and identical to the availability of
abundant labor. The availability of abundant labor
will encourage increased output generated by the
economy, in other words economic growth occurs.
Illustrated in Figure 2, the country with the largest
population density is Singapore and Hong Kong.
Nevertheless the average economic growth of the two
countries is not how high. Hong Kong's average
economic growth is ranked 21st compared to 37 other
countries, while the state of Singapore is ranked 24th.
China has the highest economic growth rate, the
average population density is ranked 21. On the other
hand, the State Japan which has the lowest population
growth rate, the average population density is ranked
31. Khotare (1999: 13) suggested that the rise in
population growth of creating a positive effect on
economic growth. But, Gilbert (2014: 126) find that
population density has no statistically significant
effect on productivity.
Some impacts need to be considered related to
population density, including The Law of
Diminishing Marginal Return. If this law applies, it
means that increasing the number of workers
Average Population Density
Countries
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
412

continuously, will not increase the output of the
economy but will even reduce the output of the
economy. This condition is caused by ineffective and
efficient labor usage.
Population density plays an important role in
harvesting societies, i.e. those that depend on
agriculture and natural resources. Too high
population density can make them poor due to low
resource endowment per capita, low population
density has a problem of too high per capita cost of
building and maintaining infrastructure to collect and
bring its resources to the market (Yegorov, 2015: 10).
Malthus (1978 in Skousen, 2005: 83) has a
pessimistic thinking about the impact of population
growth on the economy. Malthus argues that the
growing population is growing according to
geometric sequence. Rapid population increases will
result in a high dependency ratio and will reduce the
welfare of the people.
Cincotta and Engelman (1997: 5) suggested that
the relationship between population growth and
depressed economic performance is strongest among
the poorest nations of the developing world. The
growth of gross domestic product can be constrained
by high dependency ratios, which result when rapid
population growth produces large proportions of
children and youth relative to the labor force.
Because governments and families spend far more
on children than the children can quickly repay in
economic production, especially as modern
schooling and health care replaces child labor,
economists expect consumption related to children to
retard household savings, increase government
expenditure and ultimately cut into the growth of
GDP. In many cases (in the developing world) lots
of employment was being created, but not fast
enough to match the rapid growth in the labor force.
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Return can be
overcome with technical progress/technology
according to the production theory proposed by
Solow (1957 in Nicholson and Snyder, 2012: 320).
Technical progress is not only related to capital but
also the quality of labor. Quality of labor is related to
education and skill of labor.
The aim of this study is to know how the effect of
population density on economic growth. The data
analyzed include population density and economic
growth of several countries in the world in 2011-
2015.
2 METHODS
This study is an exploratory research with
quantitative method. The variables which studied:
Population density and economic growth. Each
variable is defined operationally as follows: 1)
Population density is population density of selected
countries in the world 2) economic growth is the
increase in Gross Domestic Product of selected
countries in the world. The type of secondary data
obtained from the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
and United Nations. Data analysis technique used is
panel regression analysis method.
2.1 Econometric Model
The effect of population density on economic growth
is investigated by employing the following model:
growth
r,t
= b
0
+ b
1
density
r,t
+ e
1r,t
where growth
r,t
is economic growth of country r
at time t; density
r,t
is population density of country r
at time t; b
0
is the constanta; b
1
is the regression
coefficient of population density variables; and e
1r,t
is
the error term.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This study was conducted to examine whether there
is any effect of population density on economic
growth. The proof is done using panel analysis
method. The result of data analysis of 38 countries in
the world is shown in Table 1.
Based on the results of the data, the calculated p
value (t statistics) of 0.0307 is less than the critical p
value, the null hypothesis is rejected. It can be
concluded that the hypothesis related to the effect of
population density on economic growth raised in this
study is acceptable.
Important conclusions regarding the effect of
population density on economic growth from this
study is significantly population density negatively
effect on economic growth. Population density
Increases will decreases economic growth.
How Can Population Density Affect Economic Growth?
413

Table 1: Estimation equations of the effect of population
density on economic growth on each countries.
Estimation Equations
USA
:
Growth
=
- 5.139438
- 0.006952
*density
Saudi
Arabia
:
Growth
=
- 2.282922
- 0.006952
*density
Australia
:
Growth
=
- 4.719530
- 0.006952
*density
Bangladesh
:
Growth
=
7.293546
- 0.006952
*density
Netherlands
:
Growth
=
- 2.895367
- 0.006952
*density
Belgiu
:
Growth
=
- 3.900064
- 0.006952
*density
Brazil
:
Growth
=
- 4.690624
- 0.006952
*density
Denmark
:
Growth
=
- 5.759142
- 0.006952
*density
Russian
Federation
:
Growth
=
- 4.639627
- 0.006952
*density
Philippines
:
Growth
=
0.754498
- 0.006952
*density
Finland
:
Growth
=
- 6.375810
- 0.006952
*density
Hong Kong
SAR
:
Growth
=
42.95653
- 0.006952
*density
India
:
Growth
=
2.250943
- 0.006952
*density
Indonesia
:
Growth
=
- 0.975548
- 0.006952
*density
United
:
Growth
=
- 3.462905
- 0.006952
*density
Italy
:
Growth
=
- 4.748072
- 0.006952
*density
Japan
:
Growth
=
- 4.359655
- 0.006952
*density
German
:
Growth
=
- 4.233841
- 0.006952
*density
Cambodia
:
Growth
=
0.353431
- 0.006952
*density
Canada
:
Growth
=
- 5.233552
- 0.006952
*density
Kazakhstan
:
Growth
=
- 2.556728
- 0.006952
*density
Korea.Rep.
Of
:
Growth
=
- 0.877347
- 0.006952
*density
Kuwait
:
Growth
=
- 1.964061
- 0.006952
*density
Malaysia
:
Growth
=
- 1.477232
- 0.006952
*density
Mexico
:
Growth
=
- 4.138116
- 0.006952
*density
Egypt
:
Growth
=
- 4.288494
- 0.006952
*density
Myanmar
:
Growth
=
0.563400
- 0.006952
*density
Nigeria
:
Growth
=
- 1.360809
- 0.006952
*density
Norway
:
Growth
=
- 5.603756
- 0.006952
*density
Pakistan
:
Growth
=
- 1.906173
- 0.006952
*density
France
:
Growth
=
- 5.730092
- 0.006952
*density
Singapore
:
Growth
=
50.21788
- 0.006952
*density
Sri Lanka
:
Growth
=
0.994220
- 0.006952
*density
Sweden
:
Growth
=
- 5.117437
- 0.006952
*density
Thailand
:
Growth
=
- 3.622757
- 0.006952
*density
China
:
Growth
=
1.428310
- 0.006952
*density
Venezuela
:
Growth
=
- 5.301941
- 0.006952
*density
Vietnam
:
Growth
=
0.548289
- 0.006952
*density
The findings of this study mean that Malthus
pessimistic thinking is still valid today. Population
density in an area that is an economic concentration
area (regional economic agglomeration) only creates
a high dependency burden. This high dependency
burden according to Cincotta and Engelman (1997: 5)
can be due to large proportions of children and youth
relative to the labor force.
Furthermore, Cincotta and Engelman (1997: 5)
suggested that government and families spend much
more on children than the children can quickly repay
in economic production. In many cases (in the
developing world) many of employment was being
created, but not fast enough to match the rapid growth
in the labor force.
High dependency burden resulted in the
enactment of The Law of Diminishing Marginal
Return. Population growth does not create an increase
in output, but instead will decrease output. Moreover
the availability of inadequate public access, such as
access to health and education. Empirically, most
developing country societies enjoy poor public
access, while developed country societies can enjoy
better public access.
Good public access will increase labor
productivity. Especially access to education and
health. This is in accordance with the theory of human
capital. Good education or skills will result in high
labor productivity, meaning that the output produced
is also more increased. Education and skills will
improve technical progress in producing goods and
services. Solow (1957 in Nicholson and Snyder,
2012: 320) mentions that The Law of Diminishing
Marginal Return can be overcome with technical
progress/technology according to the production
theory.
The effect of population density that hampers
economic growth, requires government policy.
Population density is related to several things that
affect such as: geographical area, population growth,
population migration, and economic concentration in
a region.
Geographical area related to the availability of
natural resources in an area that can support human
life. Humans tend to get close to the natural resources
that can support their lives, for example: water
availability, soil fertility, clean air, etc. Thus, if we do
not want an increase in population density in a given
area then the government should be able to provide
access to adequate infrastructure and easy to get it
related to basic human needs.
Population growth is related to the number of
births of the population. Humans have a variety of
thoughts about the value of children, the
understanding of the meaning of a quality family
needs to be emphasized to the community. Families
with many children, but not supported by the family's
ability to meet the basic needs of children, including
education and health, will only become a burden of
high dependence on the economy. In contrast to
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
414

families who have children who fit the ability of
families to meet basic needs, then they will have a
better quality of life. Government regulation related
to population growth is needed, so that the public
better understand the way that they can achieve
prosperous life. Developed countries began to
implement this population growth regimen.
Population migration is generally associated with
the availability of employment, the availability of
access to education, and the availability of other
public access. In developing countries, the
availability of employment, access to education and
other public access is inadequate. These conditions,
triggering populations that have the potential to
migrate from developing countries to more developed
countries. They think that they will have better
prosperity in the destination country than settled in
their home country. Thus will trigger the density of
the population in the destination country.
Economic concentration in a region, related to the
country in which a multinational company will
operate and conduct its production activities. The
company will choose production sites with several
alternative options, including: close to factors of
production, close to the market, good infrastructure
access and easy permitting access.
Close to the factors of production, related to
inputs to be used for production, both production
materials and labor. Generally companies will choose
close to production materials and with cheap labor
wages. This is related to the prediction of revenues
and expenses that must be issued company so that will
give profit for the company. Close to the market
associated with the ease of selling for the company.
Good infrastructure is related to the ease of
distribution of goods or services produced. Easy
access permissions related to the ease of opening a
business in a country. Economic concentration in a
country will cause population density in a country,
because people will migrate to the economically
centralized country in the hope that their welfare will
increase. Thus requires a common consensus that
multinational companies not only operate in one
particular country.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Important conclusions regarding the effect of
population density on economic growth from this
study is significantly population density negatively
effect on economic growth. Population density
increases will decreases economic growth.
The effect of population density that hampers
economic growth, requires government policy. These
policies include: provide access to adequate
infrastructure and easy to get it related to basic human
needs; Government regulation related to population
growth; Availability of employment, availability of
access to education, and availability of other public
access in developing country; And requires a
common consensus that multinational companies not
only operate in one particular country.
REFERENCES
Cincotta, R. P., Engelman, R., 1997. Economics and Rapid
Change: The Influence of Population Growth.
Occasional Paper Population Action International.
pai.org/wpcontent/uploads/2012/01/Economics_and
_Rapid_Change_PDF.pdf.
Gilbert, J. R., Jumbe, C., Chamberlin, J., 2014. How does
population density influence agricultural
intensification and productivity? Evidence from
Malawi. Food Policy 48 (2014), 114-128.
International Monetary Fund (IMF). 2016. World Economic
Outlook, April 2016.
Khotare, R., 1999. Does India's Population Growth Has A
Positive Effect on Economic Growth?.
pages.cs.wisc.edu/~dluu/data/papers/rkothare99.pdf.
Paper provided by Université catholique de Louvain,
Institut de Recherches Economiques et Sociales
(IRES) in its series Discussion Papers (IRES - Institut
de Recherches Economiques et Sociales) with number
2016003.
Nicholson, W., Snyder, C., 2012. Microeconomic Theory
Basic Principles and Extensions: eleventh edition.
Nelson Education, Ltd, Canada.
Skousen, M., 2005. The Maestro: Modern Economic
Theories. Prenada Media, Jakarta.
United Nations. 2015. World Population Prospects: The
2015 Revision.
Yegorov, Y., 2015. Economic Role of Population Density.
Published in World renaissance: changing roles for
people and places: programme and list of
participations: ERSA 55th Congress: in conjunction
with the 21th APDR Congress: 25-28 August 2015 -
Lisbon, Portugal. Publisher [Louvain-la-Neuve]:
European Regional Science Association.
How Can Population Density Affect Economic Growth?
415
