
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative
MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review)
Learning Model: An Experimental Study
Ai Nur Solihat and Dede Kurnia
Economics Education Department, Universitas Siliwangi, Tasikmalaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Collaborative, MURDER, Understanding of Concept.
Abstract: The research aims at investigating whether or not there is significant influence on students’ understanding of
concept by implementing Collaborative MURDER in economics subject. The investigation was conducted
through quasi-experimental method to the treatment class and control class. Techniques of collecting the data
were written test, observation, and questionnaire distributed by the teacher to the students. The data were
analyzed by using Wilcoxon's Matched-Pairs Test and Mann-Whitney U-Test calculated by SPSS 23
application pro-gram. The research result reveals that there are significant influences on students'
understanding of concept on both classes taught by implementing collaborative MURDER learning models
and conventional models before and after treatment. Furthermore, there is a different level of students'
understanding of concept on both classes taught by implementing collaborative MURDER learning models
and conventional models after treatment.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the learning process, the ability to understand must
be absolutely owned by the students. Since it is
related to Bloom's Taxonomy, this students' ability is
included in the cognitive process dimension level
two. This means that understanding ability is the
important ability that must be owned by the students,
because if the students do not have it, then the
students will never be able to follow the next learning
process which needs the high level of thinking
abilities such as applicating (C3), analyzing (C4),
evaluating (C5), and creating (C6).
In the reality, students’ ability to understand the
materials and learning concepts is still low. This is
proven by the survey results of PISA (Programme for
International Student Assessment) held by OECD
(Organization for Economic Cooperation and
Development) which shows that in 2015, from 72
countries, Indonesia is in the 64th position. Besides,
based on the median score, students' reading
achievement is increasing from 337 in 21012 to 350
in 2015. Generally, this survey result shows that
students' ability in Indonesia in mastering and
understanding the materials is still low compared with
the other countries in South Asia.
To improve students' understanding, teacher's role
in the learning process is not only as knowledge
conveyor but also to plant and cultivate knowledge
and guide the students to study independently while
the teacher monitors the development. The learning
process that can train students' understanding ability
is the learning process which is student centered.
With this principle, students will try to construct their
knowledge to get the whole understanding as the
result of the learning process.
One of the examples of learning models that refers
to student centered principle is Collaborative
MURDER learning model that is learning model
which emphasizes on the cooperation of several
students in the group to reconstruct their knowledge
and understanding on a concept. In addition,
Collaborative MURDER is also a learning model that
focuses primarily on the ability to understand
students' concept of understanding, it can be seen
from the collaborative learning process MURDER
consisting of several steps.
Specifically, Gokhale (2004) explained,
“Collaborative learning refers to an instruction
method in which various performance levels at work
are responsible for helping one another to be
successful".
50
Solihat, A. and Kurnia, D.
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review) Learning Model: An Experimental Study.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 50-57
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Nevertheless, the result of the previous empirical
study showed that factors and models can influence
the improvement of understanding and show the
different results. Based on the research result by Ali
Saeedi et. al (2013) shows that the learning model that
has the positive influence towards the students'
understanding is mapping concept model, while
research by Rasaya Marimuthu (2013) shows that
understanding is significantly influenced by
Cooperative Learning model. Based on those results,
there is still no consistent variable that can improve
students’ conceptual understanding consistently. This
inconsistency in the previous empirical research
motivates the writer to study the understanding
concept with Collaborative MURDER model.
In the other hand, not all teachers are able to apply
the Collaborative MURDER learning model which is
believed to be able to train students' comprehension
abilities as a whole and comprehensive. This is
evident from the use of conventional teaching model
(lecture) which is still the main choice for teachers in
Indonesia. One of the most visible impacts of the
conventional learning is the low ability of students to
understand the material. This can be seen from the
daily assessment of the 11th Grade of Social Class
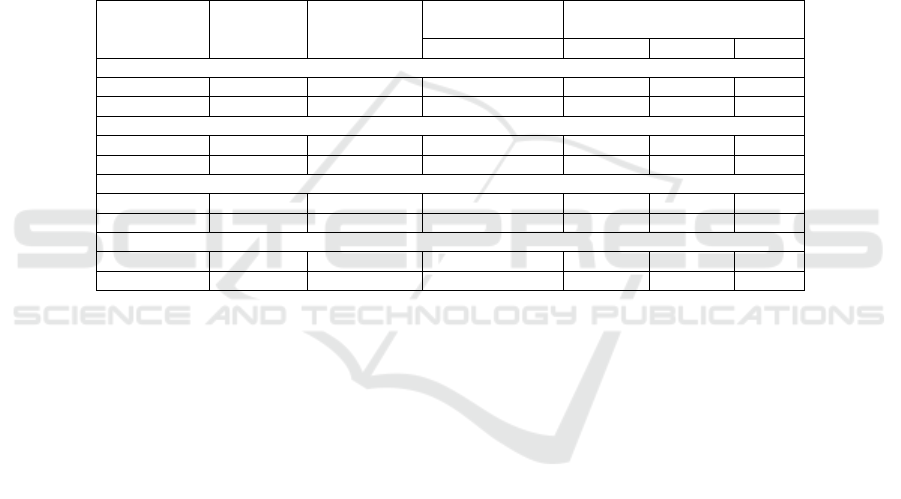
SMA Negeri 1 Tasikmalaya in table 1.
Table 1: Recapitulation of Daily Assessment Score of Economics at the 11th Grade of Social Class Academic Year 2016-
2017
```````````` Test
Minimum
Score
Students’ Score
≥ Minimum Score
Students at the Minimum Score
Students % Studen
t
%
Recapitulation of Daily Assessment XI IPS 1
1 TEST 1 78 11 33,30 22 66,50
2 TEST 2 78 14 42,40 19 57,60
Recapitulation of Daily Assessment XI IPS 2
1 TEST 1 78 12 37,50 20 62,50
2 TEST 2 78 29 90,52 3 9,37
Recapitulation of Daily Assessment XI IPS 3
1 TEST 1 78 10 31,25 22 68,50
2 TEST 2 78 10 31,25 22 68,50
Recapitulation of Daily Assessment XI IPS 4
1 TEST 1 78 8 25,00 24 75,00
2 TEST 2 78 23 71,87 9 28,13
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Basically, the process of learning and knowledge is
always dynamic, there is always change or renew-al.
In this position, students are required to have an
understanding in order to be able to link the previous
learning with new learning.
On the other hand, Anderson and Krathwohl
(2001: 66-88) states that understanding is the ability
to formulate the meaning of the message learning and
ability to communicate it in the form of oral, written,
and graph. Students understand when they are able to
determine the relationship between the newly
acquired knowledge and their past knowledge.
Understand categories consist of cognitive processes
Interpreting, Exemplifying, Classifying,
Summarizing, Inferring, Comparing and Explaining.
One of the learning models that can improve
students' concept of understanding is Collaborative
MURDER learning model. This learning model is a
model of learning adapted from The Complete
Problem Solver written by John R. Hayes. MURDER
is an acronym of the six learning steps. According to
Hayes, John R (1940: 121), that "The Acronym
MURDER stands for the six parts of Dansereau et al's
(1979) study system; Mood, Understand, Recall,
Digest, Expand, and Review. Referring to Hayes's
opinion, the MURDER learning steps are general
steps to focus on improving understanding. The steps
of MURDER is as follows:
1) Mood
Mood means to set the mood in learning.
Dansereau's sees two major problems in regulating
mood in the learning process. First, positive behavior
is in terms of overcoming fear and discomfort in
learning situations. Second, it deals with confusion in
learning.
2) Understand
At this stage, students are encouraged to read
books or sources that have relevance to the material.
Next, mark the material to be presented then ask the
students to mark the piece of material that is not un-
derstood.
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review)
Learning Model: An Experimental Study
51

3) Recall
After the students take the second step, namely the
stage of understanding, then students are required to
repeat the information that has been read.
4) Digest
At this stage, students are required to describe and
conduct a more in-depth study of what has been
understood. The trick is to do the deepening by
reading other sources.
5) Expand
Development here can be by looking for examples
of events related to the material being discussed. In
this process, students will be required to link the
various materials or information that can be
previously.
6) Review
The review process is the step to understand the
material more and to avoid forgetting.
Generally, Collaborative MURDER model is
based on two learning theories. According to Piaget
and Vygotsky in Sumarli, (2015: 42) argue that;
“Actually, Collaborative is a learning model which is
based on two learning theories, cognitive psychology
learning theory, and Social constructivist." Cognitive
psychology learning theory is a theory emphasizing
that learning is seen as an effort to understand
something. While social constructivism learning
theory believes that a knowledge is built and
constructed mutually, by that reason, a teacher must
create many learning opportunities with teacher and
friends in constructing knowledge together. This is
supported by Vygotsky (1978), "Student is capable of
performing at higher intellectual levels when asked to
work in collaborative situations than when asked to
work individually".
3 METHODS
3.1 Research Method
The method used in this research is the quasi
experiment.
3.2 Research Design
The design used in research is Nonequivalent Control
Group Design.
3.3 Research Object
The object of this study is the ability to understand
students' concepts. While the subjects of this research
are a population consists of four classes. The
population is presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Description of Data Population
Class Students
XI IPS 1 33 Students
XI IPS 2 32 Students
XI IPS 3 32 Students
XI IPS 4 32 Students
Two samples are taken based on the above population
by using Simple Random Sampling Technique. This
technique took two of four classes randomly without
paying attention to the degree existed in that
population. From the sample collection, it is decided
that Class 11 IPS 1 and 3 are the samples. Class IPS
1 is as experiment class and IPS 3 is as control class.
3.4 Data Collection Instrument
a. Understanding Test Tools
The test tool used in this research is multiple
questions consist of 45 questions.
b. Observation
Observation used in this research is not a participant.
c. Questionnaire
The questionnaire is only used as data supporting the
results of research and to know the students’
responses towards the learning model Collaborative
MURDER.
3.5 Data Analysis
Data analysis performed in this research include
Normality test with Shapiro Wilk technique,
homogeneity test through Levene Test, and test of
nonparametric statistic hypothesis with Mann-
Whitney U Test and Wilcoxon's Matched Pairs test.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Description of Learning Model
Implementation
In the experimental class that received treatment with
Collaborative MURDER learning model, the first
meeting, students were given pretest, then in the
second to the fourth meeting, the learning was done
by Collaborative MURDER learning model. Then, at
the fifth meeting students were given Post-test. In
general, the learning model of Collaborative
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
52
MURDER consists of six steps that are implemented
in the classroom.
Steps in this learning model are suited with
psychology cognitive learning theory stated that
learning is seen as an effort to understand something.
The adherents of this theory believe that the
knowledge possessed previously determines the
success in learning new knowledge. This cognitive
learning theory is concerned with the realization of
the exchange of concepts among group members on
collaborative learning so that in a group there will be
a process of transforming knowledge to each
member.
Involvement of students in learning will be able to
improve students' ability in improving understanding
of learning materials that are being taught. This is in
accordance with the theory of learning underlying the
Collaborative MURDER model, the theory of social
constructivism learning which assumes that students
will reconstruct their knowledge through social
interaction with others. Bearison and Dorval in
Santrock, (2007: 390) Affirms, "the social context of
learning and that knowledge is constructed and
constructed together (mutual)".
4.2 Student's Response to Collaborative
Learning Model MURDER
In the implementation of learning by using
Collaborative MURDER model, students become
more motivated to be involved directly in the learning
process, because of the learning model Collaborative
MURDER. This is relevant to the various learning
theories that underlie this learning model, so that
through this kind of learning activities can improve
students' understanding because in the learning pro-
cess takes place, students not only listen and record
teacher explanations, but the students are directly
involved in learning activities so that Students'
understanding of a concept may increase.
Improved understanding of concepts formed
through Collaborative Learning MURDER this
happens because students can exchange information
and knowledge with the environment. This is as
revealed by Sudarman (2008: 94) that: "Collaborative
Learning is a process of group learning that each
member contributes information, experiences, ideas,
attitudes, opinions, abilities, and skills to equally
enhance the understanding of all members.”
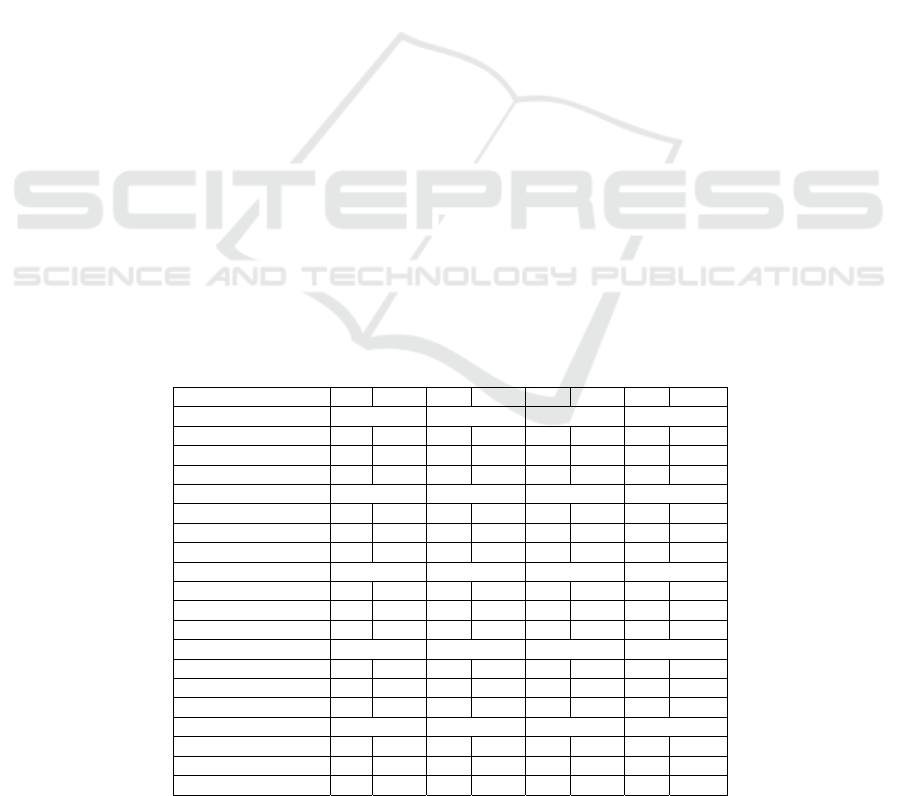
In Table 3 the overall student response to the
Collaborative MUR-DER learning model provides a
positive response. This is apparent from the answers
of the majority of students who gave "Yes" more than
50% for questionnaires with positive statements.
While for statements 1 and 5 are questionnaires with
negative statements, however for both numbers,
students give negative answers that implicitly have a
positive meaning. This can be seen from the
percentage of students who answered "No" answer at
number 1 and 5 reached 50% more.
Table 3: Students’ Response to Collaborative MURDER Learning Model
Students’ Response F % F % F % F %
Numbe
r
123 4
Yes 8 24,2 30 90,9 27 81,8 28 84,8
No 25 75,8 3 9,1 6 18,2 5 15,2
Total 33 100 33 100 33 100 33 100
Numbe
r
567 8
Yes 12 36,4 32 97 31 93,9 28 84,8
No 21 63,6 1 3 2 6,1 5 15,2
Total 33 100 33 100 33 100 33 100
Numbe
r
9101112
Yes 31 93,9 18 54,5 24 72,7 11 33,3
No 2 6,1 15 45,5 9 27,3 22 66,7
Total 33 100 33 100 33 100 33 100
Numbe
r
13 14 15 16
Yes 26 78,8 14 42,4 31 93,9 31 93,9
No 7 21,2 19 57,6 2 6,1 2 6,1
Total 33 100 33 100 33 100 33 100
Numbe
r
17 18 19 20
Yes 25 75,8 30 90,9 31 93,9 25 75,8
No 8 24,2 3 9,1 2 6,1 8 24,2
Total 33 100 33 100 33 100 33 100
Source: Student Response Questionnaire, processed data
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review)
Learning Model: An Experimental Study
53
In addition, for the 12th item, students about
response students on the media used indicate a lower
percentage, ie 33.3% for the "Yes" answer, while the
"No" answer reaches 66.7%, the condition This is not
without reason, because the conditions in the
experimental class of researchers found a fairly heavy
constraints, namely projector, and Screen view
commonly used to damage. On the other hand, the
backup projectors provided by the school are always
used by other teachers.
Through this student response, we can more in
detail see the students' enthusiasm in the use of
Collaborative MURDER learning model, in addition,
the result of this student response, we can see what
things need to be improved in order to increase
understanding of student concept can be more
optimal. Through the good response that students
show to the use of this MURDER Collaborative
model, it implicitly shows that students find it helpful
to understand the theories as well as the economic
concepts. That is, it reinforces the theory of cognitive
psychology and social constructivism theory that
Collaborative MURDER model can improve
students' conceptual understanding.
4.3 Data Processing
4.3.1 Research Results on Pretest and
Posttest in Experiment Class
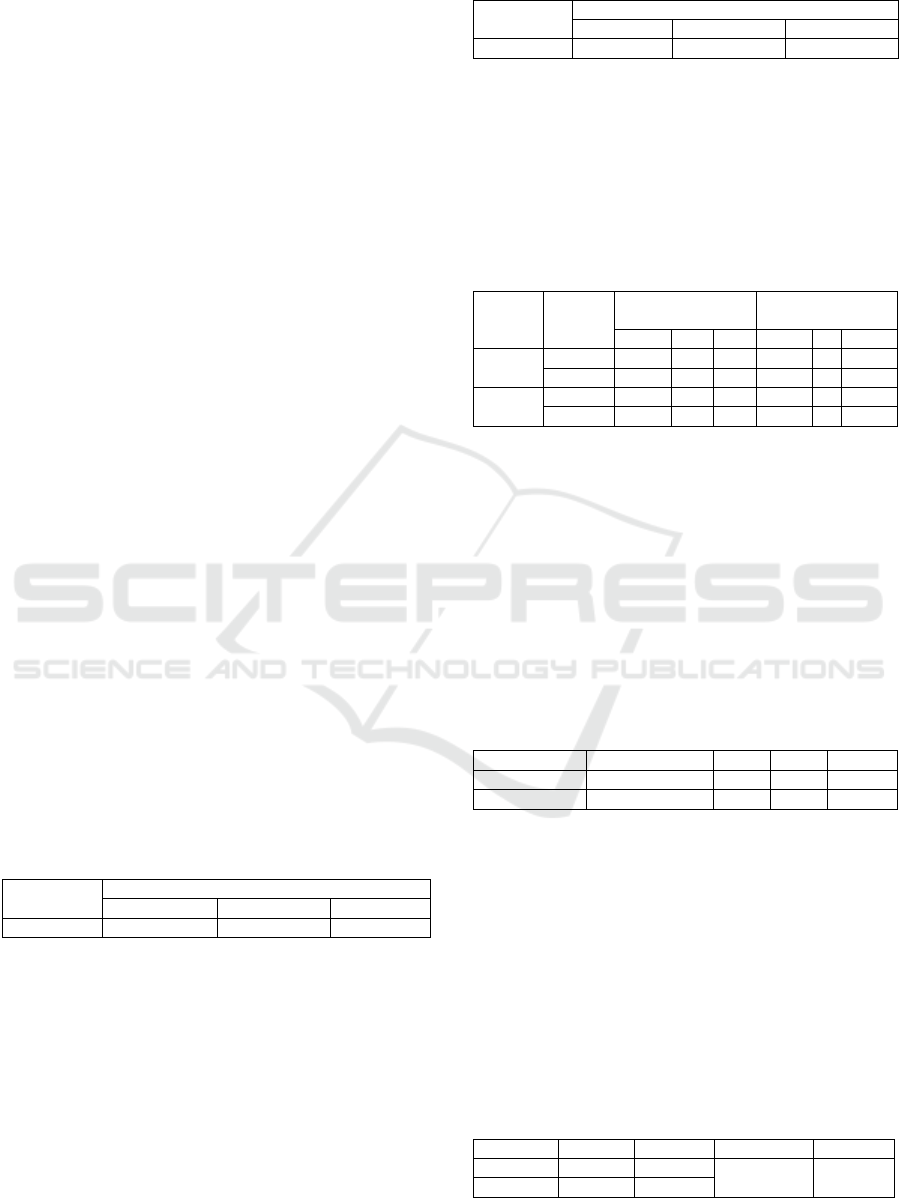
Table 5 shows the pretest and posttest score for the
basic competencies tested in the experimental class
using the MURDER collaborative learning model.
These results show the average acquisition value of
51.91 to 76.94. As for the average increase of pretest
value to the post-test value of 0.509. This means that
the increase in value is moderate.
Table 4: Mean Score of Experiment Class
Students Mean Score
Pretes
t
Posttes
t
N-Gain
33 51,91 76,94 0,509
4.3.2 Research Results on Pretest and
Posttest in Experiment Class
The data in Table 5 shows the average pretest and
post-test values for the basic competencies tested in
the control class using the conventional learning
model showing an increase from 54.89 to 72.41.
However, the magnitude of the increase in the pre-test
and post-test values is only 0.364. That is, the
increase in value is moderate.
Table 5: Mean Score of Control Class
Students Mean Score
Pretes
t
Posttes
t
N-Gain
32 54,89 72,41 0,364
4.4 Data Analysis Result
4.4.1 Normality Test
In this study, the normality test is performed to
determine whether the data pretest and post-test
results are normally distributed or not.
Table 6: Normality Test Pretest and Posttest
Based on normality test results, for pretest and post
test grade of experiment class and control class can be
seen in Table 6. Indicates that all pretest and posttest
scores of both the experimental class and the control
class are normally distributed.
4.4.2 Homogeneity Test
Based on homogeneity test results, for pretest and
post test grade of experimental class and control class
can be seen in Table 7.
Table 7: Homogeneity Test Pretest dan Posttest
4.4.3 Result of Hypothesis Test
a. First Hypothesis
The first hypothesis is that there is a different
under-standing of the concept of the students in the
experimental class group using the Collaborative
MUR-DER learning model on the initial
measurement (Pre-test) and on the final measurement
(Posttest). Data processing is done by SPSS 23
program
Table 8: Summary of the First Hypothesis Test
Test Students Mean Z hitung
P
-Value
Pretest 33 51,91
-5,018 0,000
Posttes
t
33 76,94
Class Test
Kolmogorov
Smirnov
Shapiro Wilk
Statisti
k
df Sig. Statisti
k
df Sig.
Experi-
ment
Pretes
t
0,087 33 0,200 0,979 33 0,749
Posttes
t
0,121 33 0,200 0,954 33 0,177
Kontrol
Pretes
t
0,158 32 0,041 0,963 32 0,338
Posttes
t
0,149 32 0,069 0,959 32 0,250
Class Levene Statistic df1 df2 Sig.
Experiment 4,769 1 64 0,033
Control 4,343 1 62 0,041
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
54
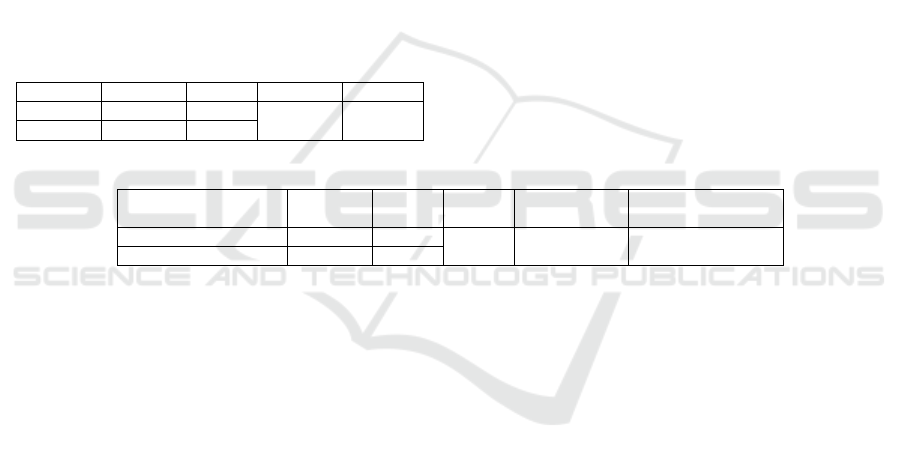
In Table 8, it appears that there is a probability
that the average value of pretest to the Posttest value
is 51.91 to 76.94. These improvements indicate that
the use of the Collaborative MURDER learning
model can improve students' conceptual
understanding. The above data also shows that Z
arithmetic reaches -5.018 with P-value smaller than
0.05, it means that the first hypothesis is acceptable
that there is the different understanding of the concept
of students in the experimental class group using the
learning mod-el Collaborative MURDER on initial
measurement (Pre-test) and on final measurement
(Posttest).
b. Second Hypothesis
The second hypothesis is that there is a difference
in the students' understanding of the control class
using the Conventional learning model on the initial
measurement (Pretest) and on the final measurement
(Posttest).
Table 9: Summary of Second Hypothesis Test Result
In Table 9, it appears that there is an increase in
the average value of pretest to the Posttest value of
54.89 to 72.41. These improvements indicate that in
the control class there is also an increase in
understanding of students' concept of understanding,
although the increase is relatively small. In addition,
the data above shows that Z arithmetic reaches -4.944
with a P-value smaller than 0.05, meaning that the
second hypothesis is acceptable that there is a
difference in students' understanding of the control
class using the Conventional learning model on initial
measurement (Pretest) and on final measurement
(Posttest).
c. Third Hypothesis
The third hypothesis is that there is a difference in
the comprehension of the concept of the students of
the experimental class using the Collaborative
MURDER learning model with the control class
students using the convention-al-learning model.
Table 10: Summary of Third Hypothesis Test Result
Students
Mean
Ran
k
Z
hitung
Eta Squared P-Value (2-Tailed)
N-Gain Experimen
t
33 40,15
-3,101 0,14794 0,002
N-Gain Control 32 25,63
Table 10 shows that it appears that the value of t is -
3.101 with the significance test value (2-tailed) 0.002.
That is, H0 is rejected, the test results significantly.
Thus, there is a difference in the increased
understanding of concepts in experimental class
students using the Collaborative MURDER learning
model with control class students using the
conventional learning model. On the other hand, this
means that in enhancing the conceptual
understanding of economic subjects, the
Collaborative MUR-DER learning model tends to be
more effective than conventional models.
4.5 Discussion
4.5.1 Differences Understanding Student
Concept Experiment Class on Pretest
and Posttest Measurements
From the result of the research, there are differences
of understanding of student concept which in the
learning process using the Collaborative MURDER
learning model before and after treatment. In Table 4
shows an increase in the average increase that the pre
test and Posttest values are from 51.91 to 76.94.
Hypothesis test results stated that Ha ¬ accepted,
meaning there is a different understanding of the
concept of students in experimental class groups that
use Collaborative MURDER learning model on the
initial measurement (Pretest) and on the final
measurement (Posttest).
In practice, before the treatments are done by the
researcher, the teacher teaches in a conventional way.
The most visible condition of the conventional
learning model is the students easily feel bored in
listening to the lessons conveyed by the teacher. To
reduce the saturation, the Collaborative MURDER
learning model is believed to anticipate such a
situation. It was proven to be a questionnaire of
students' responses to the 11th item, out of 33 students
in the experimental class, 72.7% gave the answer
"Yes". This means that the Collaborative MURDER
learning model is considered not saturated by the
majority of students in the experimental class.
Test Students Mean Z hitung
P
-Value
Pretest 32 54,89
-4,944 0,000
Posttes
t
32 72,41
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review)
Learning Model: An Experimental Study
55

In the application of conventional models,
teachers are generally more often present the concepts
in the text of the book. This condition resulted in
students lacking a deep understanding of the concept
of the material discussed. In addition, the
conventional learning model is less stimulate students
to look for facts related to the material, because in
conventional models, students are only positioned as
the recipient of information and not actively involved
in reconstructing their understanding.
The effects of using conventional models and the
lack of innovation by teachers to improve students'
conceptual understanding are evident when students
are given in-depth and detailed test questions when
pretest. The average result of the pretest value shows
a low value.
Based on the questionnaire of students 'responses
to the Collaborative MURDER learning model, the
students showed positive responses on the 3rd, 4th,
and 7th items. This was evident from the percentage
of students answered "Yes" exceeding 80%, the
students' answers to these three items proved that the
Collaborative MURDER Is a model of learning that
makes students understand more about the material
being studied. In addition, this model makes students
more active in exploring students' abilities.
The active participation of students in exploring
their own capabilities has become the basis for more
searching for information relevant to the material
discussed in the classroom. This means that with the
Collaborative MURDER learning model, students are
not only positioned as recipients of information, but
students become part of the information resources in
the learning process in the classroom. Such
conditions are believed to have implications for
improving students' understanding of the concept of
economics.
To create a comfortable learning condition, in the
Collaborative MURDER learning model, the teacher
must have the ability to improve students' learning
motivation. Based on the questionnaire of student
responses on such matters, on items 8 and 17, students
answer "Yes" more than 70% of 33 students. That
means the majority of students expect motivation and
appreciation as a secondary factor in improving
conceptual understanding. In addition, proper use of
diction and loud voice also influences achievement in
the learning process.
Finally, if analyzed from the pretest and post test
results, the steps implemented in the Collaborative
MURDER learning model based on these three
educational theories succeeded in increasing the
students' understanding of the concept significantly,
with the average normalized Gain reaching 0.509
which means moderate category.
4.5.2 Differences in Understanding
Student Concept of Control Class at
Initial Measurement (Pretest) and Final
Measurement (Posttest)
Based on the results of the study there are differences
understanding of student concepts in the learning
process using Collaborative MURDER learning
model before and after treatment. Table 5 shows an
increase in the average increase that the pretest and
post-test values are from 54.89 to 72.41.
The conventional model here means the lecture
method accompanied by explanations of the division
of tasks and exercises. After the conventional model
has been implemented several meetings, the last
meeting was held by Posttest to increase the under-
standing of students' concept in understanding the
economic concept. The average value of Posttest
achieved is 72.41 that means the average value of N-
Gain is 0.364.
4.5.3 Comparison of Improved
Understanding of Stu-dent Concept in
Experiment Class Using Collaborative
Model MURDER and Student Control
Class Using Conventional Model
Based on the result of research, we get the average
gain in the experimental group using the
Collaborative MURDER model of 0,509. The
average gain in this experimental class is higher than
the average gain class gain that only reaches 0.364.
This indicates that the Collaborative MURDER
learning model tends to be more effective than the
conventional learning model in improving students'
economic concepts.
The Collaborative MURDER learning model is
more effective in enhancing the understanding of
concepts because the learning model focuses more on
the active participation of students in the learning
process. Student participation means the participation
of students in an activity which is indicated by their
physical and psychological behavior. For example;
involving student’s optimal learning will occur when
students participate responsibly in the learning
process. Participation is necessary for the learning
process because in principle learning is doing to
change behavior.
This active participation can be seen from
students' physical and psychological activity such as
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
56

visual activities, Oral activities, Listening activities,
Writing activities, mental activities, and Emotional
activities. Such an activity, based on the assumption
that understanding can be obtained by students
through their own safeguards and experiences.
Through the stages in the Collaborative MUR-
DER learning model, students become more likely to
seek information related to the subject matter. In
addition, the stages in Collaborative MURDER
learning are also considered to be more interesting
and not saturating so that students are faster and able
to understand more about the concepts taught.
The effect size of the use of Collaborative
MURDER model shows a very significant result to
the improvement of students' conceptual under-
standing that is 0.147. This means that the variability
of the understanding of the concept of understanding
in economics subjects of 14.7% is significantly
influenced by the treatment with the Collaborative
MURDER learning model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In general, from the results of the study can be
concluded that the application of collaborative
learning model MURDER is a method of learning
that can be used in improving the students’
conceptual understanding, by comparing experiment
and control class, the higher improvement of
students’ conceptual understanding is shown by the
experiment class that used Collaborative MURDER
model in learning.
REFERENCES
Anderson, Lorin W. and David R. Krathwohl (Editor).
2001. Pembelajaran, Pengajaran, dan Asesmen.
Terjemahan Agung Prihantoro. Yogyakarta. Pustaka
Pelajar.
Saeedi, A., et, al., 2013. Comparing Effectiveness of
Methods of Presentation and Providing Concept Maps
on Reading Comprehension. European Journal of
Experimental Biology. No. 3 Vol. 2.
Barkley, Elizabeth E, et.al. 2016. Collaborative Learning
Techniques. Terjemahan Narulita Yusron. Bandung.
Nusa Media.
Duffin, J., et, al., 2000. A Search for Under-standing.
Journal of Mathematical Behaviour. 18(4): 415-427.
Fraenkel, Jack R. 2012. How to Design and Evaluate
Research in Education. The United States of America.
McGraw-Hill.
Hayes, John R., 1940. The Complete Problem Solver. The
United States of America. The Franklin Institute Press.
Marimuthu, R., et al., 2013. Engaging University Student In
Online Hypertext Reading Comprehension Through
The Cooperative Learning Approach. 2nd International
Conference on Learning and Teaching (CoLT).
Razali, Mohd N., et al., 2011. Power Comparisons of
Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Liliefors and
Anderson-Darling Tests. Journal of Statistical
Modeling and Analytics. No. 1. Vol. 2.
Robert, Tim S., 2004. Online Collaborative Learning:
Theory and Practice. London. Idea Group Inc.
Santrock, John W., 2008. Psikologi Pendidikan.
Terjemahan Tri Wibowo B.S. Jakarta. Kencana Prenada
Media Grup.
Srinivas, Hari., 2012. What is Collaborative Learning?.
[Online] Tersedia: http://www.gdrc.org/kmgmt/c-
learn/what-is-cl.html [21 Desember 2016]
Sumarli, 2008. Model Pembelajaran Kolaboratif dengan
Tutor Sebaya pada pokok Bahasan Rangkaian Seri-
Paralel Hambatan Listrik. Jurnal Riset dan Kajian
Pendidikan Fisi-kaPendidikan Inovatif. No. 2 Vol. 1.
Universi-tas Ahmad Dahlan.
Vygotsky, L. 1978. Mind In Society: The Development of
Higher Psychological Processes. Cambridge: Harvard
University Press.
Gokhale, A., 2004. Collaborative Learning Enhances
Critical Thinking. [Online] Tersedia:
http://scholar.lib.vt.edu./journals/JTE/ [5 Agustus
2017)
Improving Students Understanding of Concept through Collaborative MURDER (Mood, Understand, Recall, Digest, Expand, and Review)
Learning Model: An Experimental Study
57
