
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP
Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
Pedro Juan Roig, Salvador Alcaraz and Katja Gilly
Department of Physics and Computer Architecture, Miguel Hernández University,
Avda. Universidad, s/n, 03202 Elche (Alicante), Spain
Keywords: ACP, Formal Protocol Specification, FTP, Networking.
Abstract: FTP is a well-known network protocol aimed at transferring computer files between two end devices,
following a client-server approach. In this paper, we are focusing on getting a formal description model for
both FTP modes, namely active and passive, by using manual algebraic derivations related to Algebra of
Communicating Processes (ACP) as a tool for achieving such a formal protocol specification. For that
purpose, the most commonly used FTP commands are going to be studied by applying ACP rules, proving
that the model proposed meet the expected behaviour of FTP sessions.
1 INTRODUCTION
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol and is one of
the eldest communication protocols used on
computer networks. The original specification was
written in the early seventies but the current
specification was released in the middle eighties
(RFC 959, 1985).
Back then, security concerns were not much
taken into account, but as time went by, security
breaches happened and needed to be addressed.
Therefore, further amendments were proposed in the
nineties such as (RFC 1579, 1994) and (RFC 2228,
1997) in order to cope with them.
Those extensions did not make FTP a secure
enough protocol, as information travels in plain text
throughout the network. That is why it is nowadays
recommended to replace FTP with a more secure
protocol, such as SecureFTP (SFTP) or Secure Copy
Protocol (SCP), as they both provide encrypted
capabilities due to SSH usage.
All the above protocols work with TCP, hence
they implement error checking techniques and
acknowledgement (ACK) messages. On the other
hand, when transferring files within a secure Local
Area Network, Trivial FTP (TFTP) is quite often
substituted for FTP as it is much faster because of
working with UDP, although none of the above
features apply.
Nevertheless, FTP is still of much use in all kind
of computer networks as per today, so its formal
specification is fully justified.
Regarding communication protocols, they may
well be described by using Formal Description
Techniques (FDTs), as they provide unambiguous
descriptions, more precise than any other informal
descriptions made in natural languages (Turner,
1993).
There are some FDTs around, each one suiting
different kinds of protocols, but process algebras
(Padua, 2011) may be the more adequate ones in
dealing with concurrent distributed protocols.
Among them all, Algebra of Communicating
Processes (ACP) is the preferred one as it represents
such protocols as a set of equations according to its
behaviour, thus abstracting away from its real nature
(Fokkink, 2007).
Regarding the formal description of FTP by
using ACP, there is not such information in the
literature. Therefore, in this paper we are going to
build up a model for a user and a server both
interacting by means of FTP in diferent situations, in
order to obtain the formal specification and
verification of such a model.
The organisation of this paper will be as follows:
first, Section 2 introduces FTP behaviour, then,
Section 3 shows some common FTP return codes,
next, Section 4 states the difference between Active
mode and Passive mode, after that, Section 5
presents the FTP model proposed, later, Section 6
performs the specification for the model proposed
focusing on running general commands, and in turn,
Section 7 studies specific commands run in Active
mode, whereas Section 8 does it in Passive mode,
362
Roig, P., Alcaraz, S. and Gilly, K.
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode.
DOI: 10.5220/0006465703620373
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2017), pages 362-373
ISBN: 978-989-758-265-3
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and finally, Section 9 will draw the final
conclusions.
2 FTP BEHAVIOUR
An FTP session established between a user and a
remote server needs two different TCP connections:
one for the control part and another one for the data
counterpart.
Regarding the control connection, it is unique as
it is set up at the very beginning of the interaction
and it is torn down at the very end. The user
employs an ephemeral port (eph), this is, a random
port higher than 1023, whose use is limited just for
the establishment of that connection. On the
contrary, the server always employs well-known
port 21.
Respecting the data connection, it is necessary to
open a brand new connection for each command run
for the user, where such connection will be closed
after the completion or abortion of the aforesaid
command.
As per the ports involved in the data connection,
it is to be distinguished between two working
modes. On one hand, in FTP active mode, the server
uses well-known port 20. On the other hand, in FTP
passive mode, the server uses an ephemeral port.
Anyway, the sequence of events for a user to
undertake an interactive session with an FTP server
is the following:
First, a control connection is established between
user and server,
Then, login credentials are required for the user
to access the server,
After that, the user will run a string of
commands, each one establishing and tearing
down an autonomous data connection,
And finally, when the user logs out or the FTP
session is over, the initial control connection is
torn down.
As per the control connection establishment, it is
performed by a well-known TCP 3-way handshake
in order to set up a connection.
With regards to the login credentials, it is usually
required the entry of a login user and a password in
order to get access, although it is sometimes
available a special user called anonymous, allowing
access to read-only content on a no-password basis
in order to obtain publicly available documents or
software updates.
With respect to the data connections, when the
user throws a command to the server, it is first
evaluated the FTP working mode, being active or
passive, then a new data connection is established in
order to undertake the action carried by that
command, and after completion, that data
connection is torn down.
However, the control connection opened up right
off the bat will still be established so as to allow new
commands to be run. So if another command is
launched at a later stage, the aforesaid process will
be repeated all over again, so a new data connection
will be set up and then closed.
As a side note, two different transfer kinds are
feasible, namely, ascii type (TYPE A), which is
faster as it needs 7 bits per character, but is only
available for only text-based files, and binary type
(TYPE I), which is slower, as it needs 8 bits per
character, but is available for all sort of files.
Finally, the FTP session will come to an end
when the command bye is launched by the user, and
that will cause the control connection to be torn
down.
Regarding the FTP commands run by the user, it
is to be distinguished between the Command Line
Interface (CLI) commands and the FTP internal
commands that the user actually sends to the server.
In this paper, we will be calling FTP internal
commands to the latter, whilst the former will be
referred to as FTP CLI commands.
The correspondance between the main FTP CLI
commands and its corresponding FTP internal
commands may be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: FTP CLI –vs– FTP Internal main commands.
FTP CLI
command
FTP Internal
command
Meaning
cd path CWD path change directory
ls LIST list directory
get file RETR file download a file
put file STOR file upload a file
b
ye QUIT close FTP session
3 FTP RETURN CODES
FTP server replies with a 3-digit return code,
standarised in RFC 959 and RFC 2228, followed by
some text. The number is intented to be used by
automata, each digit having a special meaning,
whereas the text plays its counterpart for human
users to understand that aforesaid 3-digit code.
The first digit shows the type of response, the
second digit states the kind of error, whereas the
third digit provides further detail of meaning for
each category defined by the second digit.
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
363
To sum it all up, Table 2 shows the most
commonly used return codes for the user to know
the state of the server.
Table 2: FTP server reply code.
Code Meaning Type
220 Service ready for new use
r
Success
331 User name OK, need password Success
230 User Logged in, proceed Success
530 Not Logged in
Error /
Incomplete
227 Entering Passive Mode Success
257 Create Directory successful Success
250
Change Working Directory
successful
Success
150
File status OK, about to open a
data connection
Success
550 Requested action not taken
Error /
Incomplete
200 Command O
K
Success
500
Syntax Error, command
unrecognise
d
Error /
Incomplete
226
Closing Data Connection,
requested action O
K
Success
426
Closing Data Connection, transfer
aborted
Error /
Incomplete
221
Service closing control
connection, logging ou
t
Success
421
Service not available, closing
control connection
Error /
Incomplete
4 FTP ACTIVE –VS– PASSIVE
FTP original specifications defaulted to Active
mode, but due to security concerns, nowadays the
number of FTP implementations choosing Passive
mode as default is ever increasing.
Both ways first establish the proper control
connection, but the differences arise when trying to
establish each data connection, just before running a
user command.
4.1 Active Mode
The user sends a PORT command including 6
parameters, composed by two hexadecimal
characters each. The first four ones (x1, x2, x3, x4)
represent the four octets composing its own IP
address and the last two ones (x5, x6) represent an
ephemeral port number on itself which will be used
to establish data connection with port 20 on the
server, according to the expression
62565 xx
.
That PORT command will be duly
acknowledged, this is, by means of a reply code 200.
Then, the data connection is established and the user
may in turn launch FTP commands to the server.
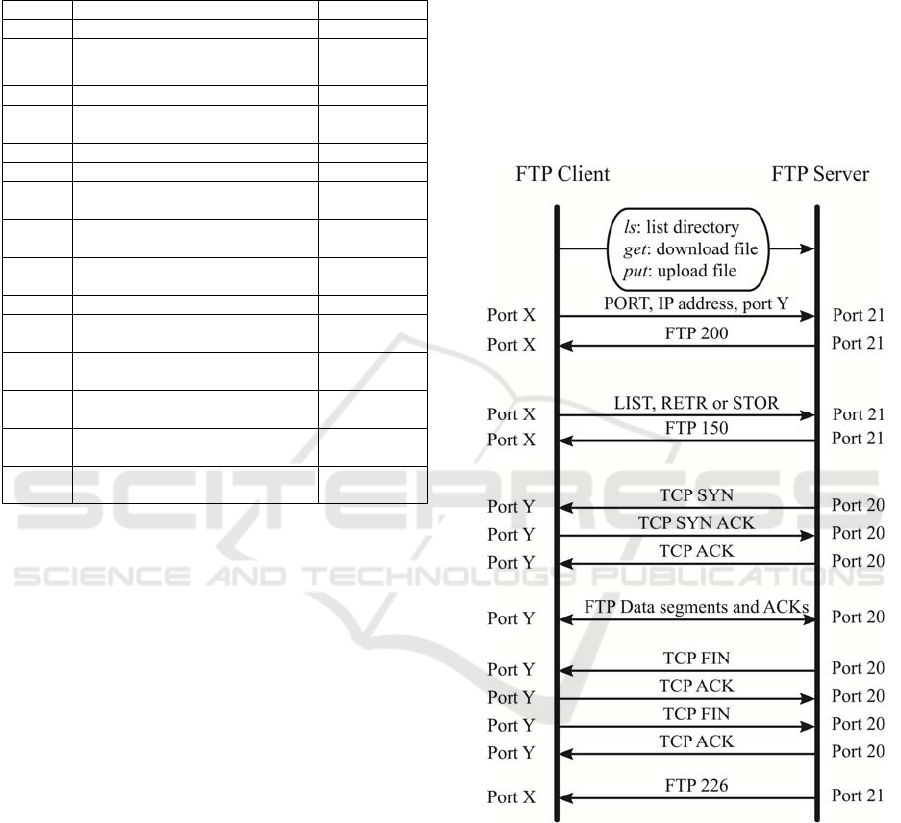
A simplified version of FTP active mode for
command launching is shown in Figure 1, being X
an ephemeral user control port and being Y an
ephemeral user data port. Acknowledgement
segments after each segment exchanged have been
avoided so as to make clearer the whole process,
despite taking them into account for the initial 3-way
handshakes and the final 4-way handshakes. Also, it
is shown the execution of just a single command,
although many of them might be executed
sequentially, until FTP session closes.
Figure 1: Executing a command in FTP Active Mode.
The main drawbacks for active mode are
twofold. The first issue is that server side starts data
connection to an ephemeral port on the user side,
requiring the use of stateful firewalls, always
looking out for FTP PORT commands. The second
problem is that this mode is prone to hacking attacks
by faking its arguments, this is, the user IP address
and port number.
In order to deal with those issues, Passive Mode
was designed, although the global behaviour for FTP
SIMULTECH 2017 - 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
364
commands remains the same as in Active Mode for
ls, get or put.
4.2 Passive Mode
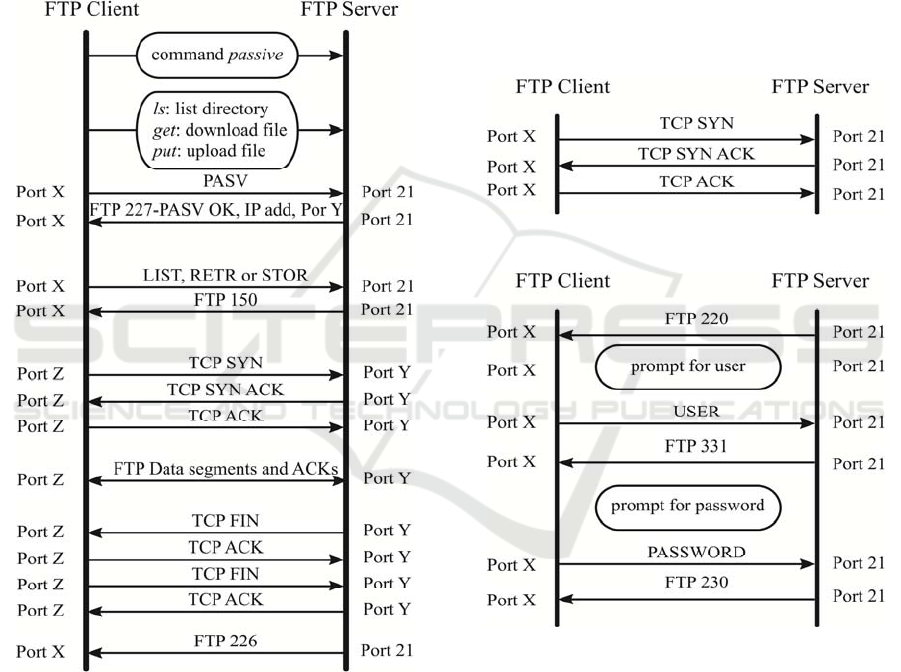
The user sends a PASV command to the server
stating its desire to enter passive mode. Then, the
server sends back a reply, including its own address
and also an ephemeral port number on itself for the
user to establish data connection with another
ephemeral port on the user, in a similar fashion as
explained previously.
Figure 2: Executing a command in FTP Passive Mode.
It is to be noted that passive mode is enabled by
launching the command passive on the prompt prior
to executing other commands. The passive mode
will be enabled until the command passive is run
again, which will be reverted the active mode.
A simplified version of FTP passive mode for
command running is exhibited in Figure 2, being X
an ephemeral user control port, being Y an
ephemeral server data control port and being Z an
ephemeral user data port.
Passive Mode behaviour is more secure than
Active Mode, although it may still cause trouble due
to clear text transfers.
5 FTP MODEL BASICS
The first step for building up an FTP model is to
identify the building blocks taking part in the FTP
protocol, as stated in Section II. Data transfer may
be performed in active or passive mode as shown
above, regardless of the rest of stages.
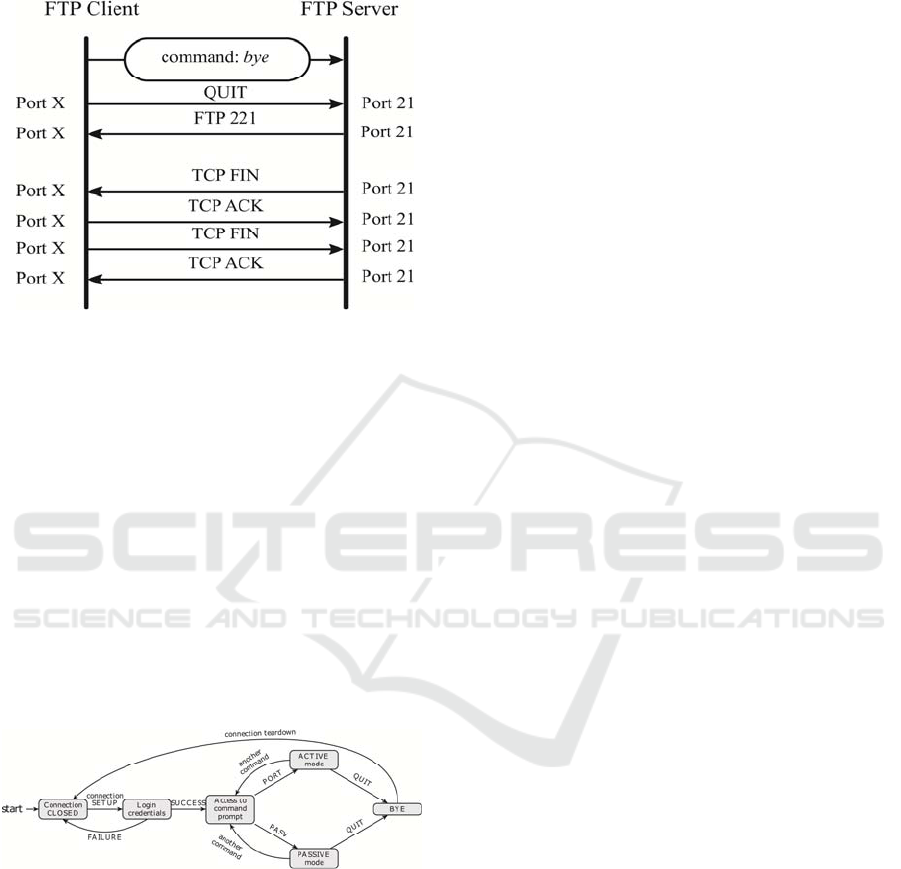
As per the control connection, it is to be quoted
the establishment, the login credentials and the tear
down, as shown below in Figures 3, 4 and 5.
Figure 3: Establishing a control connection.
Figure 4: Asking for Login Credentials.
Putting all together, the four blocks to be
considered have already been introduced, so the FTP
model to be designed needs to have them all
following the proper order given by the FTP
protocol specifications.
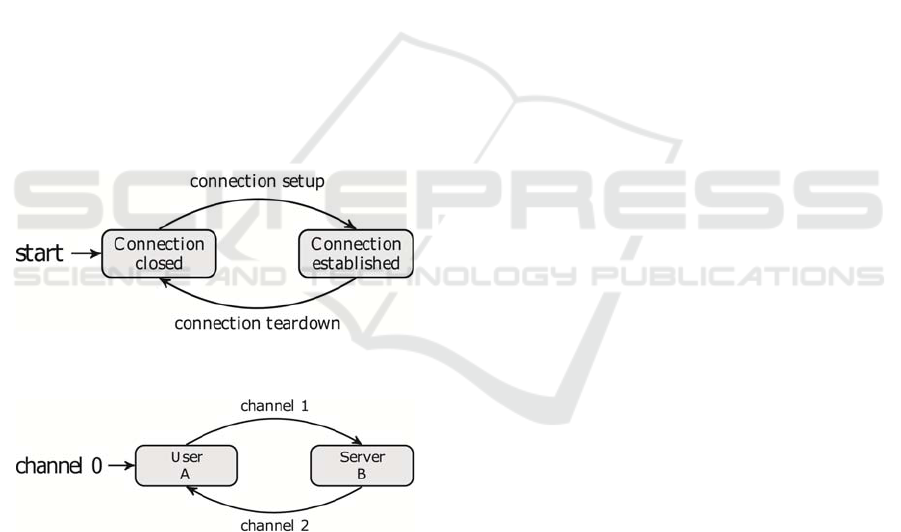
As stated above, Figure 6 gives the
representation of a whole FTP session. Initially,
every connection is closed, either the control one or
any data one. But at some point, 3-way handshake
will happen and the user will establish a connection
with the server. If the connection is a control one,
login credentials will be asked in order for the user
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
365
to access into the server. The client will use an
ephemeral port, whereas a server will use TCP port
21, establishing an FTP session if successful.
Figure 5: Tearing down a control connection.
Once the control connection is open and the
client is logged in successfully, the user may run
some FTP commands, opening a new data
connection for each command executed, and in turn,
closing it when the command launched has been
completed.
The steps to be taken when executing a
command will depend on the FTP mode chosen, that
being active or passive. As per file transfer mode, it
depends whether ascii or binary mode is selected,
although we will not be taking that into account.
Eventually, the FTP session will be closed,
whichever FTP mode is on, therefore, the control
connection will be torn down and the flow will come
back to the initial state.
Figure 6: State Diagram for an FTP session.
As previously said, the FTP model is going to be
built up by using ACP, following the axioms and
equations stated in (Bergstra and Klop, 1985) and
taking the models presented in (Fokkink, 2016) and
(Groote and Mousavi, 2014) as references. Further
research might be done by using the Expansion
Theorem shown in (Bergstra and Klop, 1986) that
permits to extend the model designed herein to more
than two entities (one user and one server) and even
more by using the detailed treatment of TCP in
(Lockefeer, Williams and Fokkink, 2016) in order to
make this model more robust and closer to what
happens in real life scenarios where different types
of errors and timeouts arise.
As per the nomenclature, we are going to
consider just two entities. We are going to have one
user trying to connect to the FTP server, which will
be regarded as entity A, whereas there is one server,
which will be regarded as entity B, and will always
be listening to that user, or entity 1.
Two atomic actions will be considered in the
model, hence sending and receiving messages, the
former being represented by s
x
and the latter by r
x
,
where x stands for 1 in case of communication
coming from the user or for 2 in case of
communication coming from the server, as the user
is always the one starting the interaction, whilst the
server is always passively awaiting for receiving a
connection.
Those actions will have some parameters, such
that the first one will be the source port, the second
one will be the destination port, and the last one will
be the relevant information involved in that
message, such as FTP response codes, TCP flags,
commands or any other key words.
An encapsulation operator
H
will be
introduced to force internal actions into
communications. In this context, set H is formed by
all sending and receiving actions, in a way that if
they both share the same subindex and arguments,
communication will take place, whereas it will yield
deadlock otherwise, represented by
.
Additionally, loops with an exit will be discarded
by applying CFAR property, thus assuming that at
some point the exit of such a loop will eventually be
taken. Finally, an abstraction operator
I
will hide
all internal communication actions, hence just the
input and output relation of the model remains,
turning the model into a black box. In this context,
set I is formed by all internal communications.
Therefore, with the help of ACP, the desired
model for the whole FTP session may be conceived
as an outer connection, that being the control
connection, which envolves the overall FTP
command exchange, followed by the login
credentials stage. At that point, a set of inner
connections will be opened and closed sequentially,
one for each command run on the user CLI.
Hence, the internal behaviour of the FTP
protocol will be enclosed by the control connection,
as initially the connection is closed, and finally it
will be closed again, as exhibited in Figure 7. Hence,
the difference from the user point of view between
SIMULTECH 2017 - 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
366
the starting point and the ending point of an FTP
connection will be whether the user has downloaded
any file.
6 FTP GENERAL MODEL
Taking into consideration the four building blocks
presented in the previous Sections, we are going to
specify them all step by step.
Regarding the subindexes of atomic actions,
namely, send and receive, they will bear the channel
identifier, as exhibited in Figure 8. So, all packets
flowing from user to server will have subindex 1,
whereas all packets flowing the other way around
will do subindex 2. Apart from that, when the user
initially attempts to connect to the server, this will
be considered as subindex 0.
Furthermore, the user will be considered as entity
A, whilst the server will be regarded as entity B. The
subindexes employed by those entities will be
lowercase letters, so as not to be confused with those
subindexes used for the channels. As an exception,
initial state for the user will be denoted by 0,
meaning closed connection.
Figure 7: State Diagram for a control connection.
Figure 8: State Diagram for ACP modelling.
6.1 Control Connection Setup
USER:
a
AstartrA )(
00
ba
ASYNephsA
),21,(
1
cb
AACKSYNephrA ),,21(
2
dc
AACKephsA
),21,(
1
SERVER:
a
BB
0
ba
BSYNephrB
),21,(
1
cb
BACKSYNephsB
),,21(
2
dc
BACKephrB
),21,(
1
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||()()||(
000 aaH
BAstartrBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 bbaaH
BASYNephcBA
)||(
),,21()||(
2
cc
bbH
BA
ACKSYNephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 ddccH
BAACKephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
This first building block just makes the connection
setup, in order for the control connection to
transition from connection closed to connection
established.
6.2 Login Credentials
USER:
ed
AephrA
)220,,21(
2
fe
AUSERephsA
),21,(
1
gf
AephrA
)331,,21(
2
hg
APASSephsA
),21,(
1
ih
AephrA
)230,,21(
2
SERVER:
ed
BephsB
)220,,21(
2
fe
BUSERephrB
),21,(
1
gf
BephsB
)331,,21(
2
hg
BPASSephrB
),21,(
1
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
367

d
ih
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)530,,21(
)230,,21(
2
2
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||()220,,21()||(
2 eeddH
BAephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 ffeeH
BAUSERephcBA
)||()331,,21()||(
2 ggffH
BAephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 hhggH
BAPASSephcBA
)||()530,,21(
)||()230,,21()||(
2
2
dd
iihhH
BAephc
BAephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
This second building block undertakes the login
credentials, in order for the server to grant access for
the user to the server.
6.3 FTP CLI Command: MKDIR
<Path>
USER:
ji
AMKDephsA
),21,(
1
i
ij
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)550,,21(
)257,,21(
2
2
SERVER:
ji
BMKDephrB
),21,(
1
i
ij
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)550,,21(
)257,,21(
2
2
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||(),21,()||(
1 jjiiH
BAMKDephcBA
)||()550,,21(
)||()257,,21()||(
2
2
ii
iijjH
BAephc
BAephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
ryMKDdirectoBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
The mkdir command creates a new directory onto
the FTP server bearing the name stated as the
compulsory argument. The default location for that
directory will be the current working directory,
although it might be any other one if a pathname is
provided along with the directory name. So, the
external behaviour is a new directory on the server,
either inside the working directory or in the path
provided.
6.4 FTP CLI Command: Cd <Path>
USER:
ji
ACWDephsA
),21,(
1
i
ij
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)550,,21(
)250,,21(
2
2
SERVER:
ji
BCWDephrB
),21,(
1
i
ij
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)550,,21(
)250,,21(
2
2
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||(),21,()||(
1 jjiiH
BACWDephcBA
)||()550,,21(
)||()250,,21()||(
2
2
ii
iijjH
BAephc
BAephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
The cd command changes the working directory to
another existing directory onto the FTP server on the
pathname presented by the compulsory argument
following this command. This change in the working
directory does not make any difference in either the
user or the server.
SIMULTECH 2017 - 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
368

6.5 FTP CLI Command: Bye
Control Connection Teardown
USER:
ji
AQUITephsA
),21,(
1
kj
AephrA )221,,21(
2
lk
AFINephrA
),,21(
2
ml
AACKephsA
),21,(
1
nm
AFINephsA
),21,(
1
02
),,21( AACKephrA
n
SERVER:
ji
BQUITephrB
),21,(
1
kj
BephsB )221,,21(
2
lk
BFINephsB
),,21(
2
ml
BACKephrB
),21,(
1
nm
BFINephrB
),21,(
1
02
),,21( BACKephsB
n
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||(),21,()||(
1 jjiiH
BAQUITephcBA
)||()221,,21()||(
2 kkjjH
BAephcBA
)||(),,21()||(
2 llkkH
BAFINephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 mmllH
BAACKephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 nnmmH
BAFINephcBA
)||(),,21()||(
002
BAACKephcBA
nnH
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
This last building block just makes the control
connection tear down, in order for the control
connection to transition from connection established
to connection closed. At that point, the FTP session
is closed.
6.6 Control Connection Timeout
USER:
02
)421,,21( AephrA
i
SERVER:
02
)421,,21( BephsB
i
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||()421,,21()||(
002
BAephcBA
iiH
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
When a connection timeout happens, the server
immediately closes its control connection to the
user, thus making the user disconnected from the
server.
7 FTP MODEL IN ACTIVE MODE
The three most important commands used in FTP
sessions are list, get and put. The first one lists the
content of the current directory, the second one
transfers a file from server to user, and the third one
does it the other way around.
All three commands are going to be modelled for
FTP Active mode by using ACP. The modelling are
going to be started right after the login credentials
have successfully been introduced, as the previous
commands have also been modelled. For data
connections, eph’ is used by the user.
7.1 FTP CLI Command: Ls
USER:
j
i
Axxxxxx
PORTephsA
)6,5,4,3,2,1,
,,21,(
1
kj
AephrA
)200,,21(
2
lk
ALISTephsA
),21,(
1
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
369

i
ml
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)550,,21(
)150,,21(
2
2
i
nm
AephrOK
OKASYNephrA
)425,',20(
),',20(
2
2
on
AACKSYNephsA
),20,'(
1
po
AACKephrA ),',20(
2
qp
AFTPDATAephrA ),',20(
2
i
rq
AephsOK
OKAFTPACKephsA
)426,20,'(
),20,'(
1
1
sr
AFINFTPDATAephrA ),',20(
2
ts
AFINephrA
),',20(
2
ut
AACKephsA
),20,'(
1
vu
AFINephsA
),20,'(
1
wv
AACKephrA ),',20(
2
i
iw
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)451,,21(
)226,,21(
2
2
SERVER:
j
i
Bxxxxxx
PORTephrB
)6,5,4,3,2,1,
,,21,(
1
kj
BephsB )200,,21(
2
lk
BLISTephrB
),21,(
1
i
ml
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)550,,21(
)150,,21(
2
2
i
nm
BephsOK
OKBSYNephsB
)425,',20(
),',20(
2
2
on
BACKSYNephrB
),20,'(
1
po
BACKephsB ),',20(
2
qp
BFTPDATAephsB ),',20(
2
i
rq
BephrOK
OKBFTPACKephrB
)426,20,'(
),20,'(
1
1
sr
BFINFTPDATAephsB
),',20(
2
ts
BFINephsB
),',20(
2
ut
BACKephrB
),20,'(
1
vu
BFINephrB
),20,'(
1
wv
BACKephsB
),',20(
2
i
iw
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)451,,21(
)226,,21(
2
2
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||()6,5,4,3,2,1,
,,21,()||(
1
jj
iiH
BAxxxxxx
PORTephcBA
)||()200,,21()||(
2 kkjjH
BAephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 llkkH
BALISTephcBA
)||()550,,21(
)||()150,,21()||(
2
2
ii
mmllH
BAephc
BAephcBA
)||()425,',20(
)||(),',20()||(
2
2
nn
nnmmH
BAephc
BASYNephcBA
)||(
),20,'()||(
1
oo
nnH
BA
ACKSYNephcBA
)||(),',20()||(
2 ppooH
BAACKephcBA
)||(
),',20()||(
2
qq
ppH
BA
FTPDATAephcBA
)||()426,20,'()||(
),20,'()||(
1
1
iirr
qqH
BAephcBA
FTPACKephcBA
)||(
),',20()||(
2
ss
rrH
BA
FINFTPDATAephcBA
)||(),',20()||(
2 ttssH
BAFINephcBA
SIMULTECH 2017 - 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
370

)||(),20,'()||(
1 uuttH
BAACKephcBA
)||(),20,'()||(
1 vvuuH
BAFINephcBA
)||(),',20()||(
2 wwvvH
BAFINephcBA
)||()451,,21(
)||()226,,21()||(
2
2
ii
ttwwH
BAephc
BAephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
NotApplyBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
The ls command is usually run without any
argument, and in such a case, it lists the current
working directory onto the FTP server, showing
information about each file and subdirectories
located therein.
It may also be run with a pathname as an
argument, and then, two cases might be
distinguished, as such an argument might be a file or
a directory. The former case might send information
about that file, whereas the latter case might do it
about each file within that directory.
There is no external behaviour for this command
as it just send information about ítems within the
FTP server.
7.2 FTP CLI Command: Get
The modelling for this command is just like the one
presented for the ls command, except for the FTP
internal command launched from user to server,
given by step k.
This is the only step to be shown below, so as not
to repeat the rest of the steps previously exhibited
for the ls command.
USER:
lk
ARETRephsA ),21,(
1
SERVER:
lk
BRETRephrB
),21,(
1
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION
)||(),21,()||(
1 llkkH
BARETRephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
RETRfileBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
The get command retrieves a file from the current
working directory of the server to the user. That file
is given by its compulsory argument and the
command external behaviour is a new copy of the
file downloaded to the user.
7.3 FTP CLI Command: Put
The modelling for this command is also just like the
one presented for the ls command, except that the
command is run from user to server, given in step k,
and also for the FTP Data transfer, given by steps p,
q, r. The difference comes in the flow direction as
the user starts and finishes data transmission.
Those are the only steps to be shown below, so
as not to repeat the rest of the steps previously
exhibited for the ls command.
USER:
lk
ASTORephsA
),21,(
1
qp
AFTPDATAephsA
),20,'(
1
i
rq
AephrOK
OKAFTPACKephrA
)426,',20(
),',20(
2
2
sr
AFINFTPDATAephsA
),20,'(
1
SERVER:
lk
BSTORephrB
),21,(
1
qp
BFTPDATAephrB
),20,'(
1
i
rq
BephsOK
OKBFTPACKephsB
)426,',20(
),',20(
2
2
sr
BFINFTPDATAephsB
),20,'(
1
NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION
)||(),21,()||(
1 llkkH
BASTORephcBA
)||(
),20,'()||(
1
qq
ppH
BA
FTPDATAephcBA
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
371

)||()426,',20()||(
),',20()||(
2
2
iirr
qqH
BAephcBA
FTPACKephcBA
)||(
),20,'()||(
1
ss
rrH
BA
FINFTPDATAephcBA
EXTERNAL BEHAVIOUR:
STORfileBA
HI
))||((
00
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
The put command stores a file from the user to the
current working directory of the server to the user.
This file is given by its compulsory argument and
the command external behaviour is a new copy of
the file uploaded to the server.
8 FTP MODEL IN PASSIVE
MODE
The same three commands seen for Active mode (ls,
get, put) may be modelled for Passive mode, but just
ls is shown.
The differences between both modes are in data
connections, where port eph’ is used instead of port
20 on the server side whereas eph’’ is used by the
user side. Moreover, the data three way handshake
flow direction starts on the user.
USER:
ji
APASVephsA
),21,(
1
kj
AxxxxxxephrA
)6,5,4,3,2,1,227,,21(
2
lk
ALISTephsA
),21,(
1
i
ml
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)550,,21(
)150,,21(
2
2
i
nm
AephephsOK
OKASYNephephsA
)425,',''(
),',''(
1
1
on
AACKSYNephephrA ),'','(
2
po
AACKephephsA ),',''(
1
qp
AFTPDATAephephrA ),'','(
2
i
rq
AephephsOK
OKAFTPACKephephsA
)426,',''(
),',''(
1
1
sr
AFINFTPDATAephephrA
),'','(
2
ts
AFINephephrA
),'','(
2
ut
AACKephephsA
),',''(
1
vu
AFINephephsA
),',''(
1
wv
AACKephephrA
),'','(
2
i
iw
AephrOK
OKAephrA
)451,,21(
)226,,21(
2
2
SERVER:
ji
BPASVephrB
),21,(
1
kj
BxxxxxxephsB
)6,5,4,3,2,1,227,,21(
2
lk
BLISTephrB
),21,(
1
i
ml
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)550,,21(
)150,,21(
2
2
i
nm
BephephrOK
OKBSYNephephrB
)425,',''(
),',''(
1
1
on
BACKSYNephephsB
),'','(
2
po
BACKephephrB
),',''(
1
qp
BFTPDATAephephsB
),'','(
2
i
rq
BephephrOK
OKBFTPACKephephrB
)426,',''(
),',''(
1
1
sr
BFINFTPDATAephephsB
),'','(
2
ts
BFINephephsB
),'','(
2
ut
BACKephephrB
),',''(
1
vu
BFINephephrB
),',''(
1
wv
BACKephephsB
),'','(
2
i
iw
BephsOK
OKBephsB
)451,,21(
)226,,21(
2
2
SIMULTECH 2017 - 7th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
372

NON-DETERMINISTIC INTERACTION:
)||(),21,()||(
1 jjiiH
BAPASVephcBA
)||()6,5,4,3,2,1,
,227,,21()||(
2
kk
jjH
BAxxxxxx
ephcBA
)||(),21,()||(
1 llkkH
BALISTephcBA
)||()550,,21(
)||()150,,21()||(
2
2
ii
mmllH
BAephc
BAephcBA
)||()425,',''()||(
),',''()||(
2
2
nnnn
mmH
BAephephcBA
SYNephephcBA
)||(
),'','()||(
1
oo
nnH
BA
ACKSYNephephcBA
)||(
),',''()||(
2
pp
ooH
BA
ACKephephcBA
)||(
),',''()||(
2
qq
ppH
BA
FTPDATAephephcBA
)||()426,'','()||(
),'','()||(
1
1
iirr
qqH
BAephephcBA
FTPACKephephcBA
)||(),
,',''()||(
2
ss
rrH
BAFINFTPDATA
ephephcBA
)||(),',''()||(
2 ttssH
BAFINephephcBA
)||(),'','()||(
1 uuttH
BAACKephephcBA
)||(),'','()||(
1 vvuuH
BAFINephephcBA
)||(),',''()||(
2 wwvvH
BAFINephephcBA
)||()451,,21(
)||()226,,21()||(
2
2
ii
ttwwH
BAephc
BAephcBA
9 FINAL CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, the most commonly used FTP
commands have been modelled by applying ACP
rules, both in active and passive mode, proving that
FTP meets the requirements.
REFERENCES
RFC 959, 1985. File Transfer Protocol (FTP). IETF.
RFC 1579, 1994. Firewall-Friendly FTP. IETF.
RFC 2228, 1997. FTP Security Extensions, IETF.
Turner, K. J., 1993. Using Formal Description
Techniques: An Introduction to Estelle, Lotos and
SDL, Ed. John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Padua, D. A., 2011. Encyclopedia of Parallel Computing,
Ed. Springer, 1
st
edition.
Fokkink, W., 2007, Introduction to Process Algebra, Ed.
Springer, 2
nd
edition.
Bergstra, J. A. and Klopp, J. W., 1985. Algebra of
communicating processes with abstraction, in
Theoretical Comp. Science, Vol. 37, pp. 77-121.
Fokkink, W., 2016. Modelling Distributed Systems, Ed.
Springer, 2
nd
edition.
Groote, J. F. and Mousavi, M. R., 2014. Modelling and
Analysis of Communicating Systems, Ed. MIT Press,
1
st
edition.
Bergstra, J. A. and Klopp, J. W., 1984. Verification of an
Alternating Bit Protocol by Means of Process Algebra,
in LNCS, Vol. 215, pp. 9-23.
Lockefeer, L., Williams, D. M. and Fokkink, W., 2016.
Formal specification and verification of TCP extended
with the Window Scale Option, in Science of
Computer Programming, Vol. 118, pages 3-23.
FTP Algebraic Formal Modelling using ACP - Study on FTP Active Mode and Passive Mode
373
