
Digital Storytelling and Think-Pair-Share to Improve the Ability of
Critical Thinking
Dini Ayu Lestari, Siswandari Siswandari and C. Dyah S. Indrawati
Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, Indonesia
dniayulest@gmail.com,namaku_ndari@yahoo.co.uk,ciciliadyahsulistyaningrum@yahoo.com
Keywords: Digital storytelling, Think pair share, Critical thinking.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to develop digital storytelling learning media in the form of website storytelling
as an effort to improve critical thinking ability of high school students. One of the learning models that educate
students to think critically is the think pair share model. According to previous research, digital storytelling
has an effect on improving students critical thinking skills. The method used in this research is the method of
Research and Development applying media for students in high school. This study is examined by the steps
of the preliminary research procedure, the development and testing stage. Data analysis technique used in this
research is simple descriptive analysis. This study compares the pretest post test results to find out the results
of the study. This research is expected to improve students' critical thinking ability in economic learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ability of critical thinking in solving problems
can prepare students to live their careers and real life
(Ramdani, 2012). Filsaime (2008) outlined the
importance of critical thinking in human daily
activities and states that only capable individuals have
the ability to continue to grow. Basically, since
childhood, people already have tendencies and skills
to think critically. As a rational being, human beings
are always compelled to think about the things around
them. The tendency of humans to give meaning to
various things and events around them is an
indication of their ability to think (Paul, 1994).
This tendency can be found in a small child who
looked at various objects around him with curiosity.
By look at him we can gain an understanding of how
children think and give meaning to the environment.
We can also see how they experiment with everything
that provokes his curiosity and draws conclusions
from the things he meets. With an understanding of
the cognitive condition of learners and their high
learning ability, it can be concluded that education for
critical thinking should have been given to children
since very young, in addition to preparing them in
adulthood later, also to familiarize openness to
various information from an early age. Indarti et al.
(2013) reveals that when students are accustomed to
selecting and trying to process the information they
have acquired, they will be trained to solve problems,
think critically, creatively, systematically and
logically. Lack of critical thinking education can lead
learners to the habit of doing various activities
without knowing the purpose and why they are doing
it. This habit is already often seen in the less educated
students do not even get the education of critical
thinking.
The purpose of this research is to develop digital
storytelling learning media with think-pair-share that
are eligible to be used in the learning process to
determine the effectiveness of digital storytelling
media based on think pair share in an effort to
improve students' critical thinking skills on the
economic subjects. The method of research that will
be used is a research and development method (R &
D). Research and development according to Borg &
Gall (2007: 58) is "an industry-based development in
which the findings of the research are processed and
tested, evaluated and Refined until they meet specific
criteria of effectiveness, quality or similar standards."
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Ability of Critical Thinking
Thinking according to Plato is speaking in the heart.
"Thinking is putting the relationship between the
184
Lestari, D., Siswandari, S. and Indrawati, C.
Digital Storytelling and Think-Pair-Share to Improve the Ability of Critical Thinking.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 184-190
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

parts of our knowledge". Ennis pointed out, "The
definition of critical thinking is reflective thinking by
emphasizing decision-making about what to believe
or do". Implicitly, critical thinkers evaluate the
implicit thoughts of what they hear and read, examine
the process of self-thinking when writing, solving
problems, making decisions, or, or developing a
project (Surya, 2013: 159). Alec Fisher (Ennis) stated
"Critical thinking is a sensible and reflective thinking
that focuses on deciding what to believe or do."
According to Webster's New Encyclopedic All
New 1994 Edition cit, Amri (2010: 62), "critical" is
"implement or practice the careful assessment and
objective" so that "critical thinking" can be
interpreted as thinking that requires precision in
making decisions.
Another definition given by Ennis (Suryanti et al,
2008: 31) is critical thinking is a process that aims to
make sensible decisions about what we believe and
what we do. Critical thinking is one step higher level
thinking into four groups which include problem
solving, decision making, critical thinking, and
creative thinking (Amri & Ahmadi, 2010). Wijaya
(Suryanti et al, 2008) says that critical thinking skills
as part of thinking skills should be owned by every
member of society, because there are so many
problems in life that must be done and resolved (Amri
and Ahmadi, 2012: 66).
Based on the above opinion it can be concluded
that critical thinking describes an active process of
thinking, or not just take for granted the ideas of
others. Critical thinking shows that there is reason to
believe in something and for that ability is part of the
critical thinking skills that learners must have in order
to solve all problems.
Hendra Surya (2012: 179) stated that critical
thinking steps that can be grouped into 3 namely: (1)
Recognition of problems, assessing information, and
solving problems or drawing conclusions, (2) Assess
relevant information, (3) Troubleshooting or drawing
conclusions.
Wahab Jufri (2013: 104) states that the indicator
of critical thinking skills is to formulate problems,
give arguments, deduce, induce, evaluate, make
decisions and determine actions. Facione (1990) in
Liliasari and Tawil (2013: 9) identified 6 critical
thinking skills, namely interpretation, analysis,
evaluation, inference, explanation, and self
regulation. While Henri (1991) which quoted by
Liliasari and Tawil (2013: 9) identifies critical
thinking skills in 5 dimensions, namely basic
clarification, in-depth clarification, inference,
assessment, strategy, and tactics.
Based on the aspect of students' critical thinking
skills which have been proposed, this research uses
aspects of critical thinking skills according to
Facione's (1990) opinion in Liliasari and Tawil
(2013: 9) is interpretation, analysis, evaluation,
inference, explanation, and self regulation.
2.2 Review of Learning Media
2.2.1 Definition of Learning Media
Media serves as an intermediary in the dissemination
of information from the sender of information to the
recipient information. According to Anderson which
quoted by Sukirman (2012: 28) Media learning is a
medium that allows the realization of a direct
relationship between the work of a subject developer
with the students. Learning media is a means or
educational tool that can be used as an intermediary
in the learning process to enhance effectiveness and
efficiency in achieving teaching objectives (Sanaky,
2013: 4). Meanwhile, according to Gerlach & Ely that
when understood in broad outline is human, material,
or events that build conditions that make students able
to acquire knowledge, skills, or attitudes. In
particular, the meaning of media in teaching and
learning process tends to be interpreted as graphic,
photographic, or electronic tools to capture, process
and rearrange visual or verbal information (Arsyad,
2013: 3). Winkell quotes from De Corte (2005) who
stated that instructional media is a non-personal (non-
human) means used or provided by faculty who play
an important role in teaching and learning, to achieve
the instructional objectives.
Based on the above opinion, it can be drawn
understanding of instructional media which is
anything that can be used to communicate the
message to students centered on the students so that
students are more motivated to learn through
discussion of material that students are interested in.
2.2.2 Characteristics of Learning Media
According to Bretz which quoted by Sadirman (2006:
2) identifies the main characteristics of instructional
media, among others: (1) Sound, is distinguished also
be a broadcast media (telecommunications) and the
recording media. 2) Visual, divided into three namely
images, lines, and symbols that are one continuum of
the form that can be caught by the sense of sight.
According to Gerlach and Ely which quoted by
Arsyad (2013: 15-17), there are three characteristics
of the media, namely: Marks fixatives (fixative
Digital Storytelling and Think-Pair-Share to Improve the Ability of Critical Thinking
185

property), manipulative (manipulative property),
characteristic Distributive (distributive property).
Based on the above opinion, it can be drawn
characteristics of good learning media which is a
learning medium in the form of learning aids that can
be sound, pictures, recordings, film or video, lines,
symbols that may be changed in the form of objects
in the form of a summary of events later Displayed
again as an overview.
2.2.3 Learning Media Functions
There are several functions of learning media
according to Rusman (2012: 162) in the learning
include: (1) As a tool in the learning process, (2) As a
component of sub learning, (3) As an influence in
learning, (4) As a game to draw the attention and
motivation of students in learning, (5) Improve results
and learning process, (6) Reduce the occurrence of
verbalism, and (7) Overcoming the limitations of
space, time, energy, and power of the senses.
According to Levie & Lentz in Sukirman (2012:
38-39) There is a function of learning media that is:
(1) attention function, (2) affective function, (3)
cognitive function, and (4) compensatory functions.
Based on the above opinion about the function of
instructional media, it can be drawn the function of
instructional media as an effort in improving
motivation, interest in learning students in presenting
lesson discussion information submitted by teachers
in achieving learning objectives planned before
learning.
2.2.4 Benefits of Learning Media
According to Sanaky (2013: 5) there are benefits of
learning media as follows: (1) Learning will draw
more attention so as to motivate students to learn, (2)
Learning materials will be more clear meaning that
can be better understood by students and enable
students to master the goal of learning better, (3) The
learning method will be more varied, not solely verbal
communication through the narrative of words by the
teacher does not run out of steam, especially when
teachers teach each lesson, and (4) Learners do more
learning activities, because not only listen to the
teacher's description, but also other activities such as
observation, performing, demonstrating and others.
Based on the above opinion, it can be drawn benefit
from the use of learning media in the learning process
which is to improve student motivation in teaching
and learning process so that students achieve optimal
results.
2.3 Review of Digital Storytelling
2.3.1 Definition of Digital Storytelling
According to Echols which quoted by Aliyah (2011)
storytelling consists of two words is story and telling.
The merging of two word storytelling means telling
stories or telling a story. Additionally, as proposed by
Malan, storytelling is telling a story based on oral
tradition. Storytelling is an attempt by storytellers in
conveying the contents of feelings, thoughts, or a
story to children as well as orally. While in the Great
Dictionary of Indonesia (Ikranegarkata & Hartatik),
the story is a story, a fairy tale, a speech depicting a
process of events at length, a play that presents the
course of events, the play embodied in the show
(about drama, film, etc).
Based on the above opinion, it can be understood
that storytelling is an art of narrating the stories in
verse or prose, which is performed or led by one
person in front of the audience directly where the
story can be narrated in a way described or sung, with
or without music, pictures, or with other
accompaniments that may be learned orally, either
through printed sources, or through a source of
mechanical recording.
2.3.2 Benefits of Digital Storytelling
According to Hibana which quoted by Kusmiadi
(2008) The benefits of this storytelling activity are:
(1) Develop fantasy, empathy and different kinds of
feelings, (2) Grow interest in reading, (4) Build
closeness and harmony, (5) Instructional Media.
The other benefits for children with storytelling,
among others are: (1) Develop thinking power and
imagination of children, (2) Develop children's
speaking skills, (3) Develop child socialization, (4)
Means of communication with the child's parents, (5)
Media therapy for children with problems, (6)
Developing a child's spirituality, (7) Grow motivation
or life spirits, (8) Embedding values and character, (9)
Building inner contact between educators and
students, and (10) Build characters, (11) Developing
cognitive (knowledge), affective (feeling), social, and
cognitive aspects (appreciation).
2.4 Think Pair Share Learning Model
Think Pair Share learning model originally developed
by Frank Lyman, et al at the University of Maryland
pad 1985 (Majid, 2013: 191). Think Pair Share has
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
186
procedures set out explicitly to give more time to the
students to think, respond, and help each other.
According to Lie (2008: 57) that Think Pair Share
is a simple cooperative learning model that provides
an opportunity for the students to work on their own
and in collaboration with others. The advantages of
this learning model, which is able to optimize student
participation.
The stages in the learning Think-Pair-Share by
Ibrahim (2000: 26-27) as follows: (1) Thinking; The
teacher asks questions related to the subject matter.
Then the students are asked to think about the
question or issue independently for a few moments,
(2) Pairing; The teacher asks students to pair up with
other students to discuss what he or she has been
thinking at the first stage. At this stage, each member
of the group compares their answers or thoughts by
formulating the answer that is considered the most
correct or most convincing, (3) Sharing; In the final
stages, the teacher asks the couple to share with the
whole class what they have been talking about, the
sharing skills in the whole class can be done by
appointing a couple who voluntarily willing to attach
the work of the group or take turns with a partner until
about a quarter of couples have the opportunity to
report.
Cooperative learning model Think Pair
Shareencourages students to be familiar with the
activities of other people share your opinion with the
expected students can gain a lot of knowledge,
because it will be the students will get a lot of
different learning experiences during the learning
process.
According to Lie (2008: 86), there are some
advantages methods Think Pair Share (TPS) which
are increase student participation in learning, suitable
for simple tasks, provide more opportunities for the
contribution of each group member, interaction
between partners is easier, easier and faster to form
the group
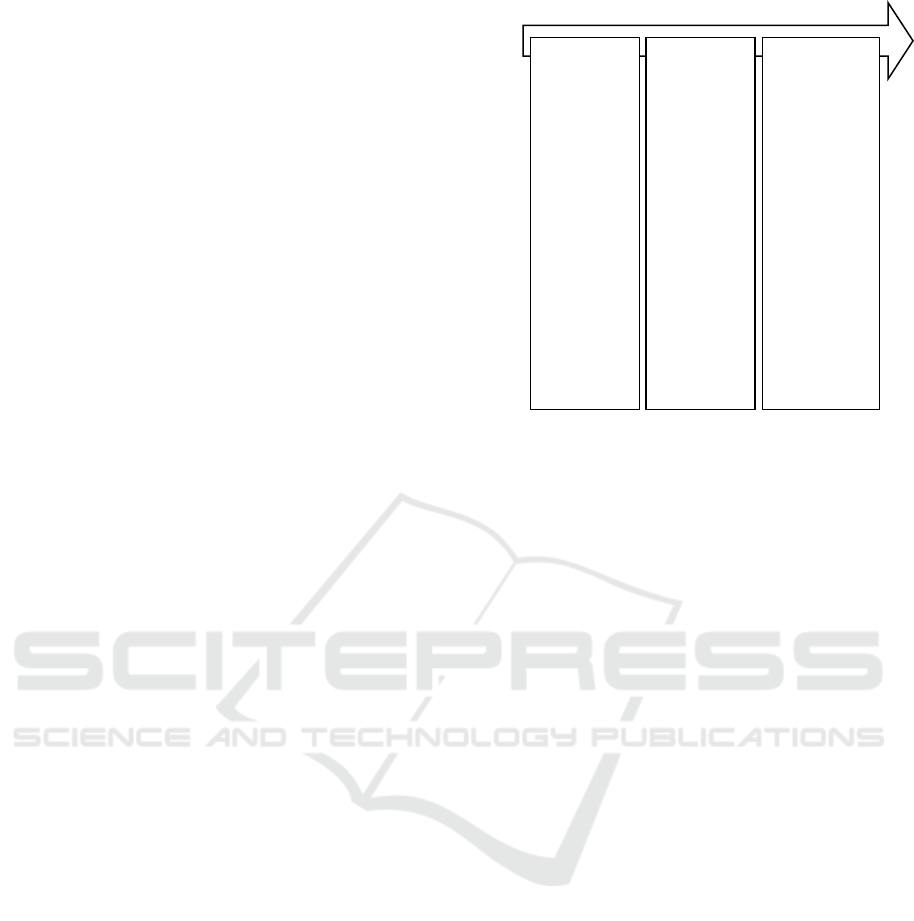
Here are the stages model Think Pair Share
developed researcher:
Figure 1: Schematic of the think pair share learning model
Think Pair Share cooperative mode on digital
learning media storytelling explanation:
1. Thinking; the teacher explained the plan and
purpose of learning and then presents the
problems relating to the subject matter. Then
the students are asked to think about the
issue independently for some time.
2. Pairing; the teacher asks the students pair up
with other students to discuss what he thinks
in the first phase. At this stage, each member
of the group compares their answers or
thoughts by formulating the answer that is
considered the most correct or most
convincing.
3. Sharing; the final stage is done by sharing or
presenting the results of the discussion.
Activity is stopped according to the
accumulated time during the learning and
the teacher's targeted conclusions.
3 METHODS
On this research, researchers using research and
development method by Borg and Gall. The research
and development procedure consists of three steps:
preliminary, development, and evaluation.
The Preliminary step is literature study and
preliminary study. The development step is to design
the product, after the initial product is finished, then
the expert validation consisting of media validation,
language validation, material validation and
validation of practitioners. After validation, then
(1) Think
The teacher
provides the
material in
the form of
digital
storytelling
and
provides
time for
students to
find ideas to
solve
problems.
(2) Pair
Students
pair up with
friends or
randomly,
then discuss
the results
of each
thought.
(3) Share
Students
share with
classmates
by presenting
the results of
their
discussion.
Digital Storytelling and Think-Pair-Share to Improve the Ability of Critical Thinking
187

continued with product trial. The first trial is a group
trial, and then the product is revised again. After the
product has been revised, it will be continued with a
field trial, after completion of field trials, if anything
needs to be revised, the product will be revised again.
The evaluation stage is the final step in this research
and development, at this stage the effectiveness test
media developed, effectiveness test carried out in two
classes, namely experimental class and control class.
Experimental class is a class that gets treatment with
the media of development, while the control class is a
class that is taught with ordinary or without getting
treatment with learning media development results.
This research and development was conducted in
Senior High School in economic subject to know
whether digital learning storytelling media is feasible
and effective to improve the critical thinking ability
of senior high school students.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A statement by Scriven & Paul, presented at the 8th
Annual International Conference on Critical
Thinking and Education Reform, Summer 1987.
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined
process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing,
applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating
information gathered from, or generated by
observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or
communication, as a guide to belief and action. In its
exemplary form, it is based on universal intellectual
values that transcends subject matter divisions:
clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance,
sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and
fairness.
Critical thinking demands a vigorous effort to
examine every assumption or assumptive knowledge
on the basis of its supporting evidence and the
subsequent conclusions it brings. Thinking critically
is that deeply or actively think together to seek truths
or reasons about a knowledge so that it can be trusted.
As stated above that critical thinking is an
important part of one's life aspect, including students.
As an illustration, it is easy to teach students about an
information, for example the definition of human
needs. Teachers are also easier to evaluate, simply by
making a problem around the definition of human
needs. And for students do not even feel the need to
understand the definition of human needs, but simply
memorize the definition given by the teacher. The
question is, is it useful for students outside of school?
What does a student get for a life when the student
has graduated? The answer is of course nothing useful
for the students in his life except for just a few.
Therefore there must be a paradigm shift in teaching
from just giving information to teaching how to find
information and using it for other useful things.
In the preliminary study that researchers have
done in one of the high school, obstacles experienced
in teaching critical thinking skills on economic
subjects is due to the still frequent learning that is still
centered on the teacher (teacher-centered), The
teacher is too lazy to design a learning activity that
gives students the opportunity to actualize
themselves. So that students become not interested to
learn economic lessons that are being taught by
teachers.
Another constraint is on a scoring system, a
classic but difficult to solve. During this time more
assessment toward low-level cognitive abilities. The
students are said to be successful if students pass the
test and get good grades. Until now this problem is
still a polemic and there is no good solution.
To teach critical thinking skills can be done with
various methods. For example by applying a
constructive learning model. The model of learning
done in schools in general has been using the
paradigm of constructivism. The existing learning,
emphasizing the main activities that affect the success
of educational attainment goals. Constructivism
Learning is that in the learning process students learn
together with the group and help each other so that
students can interact actively and positively in the
group. The purpose of group formation is to provide
opportunities for students to be actively involved in
the thinking process. One model of cooperative
learning that allows students to be actively involved
in thinking and learning activities in pairs is Think
Pair Share (TPS).
Cooperative learning type of TPS designed as an
effort to influence the pattern of student interaction in
learning. In the learning process, the teacher asks a
question or problem associated with the lesson, and
asks the student to take a few minutes to think of the
answer or problem. The second step is pairing, then
the teacher asks students to pair and discuss what they
have gained. Furthermore, in the final step the teacher
asks the couples to share with the whole class that the
students have been talking about in the on going
lesson.
According to Laura, quoted by Septriana &
Handoyo (2006: 48) the advantages of the TPS model
is easy to apply to various levels of thinking ability
and in every opportunity so that it can be applied at
every level of education. Another advantage is
optimizing students 'participation in learning,
improving knowledge, improving students' mindset,
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
188

students can review and solve problems from
different points of view, but the purpose of the
answers go in the same direction, in addition to
training teachers in formulating problems that In
accordance with the cognitive level and cause
curiosity of students to be interested to learn and find
a solution (Alma, 2009: 91).
The advantages of the TPS learning model can be
used as a reference for the development. Learning
digital storytelling media based on TPS learning
model is a learning media that can help train students'
attitude and thinking ability.
In previous research conducted by Yang & Wu
(2013), The results of this quasi-experimental study
suggest that after 20 weeks of DST instruction, senior
high school students demonstrated significant
improvement in critical thinking. Interpretation and
evaluation of arguments (as measured By Butthe-
CTT-I) and task value and self-efficacy (as measured
by the MSLQ). Furthermore, qualitative feedback
from interviews with the instructor and students
support the potential of DST as an approach for
fostering collaborative second language learning in
an environment that fosters higher order thinking and
learning motivation.
Research conducted by Yang & Wu can be used
as a reference to develop a digital learning-based
storytelling think pair share this. Attitudes and
students' thinking ability can be developed through
the steps used in the think pair share learning model.
These steps give students more time thinking,
responding, and helping each other, and are supported
with drawings aimed at training students' skills to
solve problems and seek solutions in a row. The
learning is indicated in the attitude and empowerment
ability of thinking and interest and interest of student
so that student learning result can rise significantly.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Critical thinking skills is a competence that must be
trained to the students. In a preliminary study that
researchers have done in Senior High School,
researcher has found that critical thinking skills in
economic subjects is still low because of the frequent
learning that is still centered In teachers (teacher-
centered), the teacher is too lazy to design a learning
activity that gives students the opportunity to
actualize themselves. So that students not become
interested to learn and understand the economic
lessons that are being taught by teachers.
This research produces an idea to develop a
learning media that is integrated with a model of
learning think-pair-share, so that it can help improve
the critical thinking skills of students in economic
subjects in senior high school. The media developed
is a digital storytelling learning media with think-
pair-share model. The results of this development will
be used in the economic learning process as an effort
to improve the ability of critical thinking students in
senior high school.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Special thanks to magister of economic education
universitas sebelas maret surakarta and people who
supported me when working on this paper.
REFERENCES
Arsyad, A., 2013. Media Pembelajaran. Jakarta: PT.
RajaGrafindo Persada.
Baker, M., Rudd, R. 2001. Relationships between critical
and creative thinking. Journal of Southern Agricultural
Education Research, Vol. 51, Number 1, 01,
Ennis, R. H., 2011. The Nature of Critical Thinking: An
Outline of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities.
Prentice Hall: University of Illinois.
Fisher, Alec., 2011. Critical Thinking. Cambridge
University Press.
Filsaime, D. K., 2008. Menguak rahasia berpikir kritis dan
kreatif. Jakarta: Prestasi Pustaka.
Rusman. 2012. Model-Model Pembelajaran. Bandung:
Rajawali Pers.
Sadik, A., 2008. Digital storytelling: a meaningful
technology-integrated approach for engaged student
learning. Educational Technology Research and
Development, Vol 56, No 4.
Sanaky, H., 2013. Media Pembelajaran Interaktif-Inovatif.
Yogyakarta: Kaukaban Dipantara
Sukirman., 2012. Pengembangan Media Pembelajaran.
Yogyakarta: PT. Pustaka Insan Madani.
Aliyah, S., 2011. Kajian Teori Metode Storytelling Dengan
Media Panggung Boneka Untuk Meningkatkan
Kemampuan Menyimak dan Berbicara Anak Usia Dini:
Studi Eksperimen Quasi di TK Negeri Pembina
Kabupaten Majalengka. Tesis Universitas Pendidikan
Indonesia.
Borg, W. R., Gall, M. D., 2003. Educational research: an
introduction (7th ed.). New York: Longman, Inc.
Buchari, Alma. (2009). Manajemen Pemasaran dan
Pemasaran Jasa, Cetakan kedelapan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Handoyo, B., Septriana, N., 2006. Penerapan Think Pair
Share (TPS) Dalam Pembelajaran Kooperatif untuk
Meningkatkan Prestasi Belajar Geografi. Jurnal
Pendidikan Inovatif Volume 2 Nomor 1.
Digital Storytelling and Think-Pair-Share to Improve the Ability of Critical Thinking
189

Ibrahim, M., 2000. Pembelajaran Kooperatif. Surabaya:
University Press.
Alec F., 2009. Berpikir Kritis Sebuah Pengantar. Terj.
Benyamin Hadinata. Jakarta: Erlangga
Yang, Wu., 2011. Digital storytelling for enhancing
student academic achievement, critical thinking adn
learning motivation (a year-long experimental study).
Institute of Education & Centre for Teacher Education,
National Cheng Kung University, No. 1, Ta-Hsueh Rd.,
Tainan 701, Taiwan, ROC
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
190
