
Analysis of Brain Waves in Violent Images
Are Differences in Gender?
Juan Andrés Martínez-Escobar, Silvia B. González-Brambila and Josué Figueroa-González
Systems Department, Universidad Autonoma Metropolitana, San Pablo Av. 180, Mexico City, Mexico
Keywords: Violence Images, Data Mining, EEG, Gender.
Abstract: We collected information using the Electroencephalograph (EEG) EmotivEpoc, and the software complement
of the Eye Tracking system SMI RED250mobile. As a first step, it was stored in text files, the readings of
each EEG sensor during the time the presentation of 5 violent images and 5 non-violent images were observed.
The database was collected with 50 volunteers, consisting of 25 men and 25 women. The database was later
loaded into R, for the execution of the algorithms of data mining, K-means, K-medoids, Hierarchical
Clustering, Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machines, Adaboost and Decision trees. In the clustering methods,
a random clustering was presented and with little information, with the Naive Bayes, SVM and Adaboost
models, a classification with a high percentage of error was obtained using the Decision Trees method, we
obtained one of the worst results, with the highest error rates in the classification performed with the test data
of selected method. Based on the results obtained, no significant difference was found in the individual's
gender, which affected his reaction when viewing images with violent and non-violent content.
1 INTRODUCTION
Humans analyze and react in different ways when see
or observe different situations; however, it is
desirable to identify patterns that allow classification.
Due to the easy access to Internet, people can
access to a lot of information, but this privilege has
brought with it a great danger, graphic violent content
may be unfit or disturbing for many people. As a
result, several works have been done related with the
classification of videos and images into violent and
non-violent content under different criteria, which has
been a topic of interest and research in recent years.
In this project we analyzed the brain waves of
people when they witnessed images that could be
classified as violent or non-violent, in order to
compare the results obtained, for determining if there
are differences or not in the gender.
First we acquire brainwave data of people
observing the violent and non-violent images using
the EmotivEpoc, this data was stored in a database.
Then, this data was schematized using the software R,
and processed using some data mining algorithms
using packages of the same software. The goal was to
classify the samples in at least two groups, Male and
Female samples. The EmotivEpoc is a wireless EEG
of 14 channels, designed for research and advanced
brain computer interface.
There are some related works about violence in
images and videos; recognizing acts of violence on
videos with crowds, without audio (Hassner, 2012).
Classifying images in violent and non-violent using
the BoW model integrated with the SPM scheme and
soft voting strategy (Wang, 2012). There area also
some works related with the consequences of
watching violence on TV (Tisserom, 2006), and
recording with an EEG how young men react while
they do a laboratory test called Taylor Aggression
Paradigm (Wiswede, 2011). A recent work
(Manrique, 2014) used some data mining algorithms
to classify the sound of firearms shots.
(Lotte, 2007) focus on the classification
algorithms used to design EEG-based Brain-
Computer Interface (BCI) and the used features, they
aware that problems may be different if used outside
the laboratories. The classification algorithms used to
design BCI systems were divided into five categories:
a) Linear classifiers (LDA, Linear Discriminant
Analysis and SVM, Support Vector Machine), b)
Neural Networks (MLP, MultiLayer Perceptron and
other architectures), c) NonLinear Bayesian
classifiers (Bayes quadratic and HMM, Hidden
Markov Model), d) Nearest Neighbor classifiers
408
Martínez-Escobar, J., González-Brambila, S. and Figueroa-González, J.
Analysis of Brain Waves in Violent Images - Are Differences in Gender?.
DOI: 10.5220/0006485304080414
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications (DATA 2017), pages 408-414
ISBN: 978-989-758-255-4
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
(kNN and Mahalanobis distance) and e) combinations
of classifiers. They conclude that SVM are
particularly efficient for synchronous BCI and
combinations of classifiers and dynamic classifiers
also result very efficient in synchronous experiments.
The present work pretends to be an antecedent of
future studies on repercussions to the mind of the
human being when observing violent content,
depending if the person observing it is of the feminine
or masculine gender. The goal, carrying out a study
on the cerebral activity that generates the viewing of
images classified as violent or non-violent, is trying
to detect whether is a difference in gender or not.
For the statistic analysis and data mining prcess,
was used the R software. R is a GNU project that has
a wide variety of statistical and graphical techniques
and is extensible. It is a complete computer language
and allow additional funcionality so it can be
extended via packages (R, 2017).
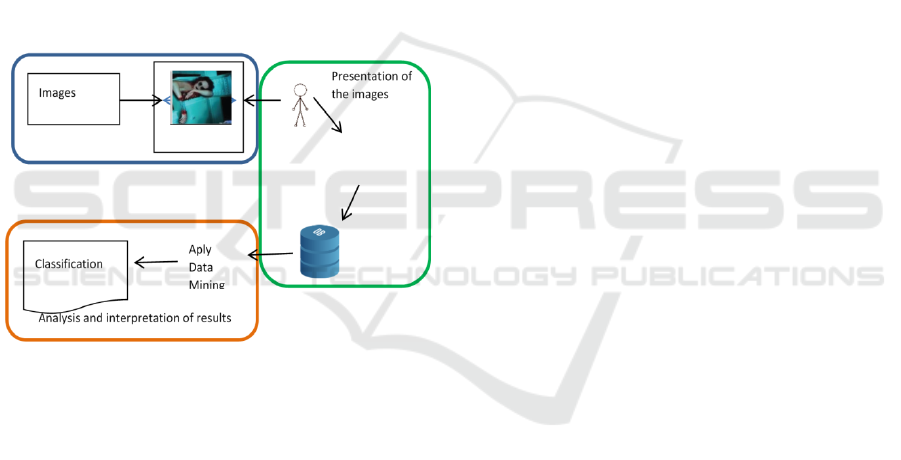
The general diagram is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Components diagram of the project.
This paper is organized as follows, in section 2 we
present the process for collecting the information,
which includes the construction of the database,
presentation of images and the collection of EEG
data. In section 3, we present the analysis and the
interpretation of results obtained from each
algorithm. Finally, in section 4, we expose our
conclusion and comment about future related works.
2 GATHERING INFORMATION
2.1 Building the Image Database
There is no database available with classified images
in violence and no violence, so we had to make one,
by searching and collecting images through the online
search engine “Google”, using query words such as
“violence”, “horror”, “explosion”, “blood”, “shots”,
“war”, and similar, to those used in the construction
of the VID database (Wang, 2012). After creating the
database, 10 images were selected, 5 classified as
violent and 5 non-violent, by personal criteria of a
group of undergraduate and graduate students. For the
presentation that would be shown to the volunteers of
the project, these images must had a minimum
resolution of approximately 1000x800 and
1200x1000 pixels. These images must maintain a
certain parallelism of the contents, as for example:
people, scenes, objects, etc.
2.2 Image Presentation
Violent and non-violent images were presented with
the help of the Eye Tracking system, 50 volunteers
from the university community, 25 from male gender
and 25 from female gender. First we had to place the
EEGdevice, which requires that the electrodes were
sufficiently hydrated with saline solution for the
correct measurement, so that some potential
volunteers, could not perform the test due to hair
products that blocked or didn’t allowed the electrodes
to contact the skin.
2.3 Collecting the EEG Data
After having placed the data channels and obtained a
good signal of the EmotivEpoc device, we proceeded
to the present the violent and non-violent images in a
monitor.
Each image was exposed for three-second to each
volunteer, that duration was selected by suggestion of
M.D. Roberto García, whom from personal
experience of previous works, pointed out that it
didn’t require more time for the image to cause a
reaction in the observer.
After collecting the EEG data of the 50
volunteers, the EEG database was extracted with the
SMI Experiment Suite software in the Laboratory,
which also allowed us to observe the path of the
volunteer’s vision during the exposure to the picture.
The database information was processed to a text
file, separated by tabulations, which contains: name
of the volunteer, name of the image that was observed
at a moment, values registered from the 14 electrodes,
information of the gyroscope and emotion values that
were automatically calculated by the EEG device,
with an average performance of 60 values per second
registered by the EmotivEpoc diadem.
Analysis of Brain Waves in Violent Images - Are Differences in Gender?
409
3 ANALYSIS AND
INTERPRETATION OF
RESULTS
Due to the large amount of data obtained through the
EmotivEpoc equipment, since several values per
second were extracted in each of the electrodes, we
proceeded to form tables, as objects of R, where for
each volunteer their maximum, mean, median and
variance values of each EEG channel were showed
during the exposure of each of the violent and non-
violent images.
It should be mentioned that in the creation of
tables, a column was added, indicating if the sample
corresponded to a person of masculine or feminine
gender, this, for its later use in algorithms of data
mining. In the same way, three columns were
excluded, because two of them were signal of the
gyroscope integrated to the EEG device, and another
one, sampled an extra value to the 14 necessary
electrodes, that very concurrently took a null value.
At this stage, the R table objects are analyzed
through the application of clustering, classification
and automatic learning methods, for determining if
these algorithms were able to recognize or predict the
gender of the volunteer.
All the data mining techniques used in this project
took as parameters the columns corresponding to the
maximum, mean, median and variance values that the
EEG channels of the EmotivEpoc diadem produced,
and the rows represent the samples of the volunteers
during the time of exposure to the images.
3.1 Data Mining Algorithms
In this section we present the main results obtained
using K-means, K-medoids, hierarchical clustering,
support vector machines, decision trees, Naive Bayes,
and Adaboost.
In the results presented in the form of tables,
contractions will be used for naming generated
datasets, e.g. v1, v2 and v3, refer to violent images
one, two and three, while nv1, nv2 and nv3, refers to
non-violent images one, two and three, likewise, for
sets with maximum (max), mean (mean), median
(median) and variance (var), resulting in naming the
datasets generated in this way, for example: v1max,
v3mean, nv2median, nv5var.
When executing the K-means method, with two
and three clusters, a very large cluster were formed,
and one or two with few objects in it, as can be seen
in Table 1.
Table 1: K-means with maximum values using k=2 & k=3.
Clusters size
Data
k=2 k=3
Cluster
1
Cluster
2
Cluster
1
Cluster
2
Cluster
3
v1max 1 49 1 5 44
v2max 5 45 44 2 4
v3max 5 45 3 2 45
v4max 8 42 9 39 2
v5max 5 45 39 8 3
nv1max 1 49 40 1 9
nv2max 8 42 8 41 1
nv3max 1 49 45 4 1
nv4max 46 4 40 6 4
nv5max 7 43 7 1 42
We increased the “k” number of clusters to 10,
due to the results observed with 2 and 3 clusters,
trying to divide the main cluster who appeared using
k=2 & k=3, hoping that the new clusters could contain
sub-groups from one gender, or other classifications,
unfortunately the clusters created did not include sub-
groups from just one gender, and at that moment, we
did not asked to the volunteers for their personal
information, such as age, occupation, or other
relevant data.
Obtained results with k from 2 to 10 were very
similar, small clusters and always one of a larger size,
as can be seen in Table 2.
Table 2: K-means with maximum values using k=10.
Data
Cluster and size
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10
v1max 1 1 2 7 1 3 4 1 6 24
v2max 5 6 2 1 4 3 1 3 24 1
v3max 1 19 1 2 7 1 2 9 2 6
v4max 18 1 11 6 2 1 1 1 5 4
v5max 3 4 5 2 1 11 15 4 3 2
nv1max 2 8 2 3 4 1 1 25 1 3
nv2max 16 3 1 1 1 4 9 8 3 4
nv3max 1 1 1 1 13 26 1 1 1 4
nv4max 1 1 3 4 1 1 19 10 5 5
nv5max 1 2 28 1 2 1 1 9 4 1
When applying the K-medoids method, using any
of the two functions of R, pam () and pamk (), the
results obtained did not generate any distinction
between the genders. As discussed in Tables 3 and 4,
on the use of these methods, there was the same
problem as with the use of K-means, a cluster was
KDCloudApps 2017 - Special Session on Knowledge Discovery and Cloud Computing Applications
410
formed that contained most of the objects, and
another one with little amount of data.
Table 3: pam() with mean values using k=2.
Data
Clusters Size
C1 C2
v1mean 43 7
v2mean 48 2
v3mean 45 5
v4mean 43 7
v5mean 49 1
nv1mean 49 1
nv2mean 48 2
nv3mean 49 1
nv4mean 47 3
nv5mean 49 1
Table 4: pam() with mean values.
Data
Clusters Size
C1 C2 C3 C4
v1mean 41 1 7 1
v2mean 48 2
v3mean 45 5
v4mean 43 7
v5mean 49 1
nv1mean 49 1
nv2mean 48 2
nv3mean 49 1
nv4mean 47 3
nv5mean 49 1
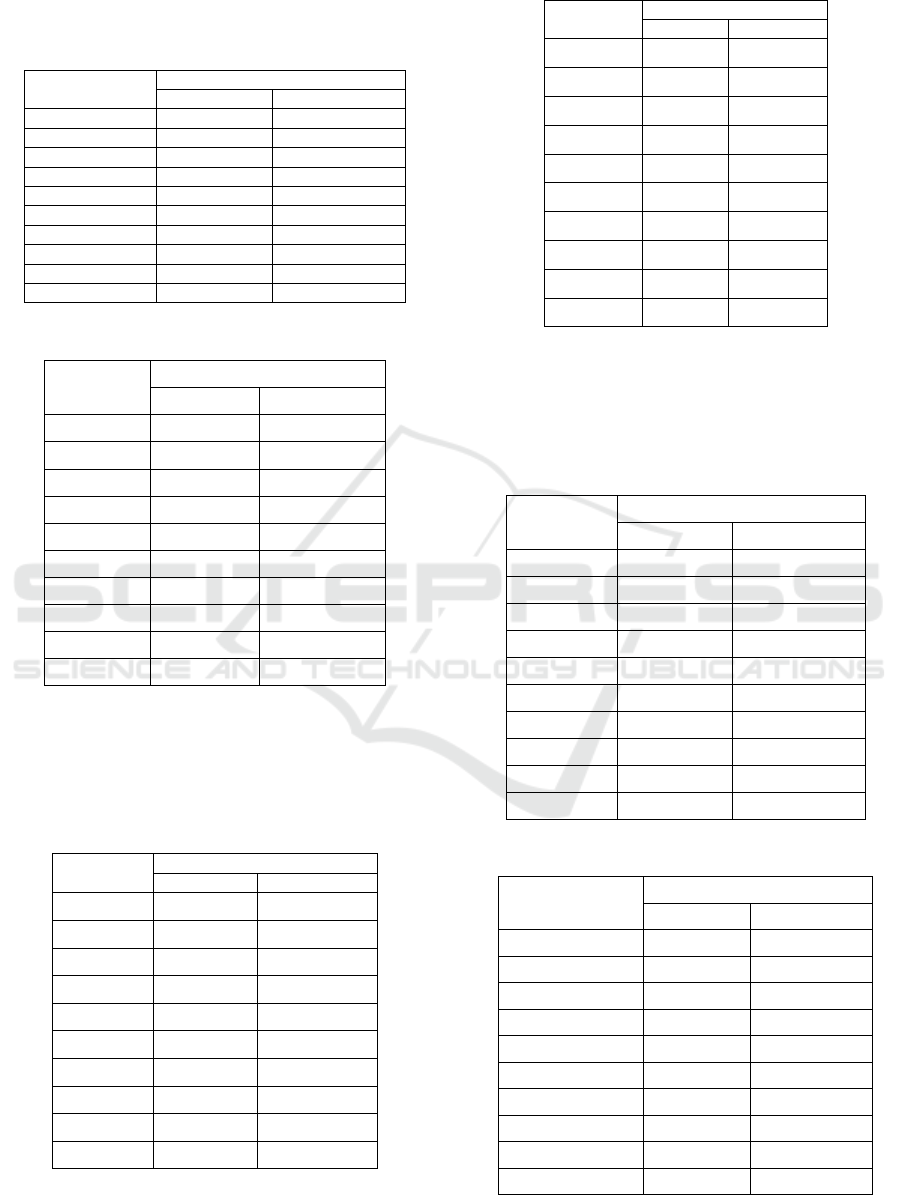
In the call to the hierarchical clustering method it
was noticed that was generated a similar result to the
previously described clustering methods, when
partitioning in 10 clusters, the dendrogram printed by
the method showed a cluster with most objects and
very small ones, It can also be seen in Figure 2 that
objects or samples belonging to both genders (M and
F) are housed in the formed clusters.
Figure 2: Hierarquical Clustering using k=10.
Training a SVM for classification and regression
involves solving a quadratic optimization problem.
Using a standard quadratic problem solver for
training an SVM would involve solving an
exponential problem. To handle this issue, methods
like SMO (Platt 1998), chunking (Osuna et al., 1997)
and simple SVM (Vishwanathan et al., 2003) exist
that iteratively compute the solution of the SVM and
scale O(N2.5). In package e1071 (Karatzoglou et al.,
2006), used in this project, the training patterns,
called support vectors, carry all relevant information
about classification problem.
The results obtained using the SVM algorithm on
the different tables didn’t show a good solution when
classifying test data. As can be seen in Tables 5 and
6, where the percentage of correctness and error
obtained on the classification of the selected samples.
Table 5: SVM with maximum values using lineal kernel.
Data
%
Error Success
v1max 42.1053 57.89474
v2max 38.4615 61.53846
v3max 71.4286 28.57143
v4max 50 50
v5max 42.8571 57.14286
nv1max 50 50
nv2max 38.4615 61.53846
nv3max 41.1765 58.82353
nv4max 57.8947 42.10526
nv5max 37.5 62.5
Table 6: SVM with variance values using lineal kernel.
Data
%
Error Success
v1var 28.5714 71.42857
v2var 66.6667 33.33333
v3var 41.1765 58.82353
v4var 36.3636 63.63636
v5var 50 50
nv1var 50 50
nv2var 44.4444 55.55556
nv3var 46.1538 53.84615
nv4var 50 50
nv5var 38.4615 61.53846
The results obtained using the Naive Bayes
algorithm yielded very different percentages of error
and correctness in classifying the test data, as can be
Analysis of Brain Waves in Violent Images - Are Differences in Gender?
411
seen in Tables 7 and 8, showing a very erratic
classification in the majority of the tests performed.
Table 7: Naïve Bayes with mean values.
Data
%
Erro
r
Success
v1mean 27.2727 72.72727
v2mean 41.6667 58.33333
v3mean 41.6667 58.33333
v4mean 42.8571 57.14286
v5mean 60 40
nv1mean 41.1765 58.82353
nv2mean 20 80
nv3mean 40 60
nv4mean 60 40
nv5mean 33.3333 66.66667
Table 8: Naïve Bayes with maximum values.
Data
%
Error Success
v1max 42.8571 57.14286
v2max 50 50
v3max 55.5556 44.44444
v4max 28.5714 71.42857
v5max 50 50
nv1max 63.6364 36.36364
nv2max 55.5556 44.44444
nv3max 36.3636 63.63636
nv4max 44.4444 55.55556
nv5max 45.4545 54.54545
The results obtained using the classification
algorithm with a decision tree, showed a very low
percentage of correctness in the gender classification
of the test objects as can be seen in Tables 9 and 10.
Table 9: Decision tree with maximum values.
Data
%
Erro
r
Success
v1max 53.8462 46.15385
v2max 61.1111 38.88889
v3max 52.9412 47.05882
v4max 53.3333 46.66667
v5max 58.8235 41.17647
nv1max 56.25 43.75
nv2max 50 50
nv3max 73.3333 26.66667
nv4max 57.1429 42.85714
nv5max 53.8462 46.15385
Table 10: Decision tree with mean values.
Data
%
Erro
r
Success
v1mean 68.75 31.25
v2mean 52.6316 47.36842
v3mean 57.8947 42.10526
v4mean 53.8462 46.15385
v5mean 53.8462 46.15385
nv1mean 52.9412 47.05882
nv2mean 70 30
nv3mean 60 40
nv4mean 62.5 37.5
nv5mean 61.5385 38.46154
The results obtained using Adaboost on the data
set did not obtain a good solution when classifying
samples by gender, obtaining very high percentages
of error, as shown in Tables 11 and 12.
Table 11: Adaboost with maximum values.
Data
%
Error Success
v1max 42.1053 57.89474
v2max 38.8889 61.11111
v3max 42.8571 57.14286
v4max 60 40
v5max 27.7778 72.22222
nv1max 52.9412 47.05882
nv2max 47.0588 52.94118
nv3max 30 70
nv4max 42.1053 57.89474
nv5max 50 50
Table 12: Adaboost with median values.
Data
%
Error Success
v1median 58.3333 41.66667
v2median 18.75 81.25
v3median 43.75 56.25
v4median 50 50
v5median 35.2941 64.70588
nv1median 41.6667 58.33333
nv2median 37.5 62.5
nv3median 66.6667 33.33333
nv4median 47.0588 52.94118
nv5median 30 70
KDCloudApps 2017 - Special Session on Knowledge Discovery and Cloud Computing Applications
412

4 CONCLUSIONS
A database was obtained through the EmotivEpoc
EEG device and specialized software for the
collecting raw data which was analyzed with several
algorithms and data mining methods, in order to
determine if there was a difference in gender when
observing violent images. The database was built,
showing for thirty seconds, five violent images and
five non-violent images (three seconds per image) to
a group of 50 volunteers, of whom half were women
and the other half men.
The K-means method applied to all generated
tables, didn’t show good results, performing a
separation of 2, 3 and 10 clusters, in all cases, was
created a cluster which groups the majority of the
objects of both genders, and others clusters were very
small, grouping up to a single object, from which it’s
deduced that it’s not a good classification.
The Hierarquical method used didn’t obtain
different results to the K-means, the cut was carried
out to 10 clusters and it’s observed that the clusters
contain one or very few objects of both genders, and
there are one or two clusters of bigger size, that
contain the majority of samples for both genders. So
we didn’t get a good gender classification with this
Hierarquical method. Using the K-medoids method to
the calculated values tables, good results weren’t also
generated, using the pam() function of R, results
obtained were similar to K-means with two clusters,
since a cluster contained almost all of the samples,
and in these clusters, no gender classification was
found. With the pamk() function of R, we obtained
similar results to those of the pam() function,
however in some cases, it generated one or two more
clusters, although this didn’t result in a better
classification, since a large cluster was maintained,
there wasn’t any classification that could be identified
due to gender.
The Support Vector Machine (SVM) with linear
kernel, didn’t produce better results than the
clustering methods mentioned above, reaching, in the
worst cases, a success rate that was around 30-45%,
considering that it didn’t obtain a good classification
of gender due to it classified all the samples of test
like a single gender.
The Naive Bayes classification algorithm
presented results with very little success percentage
on the test data, the less successful tests were around
40% and the best classification was between 70% and
80%, although there were many tests with results
between these cases, it was not possible to obtain
good conclusions for using this algorithm in gender
classification of objects.
The decision trees methods gave us very high
rates of error in the gender classification, reaching
over 70% error and not less than 50% on the test data.
This indicates that this algorithm was not useful for
the classification of the samples of the database.
Finally, the Adaboost algorithm registered an
error rate between 40% and 70%, just as with the
percentage of success in the tests, the model created
fails to distinguish with certainty the samples in order
to classify them by gender.
Summarizing, the results obtained when using
clustering methods didn’t achieve a minimum
classification, as the number of clusters increased, the
cluster in which the majority of the samples were
concentrated didn’t decrease considerably its size,
and only generated other clusters with even a single
object. Thus, the results of these clustering methods
were not expected, since they failed to recognize or
classify the samples of different gender and the
generated clusters were very different in size and
samples of the same gender contained.
About using Support Vector Machines, Naïve
Bayes and Adaboost, the obtained results were not as
expected, since the formed models failed to perform
a classification of the test data with a considerable
percentage of success, reaching a success rate that
was around 40% to 60%.
Considering this, can be told that none of the
algorithms and methods presented and used here were
able to classify a reaction of viewing violent images
per gender.
In the execution of this project the specific
objectives were fulfilled, based on the results
obtained from the application of data mining
algorithms, it was not possible to determine if there is
a difference in gender when observing violent and
non-violent images. Probably the study should be
carried out with a larger number of people, belonging
to a more specific range of age, and a community
better delimited to avoid in a certain way that isolated
cases affect the methods of data mining, and so
perhaps to obtain other conclusions.
Other factors may affect outcomes, such as age,
environment, vision problems, past events that may
psychologically affect the human being, use of drugs,
medicines, or substances can affect the nervous
system
In the development of the project we presented
certain problems that were solved with a better use of
the R environment for data management, although the
notions acquired from the R language were sufficient
for the application of data mining is expected to
extend this knowledge of Data mining in the future.
In order to carry out related future work, the
Analysis of Brain Waves in Violent Images - Are Differences in Gender?
413

opinion of experts on violence should be considered
in order to determine the initial classification of the
images to be used, it should also be taken into account
that gender is not the only thing that can be inferred
in the reaction of the human brain before the
visualization of violent images or not.
Also, the creation of a more extensive database
with a greater number of participants, in order to be
able to contemplate cases that reacted abnormally to
the presence of violence could help in the training
stage for several algorithms such as SVM or
Adaboost. It could also be an option, to use videos
with violent or non-violent content instead of images
for future works.
REFERENCES
Hassner, T., Itcher, Y., Kliper-Gross, O., 2012, "Violent
flows: Real-time detection of violent crowd
behavior," Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Workshops (CVPRW), 2012 IEEE Computer Society
Conference on, Providence, RI, pp. 1-6.
Wang, D., Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Wang, L., Tan, T., 2012,
"Baseline Results for Violence Detection in Still
Images," Advanced Video and Signal-Based
Surveillance (AVSS), 2012 IEEE Ninth International
Conference on, Beijing, pp. 54-57.
Tisserom, S., 2006, "Los 11-13 años frente al estrés de las
imágenes violentas", Subjetividad y procesos
cognitivos, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 177-197.
Wiswede, D., Taubner, S., Münte, T., Roth, G., Strüber, D.,
Wahl, K., Krämer, U., 2011, “Neurophysiological
correlates of laboratory-induced aggression in young
men with and without a history of violence”, PLoS
ONE.
Manrique, C. J., 2014, “Detección acústica de disparos de
armas de fuego usando técnicas de minería de datos”
proyecto terminal, División de Ciencias Básicas e
Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana,
México.
R Core Team, 2017. R: A language and environment for
statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-
project.org/.
Meyer, D., Dimitriadou, E., Hornik, K, Weingessel, A.,
Leisch, A., 2015. e1071: Misc Functions of the
Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group
(Formerly: E1071), TU Wien. R package version 1.6-7.
https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=e1071
Chatterjee, S., 2016. fastAdaboost: a Fast Implementation
of Adaboost. R package version 1.0.0. https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=fastAdaboost
Hothorn, T., Hornik, K., Zeileis, A., 2006. Unbiased
Recursive Partitioning: A Conditional Inference
Framework. Journal of Computational and Graphical
Statistics, 15(3), 651--674.
Hennig, C., 2015. fpc: Flexible Procedures for Clustering.
R package version 2.1-10. https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=fpc
Maechler, M., Rousseeuw, P., Struyf, A., Hubert, M.,
Hornik, K., 2016. cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and
Extensions. R package version 2.0.5.
Lotte F, Congedo M, Lécuyer A, Lamarche F, Arnaldi B.,
2007, “A review of classification algorithms for EEG-
based brain-computer interfaces”. Journal of Neural
Engineering, IOP Publishing, 4, pp. 24
Karatzoglou, A., Meyer, D., & Hornik, K., 2006. Support
Vector Machines in R. Journal of Statistical Software,
15(9), 1 - 28.
Platt JC., 1998. “Fast Training of Support Vector Machines
Using Sequential Minimal Optimization.” In B
Schölkopf, CJC Burges, AJ Smola (eds.), “Advances in
Kernel Methods – Support Vector Learning,” pp. 185–
208. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Osuna, E., Freund, R., Girosi, F. 1997. "An improved
training algorithm for support vector machines," Neural
Networks for Signal Processing VII. Proceedings of the
1997 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop,
Amelia Island, FL, pp. 276-285.
Vishwanathan SVN, Smola A, Murty N., 2003.
“SimpleSVM.” In “Proceedings of the Twentieth
International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-
2003), Washington DC” AAAI Press.
KDCloudApps 2017 - Special Session on Knowledge Discovery and Cloud Computing Applications
414
