
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud
Environment
Saadia Ghribi, Amel Meddeb Makhlouf and Faouzi Zarai
New Technologies and Telecommunications Systems(NTS’Com) Research Unit, ENET’COM, University of Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Intrusion Detection, DDoS, Agents, Correlative Algorithm.
Abstract: In recent years, Cloud Computing had met a rapid development and an increasing popularity that have boosted
the rate of its adoption. Pay for use, low-cost and rapid elasticity are some of advantages provided by Cloud
Computing. However, this technology is facing many security challenges caused basically by the
virtualization feature. Thus, Intrusion Detection is become crucial to secure the cloud environment. In fact,
many security solutions have been proposed to overcome security issues and increase customers’ trust on
Cloud Computing paradigm. After discussing existing Intrusion Detection Systems, deployed for Cloud
Computing, we propose, in this paper, an approach that is based on cooperative and distributed intrusion
detection, where a Cooperative Intrusion Detection approach is deployed for the Cloud Computing
architecture in order to reinforce its security. In the implementation, many DDOS attacks type have been
launched to test the performance of the proposed IDS. The experiment has lead to an effective Cloud IDS
with lower false positive rate.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, Cloud Computing is remained the most
potential technology that enterprises used to migrate
their applications and data. Cloud Computing offers
numerous benefits both to end users and businesses.
Pay for use, on demand self-service, low-cost and
rapid elasticity are some of features contributing to
the popularity of the Cloud Computing. However,
many security challenges and vulnerabilities are
facing this technology because of the multi-tenancy
and virtualization related to the Cloud Computing.
There are many types of attacks through which data
can be hacked or damaged. For instance, DDOS
attack attempts to compromise the availability of
cloud resources, Malware Injection attack where
applications and embed malicious codes into it that
changes the course of its normal execution. Thus,
intrusion detection is becoming the biggest concern
that can influence the adoption of Cloud technology.
Companies and customers have to trust their cloud
service vendors that they will protect their data. It is
the up to the cloud service providers to manage,
protect and retain them. Hence, Intrusion detection is
becoming a necessity in order to secure cloud
environment. Using Distributed Intrusion Detection
System (DIDS) is very crucial for cloud security,
because it deals with heterogeneous environments,
where monitoring and controlling all the network
traffic to allow early threat detection. An IDS is based
on three main components (Rashmi MR, 2015)
Information Collection Agent, Data Analysis Agent
and Response Agent. With these agents, IDS
evaluates and controls a huge volume of data
collected from different network access points.
However, the commonly used IDS brings some issues
that the most common one is the absence of
cooperative layer detection. This can limit IDS’s
performance.
To enhance the way of detecting intrusions in the
cloud networks, we propose a cooperative intrusion
detection approach using agents deployed in each
layer of the cloud network. In fact, Cloud Computing
is composed of three layers: Software as a Service
(SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). These layers offer
different services to end users and have a deep
dependency between them. Therefore, any threat at
any Cloud layer can compromise other layers. Each
agent is able to detect specific intrusions targeting a
specific layer by collecting attack's details based on
an up-to-dated signature database.
In the rest of this paper, we will define
requirements for successful IDS. We present some
36
Ghribi, S., Makhlouf, A. and Zarai, F.
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0006427100360044
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2017) - Volume 6: WINSYS, pages 36-44
ISBN: 978-989-758-261-5
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
existing Intrusion Detection Systems and their major
related issues (Section 2). Further, we review our
proposed solution architecture for a cooperative IDS
based on the cooperative between cloud computing
layers in the intrusion detection (Section 3). In
Section 4, we discuss the implementation issue of the
proposed approach. Section 5 introduces a
comparison study with an existing distributed
intrusion detection approach. Section 6 concludes the
paper.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Existing Intrusion Detection
Systems
An efficient Intrusion Detection System must
guarantee some requirements like real-time,
adaptability and scalability. These mentioned
requirements (Y. Wang and C. Wang, 2015) have
brought many researches in order to make a new
generation IDS that feet all these requirements. Often,
IDS is commonly composed with five components
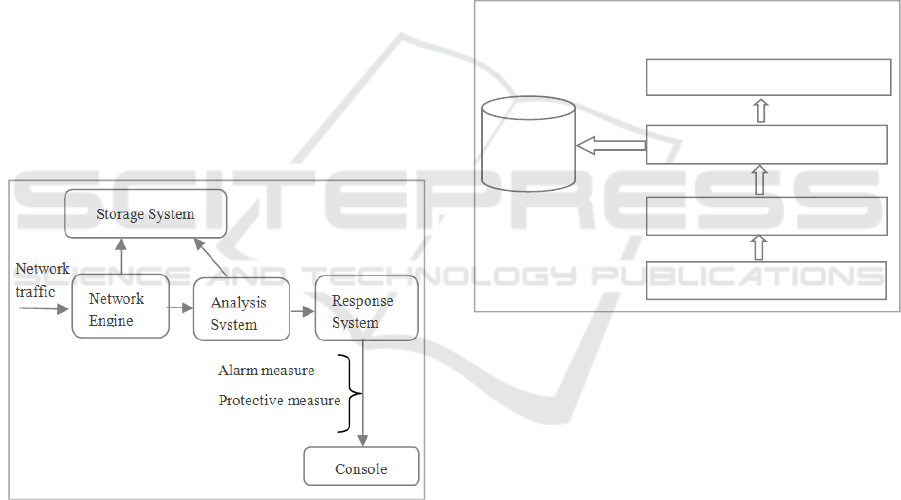
that are illustrated in Fig.1.
Figure 1: IDS’s components (Y. WANG AND C. WANG,
2015).
The principal function of Network Engine is to read
all network traffics (protocol, port, subnets …) and
communicate it to the Analysis System which is
considered as the core of the IDS. It is responsible for
detecting intrusions. The Analysis System contains a
pretreatment module, a rule knowledge base, a
protocol analysis module, a data analysis module and
secure communications of five parts. It role is to
analyze data received from Network Engine. When
an intrusion is detected, the Response System has to
make the corresponding measure: alarm measure or
protective measure. These measures are
communicated to the Console in order to be shown to
users. To perform intrusion detection, many solutions
have been developed.
2.1.1 Intrusion Detection System using
Mobile Agent
This proposed solution adds Mobile Agent (MA) in
order to improve the functionality of the IDS. First of
all, MA is an autonomous software program
consisting of data and code that can migrate from one
machine to the other and resume its execution on the
destination machine. It role is to correlate all
suspicious events occurred in different monitored
hosts. The architecture of this proposed technique is
given by Fig.2. (Y. Mehmood, M. A. Shibli, A.
Kanwal, and R. Masood, 2016)
Figure 2: IDS using Mobile Agent Architecture.
Every level contains specific agent that is able to
move from one machine to another. The Down Level
has a Sniffer Agent that is responsible for gathering
all events present in the host, using a sniffing file to
store the gathered data. The Sniffer Agent is an active
agent which is able to move from one location to
another. The Sniffing file is sent to the Pretreatment
Level, especially to the Filter Agent which will treat
all data collected from the Sniffing Agent and filter
them according to their destination or category of
packet (TCP, IP). The Kernel of IDS contains an
Analyzer Agent which has the role of analyzing data
coming from the Filter Agent. If there is a
correspondence with Attack Signature, this agent
alerts the Decision Agent in the Upper Level. The
Decision Agent will then take a decision according to
alert generated by the Analyzer Agent. Thus, this type
of IDS based on Mobile Agent shows superior
performance than centralized IDS and is able to report
intrusion instantly.
Attack
Signature
Down Level
Pretreatment Level
Kernel Level
U
pp
er Level
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud Environment
37
2.1.2 New Generation Ids
This IDS consists on predicting intrusions at early
time by collecting information about attackers. In
fact, this IDS use mobile agent to collect and
supervise the behavior of attackers in order to
generate alert if a specific activity or behavior has
been detected. The objective from New Generation
IDS is to create intelligent, autonomous and proactive
IDS. To achieve its functionality, this proposed IDS
uses intelligent and mobile agent to detect intrusions
based on attacker’s behavior (S. Khobragade and P.
Padiya, 2015). This model uses the honeypot to
attract attackers for anticipating and studding their
behavior. With these honeypots, attacker’s traces are
collected which make an early intrusion detection,
before the occurrence of the attack.
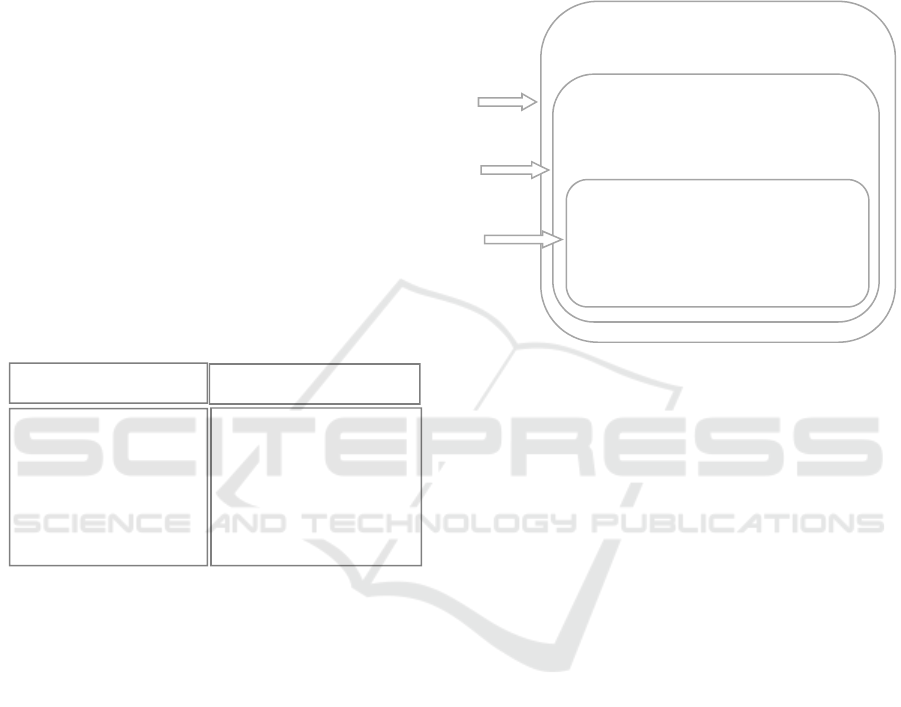
The architecture of New Generation IDS is
illustrated in Fig.3 where Mobile Agent uses
honeypots to monitoring network traffic and collect
information about attackers. Then, it makes the
corresponding changes to prevent system from
attacks.
Figure 3: Architecture of New Generation IDS.
2.2 Related Security Issues
We have presented some recent IDS solutions which
are based on using Mobile Agent to detect attacks in
the network. Mobile Agents are entities that analyze
and take predefined actions against malicious
activities. They could be applied as software running
on server and host or as separate devices segments.
These IDS solutions have provided many advantages
like:
Reducing Network Load: These Mobile Agents
work together in the network. Thus, data is
transferred from one agent to another which can
reduce network load.
Overcoming Network Latency: Agents operate
directly on the host.
Dynamic Adaption: These agents are
reconfigurable at run-time.
Upgradability: Signature database and the
detection algorithms are up-to-date.
Although, benefits offered by IDS based on Mobile
Agent, they bring many security issues that can affect
cloud computing layers. Security issues related to
cloud computing layers are illustrated in Fig.4 which
shows the high dependency between them.
Figure 4: Cloud Computing Layers.
Because of the deep dependencies between all layers
of Cloud architecture, any attack to any cloud service
layer can compromise the upper layers. Thus, our
proposed intrusion detection solution aims to make
cooperation between all cloud computing layers in
order to make efficient intrusion detection in cloud
computing environment.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH OF
COOPERATIVE IDS
In this section, we will expose firstly main attacks that
menace each cloud layer. Secondly, we will present
the objectives of the proposed system and its
architecture. Finally, a discussion section will be
introduced to expose the advantages and the
achievement of our solution.
3.1 Related Security Issues
3.1.1 Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
A denial of service (DoS) attack aims to make a
server or a network resource inaccessible to
users, sometimes by briefly interrupting or
suspending the services of a bunch connected to
the net. In cloud environment, the VM (VMware)
Honeypot
-Monitoring
Network traffic
-Ca
p
turin
g
data
-Analyzing data
captured
Mobile Agent
- Adapting changes
automatically according
to information captured
by Honeypot.
SaaS
P
aaS
IaaS
SaaS users have less control over
security
Two security software layers:
Security of the runtime engine and
Security of customer
applications.
Secure their systems to minimize
security threats that result from
creation, communication, etc.
WINSYS 2017 - 14th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
38

are used to launch a specific attack with the aim
of denying the normal service or degrading the
quality of services. One of the reasons why the
DoS attacks are very threatening is the automated
tool. Because of using the automated attack
process, if once the attacker finds the systems
with weak security, it does not take above 5
seconds to install the tool and attack the victim.
And it takes thousands of hosts only one minute
to be invaded (S. Khan and Z. Farooqui, 2016)
(Saadia Ghribi, 2016).
3.1.2 Data Breaches Attacks
In the case of a poorly designed multitenant Cloud
service database, a flaw in one client’s application
could allow an attacker access the data of that client
and all other clients. In 2012, researchers introduced
a side-channel attack by which one Virtual Machine
(VM) can extract private cryptographic keys on the
same physical machine. Mitigation of this threat is not
a simple task. One way of eliminating data breaches
is to encrypt all of the client’s data. However, if the
encryption key is lost, the client would have a
complete data loss. Thus, the client would need to
have a backup copy of the data, somewhere else, or
even offline backup. The client should keep in mind
that having more copies of the data would potentially
increase the probability of data breaches. (M. M.
Alani, 2014)
3.1.3 Cloud Malware Injection
It is the first considerable attack attempt that inject
implementation of a malicious service or virtual
machine into the Cloud. The purpose of malware cloud
is anything that the adversary is interested in, it may
include data modifications, full functionality
changes/reverse or blockings. In this attack adversary
creates its own malicious service implementation
module (SaaS or PaaS) or virtual machine instance
(IaaS), and add it to the Cloud system. Then, the
adversary has to pretend to the Cloud system that it is
some the new service implementation instance and
among the valid instances for some particular service
attacked by the adversary. If this action succeeds, the
Cloud automatically redirects the requests of valid user
to the malicious service implementation, and the
adversary’s code is executed. (Y. Wang and C. Wang,
2015)
3.1.4 Side Channel Attacks
Associate degree assaulter may decide to compromise
the cloud by inserting a malicious virtual machine in
shut proximity to a target cloud server then launching
an aspect channel attack. In a side-channel attack, the
attacker gains information about the cryptographic
technique used by analyzing physical characteristics
of the cryptosystem implementation. In Cloud
Computing, side-channels attacks are conducted
through gaining access to the physical node hosting
the target VM. This access can be available through
creating a VM in the same physical node that is
hosting the target VM. The attacker can keep creating
VMs in the Cloud until one VM is created in the same
physical node of the target VM. Afterwards, the
attacker can start collecting information necessary to
conduct the attack. An attacker attempts to
compromise the Cloud system by placing a malicious
virtual machine in close propinquity to a target Cloud
server system and then debut a side channel attack.
(S. Khan and Z. Farooqui, 2016)
3.1.5 Authentication Attacks
Authentication could be a liability in hosted and
virtual services and is often targeted. There square
measure many alternative ways that to manifest users.
For example, supported what someone is aware of,
has, or is. The mechanisms wont to secure the
authentication method and also the ways used square
measure a frequent target of attackers. Currently,
concerning the design of SaaS, IaaS and PaaS, there's
solely IaaS giving this sort of data protection and
encryption.
These categories of security attacks can affect
specific cloud layer and compromise it. We note also
that all these mentioned attacks are considered as
distributed attacks. (S. Khan and Z. Farooqui, 2016)
3.2 Objectives of the Proposed
Approach
The proposed solution aims basically to reduce the
impact of several types of attacks in the cloud
Computing. The architecture proposed in our work
includes two types of Intrusion Detection System
(IDS) placed at different Cloud model (IaaS or SaaS),
a correlative algorithm and Manager. The objectives
of this approach are grouped as follows:
Intrusion detection on IaaS and SaaS layers. We
use IaaS Based IDS (I-IDS) at IaaS layer to
collect and detect attacks specific to this layers
from all the attacked VM. In case of attack, I-IDS
updates its signature database and sends a
security alert including all information about the
attack to S-IDS located on the same physical
node.
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud Environment
39
Correlation between all generated security alerts
using a correlative algorithm that permits to
categorize received alerts into real attack or false
alert.
We used a Manager that manages all attack
scenarios obtained by different Correlator. Its
role is to store these signatures in order to use
them to rapidly detect intrusion in the whole of
cloud environment.
(Saadia Ghribi, 2016)
3.3 Components of the Proposed
Approach
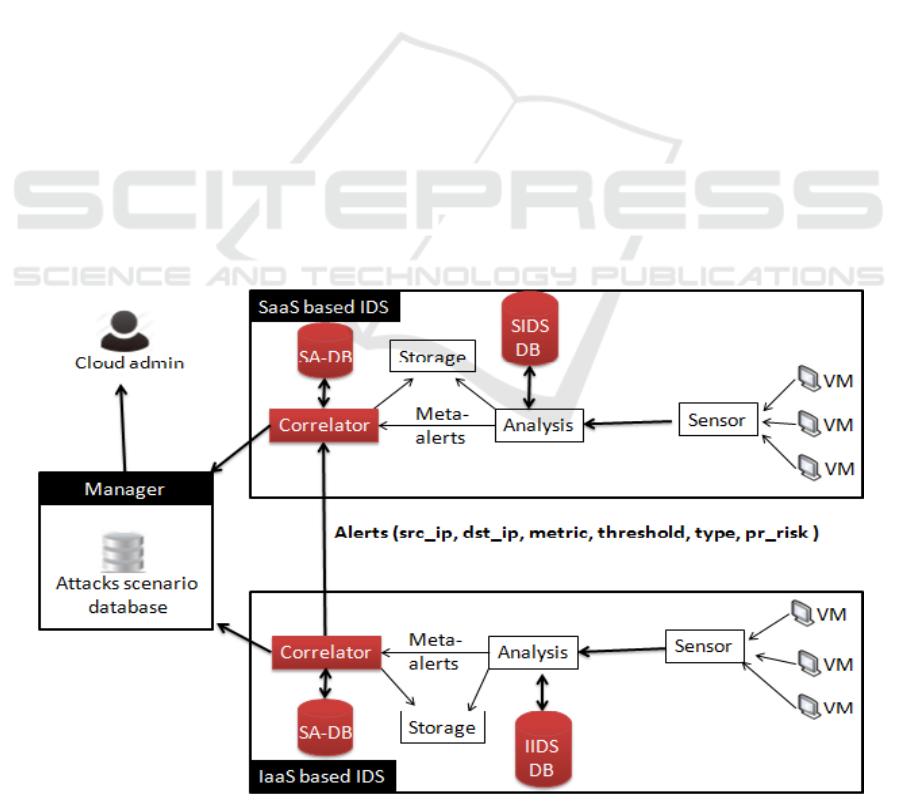
As shown in Fig.5, the proposed approach combines
two types of IDS: IaaS Based IDS (I-IDS) placed at
IaaS layer and SaaS Based IDS (S-IDS) placed at
SaaS layer. In fact, the IDS at IaaS is in charge of
collecting and detecting attacks related to IaaS layer
and the IDS at SaaS attempts to stop attacks related to
SaaS layer. Each layer based IDS is composed from
four main components: the Sensor, the Analysis unit,
the Storage unit and the Correlator. Sensors are used
to collect the network traffic which is used as an entry
for the Analysis unit. Based on related signature
database, the analysis unit analyses the collected data
in real time and detects the suspicious behavior from
gathered network traffic. In case of intrusion
detection, the analysis unit generates alerts that will
be sent to the storage unit and to the correlator. The
correlator uses a specific correlative algorithm in
order to correlate and categorize all received alerts. It
use a scenario attacks database to gather alerts into
groups of scenarios of attacks. The correlative
algorithm permits also to correlate scenario attacks
with other neighbor Cloud layers by sending alert
message containing all information about the detected
attack. A Manager unit stores data about detected
attacks and updates them if a new alert is generated.
IaaS/SaaS based IDS: The IDS is able to
perform real-time traffic analysis, content
searching and content matching. It comprises of
multiple components that communicate with
each others in order to detect intrusions
according to its signature database. It is
configurable and constantly updated. In our
proposed architecture, I-IDS is an IDS placed at
IaaS cloud model. Its role is to collect and detect
attacks that threat the IaaS layer. It is based on a
signature database. This database includes only
signatures of attacks specific to IaaS layer. The
second type of IDS is the S-IDS. It is an IDS
placed at SaaS cloud model. Its role is to collect
and detect attacks that threat the SaaS layer. It is
based on signature database that includes only
signatures of attacks specific to SaaS layer.
Sensor Agent: It is placed at the entry of the
network. Its basic role is to collect all network
traffic received from all VM in its
neighbourhood.
Figure 5: Proposed Architecture
WINSYS 2017 - 14th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
40
Analysis Unit: This component analyses, in real-
time, all data traffic received from Sensor
Agents. According to the signature database,
containing the attack signature specific to each
cloud layer, if a suspicious behaviour is detected,
the analysis unit provides a sequence of events
that reflects the type of the detected intrusion. In
fact, it generates the security alerts that are stored
into the storage unit in order to be used by the
Correlator.
Storage Unit: Its role consists on storing all
received alerts from the analysis unit. These
alerts will be the entry of the Correlator
component.
The IDS could generate large number of alerts with
true alerts mixed with false ones. Manually managing
and analyzing these alerts is time-consuming and
error-prone. Thus, Alert correlation (Patel, M.
Taghvi, K.Bkhtiyari, and J. Celestino Junior, 2013)
allows for automatic alert clustering, which groups
logically interconnected alerts into one groups and
allows easy analysis of attacks and enables network
administrators to launches appropriate response to
stop attacks and prevent them from escalating.
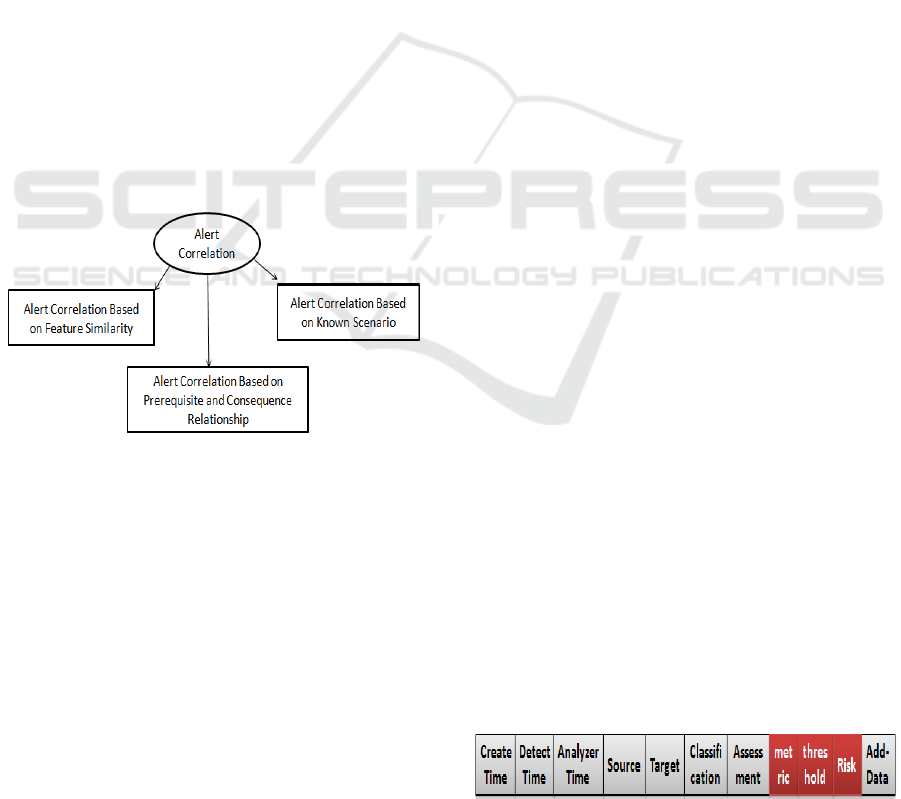
There are three types of Alert Correlation given by
Fig. 6.
Figure 6: Alert Correlation Categories
In the proposed approach, the Correlator component
is based on Alert Correlation.
Correlator: Correlating security events is the
key to an effective security management
solution. Thus, in our approach different security
alerts are given as inputs to the Correlator. This
correlator, based on a correlative algorithm,
involves collecting generated alerts from
different sources (I-IDS or S-IDS) and
normalizes them according to a Correlative
Algorithm. With this algorithm, normalized
events are fused into groups. These groups of
events are considered as complete description of
possible attack scenarios that are given to
Manager in order to be saved into a related
database.
Manager: The Manager collects all received
attack scenarios from the different Correlator and
stores them in a related database. A copy of the
scenario is also presented to Cloud administrator
for further actions. The database of the Manager
is used to synchronize all activities in order to
recognize and apply appropriate responses or
modify a particular component system or whole
network configuration.
3.4 Alerts Generated by Proposed
Architecture
In the proposed architecture, two categories of alerts
are generated: alerts in the same layer and alerts
between different cloud layers. All these alerts obey
to Intrusion Detection Message Exchange Format
(IDMEF). The standard IDMEF recommends an
XML representation of the alerts exchanged. In each
IDMEF message, we find basic entries: Create time
for date of creation of the alert, Detect time for alert
detection time by the analyzer, Analyser time for time
the alert was sent by the analyzer, Source for the
origin of the attack (node, user…), Target for target
of the attack, Classification for the name and
references of the attack, Assessment for the evaluation
of the attack (impact, severity…) and Additional data
to add other options for more detail.
We are based on IDMEF standard and we add new
entries specific to every layer based IDS.
- Alerts in the same layer (IaaS to IaaS): In this
case, the alert message is sent by Correlator on I-IDS
to Correlator on neighbor I-IDS when an intrusion has
detected. This alert is used in order to notify the I-IDS
on the neighborhood about detected attacks in the I-
IDS located in the same physical node. This alert
format is given by Fig.7. There are three new added
entries to the IDMEF. They are used to give more
information about the detected intrusion:
Metric: the metric used for attack detection like
Resources requested by the user, false positive rate…
Threshold: It indicates the maximum of the used
metric. If this threshold is exceeded, an alert will be
generated.
Risk: it is used to indicate the probability of the
risk caused by the detected attack.
Figure 7: Alert IaaS to IaaS format.
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud Environment
41

-Alerts between different layers (IaaS to SaaS): If
an attack is detected, these alerts are sent by
Correlator on I-IDS to the Correlator on S-IDS. This
type of alerts includes all information about the
detected intrusion (source IP address, destination IP
address, metric, threshold, IDS identifier, risk rate...).
The basic alert format is given by Figure 8.
Figure 8: Alert IaaS to SaaS format.
Comparing to the first type of alert format, we added
the type_id entry in order to indicate the type (I-IDS,
S-IDS or P-IDS) and the identifier of the IDS that sent
the alert. The identifier is a random number that
identify each IDS separately.
3.5 Proposed Correlative Algorithm
3.5.1 Correlative Algorithm at IaaS Layer
The Alert correlation on the I-IDS is assured by a
Correlator that operates as the following algorithm.
For(i=0; i<nbre_alert; i++){
If alert (i) exist on SaDB then
{
Add alert (i) into SaDB
} else {
Create new entry into SaDB
}
}
In fact, if the Correlator has received an alert from the
analyzer, it checks if this alert exists already in its
related Scenario Attack database. Two cases are here:
if the alert is related to an existent scenario attack
entry in alert scenario database (SaDB), it will be
added to this category of scenario attack. The other
case is if this alert is not related to any scenario attack
entry, then a new scenario attack entry will be added
into SaDB.
3.5.2 Correlative Algorithm at IaaS Layer
In SaaS layer, the cooperative algorithm operates as
the following algorithm:
For(i=0; i<nbre_alert; i++){
If alert(i) exist on SaDB and
prob_risk(alert(i))>str_risk(Sa) then {
Add alert(i) into SADB
update value of str_risk
} else if alert(i) exist on
SaDB and
prob_risk(alert(i))<str_risk(Sa) then {
Add alert(i) into SaDB
}
else {
Create new entry into SaDB
}
}
Thus, based on SaDB, the correlator checks if the
alert is related to an existing SaDB entry and the risk
probability is higher than the current risk probability
value, the alert will be included in the correspond
SaDB entry and the current risk probability will be
updated to the new risk probability value. In the other
case, only the alert will be added to the related SaDB
entry.
4 IMPLEMENTATION OF
PROPOSED IDS
In order to assess the overall performance of our
proposed IDS in a realistic scenario, a prototype of
the proposed architecture was implemented using the
Snort 2.9.9. Snort is an open source and signature
based network intrusion detection developed by
Sourcefire. It has been widely used for IPS/IDS
(Roesch, 1999). Snort uses a database of rules and
recognizes malicious traffic by matching it with these
rules. In the proposed IDS, we choose Snort as the
signature-based IDS. Snort instances with specific
signature database for every Cloud layer are used. In
fact, in each Snort instance we have activated rules
for detecting attacks menacing the related cloud layer.
The implementation of the proposed prototype has
been developed with Eclipse using java language.
Each agent is an IDS based on Snort and configured
to detect malicious activities against respective hosts.
In addition, each Snort agent is programmed to detect
malicious behaviour according to specific rules for
every cloud layer. We use also the open source library
JPCAP (Java library for CAPturing and sending
network Packets) for capturing and sending network
packets. Through this implementation, we have the
aim to focus on evaluating the performance of the
proposed architecture in terms of detection time and
false positive rates. During the evaluations, Detection
results are encoded in IDMEF.
To evaluate the proposed Cooperative IDS, we
have considered an attack model that contains mainly
well known distributed attacks facing the Cloud
environment. In Cloud, Attackers can target
bandwidth, processing power, storage capabilities
and resources of Cloud network. Thus, we have
interested to DDOS Attack in IaaS that can
WINSYS 2017 - 14th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
42

compromise other Cloud layer (SaaS, PaaS). To
detect this distributed attack, traces of intrusion have
to be collected from multiple hosts placed at every
layer and analyzed. This attack has also been used to
evaluate IDS using Mobile Agent and New
generation IDS to make a comparison with the
proposed IDS. We have considered in our experiment
the two type of DDOS attack: ping of death and smurf
which are well known examples of DDOS attack.
Ping of Death: The ping of death attack can
cripple a network based on a flaw in the
TCP/IP system. The maximum size for a
packet is 65,535 bytes. If one were to send a
packet larger than that, the receiving host
would ultimately crash from confusion.
Smurf: When conducting a smurf attack,
attackers will use spoof their IP address to
be the same as the victim’s IP address. This
will cause great confusion on the victim’s
network, and a massive flood of traffic will
be sent to the victim’s networking host, if
done correctly.
The first step in implementing a Cooperative IDS
is the identification of information that is required to
detect any suspicious behavior at every Cloud layer.
In fact, we have categorized attacks into groups
according to the target Cloud layer. Currently, the
logs generated by layer-based IDS are used as sources
of data for detecting any signs of intrusion behavior.
As we use Snort instance, we are focusing on
ddos.rules file. This file is used to save generated
alerts when one of the tested attacks (ping of death or
smurf) is detected. In fact, DDOS is the major attack
that can compromise Cloud environment and lead to
sophisticated damage on Cloud resources. In the
proposed approach, we have firstly created two snort
agents: the first using a signature database containing
only signature of attacks menacing the IaaS Cloud
layer. And the second snort agent is based on
signature database related to attacks on the SaaS
layer. We have also used an attacker agent that will
launch the ping of death attack at first and the smurf
attack on the target victim system. A java file
including the correlative algorithm has been also used
to guarantee the alert correlation assured by the
proposed Cloud IDS in case of intrusion detection on
one Cloud layer. In fact, in IaaS layer, the I-IDS
generates an alert that is sent to the Correlator on the
detection of any DDoS activity such as ping of death
or smurf. For instance, in case of ping of death, a large
number of continuous ICMP-ping requests for a
certain period of time in the Snort log file indicate
such a DDoS activity. The correspondent Correlator
gathers statistical data related to DDoS activity from
the IaaS based IDS that have reported such activity.
The Correlator uses the previous mentioned
correlative algorithm to correlate and gather all
received alerts. Then, the Correlator sends these
correlated alerts to Manager in order to be
communicated to the Cloud Administrator for further
actions. Another alert is also sent to the S-IDS with
more information about the detected DDOS activity.
All these alerts are encoding using the standard
IDMEF.
5 EXPERIMENT RESULTS AND
COMPARISON
The objective of this experimentation is to make the
system more generic and able to identify more types
of attacks through the categorization of attacks
specific to each Cloud layer. The use of distributed
system, interactions between agents placed on every
Cloud layer, which, as it uses several sources of
information, is expected to reduce the false positive
rates.
Thus, we evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency
of the proposed DDoS detection based on a
cooperative and distributed IDS by making a
comparison with IDSs using Mobile Agent. For
testing the attack detection capability and false
positive rates, different types of attacks (ping of
death, smurf) have being simulated from some VM
on the others. The current implementation has been
evaluated with regards to IDS effectiveness in
reducing false alert rate and then time of detection.
The ping of death and the smurf attacks were then run
against the target by the attacker to compare the
number of false positives produced by the proposed
Cooperative IDS and the IDS using Mobile Agent.
The results are shown in Figure 10. We notice that in
all this paper we considered IDS using Mobile Agent
as M-IDS and our Distributed and Cooperative IDS
as C-IDS. The false positive and true positive rates
are calculated as follows:
False positive rate =
Falsepositive
Totalalerts
x100
(1)
True positive rate =
Truepositive
Totalalerts
x100
(2)
Multi-layer Cooperative Intrusion Detection System for Cloud Environment
43
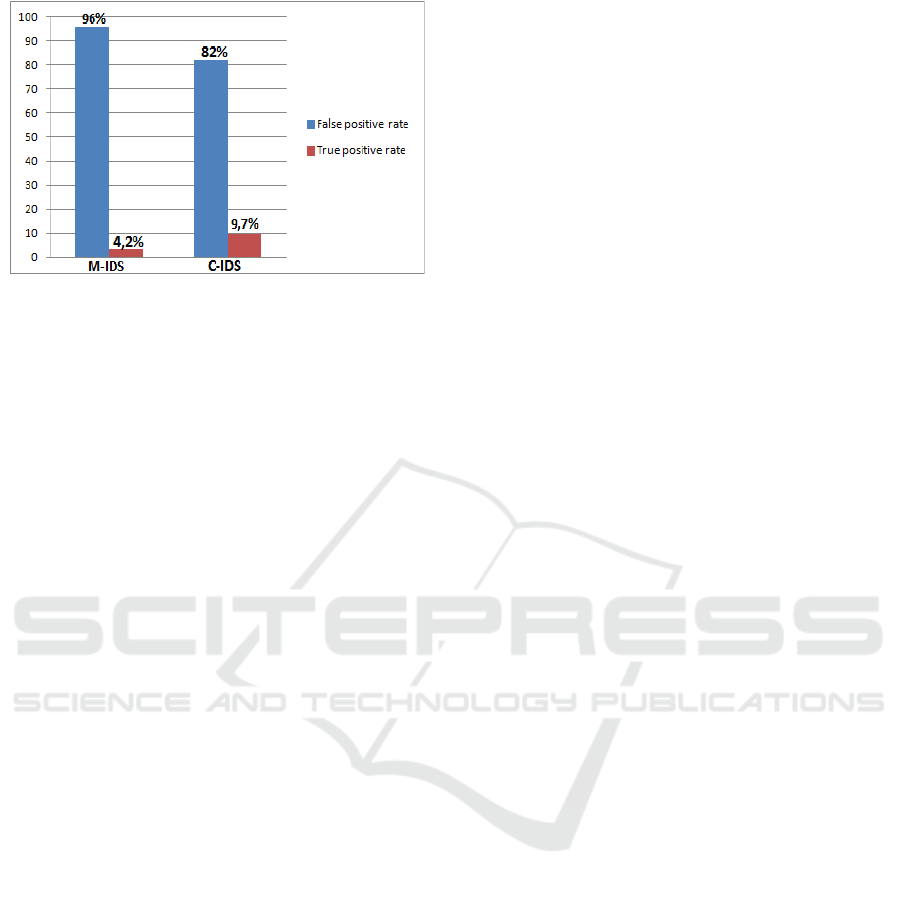
Figure 9: Alert rate in proposed C-IDS.
Figure 9 summarizes the results of the experiment,
where the number of false positives largely
overwhelms the number of generated true positives.
Thus, for the used types of DDOS attacks, the C-IDS
generates a lower false positive rate than the M-IDS. In
fact, in M-IDS, the lack of knowledge or awareness
about the complexity of network by IDS technology
has led to the generation of excessive amount of false
alarms. Thus, as in a good detection system, the rate of
true positives alerts should not be exceeded by the rate
of false positives generated alerts, the results show that
the performance of the proposed IDS is quite
encouraging particularly in terms of successful
detection of attacks. Also, the time spent on
aggregation and correlation alerts by the Correlator
component determines intrusion detection response
time of the IDS. In case of attack detection, this time is
lower in the proposed IDS comparing to the IDS using
Mobile Agent. This is due to the distribution of the alert
correlation among the cloud layers for the proposed
Cooperative IDS.
In summary, based to these results, we can
conclude that the proposed IDS enhances, efficiently
the cloud security per layer (IaaS, SaaS, PaaS). The
current proposed Cloud IDS has been implemented
using snort agent with specific database signature to
every cloud layer.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We have presented a distributed intrusion detection
system called Distributed and Cooperative IDS,
which addresses some of the disadvantages of the
existing distributed intrusion detection systems using
mobile agents. The Cooperative IDS employs static
agents as host monitors and Correlator component in
every Cloud Layer for the aggregation and correlation
of alerts between generated alerts, and to respond to
any attack at every Cloud layer. Cooperative IDS
guarantees the benefits of employing mobile agents
such as reduced network bandwidth usage, increased
scalability and flexibility, and ability to operate in
heterogeneous environments and adds more
important security features. Our proposed IDS is
developed to detect two types of DDoS attacks using
Snort instances with specific signature database and
placed at Cloud layers. This criterion has made the
proposed IDS more effective and convenient in term
of attack detection and false positive rate.
For future work, more development is needed to
improve the proposed IDS performance. So, we plan
to ameliorate the effectiveness of our proposed
approach in term of time detection and false positive
rate by implementing it in real cloud architecture.
REFERENCES
Rashmi MR., 2015. "A novel distributed intrusion detection
framework for network analysis". In International
Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology,
04(08), pages 246-251.
Y. Wang and C. Wang., 2015. "Based on the ant colony
algorithm is a distributed intrusion detection method".
In International Journal of Security and Its
Applications, 9(4), pages 141-152.
Roesch. M, 1999. "Snort-lightweight intrusion detection for
networks." In Proceedings of the 1999 USENIX LISA
conference. Pages 229-238
Saadia Ghribi., 2016. "Distributed and cooperative
intrusion detection in cloud networks." In Proceedings
of the Doctoral Symposium of the 17th International
Middleware Conference (p. 7). ACM.
Y. Mehmood, M. A. Shibli, A. Kanwal, and R. Masood,
2016. "Distributed intrusion detection system using
mobile agents in cloud computing environment”. In
Information Assurance and Cyber Security (CIACS),
2015 Conference.
S. Khobragade and P. Padiya, 2015. "Distributed Intrusion
Detection System Using Mobile Agent," International
Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology
(IJEIT), 5(4), pages 113-119.
M. M. Alani, 2014. "Securing the cloud: Threats, attacks
and mitigation techniques". In Journal of Advanced
Computer Science & Technology, 3(2), pages 202.
S. Khan and Z. Farooqui, 2016. “A survey on cloud security
and various attacks on cloud”. In International Journal
of Computer Applications, 147(14), pages 17-20.
A. Patel, M. Taghvi, K.Bkhtiyari, and J. Celestino Junior,
2013. “An intrusion detection and prevention system in
cloud computing: A systematic review”. In Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, 36(1), pages
25-41.
WINSYS 2017 - 14th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
44
