
Financial Literacy Analysis on Students of Economic Faculty
Feri Febriandi, Agung Haryono, and Ro’ufah Inayati
Economic Faculty, State University of Malang, Indonesia
Keywords: Financial literacy, branchless banking.
Abstract: This study aims to describe the users of Branchless Banking financial literacy and students’ consideration
factors in financial management. This research used qualitative method and case study approach. The
sampling technique used was snowball sampling. Data were obtained by in-depth interview technique and
observation, while sources triangulation was used to check the validity of data. The results show that, Faculty
of Economics students who use branchless banking service are categorized to have good financial literacy.
Students with good financial literacy have high rationality in consumption strategies, efficiency, resource
optimization, and risk management consideration in making decision. On the other hand, there are a small
number of students who have low financial literacy, their actions are still inclined to spend money only for
satisfaction in consuming. Implication are presented to department and faculty of Economics to improve
practicing for the students through non-academic activity that can create equity of student financial literacy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid development of technology affect has an
impact on the increase of technology based economic
activity. For instance, banks have used technology
based services since the introduction of branchless
banking. The advanced development of economics
and finance information technology needs to be in
line with the rate of decision making. One of the
abilities that must be possessed to make decision
quickly and properly is financial intelligence.
Financial intelligence a competence that can be built
from financial literacy, it is an ability to manage
assets which always consider the benefits, costs, and
outcome of any decision made (Bosshardt and
Walstad, 2014: 68). Financial problems are not only
caused by the lack of income, but can also occur due
to the lack of proper management and financial
planning. Financial literacy is very important in
supporting the realization of individual goals in
decision making. This study aims to describe the
users of Branchless Banking financial literacy and
students’ consideration factors in financial
management on Students of Economic Development
Department.
The result of Otoritas Jasa Keuangan (OJK)
survey shows that the index of public financial
literacy reached 21.84% in 2013 to 29.66% in 2016
(OJK: 2016). As knowledgeable people, students are
expected to have better awareness and understanding
of financial management than common people.
However, Rishang (2014) stated that high consumer
attitudes among students and other young people
recently cause financial management becomes a
difficult task. Apart from these attitudes, many young
people do not yet have financial management
knowledge.
To improve financial literacy and public access to
banks, the government propose Strategi Nasional
Inklusi Keuangan (SNIK) programs. One of the
programs is through branchless banking, is a limited
payment and financial service which is done not
through offices, but by means of technology.
The benefits of the increase of financial inclusion
according to Bank Indonesia are: (1) Improve
economic efficiency. (2) Support the stability of the
financial system. (3) Reduce shadow banking or
irresponsible finance. (4) Support financial markets
deepening. (5) Provide new market potential for
banking. (6) Supports the improvements of
Indonesian Human Development Index (HDI). (7)
Positively contribute to local and national economic
development sustainably.
OJK expects that Branchless Banking can
improve the understanding of less literate people on
financial institution, utilization and condition, and
financial management. By providing easy,
convenient, and more efficient access, it will
encourage the utilization of financial institution
services for well literate people.
40
Febriandi, F., Haryono, A. and Inayati, R.
Financial Literacy Analysis on Students of Economic Faculty.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship (ICEEE 2017), pages 40-45
ISBN: 978-989-758-308-7
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Lusardi and Mitchell (2006) suggest that men
have a higher level of financial literacy than women.
While Erner, Menke and Oberste (2016) the basic
financial literacy is influenced by gender, age, IQ and
mathematical skills. As for the more complex
financial literacy influenced by gender, age,
occupation, IQ and foreign language skills.
2 METHODS
This research used qualitative method and case study
approach. This research was conducted in di Faculty
of Economy, Universitas Negeri Malang, and the
subject were the Branchless Banking users who are
majoring in Development Economics. Samples were
taken by Snowball technique on 15 students. Data
were obtained by using Indepth interviews and
observation. Interviews were conducted intensely in
order to explore all information related to the rational
use and the type of service used, while observation
was conducted to view related documents to the use
of branchless banking services.
The data analysis technique used in this research
was qualitative data analysis, following the concepts
by Miles, Huberman and Spradley. Miles and
Huberman in Sugiyono (2014) suggests that the ac-
tivities in qualitative data analysis are done
interactively and continuously in every stages of
research until it is complete. The validity of the data
in this study were checked by using observation and
triangulation.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Students Financial Literacy
3.1.1 Well Literate Student of Branchless
Banking User Service
Well Literate students are able to combine the
management and the use of their resource for
consumption needs and increase their revenue
through the production process. In utilizing their
money for goods or services, students at this level
tend to acquire some information before. This shows
how the students tend to make analytical spending or
consumption decisions or policies effectively and
efficiently based on some considerations. Students in
this state have already had deep knowledge of
financial institutions, as well as reliance to the
institution, especially in banking. Students also
optimize the use of banking services, by considering
the benefits and risks of using the services. Below is
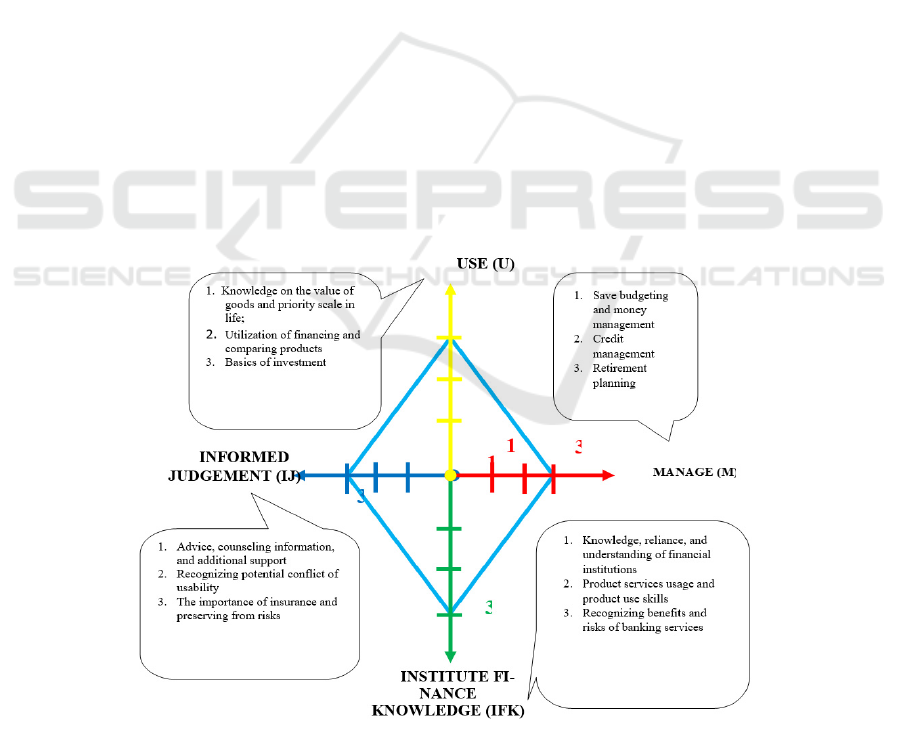
a diagram of the Well Literate level:
Figure 1: Graph of Students of Branchless Banking Service User with Well Financial Literacy
Financial Literacy Analysis on Students of Economic Faculty
41
The figure 1 shows that the ideal conditions of student
financial literacy are on the light blue line, this
indicates that the student has a balanced level of
economic literacy and management, planning, and
optimal and smart decision making. Students of
Branchless Banking users with financial literacy on
M =3; IFK = 3; IJ = 3; and U = 3, have the best
financial use and management from their experience,
along with good knowledge and use of banking
products. (M = 3) in this state of their perception have
been on good financial management, from savings
lifestyle and the desire to prosper their life through
seeking other sources of finances such as producing.
(IFK = 3) in this state, informants already have a deep
knowledge on financial institutions, as well as
reliance to the institution, especially banking.
Informants also optimize the use of banking services,
for instance the benefits and risks of service use.
Informants also understand and have the purpose in
using the service. (IJ = 3) Stu-dents have been able to
overcome the conflicts and financial problems by
making the right decisions. (U = 3) those students
have a good consideration in man-aging their
finances, knowing their needs in depth and having the
fundamentals of investment for financial welfare that
will come. Well Literate students, have had the
awareness and ability to manage and the use of their
funds, so they are safe from the financial risks and
financial management failures
3.1.2 Sufficient Literate Student of
Branchless Banking User
Sufficient literate students combine the management
and use of their funds for consumption needs, their
financial management tends to be able to meet the
needs without increasing their income. Benefits that
can be taken by those informants from spending and
comparing products are the satisfaction in fulfilling
their needs.
Students of this level do not yet have an
understanding of the fundamentals of investment for
their future especially in raising the income in their
finances. Students in this level are quite good at
understanding the financial institution, the use of in-
depth financial services and a deep understanding of
the benefits and risks of using the services. The
following graph illustrates the level of literacy of the
Sufficient Literate category.
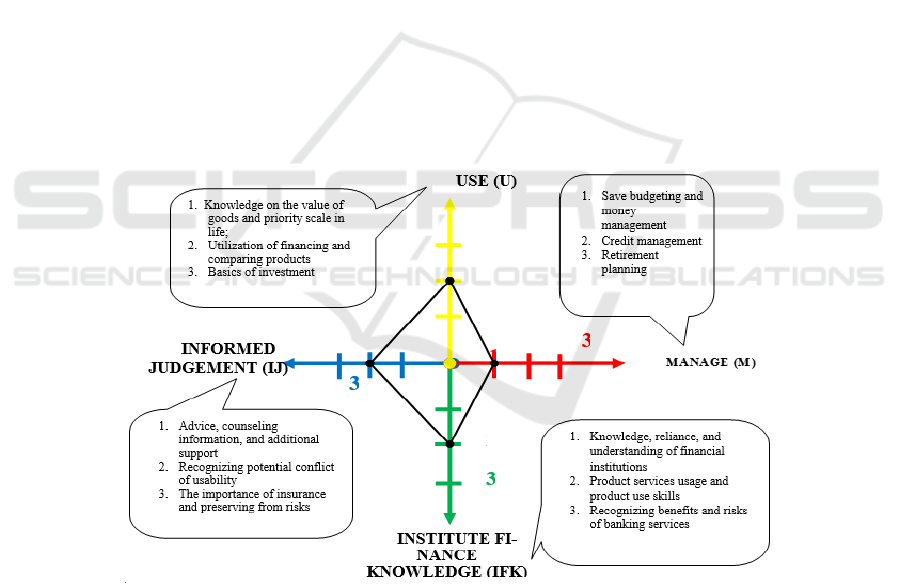
Figure 2: A Graph on Students’ Financial Literacy on the Use of Branchless Banking Service in Sufficient Literate Category
The figure 2 presents the ideal condition of students’
financial literacy is on the blue line. It indicates that
students have the level of economic literacy which is
offset by management, planning, optimum decision
making. Students who use Branchless Banking
service with financial literacy under the condition
M=1; IFK=2; IJ=2 and U=2, have good enough
ability in using and managing their finance. (M=1)
students under this condition be-long to average in
managing their finance starting from their saving
habit and budgeting their finance. The informants’
paradigm tends to desire to have what is wanted,
without any thought to get other sources of revenue.
(IFK=2) students in this condition are good enough in
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
42
understanding financial institution, less indepth in the
use of financial service as well as enough
understanding in knowing the benefits and risks of the
service use. (IJ=2) in this category, students could
overcome the financial conflict although sometimes
they need their parents’ help. (U=2) this category
shows that the use of funds by the informants have
been wise, they are more precise and selective during
the consideration process. Students in Sufficient
Literate type have already had the ability in managing
and spending funds, yet they do not have enough
skills in managing their money thus they are prone to
risks and failure resulting from the management.
3.1.3 Less Literate Student of Branchless
Banking User
Students in Less Literate category combine the
management and the usage of their funds as
consumption needs, to fulfil their needs, they have
never made a clear planning but a budgeting merely
for the primary needs. In saving and consuming, they
do not have special allocation. The desire to meet
their satisfaction beats rationality in self-control for
economic activity.
Students in this type do not have fine knowledge
on the value of things and priority scale in their life as
students. The priority scale as students that must put
life and education first are often interrupted due to the
desire to meet their private needs.
There is no willingness in maximizing the income
that they have as students since they only need to
fulfil their consumption needs. Parents who let their
children manage their own money make these
students excessive in spending their money. All
financial problems will be handed over the parents.
Students in this category tend to use banking
service only to withdraw money and check the
balance thus they do not use the service optimally.
They do not have sufficient knowledge on the
benefits and risks of banking service thus created an
impression that they use the service merely to
withdraw money since they are far from their parents.
The following graph presents the literacy of the Less
Literate category
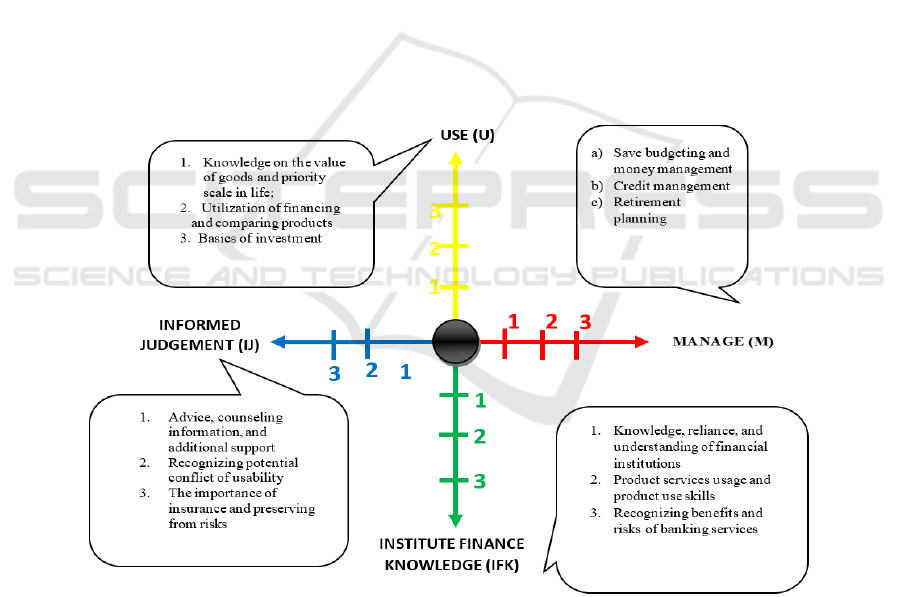
Figure 3: A Graph on Students’ Financial Literacy on the Use of Branchless Banking Service in Less Literate Category
The figure 3 above depicts that users of Branchless
Banking service with financial literacy on M=0;
IFK=0; IJ=0; and U=0 have the lowest financial
ability skill compared to the others. (M=0) those type
of students commonly have no skill and experience in
managing their finance due to less control from the
parents and allow them to be in charge of their
finance. (IFK=0) this type of students tend to use
banking service merely to withdraw money and check
the balance therefore they do not use the service
optimally. They do not have sufficient knowledge on
the benefits and risks of banking service thus created
an impression that they use the service only to
withdraw money since they live far from their
Financial Literacy Analysis on Students of Economic Faculty
43

parents. (IJ=0) students on this type are more
emotional in using their money. They are ignorant on
others’ opinions and tend to hand over the financial
problems to their parents. They manage the money for
something that they want without having further
consideration. (U=0) These students have already had
thoughts on how to spend their funds, yet they lack of
control and are more emotional in meeting their in-
ward fulfilment.
3.2 Students Consideration in Managing
Funds
3.2.1 Well Literate Students
Students in this category have more consideration on
arranging and managing funds to meet their needs as
well as obtain more income. They do not use the
funds for consumption satisfaction. They are likely to
dig deeper information on the quality, price and use
of the products. In fact, some students have thoughts
on how the goods could provide additional income. It
illustrates that students have effective and efficient
analytical decision in expenditure. In handling the
risks, they often look for preventive and effective
actions to solve them. They have thought and
considered the short term and long term possibilities.
These results are in line with Need Achievement
theory (McClelland: 2010) and studies Satrio Y.D
(2012).
3.2.2 Sufficient Literate Students
Students under this criteria spend their money to
fulfill their consumptive desire. The consideration on
how to spend the money for goods or services is
frequently changing depends on their eagerness.
Their analytical thoughts are more on the price and
quality of certain products. Generally, students on this
type rely their funds only to their parents. The failure
in managing their money is tolerable and can be a
lesson for them.
3.2.3 Less Literate Students
These students heavily depend on their parents to
meet their needs. They are more emotional in
spending their money. After receiving money from
their parents, they think about how they could spend
all the money to earn what they want. They do not
have good analytical thoughts in spending the money
com-pared to other types. Failure in managing the
funds is not a problem to them. When they face such
problems, they will ask their parents for help. These
results are in line with previous studies, suggesting
that democratic characteristic and parent’s
socioeconomic are systematically related to literacy
levels (Erner C. et. All: 2016).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The majority of Economics students who use the
Branchless Banking service have fine financial
literacy. The high financial literacy covers the
budgeting, saving and managing money, the bases of
investment and knowledge about the value of good
and priority scale of their lives. In addition, it also
covers the potential of conflicts and benefits, under-
standing and belief in banking service and its benefits
and risks and finding additional information and
support.
Students with high financial literacy are not only
prioritize their desire but also eager to have additional
income. They are likely to look for further
information on the quality, price and use of the
products. They tend to have effective and efficient
analytical thoughts. Students with average level of
financial literacy often use the money to fulfill their
wish. The consideration on how to spend the money
for goods or services is frequently changing depends
on their eagerness. Students with low financial
literacy tend to spend the money without taking into
account the economic consequences. They do not
have good analytical thoughts in spending the money
and failure in managing the funds is not a problem to
them.
A few students have low financial literacy.
Therefore, the faculty and department of economy
have to develop either academic or non-academic
activity to involve students thereby encouraging
students’ level of financial literacy.
REFERENCES
Bosshardt W, and Walstad W. B. 2014, National Standards
for Financial Lit-eracy: Rational and Content. The
Journal of Economics Education, 45 (1), 63-70.
Bank Indonesia, Keuangan Inklusif di Indonesia. Diakses
dari http:// www. bi.go.id/ /perbankan/ keuanganin-
klusif/Indonesia/Contents/Default.aspx
Erner C. Goedde-Menke M, and Oberste M. 2016.
Financial Literacy of High School Student: Evidence
from Germany. The Journal of Economic Education
2016, Vol 47 no. 2, 95 – 105
Lusardi, A and Mitchell, O. S. 2006. Financial Literacy
and Planning: Implications for Retirement Wellbeing.
Google.com- Financial Literacy.
ICEEE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Economic Education and Entrepreneurship
44

McClelland, D.C. (Inggris) The Achieving Society, New
York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1961, hal. 63-73 (online,
diakses pada wikipedia.com tanggal 2 Juni 2012)
OJK. 2013. Strategi Nasional Literasi Keuangan
Indonesia. Jakarta: Direktorat Informasi dan Edukasi.
OJK, 2016. Hasil Survey Nasional Indek Literasi keuangan
Masyakat, diakses dari http://www.rappler.com/
indone-sia/ekonomi/159498-ojk-literasi-keuangan-
indonesia-2016.
Rishang. 2014. Analisis Literasi Keu-angan Mahasiswa
Jurusan EKP Prodi Pendidikan Ekonomi Angkatan
2010 Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Malang.
Skripsi tidak diterbitkan. Malang: FE.
Satrio, Y .D. 2012. Analisis Tingkat Fi-nancial Literacy
Mahasiswa Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri
Malang. Tesis tidak diterbitkan. Malang: FE.
Sugiyono. 2014. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif
dan R and D, Bandung: Alfabeta
Financial Literacy Analysis on Students of Economic Faculty
45
