
Satisfaction with E-Government Portals: Perspective of Senior
Citizens
Ching Seng Yap
1
, Rizal Ahmad
2
, Cordelia Mason
3
and Farhana Tahmida Newaz
2
1
Faculty of Business, Curtin University, Malaysia, Miri, Malaysia
2
Graduate School of Business, Universiti Tun Abdul Razak, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
3
Independent Researcher, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Keywords: E-Government Portals, E-Government Services, Perceived Value, Social Influence, Senior Citizen
Satisfaction, Continuous Use Intentions, Malaysia.
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the level of user satisfaction with the services provided by e-government
portals and to examine the effect of perceived value and social influence on senior citizens’ satisfaction and
their continuous use intentions. Through a questionnaire survey, primary data are collected from 123 senior
citizens who use e-government portals. The findings show that senior citizens are moderately satisfied with
the services provided by e-government portals and positive on their continuous use intentions. E-
government portals in the area of health and tourism are used more heavily than others. Both perceived
value and social influence relate positively with senior citizens’ satisfaction, but perceived value has a
relatively stronger effect on satisfaction than social influence. Senior citizens’ satisfaction also positively
affects their continuous use intentions of e-government portals. The findings enhance the understanding of
e-government portals that senior citizens consider valuable and additionally, highlight the role of social
influence in affecting their satisfaction and subsequently their continuous use intentions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electronic government (e-government) initiative was
first introduced in Malaysia in 2004 and it is
enjoying a high rate of adoption. Information and
communication technology (ICT) has become
increasingly ubiquitous; and in view of that the
research chooses to focus on expanding its breadth
and depth by capitalising on the latest Web 2.0
applications and mobile technology. With Web 2.0
applications, users can perform real-time
interactions with other users within their online
communities. Active user behaviours such as the
searching for information, evaluating alternatives,
making online decisions, and sharing of experience,
are influenced by how they perceive the value they
gained from using those applications and others who
they regard as important people. In the context of e-
commerce, the role of perceived value and social
influence in shaping consumer behaviour has been
widely researched in the e-commerce context but
similar studies on e-government services are
relatively scarce. Moreover, existing literature on e-
government in Malaysia is mostly about the
assessment of e-government portals and factors
affecting adoption or use intentions. A research on
the how users perceive the benefits from using e-
government portals and are affected by social
influence may shed light on how e-government
portals can be further enhanced. This study aims to
investigate the level of satisfaction with services
provided by e-government portals and to examine
the effect of perceived value and social influence on
satisfaction and continuous use intentions. Senior
citizen, as a sample, is selected for two reasons.
Firstly, Malaysia is moving toward having ageing
population where senior citizens constituted 9.2% of
the total population in 2015, and the figure is
expected to reach 15% in year 2035. In 2050, 9.6
million of population (23.6%) is expected to be
senior citizens (United Nations, 2015). These
statistics have important implications for the
government and other stakeholders in developing
sustainable policies, which would address the needs
of senior citizens in the country particularly in terms
of their participations in economic, social,
healthcare, and environmental activities.
Yap C., Ahmad R., Mason C. and Newaz F.
Satisfaction with E-Government Portals: Perspective of Senior Citizens.
DOI: 10.5220/0006498000410049
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (KMIS 2017), pages 41-49
ISBN: 978-989-758-273-8
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Providing government services to senior citizens
through e-government portals is one of the many
important initiatives the government could take to
encourage senior citizens’ participation within the
constraint of the limited resources. Therefore, it is
considered timely to investigate the level of senior
citizens’ satisfaction with e-government portals as
well as to examine the determinants and
consequences of their satisfaction. In this study, data
are collected from 123 senior citizens and analysed
using Partial Least Squares Path Modelling (PLS-
PM) technique.
The paper is structured as follows. The next
section reviews the literature of citizen satisfaction
with e-government services, and develops research
hypotheses. Research methods about data collection,
sampling procedures, and operationalisation of
variables are then presented and that is followed by a
report on research findings. The last section
concludes the study by discussing research
implications, limitations and recommendations for
future research.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Satisfaction with E-Government
Services
Prior research conducted on senior citizens’ use of
computers, Internet and online services were mainly
focused on their adoption intentions, for instance,
technology usage (Mitzner et al., 2010), health-
related Internet and ICT (Heart and Kalderon, 2013;
Wong et al., 2014), mobile phone (Conci, 2009), e-
banking (Amma, 2013), and e-commerce (Law et
al., 2016). Apart from Phang et al. (2006) who
examined the e-withdrawal intention among senior
citizens in Singapore, published literature on senior
citizens’ satisfaction with e-government services
was limited. Consistent with prior technology
acceptance research, they found that perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use were
significant determinants of e-withdrawal intention.
Besides, they also found that perceived Internet
safety had an influence on acceptance of this online
service.
The scholarly literature about e-government
research in Malaysia is scarce. The existing
literature examined the adoption intentions of e-
government among citizens (Hussein et al., 2011;
Mohd Suki and Ramayah, 2010; Ooh et al., 2009),
challenges businesses face in implementation of e-
government (Kaliannan and Awang, 2010; Aman
and Kassimin, 2011), the adoption of electronic
procurement systems among service providers to the
government (Sambasivan, Wemyss, and Che Rose,
2010), and the intention to use multipurpose
smartcard among citizens (Loo, Yeow, and Chong,
2009). Despite the fact that many prior studies had
investigated factors affecting citizens’ acceptance or
adoption of e-government, few studies had clearly
shown the relationships between different factors
that influence citizen satisfaction with services
offered by e-government portals. The only study
focusing on user satisfaction with e-government
systems was conducted by Mohamed et al. (2009)
but the sample was limited to the employees of
government departments instead of individual
citizens at large. Furthermore, none of the research
conducted in Malaysia focused on the level of
satisfaction with e-government portals.
Prior research adopted the technology acceptance
model (TAM), the theory of planned behaviour
(TPB), and the diffusion of innovation (DOI) theory
or combination of these theories to test the intention
to use e-government services. Among the significant
determinants found were trust, perceived usefulness,
relative advantage, and perceived image (Ooh at al.,
2009), and social norms (Mohd Suki and Ramayah,
2010). Sambasivan et al. (2010) reported that
perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use,
assurance of services, responsiveness of service
providers, facilitating conditions, and web design
(service quality) as the significant determinants of
actual usage of e-procurement systems among
services providers to the government.
Kalliannan and Awang (2010) examined the
factors that influence the government suppliers’
readiness in adopting and using e-procurement
system. All three factors – organisational,
technological, and environmental are found to
strongly correlate with e-procurement usage.
However, a regression analysis to examine which
factor has a stronger impact on e-Procurement usage
was not tested. On the other hand, Amin and
Kassimin (2011) examined the implementation
issues of e-procurement system in the government
sector. These issues included challenges in terms of
software integration, data management and roll-out
strategy, legal and administration procedures,
information technology (IT) infrastructure,
outsourcing contract and IT skills.
As the research in individual-level IT adoption
has become one of the most mature streams of IS
research (Venkatesh, Davis, and Morris, 2007), this
study differs from the prior studies by examining
citizens’ satisfaction with the services provided by e-

government portals and subsequent continuous use
intentions in the context of senior citizens as users.
This study posits that perceived value of using e-
government portals and social influence lead to
senior citizens’ satisfaction, which in turn, influence
their continuous use intentions.
2.2 Hypothesis Development
Perceived value or perceived benefits has been
widely examined in the context of e-commerce
(Anderson and Srinivasan, 2003; Chen and
Dunbisky, 2003; Chiu et al., 2014). However, Scott,
DeLone, and Golden (2016) was the only study
focusing solely on the perceived benefits of e-
government. Based on the public value theory, they
conceptualised perceived value into three clusters –
efficiency, effectiveness, and social value which
were operationalised as having nine items including
cost, time, personalization, communication, ease of
information retrieval, trust, well-informedness,
participation in decision-making, and convenience.
The operationalisation provided a strong foundation
for measuring the myriad dimensions of perceived
value in the e-government setting.
On the other hand, Venkatesh et al. (2016)
developed three factors in predicting the use
intention of e-government and the subsequent
satisfaction. The factors were information quality
characteristics (accuracy and completeness), channel
characteristics (convenience and personalization),
and means of uncertainty reduction (transparency
and trust). Besides information quality
characteristics, the dimensions of the remaining two
factors overlapped with that of Scott et al. (2016).
Among the six items under the three factors,
convenience was found to have the relatively
strongest influence on the intention to use e-
government services.
This study argues that senior citizen satisfaction
is the result of their perception of value or benefits
obtained from using services provided by e-
government portals. We, therefore propose:
H
1
: Perceived value relates positively with senior
citizen satisfaction with the services provided by e-
government portals.
Social influence or subjective norm refers to the
degree to which individuals believe that people who
are important to them think they should perform the
behavior (Fishbein and Ajzen, 1975). Social
influence has long been established as a significant
determinant to technology and online services
research such as intention to use information
technology (Taylor and Todd, 1995), acceptance of
e-commerce services (Bhattacherjee, 2000), and
adoption of m-commerce services (Wu and Wang,
2005). There are literature which examined the
effects of social influence on e-government such as
subjective norm and adoption intention of e-
government services by Horst, Kuttschreuter, and
Gutteling (2006), interpersonal influence and user
acceptance of m-government services (Hung, Chang,
Kuo, 2013). In the Malaysian context, Mohd Suki
and Ramayah (2010) found a strong and positive
influence of social norm on the intention to use e-
government services.
Prior research on the relationship between social
influence and satisfaction in the online environment
is scarce. The most recent includes Al-Athmay,
Fantazy, and Kumar (2016) which found a positive
relationship between social influence and
satisfaction of using e-government services in
United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Chopra and Rajan
(2016) which confirmed the relationship between
social influence and salespersons’ satisfaction of
using point-of-sale machines mandated by the
Chhattisgarh government in India. However, those
two studies did not specifically argue the role of
social influence on user satisfaction. On the other
hand, Medina, Rufin, and Rey (2016) confirmed the
relationship between expectation disconfirmation of
social influence and satisfaction of using e-learning
platform among students. This study argues that the
influence exerted by the important people around an
individual will lead to one’s satisfaction with
services provided by e-government portals. In the
case of senior citizens, the influence important
persons have upon their decision to use e-
government portals enhances their satisfaction of
using such portals. Therefore,
H
2
: Social influence relates positively with senior
citizen satisfaction with the services provided by e-
government portals.
The concept of continuous use of e-government
services can be rooted in the information systems
(IS) continuous model by Saga and Zmud (1994)
where the use of IS is discussed according to the
phases of IS implementation in organisations. The
first phase is acceptance where employees are
committed to using the systems. The second phase is
routinisation where the use of IS is integrated into
work processes and employees continue using it as
part of their work routines. The last phase is infusion
where employees use the functions of IS deeply and
comprehensively in their work routine. IS literature
has generally agreed that the most successful IS
implementations should include a higher level usage
of IS features (Jasperson et al., 2005). A higher level
of IS usage behaviors can only be achieved if the
systems have been fully integrated into the
organisation and are used continuously by the users
to accomplish their work tasks (Routinisation).
The literature in consumer behaviour stresses the
importance of customer satisfaction in predicting
repurchase behaviour (Anderson and Sullivan, 1993;
Cronin et al., 2000). Similar findings had been
confirmed in the online environment in terms of
loyalty, repurchase intentions, or continuous use
behaviours in the context of e-commerce (Tsai and
Huang, 2007), m-commerce (Lin and Wang, 2006),
e-learning (Roca, Chiu, and Martinez, 2006), and e-
government (Chai et al., 2006).
As the use of e-government services or portals in
Malaysia is not mandatory, dissatisfied senior
citizens in the voluntary setting may opt to
discontinue the use of e-government. On the
contrary, satisfied senior citizens may continue to
use e-government portals. Therefore,
H
3
: Senior citizen satisfaction with the services
provided by e-government portals relates positively
with their continuous use intentions.
3 METHOD
3.1 Sample and Sampling Procedures
The target population of this research is Malaysian
senior citizens aged 50 and above who are using e-
government portals. The convenience sampling
technique is used to approach and select respondents
wherever the researchers can reach them
conveniently. Two hundred individuals at the
government departments and agencies in Kuala
Lumpur and Penang are approached and briefed
about the purpose of the survey before the age is
obtained to ensure that only senior citizens are
selected as the sample, of which, only 123 complete
and usable responses are obtained, a response rate of
61.5%. In this survey, male respondents (72%)
outnumber the female counterparts (28%). A
majority of the respondents (80%) are aged between
50 to 59 years old and the remaining 20% are aged
60 and above. More than half of them (61%) possess
an academic qualification of a Bachelor’s degree or
higher. Slightly over half (50.4%) of the respondents
are still working and 27% of them are earning a
monthly income of between RM2,001 and RM5,000.
Over half of the respondents (62%) have access to
the Internet all the time. The sample profile is
presented in Table 1.
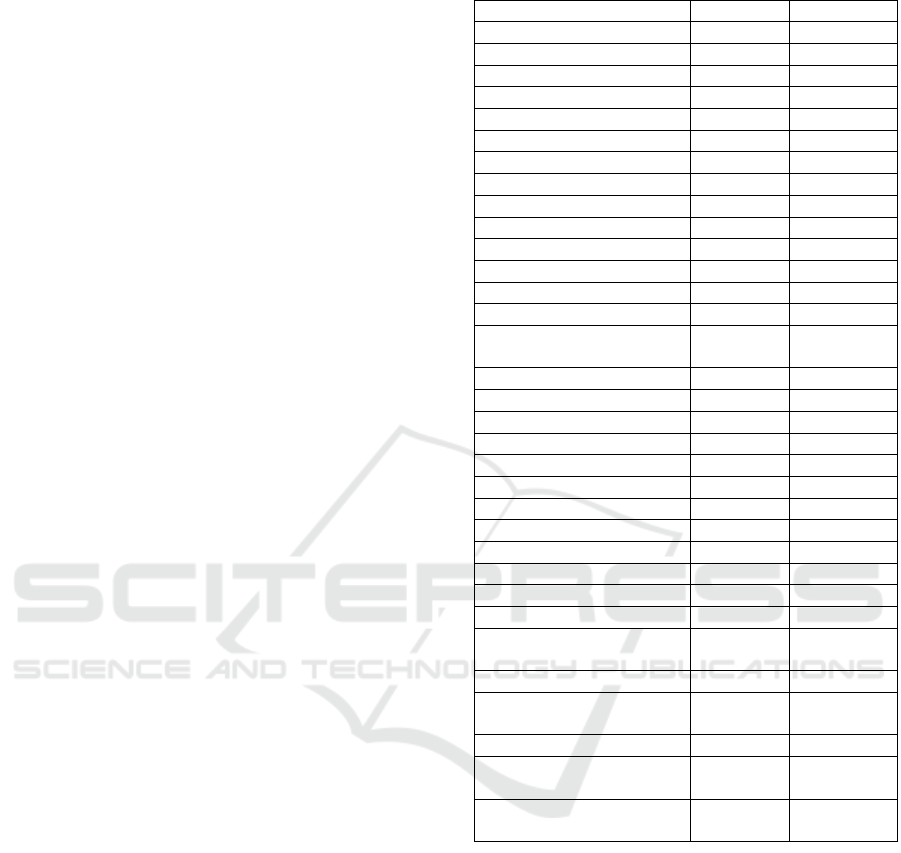
Table 1: Sample Profile (n=123).
Variable Frequency Percentage
Gender
Male 89 72
Female 34 28
Age
50 – 59 99 80
60 and above 24 20
Highest Educational Level
Secondary 18 15
High School 13 11
Diploma 17 14
Bachelor’s Degree 39 32
Master’s Degree 27 22
Doctoral Degree 9 7
Occupation
Office-based staff other
than manager
18 15
Manager and equivalent 26 21
Non-office-based staff 1 1
Self-employed 17 14
Home maker 3 2
Retiree 34 28
Others 24 20
Monthly Income (RM)
<= 2,000 25 20
2,001 – 5,000 33 27
5,001 – 8,000 23 19
8,001 – 10,000 16 13
>10,000 26 21
Accessibility to the
Internet
All the time 76 62
All the time during
working hours
11 9
Half of working hours 10 8
Less than half of working
hours
6 5
Only outside working
hours
20 16
3.2 Variables and Measurement
Perceived Value. Perceived value is adapted by
combining the public value net benefits model
developed by Scott, DeLone, and Golden (2016) and
the value cluster by Venkatesh et al. (2016). Eleven
dimensions with 38 items are tested – cost, time,
personalization, communication, ease of information
retrieval, trust, well-informedness, participation in
decision-making, convenience, completeness, and
accuracy. All items are measured on the 7-point
Likert scale from 1 – “strongly disagree” to 7 –
“strongly agree”.
Social Influence. Social influence is measured by
three items adopted from Venkatesh and Morris,
(2000) and used by Bhattacherjee (2015). The
sample item includes “People who are important to
me think that I should use e-government portals”.
All items are measured on the 7-point Likert scale
from 1 – “strongly disagree” to 7 – “strongly agree”.
Senior Citizen Satisfaction. Senior citizen
satisfaction is measured using nine items adopted
from Verdegem et al. (2009). The items include
infrastructure, availability, awareness, cost, technical
aspects, friendliness, privacy and security, content
quality, and usability. All items are measured on the
7-point Likert scale from 1 – “very dissatisfied” to 7
– “very satisfied”.
Continuous Use Intentions. The intentions to
continue using the e-government portals is measured
using four items adapted from Hausman and Siekpe
(2009) and Li et al. (2006). All items are measured
on the 7-point Likert scale from 1 – “strongly
disagree” to 7 – “strongly agree”.
Use of E-Government Portals. Respondents are
asked to indicate the frequency of accessing the 20
listed government portals for the purposes of
searching for information, performing transactions,
downloading forms, participating in events,
providing feedback, and sharing opinions based on
the scale from 0 – “not at all / never”, 1 – “rarely /
occasionally”, 2 – “often / frequently”, and 3 –
“always/ continuously”.
Demographic Information. The questionnaire
includes six demographic variables – gender, age,
highest educational level, occupation, monthly
income, and accessibility to the Internet.
4 RESULTS
This study utilizes Partial Least Squares Path
Modelling (PLS-PM) with R (Sanchez, 2013) in data
analysis and hypothesis testing. PLS-PM is a
multivariate statistical technique that allows
simultaneous evaluation between multiple variables
and higher order factor (i.e., perceived value). PLS-
PM involved two stages of analysis – evaluation of
measurement model and structural model. The
measurement model evaluates the reliability and
validity of items and constructs while the structural
model assesses effect size, direction, and
significance of the hypothesized relationships.
4.1 Assessment of the Measurement
Model
As shown in Table 2, all constructs are deemed
reliable and valid as all scores exceed the acceptable
thresholds of Cronbach’s alpha, composite
reliability, and average variance extracted (AVE)
(Nunnally, 1978). The discriminant validity of the
items is determined by comparing the squared roots
of AVE and correlation coefficients between
constructs. All the squared roots of AVE on the
diagonal line score higher than the correlation
coefficients between constructs, signifying
discriminant validity at the construct level. All
measures are found to have adequate convergent
validity and discriminant validity at the item level as
all the factor loadings score higher than 0.70 within
the respective constructs – perceived value
(0.72 - 0.91), social influence (0.97 - 0.98), citizen
satisfaction (0.74 - 0.93), and continuous use
intentions (0.94 - 0.97), and score lower on other
constructs. The data analysis proceeds to evaluate
the structural model after having met the
requirements of reliability, convergent validity, and
discriminant validity at both construct and item
levels.
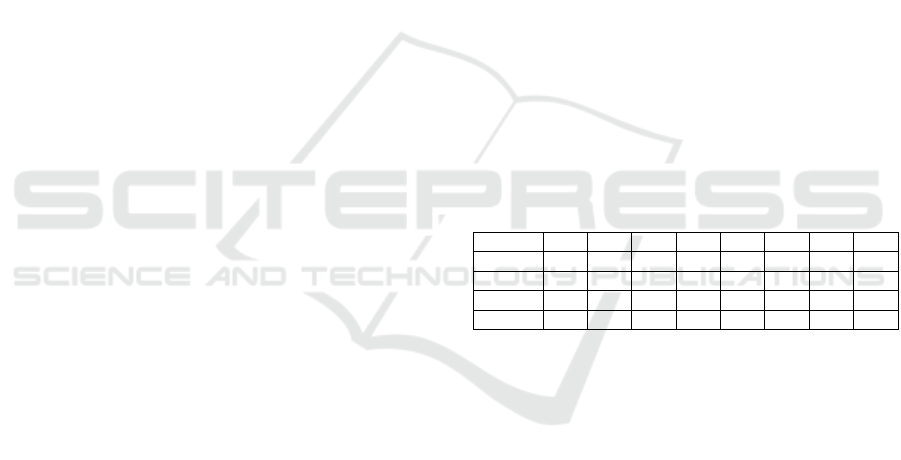
Table 2: Correlation Matrix.
Variable
M SD α CR 1. 2. 3. 4.
1. PV 5.0 1.0 .95 .96
.80
2. SI 4.4 1.4 .97 .98 .64
.97
3. CS 4.4 1.2 .96 .96 .68 .58
.86
4. CU 5.2 1.2 .97 .98 .76 .61 .60
.95
Note. PV – Perceived Value; SI – Social Influence; CS – Citizen
Satisfaction; CU – Continuous Use Intentions; Diagonal values
are squared root of AVE; α – Cronbach’s alpha; CR – Composite
reliability.
4.2 Assessment of the Structural Model
As presented in Figure 1, the structural model
indicates that both perceived value and social
influence are significantly related to senior citizen
satisfaction with the services provided by e-
government portals. However, the relationship
between perceived value and senior citizen
satisfaction (β = .52, t = 6.15, p < .001) is much
stronger than the relationship with social influence
(β = .24, t = 2.87, p < .01). Both perceived value and
social influence explain almost half (49%) of the
variance for senior citizen satisfaction (R
2
= .49). It
is also found that satisfaction is positively and
strongly related to continuous use intentions (β =
.60, t = 8.24, p < .001). Senior citizen satisfaction
explains 36% of the variance for continuous use
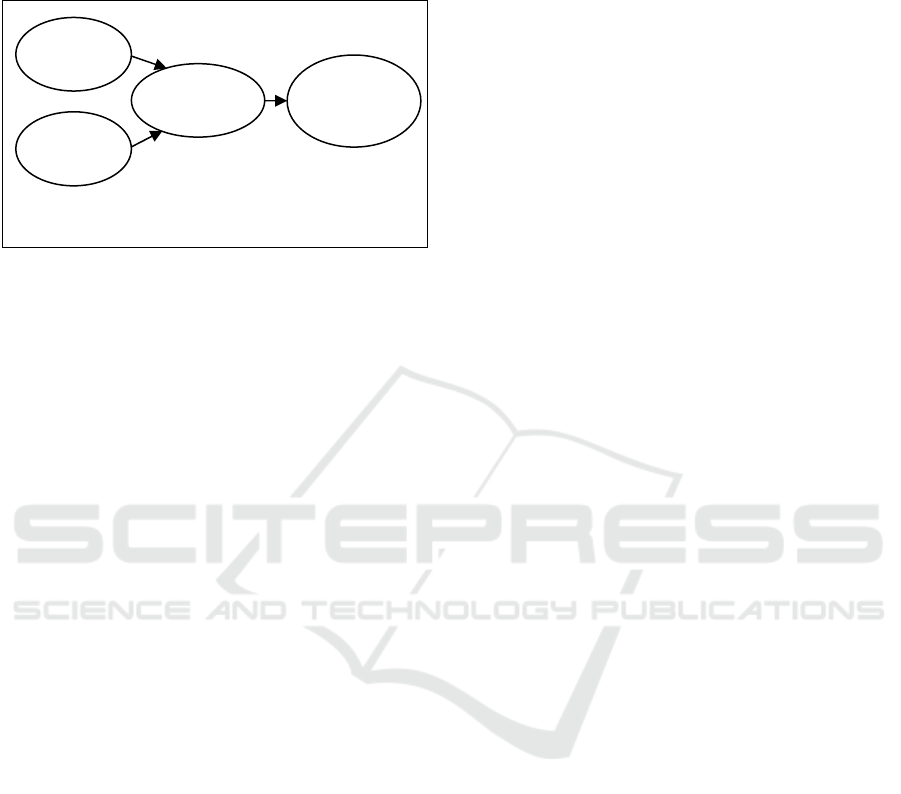
intentions (R
2
= .36). In sum, all the three
hypotheses tested in this study are supported by the
data.
GoF = .564
Note: *** p < .001; ** p < .01
Figure 1: Structural Model.
4.3 Discussion
Generally, the senior citizens are moderately
satisfied with the services provided by e-government
portals (M=4.38) and have favourable continuous
use intentions (M=5.20). Only a small percentage
(below 25% across all portals but Inland Revenue
Board portal) of the respondents quote that they
frequently use e-government portals. Occasionally
they use e-government portals which are related to
health, police, tourism, and immigration. The study
finds that perceived value is strongly and positively
related to senior citizen satisfaction (Scott et al.,
2016; Venkatesh et al., 2016). Similarly, social
influence also leads to senior citizen satisfaction.
The findings are consistent with Al-Athmay et al.
(2016), Chopra and Rajan (2016), and Hsu and Chen
(2007). Furthermore, this study finds that senior
citizen satisfaction with the services provided by e-
government portals relates positively and strongly
with continuous use intentions. The strength of
relationship between the two constructs is much
stronger than the study by Chai et al. (2006).
5 IMPLICATIONS AND
CONCLUSION
5.1 Implications for Research
Firstly, the study is one of the first empirical
research to examine the satisfaction of senior
citizens with e-government portals. Secondly, this
study integrates the concept of perceived value of
using e-government portals from Scott et al. (2016)
and Venkatesh et al. (2016) and is supported by the
empirical data. Thirdly, the study includes the
concept of social influence as the determinant of
senior citizen satisfaction with e-government portals
and finds support for the argument. Finally, the
study includes continuous use intention in the
conceptual framework to provide greater
comprehensiveness and criterion validity. The
results provide empirical support for the proposed
conceptual framework. Overall, the integration of
perceived value and social influence to explain
senior citizen satisfaction with e-government is the
core theoretical contribution.
5.2 Implications for Practice
Senior citizen satisfaction is a manifestation of their
experiences when using e-government portals and
that depend on their perceptions of benefits they
acquire from using those portals. The eleven
dimensions of perceived value confirmed by this
study show that government departments and
agencies need to identify specific value dimensions
which may enhance senior citizens’ satisfaction and
increase their continuous use intentions. By
providing complete, accurate, and up-to-date
information about the services on the e-government
portals, respective government departments and
agencies would allow senior citizens to be better
informed on current news and events, new
functionalities, and latest development. Besides, in
designing e-government portals and their
complementary human-computer interactive features
that are efficient, effective and have social value,
one needs to identify important value dimensions.
Government departments and agencies must be
aware of the needs and expectations of senior
citizens from using e-government portals. With the
projection of population ageing by 2035, Malaysian
government anticipates an increase in the use of e-
government portals among the senior citizens who
have higher Internet access and are more interested
and competent in using online services. In view of
that, e-government portals should be enhanced with
more advanced functionalities in order to meet the
needs of this group of users.
Besides, awareness campaigns to enhance the use
of e-government portals among senior citizens
should be conducted regularly especially after new
functionalities are introduced. Younger users who
are the family members, friends and peers in
workplace should actively promote the use of e-
government portals amongst senior citizens by
providing the necessary assistance. The significant
effect exhibited by social influence in this study
Perceived
Value
Continuous
Use
Intentions
Social
Influence
R
2
=.49
R
2
=.36
Citizen
Satisfaction
.52***
.24**
.60***

implies that the important individuals surrounding
the senior citizens could play an important role in
enhancing their satisfaction with e-government
portals.
5.3 Limitations and Recommendations
for Future Research
This study suffers from a number of limitations and
further research in this area is recommended.
Firstly, the sample is relatively small (n=123)
and selected using convenience sampling procedure.
As such, the results may not be generalisable to the
population. The responses of every variable under
investigation depend largely on the sample
characteristics. To improve the external validity of
the research, future researchers are recommended to
identify a group of homogeneous senior citizens, for
instance, retirees, home makers, working or senior
citizens with low income and with low educational
qualifications.
Secondly, this study employs a cross-sectional
design and thus it is difficult to establish causal
relationship among the constructs. Future
researchers may consider using a longitudinal design
to collect data from the same group of respondents
over multiple periods of time. Alternatively, an
experiment design is considered to be more
appropriate if establishing causal relationships is
crucial in the study. Face-to-face interviews can be a
better approach to collecting data from senior
citizens.
Thirdly, no specific e-government services and
portals is referred to in the survey questionnaire as
by doing so could have taxed the memory of the
respondents who might have different perceptions of
benefits obtained from different e-government
portals as well as their satisfaction level of using
these portals. As such, respondents may find it
difficult to relate their responses to the use of e-
government portals. Future researchers may identify
and test a specific e-government service or portal
with the associated benefits.
6 CONCLUSION
The study proposes and tests a conceptual frame-
work with two determinants and a consequence of
satisfaction with e-government portals in the context
of senior citizens. Based on the results of a survey of
123 senior citizens, this study finds support for the
proposed conceptual framework which hypothesises
that perceived value and social influence affect
senior citizens’ satisfaction, which in turn, influence
their continuous use intentions of e-government
portals. This proposed conceptual framework can
serve as a starting point for pursuing future research
into specific e-government services or portals in
Malaysia and in other countries with ageing
population.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research project is funded by the Fundamental
Research Grant Scheme (FRGS), Ministry of Higher
Education, Malaysia.
(FRGS/1/2015/SS01/UNIRAZAK/02/2).
REFERENCES
AL Athmay, A. A. A., Fantazy, K., and Kumar, V. (2016).
E-Government Adoption and User’s Satisfaction: An
Empirical Investigation. EuroMed Journal of
Business, 11(1), 57-83.
Aman, A., and Kassimin, H. (2011). E-Procurement
Implementation: A Case of Malaysia government.
Transforming Government: People, Process and
Policy, 5(4), 330-344.
Amma, K. S., and Panicker, S. M. (2013). Senior Citizens'
Acceptance of Information Communication
Technology: A Study of E-Banking in India. Journal
of Information Technology and Economic
Development, 4(1), 1-8.
Anderson, R.E., and Srinivasan, S.S. (2003). E-
Satisfaction and E-Loyalty: A Contingency
Framework. Psychology and Marketing, 20(2), 123-
138.
Anderson, E.W., and Sullivan, M.W. (1993). The
Antecedents and Consequences of Customer
Satisfaction for Firms. Marketing Science, 12(2), 125-
143.
Bhattacherjee, A. (2000). Acceptance of e-commerce
services: The case of electronic brokerages. IEEE
Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part
A: Systems and Humans, 30(4), 411-420.
Chai, S., Herath, T.C., Park, I., and Rao, H.R. (2006).
Repeated Use of E-Gov Web Sites: A Satisfaction and
Confidentiality Perspective. International Journal of
Electronic Government Research, 2(3), 1-22.
Chen, Z., and Dubinsky, A.J. (2003). A Conceptual Model
of Perceived Customer Value in E-Commerce: A
Preliminary Investigation. Psychology and Marketing,
20(4), 323-347.
Chiu, C.-M., Wang, E.T.G., Fang, Y.-H., and Huang, H.-
Y. (2014). Understanding Customers' Repeat Purchase
Intentions in B2C E-Commerce: The Roles of
Utilitarian Value, Hedonic Value and Perceived Risk.
Information Systems Journal, 24(1), 85-114.

Chopra, S., and Rajan, P. (2016). Modeling intermediary
satisfaction with mandatory adoption of e-government
technologies for food distribution. Information
Technologies and International Development, 12(1),
1-15.
Conci, M., Pianesi, F., and Zancanaro, M. (2009). Useful,
Social and Enjoyable: Mobile Phone Adoption by
Older People. In: Gross T. et al. (Eds.) Human-
Computer Interaction – INTERACT 2009. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, vol 5726. Berlin,
Heidelberg: Springer.
Cronin, J.J., Brady, M.K., and Hult, G.T.M. (2000).
“Assessing the Effects of Quality, Value, and
Consumer Satisfaction on Consumer Behavioral
Intentions in Service Environments. Journal of
Retailing, 76(2), 193-218.
Fishbein, M., and Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, Attitude and
Behavior. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
GEAR (2011). Government E-Payments Adoption
Ranking. (http://graphics.eiu.com/upload/eb/Visapay
ments.pdf)
Hausman, A.V., and Siekpe, J. S. (2009). The Effect of
Web Interface Features on Consumer Online Purchase
Intentions. Journal of Business Research, 62(1), 5-13.
Heart, T., and Kalderon, E. (2013). Older Adults: Are
They Ready to Adopt Health-related ICT?
International Journal of Medical Informatics, 82(11),
e209-e231.
Horst, M., Kuttschreuter, M., and Gutteling, J. M. (2007).
Perceived Usefulness, Personal Experiences, Risk
Perception and Trust as Determinants of Adoption of
E-Government Services in the Netherlands.
Computers in Human Behavior, 23(4), 1838-1852.
Hsu, F. M., and Chen, T. Y. (2007). Understanding
Information Systems Usage Behavior in E-
Government: The Role of Context and Perceived
Value. PACIS 2007 Proceedings, 41.
Hung, S. Y., Chang, C. M., and Kuo, S. R. (2013). User
acceptance of mobile e-government services: An
empirical study. Government Information Quarterly,
30(1), 33-44.
Hussein, R., Mohamed, N., Ahlan, A. R., Mahmud, M.,
and Aditiawarman, U. (2010). G2C Adoption of E-
Government in Malaysia: Trust, Perceived Risk and
Political Self-Efficacy. International Journal of
Electronic Government Research, 6(3), 57-72.
Jasperson, J. S, Carter, P. R., and Zmud, R. W. (2005). A
Comprehensive Conceptualization of Post-Adoptive
Behaviors Associated with Information Technology
Enabled Work Systems. MIS Quarterly, 29(3), 525-
557.
Kaliannan, M., and Awang, H. (2010). Adoption and Use
of E-Government Services: A Case Study on E-
Procurement in Malaysia. WSEAS Transactions on
Business and Economics, 88-93.
Law, M., Kwok, R. C. W., and Ng, M. (2016). An
Extended Online Purchase Intention Model for
Middle-Aged Online Users. Electronic Commerce
Research and Applications, 20, 132-146.
Li, D., Browne, G.L, and Wetherbe, J.C. (2006). Why Do
Internet Users Stick with A Specific Web Site? A
Relationship Perspective. International Journal of
Electronic Commerce, 10(4), 105-141.
Loo, W. H., Yeow, P. H., and Chong, S. C. (2009). User
Acceptance of Malaysian Government Multipurpose
Smartcard Applications. Government Information
Quarterly, 26(2), 358-367.
Ooh, K. L., Zailani, S., Ramayah, T., and Fernando, Y.
(2009). Factors Influencing Intention to Use E-
Government Services among Citizens in Malaysia.
International Journal of Information Management,
29(6), 458-475
Medina, C., Rufín, R., and Rey, M. (2015). Mediating
Relationships in and Satisfaction with Online
Technologies: Communications or Features Beyond
Expectations? Service Business, 9(4), 587-609.
Mitzner, T. L., Boron, J. B., Fausset, C. B., Adams, A. E.,
Charness, N., Czaja, S. J., ... and Sharit, J. (2010).
Older Adults Talk Technology: Technology Usage and
Attitudes. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6),
1710-1721.
Mohd Suki, N., and Ramayah, T. (2010). User Acceptance
of the E-Government Services in Malaysia: Structural
Equation Modelling Approach. Interdisciplinary
Journal of Information, Knowledge, and Management
(5).
Nunnally, J. (1978). Psychometric Methods. New York:
McGraw-Hill.
Phang, C. W., Sutanto, J., Kankanhalli, A., Li, Y., Tan, B.
C., and Teo, H. H. (2006). Senior Citizens' Acceptance
of Information Systems: A Study in the Context of E-
Government Services. IEEE Transactions on
Engineering Management, 53(4), 555-569.
Roca, J. C., Chiu, C. M., and Martínez, F. J. (2006).
Understanding e-Learning Continuance Intention: An
Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
64(8), 683-696.
Saga, V., and Zmud, R.W. (1994). The Nature and
Determinants of IT Acceptance, Routinization and
Infusion, Proceedings of the International Federation
of Information Processing Work Group. 8(6), 67-86.
Sambasivan, M., Patrick Wemyss, G., and Che Rose, R.
(2010). User Acceptance of A G2B System: A Case of
Electronic Procurement System in Malaysia. Internet
Research, 20(2), 169-187.
Sanchez, G. (2013). PLS Path Modeling with R.
(http://gastonsanchez.com)
Scott, M., DeLone, W., and Golden, W. (2016).
Measuring eGovernment Success: A Public Value
Approach, European Journal of Information Systems,
25(3), 187-208.
Taylor, S., and Todd, P. A. (1995). Understanding
Information Technology Usage: A Test of Competing
Models. Information Systems Research, 6(2), 144-176.
Tsai, H. T., and Huang, H. C. (2007). Determinants of e-
Repurchase Intentions: An Integrative Model of
Quadruple Retention Drivers. Information and
Management, 44(3), 231-239.
United Nations (2015). World Population Ageing Report

2015. Retrieved from http://www.un.org/en/
development/desa/population/publications/pdf/ageing/
WPA2015_Report.pdf
Venkatesh, V., Davis, F.D., and Morris, M.G. (2007).
Dead or Alive? The Development, Trajectory and
Future of Technology Adoption Research. Journal of
the Association for Information Systems, 8(4), 267-
286.
Venkatesh, V., and Morris, M. G. (2000). Why Don't Men
Ever Stop to Ask for Directions? Gender, Social
Influence, and Their Role in Technology Acceptance
and Usage Behavior. MIS Quarterly, 24(1), 115-139.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J.Y.L., Chan, F.K.Y., and Hu,
P.J.H. (2016). Managing Citizens’ Uncertainty in E-
Government Services: The Mediating and Moderating
Roles of Transparency and Trust. Information Systems
Research, 27(1), 87-111.
Verdegem, P., and Verleye, G. (2009). User-centered E-
Government in Practice: A Comprehensive Model for
Measuring User Satisfaction. Government Information
Quarterly, 26(3), 487-49.
Wong, C. K., Yeung, D. Y., Ho, H. C., Tse, K. P., and
Lam, C. Y. (2014). Chinese Older Adults’ Internet
Use for Health Information. Journal of Applied
Gerontology, 33(3), 316-335.
Wu, J. H., and Wang, S. C. (2005). What drives mobile
commerce? An empirical evaluation of the revised
technology acceptance model. Information and
Management, 42(5), 719-729.
