
Cells Microenvironment Engineering
Multiphoton Absorption for Muscle Regeneration Optimization
V. Errico
1
, R. Molinaro
2
, C. Gargioli
2
, F. Ferranti
3
, M. Dinescu
4
, S. Cannata
2
, G. Saggio
1
, S. Rufini
2
and A. Desideri
2
1
Department of Electronic Engineering, University of Rome “Tor Vergata”, Via del Politecnico 1, 00133, Roma, Italy
2
Departmement of Biology, University of Rome “Tor Vergata”, Via della Ricerca Scientifica 1, 00133, Roma, Italy
3
Italian Space Agency, Via del Politecnico snc, 00133, Roma, Italy
4
National Institute of Plasma Lasers and Radiation, 409 Atomistilor Street, 077125 Bucharest-Magurele, Romania
Keywords: Muscle Regeneration, Multiphoton Absorption, Myofibers, Extracellular Matrix, Polyethylene Glycol-
Fibrinogen, Hydrogel Matrix, C2C12, Cell Culture.
Abstract: The membrane-substrate interactions have a topological valence and represent a level of information ex-
change between the cell and the extra-cellular matrix and/or between cells. The interactions can vary with
boundary conditions and can be altered by varying the chemical and/or physical properties of the substrate.
The alteration can presumably result in differentiation or specialization of the cells, but this fundamental as-
pect must still be fully understood. In such a frame, we investigated the levels of transcriptional co-
activators YAP/TAZ throughout C2C12 differentiation on standard two-dimensional substrates and on pol-
yethylene glycol-fibrinogen three-dimensional microenvironment. In detail, we observed that the use of a
three-dimensional matrix permits an earlier differentiation in muscular cells when compared to standard bi-
dimensional substrates. On such a basis, we want to investigate the modulation of a more regular three-
dimensional pattern on cells proliferation response and we propose a matrix, generable with multiphoton ab-
sorption, with regular aligned channels in order to overcome the current limitation in muscle regeneration
techniques, so a possible tool to improve the myofibers formation and alignment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Biological organisms are able to colonize different
kind of environments and to live in severe environ-
mental conditions. In particular, bio-entities are able
to modify their characteristics in order to adapt suc-
cessfully to unfavourable conditions. There is a poor
knowledge about the effects at the cellular level of
the changes of the boundary conditions, albeit the
consequences on health can be of great importance.
At microscopic level, modification of the cells rela-
tionship with the environment may induce modifica-
tion of biological signals, thus variations of the sub-
strate can impose different growing and differentia-
tion conditions to the cells. There are direct connec-
tions between membrane proteins (i.e. integrins) that
anchor the cell to its substrate and the extracellular
matrix (ECM) determining the spatial relationship
of the cell in a tissue (Miranti and Brugge 2002).
The nature and the amount of the membrane-
substrate interactions have a topological valence and
represent a level of information exchange between
the cell with the substrate and with the neighbouring
cells. The same system of interaction translates mod-
ifications of these connections as intracellular sig-
nals able to modify the cell phenotype. The under-
standing of how cell-substrate interactions may
affect the cell phenotype encases a strong theoretical
and practical value: the prediction of the cells behav-
iour with the cellular microenvironment would al-
low, among possible applications, to improve the
methodology associated with tissue regeneration.
Here, we report on our recent results on cell
modification according to the culture substrate and,
as a proof of concept, we analyse the effect of bi-
dimensional and tri-dimensional environments on
the growing and differentiation of a mouse myogen-
ic C2C12 cell line. Moreover, as a feasible applica-
tion, we propose new substrate processing method-
ologies to assist muscle regeneration. We advise that
Errico, V., Molinaro, R., Gargioli, C., Ferranti, F., Dinescu, M., Cannata, S., Saggio, G., Rufini, S. and Desideri, A.
Cells Microenvironment Engineering - Multiphoton Absorption for Muscle Regeneration Optimization.
DOI: 10.5220/0005790402410246
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 241-246
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
241

a multi-photon absorption (MPA) procedure can be
able to control effectively the ECM physical and
structural properties, thus opening the way to assist
the formation of aligned myofibers for muscle re-
generation.
2 MUSCLE REGENERATION
Despite remarkable results in recent years have im-
proved the techniques for regeneration and restora-
tion of many damaged tissues, many challenges yet
remain unsolved. As an example, in the specific case
of the skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue, the genera-
tion of insufficient contractile force, the low density
of obtained cells, and the inadequate alignment of
myofibers are important issues especially for regen-
erating large portion of tissues. The presence of local
stimuli can likely properly direct differentiation and
restore small areas of damaged muscles, however, it
is difficult to re-establish the optimal muscle func-
tionality in the case of greater damage. Regardless of
the damage extension, the repair and regeneration of
muscle tissue follows mainly three phases. In the
first phase, the muscle fibers undergo necrosis and
release factors that result in the final recruitment of
inflammatory cells into the injured site (Toumi and
Best 2003; Tidball 1995). In the second phase the
macrophages phagocyte the necrotic muscle fibers
(Novak et al. 2014) and activate the muscle progeni-
tor cells, including satellite cells, inducing the for-
mation and vascularization of new muscle fibers
(Hawke and Garry 2001; Tidball and Villalta 2010).
During the last phase, the new formed fibers reor-
ganize and merge with the existing muscle fibers.
However, if important damage occurs, the scar tissue
formation rate is greater than the proliferation of
myoblasts and of the formation of myotubes. As a
result, the scar tissue prevents the proper myofibers
formation (Turner and Badylak 2012). Therefore, in
the event of extensive damage, the natural mecha-
nisms are not sufficient to restore the original mus-
cle functionality, so an external action is required to
overcome the lack of myofibers in the injured tissue.
2.1 3D Cell Culture and Myotubes
Alignment
A common methodology to support muscle regener-
ation is the direct cell delivery into the treatment
area. However, the survival rate of the donor cells is
extremely low. A possible way to increase it is to
embed cells within materials that maintain the via-
bility (Fuoco et al. 2012) while allowing the diffu-
sion of proliferation factors: ECM implantation
containing the cultured cells has a relatively good
success rate in muscle regeneration. This technique,
applied for injured tibial muscle of mice, induced a
greater regeneration when compared to the direct
injection of the same population of cells (Boldrin et
al. 2007). Two-dimensional ECM technique consists
in growing the cells in monolayers, followed by
superimposition of the different layers. In this case,
diffusion of the nutrients limits the two-dimensional
stacked substrates total thickness since diffusion
becomes critical upon increasing the thickness: cells
that suffer from a lack of nutrient supply exhibit
apoptosis. The realization of micro-patterned surfac-
es permitted to achieve the alignment of myotubes
on each layer and the improvement in the diffusion
of nutrients and oxygen to the cells, permitting to
reach a maximum thickness of 384μm (Bian and
Bursac 2009). Moreover, additional deposited cells
were able to bind and fuse to the myotubes previous-
ly grown, and to form myofibers oriented in the
direction of the underlying monolayer (Zhao et al.
2009). It was reported also that a three-dimensional
collagen sponges constituted of randomly oriented
tubular pores could stimulate the formation of al-
most aligned myotubes (Kroehne et al. 2008). Three-
dimensional rather than two-dimensional arrays are
to be preferred since they enable cells to have more
space to proliferate, permitting the three-
dimensional natural-like disposition of the cells,
allowing the simple vascularization of the construct
and supporting the formation of multinucleated
myotubes along the walls of the structure (Kamelger
et al. 2004). Thus, three-dimensional matrix, with
proper geometries, stimulate cells in order to form
myotubes available to repair large muscle defects.
Additionally, in the case of biodegradable matrices,
uniform degradation of the 3D structure permits the
formation of new tissues at their place (Saxena et al.
1999).
2.2 Substrate Contribution
The microenvironment is an important regulator of
cellular proliferation and differentiation. The rate of
in vitro proliferation of satellite cells, that are the
progenitors of muscle cells, decreases with each step
(Renault et al. 2000), whilst the satellite cells on soft
substrates are able to self-renew (Gilbert et al.
2010). As an example, on collagen-based substrate
(elasticity of 12kPa) the cells are able to maintain
their stemness (Urciuolo et al. 2013). Muscle cells
integrated in fibrin matrix may increase their in vivo
innervation from femoral nerve. Indeed, inserted
BIODEVICES 2016 - 9th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
242
myoblasts in fibrin gel and transplanted near the
femoral nerve in rats have demonstrated contractile
forces five times greater than the control samples
(Dhawan et al. 2007). Mature muscle fibers incorpo-
rated in a fibrin gel reported the induced formation
of acetylcholine receptor clusters, which is the key
factor for the development of neuromuscular junc-
tions (Wang et al. 2013).
Two transcriptional co-activators, YAP and
TAZ, mediate cellular response to mechanical stress
and ECM properties (Low et al. 2014). Phosphoryla-
tion regulates these proteins that shuttle between the
cytoplasm and the nucleus, where they interact with
TEAD transcription factors that in turn activate
proliferation. As an example, in human mammary
epithelial cells (MEC), growing on soft matrix, the
YAP/TAZ proteins are predominantly located in the
cytosol. At variance, in the same cell line, growing
on stiff material, the proteins migrate into the nucle-
us and become active (Aragona et al. 2013). It was
also demonstrated that YAP phosphorylation is
required for differentiation of the mouse myoblast
cell line C2C12 (Watt et al. 2010).
3 MATHERIALS AND METHODS
After the seed, we cultured C2C12 myoblasts in
growth medium (Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s me-
dium (DMEM) with 10% vol/vol foetal bovine se-
rum for 24 hours. After that, we changed medium
(DMEM without foetal bovine serum) to induce
differentiation. Cells were maintained in differentia-
tion medium up to 96 hours. We grew cells both on
bi-dimensional polystyrene substrate and on three-
dimensional substrate using a semi-synthetic hydro-
gel made from polyethylene glycol and fibrinogen
(PF). In the three-dimensional case we resuspended
cells in PF solution, then added the photoinitiator
(Irgacure™ 2959; Ciba Specialty Chemicals, USA)
and immediately exposed the solution to UV light
(365 nm, 4mW/cm2) for 5 minutes. We performed
western blotting in order to evaluate the differentia-
tion level. Primary antibody for the detection of
MyoD (1:500 #sc-760; Santa Cruz, California,
USA); P-YAP antibody (1:1000 #4911; Cell Signal-
ing Technologies); Tubulin (1:1500 #T5168; Sigma-
Aldrich).
Fluorescence observations were performed with
a confocal laser scanner microscope (Olympus
Fluoview 1000). Samples were prepared by fixing
the cells in 4% formalin solution and permeabilized
with triton X-100 0.3%. We used as primary anti-
body P-YAP (1:100 #4911; Cell Signaling Technol-
ogies) and MyHC antibody (prepared in our lab).
We choose as secondary antibody anti-mouse #sc-
2785 and anti-rabbit #sc-2090 both from Santa Cruz
(California, USA). We detected nuclei with 4,6-
diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).
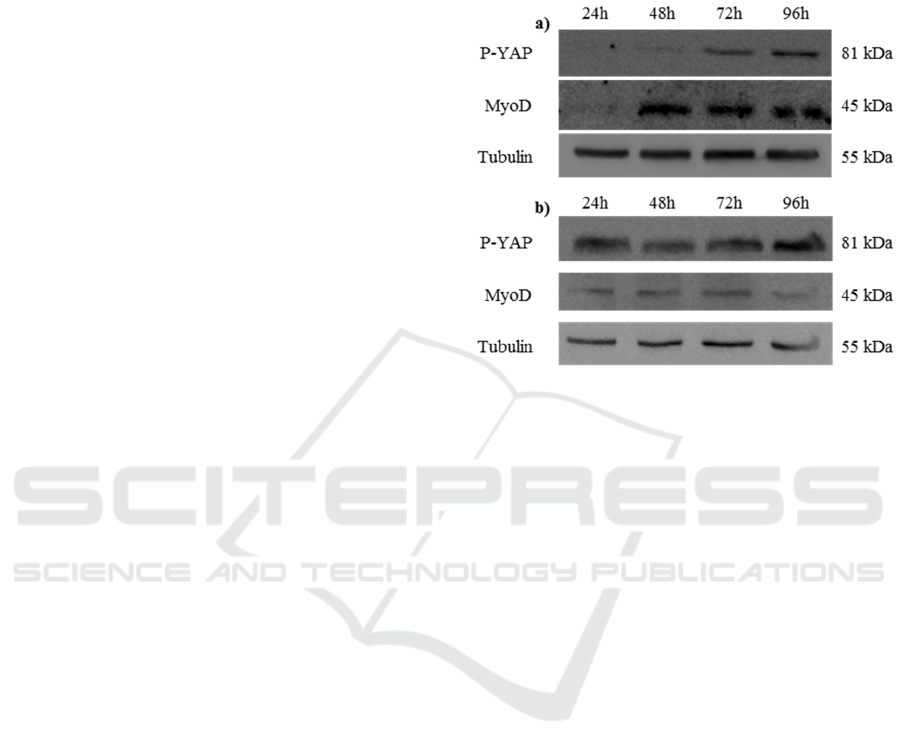
Figure 1: C2C12 cells cultured on a) bi-dimensional poly-
styrene and b) on three-dimensional PF hydrogels. Levels
of P-Yap, MyoD and Tubulin throughout C2C12 differen-
tiation.
4 RESULTS
We investigated the role of the substrate on the pro-
liferation/differentiation switch of myogenic C2C12
cells analysing the expression level of two differen-
tiation markers (i.e. the stiffness-activated YAP
protein and the transcription factor MyoD). We
analysed YAP phosphorylation level and MyoD
expression at regular intervals of 24 hours in cells
grown in standard bi-dimensional substrate or in
three-dimensional semi-synthetic hydrogel. As re-
ported in Figure 1, the time-dependent level of YAP
phosphorylation changes in the cells grown on the
two different substrates. Indeed, after 24 hours, the
P-YAP level is well detectable in the three-
dimensional hydrogel but undetectable in the bi-
dimensional substrate where its expression is evident
only after 72 hours. We also monitored the C2C12
ability to differentiate in muscle cells observing the
time-dependent MyoD expression. As visible in
Figure 1, the MyoD expression in cells, growing in
three-dimensional matrix, is evident after 24 hours,
but it occurs after 48 hours in cells grown in bi-
dimensional conditions. The results suggest that the
three-dimensional hydrogel represents a better me-
dium to promote cells differentiation when com-
Cells Microenvironment Engineering - Multiphoton Absorption for Muscle Regeneration Optimization
243
pared to the classic growth on two-dimensional
substrates.
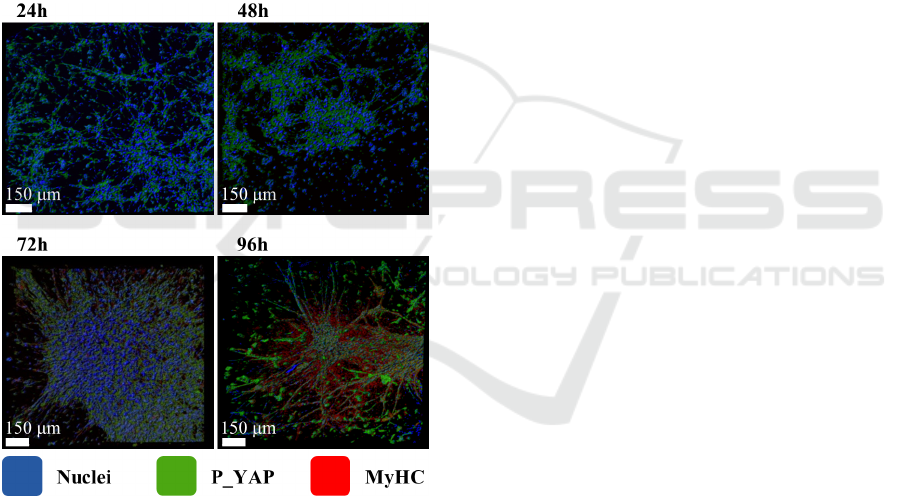
We investigated the morphological changes dur-
ing the differentiation processes of C2C12 cells in
three-dimensional PF matrix as shown in Figure 2.
Immunofluorescence analysis of C2C12 cells cul-
tured in PF hydrogels shows that both P-YAP
(green) and the muscle-specific myosin-MyHC (red)
increase as a function of time indicating the occur-
rence of cells differentiation. The nuclei alignment,
visible using counterstaining with DAPI (blue) also
indicates a time-dependent myotubes formation. We
were expecting a cell growth on hydrogel matrix
similar to a biological tissue since the cells of living
organisms sustain a three-dimensional arrangement.
However, the irregular internal network of the hy-
drogel induces random oriented myotubes as ob-
served in Figure 2 (96 hours).
Figure 2: C2C12 cells cultured in PF hydrogels. Immuno-
fluorescence shows P-YAP (green) and MyHC (red);
nuclei counterstaining with DAPI (blue).
C2C12 cells pre-cultured in three-dimensional
almost oriented pores of collagen sponges showed a
greater alignment of myotubes and a better contrac-
tile force than control culture (Kroehne et al. 2008).
Thus, an artificial matrix with perfectly aligned pore
structures could provide favourable conditions for
the optimal alignment of the forming myotubes and
consequently a good integration of the generated
tissue inside the natural muscle. We propose that
MPA technique can generate the required three-
dimensional matrix with perfectly oriented pores
resulting in an enhanced alignment of myotubes.
5 FUTURE DIRECTIONS
We propose the engineering of an artificial extracel-
lular lattice properly structured in order to encourage
the cells to differentiate and to align following pref-
erential micro-structured directions. Our expectation
is that the proper alignment of the satellite cells,
whose specialization generates fully functional myo-
fibers, will form an artificial muscle similar to the
natural case.
MPA permits the polymerization of photosensi-
tive material with a manufacturing repeatability of
the matrix lattice higher than other fabrication tech-
niques. Two Photon Polymerization (2PP)-Direct
Writing is a method allowing the construction of
complex 2D and 3D structures. Thus precise 3D
scaffold type microstructures can be produced al-
lowing the modelling and the reproduction of the
cellular microenvironment. The method is based on
the interaction of femtosecond laser radiation with a
monomer/photoinitiator/matrix (solvent) mixture
which induces a highly localized chemical reaction
leading to polymerization (Sima et al. 2013). During
the process, the simultaneous absorption of two
photons and the excitation of the molecules of a
photoinitiator takes place. The two photon absorp-
tion process presents a quadratic dependence on the
incident laser intensity (Gittard and Narayan 2010;
Weiß et al. 2009), leading to a subsequently
polymerization only in the vicinity of the focal point
(Belfield et al. 2000). Thus, the polymerization vol-
ume is much smaller compared to the dimension of
the focused laser spot (Matei et al. 2010). MPA
permits to growth cells on several symmetrical
three-dimensional structures and therefore to repli-
cate the same micro-environmental conditions to all
the cultures, thus permitting reliable statistical data
analysis. Replicas of an elementary unit produce
regular patterns that permits the cells to experience
the same local conditions thus perceiving amplifica-
tion of substrate-related effects. In addition, the
MPA matrix fabrication resolution down to 100 nm
(Sun and Kawata 2004) permits to easily realize
features fully compatible with the size of the cells,
since it has been observed that good alignment of
C2C12 murine cell line is achievable on 100μm
wide bi-dimensional micro-patches (Fuoco et al.
2015).
We expect that similar three-dimensional elon-
gated ducts realized inside the MPA matrices, as
BIODEVICES 2016 - 9th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
244

reported in the CAD modelling in Figure 3, can
improve the cells differentiation and alignment with
positive effects on their fusion helping the for-
mation of aligned muscle myofibers. Additionally,
the biodegradable material degeneration will allow
the already aligned myofibers to aggregate in the
space released by the dissolved matrix providing
fibers sorted as in a natural muscle.
Figure 3: MPA for better alignment of myotubes. Design
of three-dimensional matrix; a) orthographic view and b)
sectional view.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Cells may express a different phenotype depending
on the substrate properties. Proteins inside the mem-
brane permit to modulate the interactions of the cells
with the substrate: as an example, the phosphoryla-
tion of YAP (P-YAP) mediate the prolifera-
tion/differentiation processes and myogenic cells
grown on different substrates exhibit different levels
of P-YAP.
We investigated the levels of P-YAP during
C2C12 differentiation and achieved experimental
information on how the modification of the cellular
microenvironment and in particular of the substrate
dimensionality can influence the cells development.
The C2C12 ability to differentiate in muscle cells
was monitored following the MyoD expression. Our
conclusion is that the use of three-dimensional ma-
trices permits the cells to differentiate in muscular
tissue earlier than the standard bi-dimensional sub-
strates. Our results were confirmed in the three-
dimensional PF matrix with immunofluorescence
topographical analysis of P-YAP, MyHC and mor-
phological analysis of nuclei counterstained with
DAPI. The myofibers we obtain in this matrix are
random oriented whereas is desirable to use a medi-
um that boost cells differentiation into aligned myo-
fibers.
We are able to engineer properly the PF physical
parameters as the material stiffness, or components
percentage, even if the method does not permit to
exactly define the topography of the internal inter-
connections. Indeed, the applied diffused ultraviolet
light polymerises all the volume of the PF hydrogel
and creates random interconnections in the material.
The MPA technique permits the polymerization of
the material in a very small portion of the space
corresponding to the laser focus spot. The large
symmetry of the structures generated through the
MPA technique permits the definition of a regular
geometry of the matrix. Among feasible applica-
tions, we propose a MPA matrix with regular
aligned channels in order to help the alignment of
the myofibers and thus overcoming one important
limit of the currently used muscle regeneration tech-
niques.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by Italian Space
Agency (project no. 2014-035-R.0 “Effetto del mi-
croambiente sulla forza di adesione cellulare –
AFE”). We want to thank Gabriele Mascetti for his
support.
REFERENCES
Aragona, M. et al., 2013. A mechanical checkpoint con-
trols multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regula-
tion by actin-processing factors. Cell, 154(5),
pp.1047–1059. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/
j.cell.2013.07.042.
Belfield, K.D. et al., 2000. Near-IR two-photon photoiniti-
ated polymerization using a fluorone/amine initiating
system. Journal of the American Chemical Society,
122(6), pp.1217–1218.
Bian, W. and Bursac, N., 2009. Engineered skeletal mus-
cle tissue networks with controllable architecture. Bi-
omaterials, 30(7), pp.1401–1412. Available at:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.11.015.
Boldrin, L. et al., 2007. Satellite cells delivered by micro-
patterned scaffolds: a new strategy for cell transplanta-
tion in muscle diseases. Tissue engineering, 13(2),
pp.253–262.
Dhawan, V. et al., 2007. Neurotization improves contrac-
tile forces of tissue-engineered skeletal muscle. Tissue
engineering, 13(11), pp.2813–2821.
Fuoco, C. et al., 2015. In vivo generation of a mature and
functional artificial skeletal muscle. EMBO Molecular
Medicine, 7(4), pp.411–422.
Fuoco, C. et al., 2012. Injectable polyethylene glycol-
fibrinogen hydrogel adjuvant improves survival and
differentiation of transplanted mesoangioblasts in
acute and chronic skeletal-muscle degeneration. Skele-
tal Muscle, 2(1), p.24. Available at:
http://www.skeletalmusclejournal.com/content/2/1/24.
Cells Microenvironment Engineering - Multiphoton Absorption for Muscle Regeneration Optimization
245

Gilbert, P.M. et al., 2010. Substrate elasticity regulates
skeletal muscle stem cell self-renewal in culture. Sci-
ence (New York, N.Y.), 329(5995), pp.1078–1081.
Gittard, S.D. and Narayan, R.J., 2010. Laser direct writing
of micro- and nano-scale medical devices. Expert re-
view of medical devices, 7(3), pp.343–356. Available
at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC291
6174/.
Hawke, T.J. and Garry, D.J., 2001. Myogenic satellite
cells: physiology to molecular biology. Journal of Ap-
plied Physiology, 91, pp.534–551.
Kamelger, F.S. et al., 2004. A comparative study of three
different biomaterials in the engineering of skeletal
muscle using a rat animal model. Biomaterials, 25(9),
pp.1649–1655.
Kroehne, V. et al., 2008. Use of a novel collagen matrix
with oriented pore structure for muscle cell differentia-
tion in cell culture and in grafts. Journal of Cellular
and Molecular Medicine, 12(5a), pp.1640–1648.
Available at: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/j.1582-493
4.2008.00238.x.
Low, B.C. et al., 2014. YAP/TAZ as mechanosensors and
mechanotransducers in regulating organ size and tu-
mor growth. FEBS Letters, 588(16), pp.2663–2670.
Available at: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/
pii/S0014579314002981.
Matei, A. et al., 2010. Two Photon Polymerization of
Ormosils. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1278(1).
Miranti, C.K. and Brugge, J.S., 2002. Sensing the envi-
ronment: a historical perspective on integrin signal
transduction. Nat Cell Biol, 4(4), pp.E83–E90. Availa-
ble at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb0402-e83.
Novak, M.L., Weinheimer-Haus, E.M. and Koh, T.J.,
2014. Macrophage activation and skeletal muscle heal-
ing following traumatic injury. The Journal of Pathol-
ogy, 232(3), pp.344–355.
Renault, V. et al., 2000. Skeletal muscle regeneration and
the mitotic clock. Experimental Gerontology, 35(6-7),
pp.711–719.
Saxena, A.K. et al., 1999. Skeletal muscle tissue engineer-
ing using isolated myoblasts on synthetic biodegrada-
ble polymers: preliminary studies. Tissue engineering,
5(6), pp.525–531.
Sima, L.E. et al., 2013. Dermal cells distribution on laser-
structured ormosils. Journal of Tissue Engineering
and Regenerative Medicine, 7(2), pp.129–138. Avail-
able at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/term.507.
Sun, H.-B. and Kawata, S., 2004. Two-Photon Photopol-
ymerization and 3D Lithographic Microfabrication. In
NMR • 3D Analysis • Photopolymerization. Apvances
in Polymer Science. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp.
169–273. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/b944
05.
Tidball, J.G., 1995. Inflammatory cell response to acute
muscle injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 27(7), pp.1022–
1032. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub
med/7564969.
Tidball, J.G. and Villalta, S.A., 2010. Regulatory interac-
tions between muscle and the immune system during
muscle regeneration. American journal of physiology.
Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology,
298(5), pp.R1173–R1187.
Toumi, H. and Best, T.M., 2003. The inflammatory re-
sponse: friend or enemy for muscle injury? British
journal of sports medicine, 37(4), pp.284–286.
Turner, N.J. and Badylak, S.F., 2012. Regeneration of
skeletal muscle. Cell and Tissue Research, 347(3),
pp.759–774.
Urciuolo, A. et al., 2013. Collagen VI regulates satellite
cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration. Nature
Communications, 4(Article number: 1964), pp.1–25.
Wang, L., Shansky, J. and Vandenburgh, H., 2013. In-
duced formation and maturation of acetylcholine re-
ceptor clusters in a defined 3D bio-artificial muscle.
Molecular Neurobiology, 48(3), pp.397–403.
Watt, K.I. et al., 2010. Yap is a novel regulator of C2C12
myogenesis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research
Communications, 393(4), pp.619–624. Available at:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.034.
Weiß, T. et al., 2009. Two-Photon polymerization for
microfabrication of three-dimensional scaffolds for
tissue engineering application. Engineering in Life
Sciences, 9(5), pp.384–390. Available at:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200900002.
Zhao, Y. et al., 2009. Fabrication of skeletal muscle con-
structs by topographic activation of cell alignment. Bi-
otechnology and Bioengineering, 102(2), pp.624–631.
BIODEVICES 2016 - 9th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
246
