
Developing a Smart City by Operationalizing the Co-creation of
Value Model
Stephen Dawe and Chetan Sankar
Raymond J. Harbert College of Business, Auburn University, 405 W. Magnolia Ave, Auburn, AL, 36849, U.S.A.
Keywords: Co-creation Value Model, Smart City, Storm Drains, Infrastructure Projects, Data Analytics, Geospatial
Information Systems.
Abstract: This paper describes a project that used the co-creation of value model to collect and analyse data on storm
drains for a city so that it could become smarter in managing the water drainage issues. The city worked with
a University centre and ensured that the prerequisite conditions – mutual value-creation potential,
commitment and trust, and demonstrated delivery performance – were met. The project was able to integrate
science and technology through Information Systems, analyse, optimize, control, and monitor the conditions
of the 27,000 storm drains in the city, and enhance the decision making process of the city. This case study
provides an example of how a city and a university centre can co-create value thereby helping the city’s
management become “smarter” in managing its storm drains and the students obtain a rich field-based
educational experience.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the current popular jargons is “smart city” and
many cities are claiming to be one of them (Hollands,
2008). Unfortunately, there is little guidance for city
information technology (IT) departments and city
leadership as to what is required to be a smart city and
what models can be followed to become a smart city
(Doran and Daniel, 2014). Creating a smart city is
difficult, especially for smaller cities that do not have
the staff and the funds to take on large infrastructure
projects that require a large amount of funding and
technical expertise.
While many academic disciplines have researched
the societal impacts of a smart city on society, the
MIS community has only addressed this topic to a
limited extent. For example, Sankar and Cumbie
(2014) have created a co-creation of value model
where a university is the co-creator of value with a
city that is prone to disasters thereby making the city
smarter. We argue that the co-creation of value need
not be limited to a disaster recovery effort but for
other tasks as well. By partnering with universities,
smaller cities may benefit far more than their larger
city counter parts, simply through access to the
expertise present within universities. Universities in
and around smaller towns would benefit through
increased research opportunities and access to city
data.
According to the National League of Cities, in the
United State there are 19,235 cities with a population
under 100,000 (National League of Cities, 2015) and
therefore, the scope of the problem of making them
smarter is critical. As of 1997, almost 87% of U.S.
Cities and counties had adopted the use of a GIS
System (Esnard, 1998). The spatial nature of a city
and its infrastructure, makes using maps as excellent
place to display city resources and record their current
state. (Harrison et al., 2010).
Therefore, the research question addressed by this
paper is:
How to operationalize the co-creation of value model
for both a city government and a university so as to
create a project that can make the city smarter?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Smart City
Community Service Learning Project: Developing
a Smart City. Smart city is defined by Hall as “…a
City that integrates science and technology through
information systems, integrating the conditions of
Dawe, S. and Sankar, C.
Developing a Smart City by Operationalizing the Co-creation of Value Model.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2016), pages 47-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-184-7
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
47

their critical infrastructures, to better optimize, plan
and monitor resource utilization, and enhance the city
management’s decision making processes” (Hall et
al., 2000). There is significant disagreement and
concerns amongst different academic disciplines
within the academic community concerning the
implementation of “Smart City” technologies.
Technology companies are marketing and selling the
“Internet of Things” and how all these sensors can
monitor every movement within a city and analyze all
videos in real time (Taylor et al., 2015). This level of
mass surveillance has been criticized by many public
policy researchers as technocratic governance with
too much potential for abuse. In public administration
disciplines, concern over personal privacy is
generally seen to take precedence over the saving and
storing any personal information for long term usage.
This includes CCTV footage that includes personal
identifying features and vehicle tag information
(Shelton et al., 2015). In terms of technology, cities
must adhere to local privacy laws and must have the
appropriate governance and processes in place to
ensure their information systems are in compliance
with all local laws.
2.2 Key Success Factors of Co-Creation
Model
Co-creation, which is developing as a new paradigm
in the management literature, allows companies,
communities, and customers to create value through
interaction (Galvagno and Dalli, 2014; Rai et al.,
2010; Francesca et al., 2010). The way in which value
is created, distributed, paid for, and exploited differs
radically from the traditional demand vs supply
model. This is a well-researched area and Galvagno
and Dalli (2014) identify three different research
streams: service science, innovation and technology
management, and marketing and consumer research.
Our research will focus on collaborative and open
processes involving communities, universities, and
students and belongs to the innovation and
technology management studies stream (Alavi, 2012;
Zwass, 2010). According to this research stream, the
interaction between customers and companies, which
technological platforms often mediate, lead to
innovation, customer participation, and better
customer service. The value co-created by the
partnership between the university and the
municipality can be seen through the service-
dominant logic, that provide a focus on the process
rather than the final product Invalid source specified.
Value is always co-created, however, in our research,
there is not a sequential co-creation of value, but
value is relationally created between, the students,
university centre faculty and the city IT staff. (Vargo
and Lusch, 2011). Co-creation of value, from the
perspective of the university is in the processes and
class assignments done by the students, within the
context of a business analytics class, while the city
gains value through the production of data that can be
added to the GIS systems. The students gain context
for the possible use of the data, by contributing to the
collection process, and through interaction with
university centre faculty and city IT staff. (Vargo and
Lusch, 2011)
Given the importance of co-creation of value, it is
important to identify the critical success factors that
can lead to successful partnerships. Grover and Kohli
(2012) identify three factors that determine co-
created value: knowledge sharing, complementary
capabilities, and assets. Burdon and Feeny (2011)
discuss the difficulties in building competitive
advantage from alliances via innovation with
technical partners. They identify three prerequisites
for a successful partnership as mutual trust, mutual
commitment, and information exchange. We argue
that in the development of projects between a
university centre and a municipality, the critical
success factors will be a combination of these factors.
Complementary capabilities require that the
university centre and the municipality are committed
to utilizing compatible IT resources, such as hardware
and software. Prior to the project being released to the
classroom, the assets necessary, to perform the
project should be identified and it should be decided
whether the university centre or the municipality
should provide said assets. Information exchange
between the university centre and the municipality
should be continuous and wherever possible
unrestricted.
2.3 Develop a Research Model
We developed a research model (Figure 1) to answer
the question: How do incorporation of the key success
factors in a service learning project lead to effective
value co-creation for students and a community? The
key success factors were derived from earlier research
by Grover and Kohli (2012) and Burdon and Feeny
(2011). The community service learning project in
this study was development of a smart city through
better information on condition of storm drains.
Therefore, we used the expectations from a smart city
as discussed by Hall et al., (2000) to develop the
outcome of the model (Figure 1). When the
community service learning project includes the key
success factors, then there is a high probability of
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
48

achieving the outcomes – that of becoming a smarter
city. This model provides a framework for a
university centre and a city IT department to work
together to create community service learning
projects that enable the use of new technologies. We
used this model as a theoretical basis to develop a
project that helped a city become smarter by mapping
the location of the storm drain system. This model
provides a framework for a university centre and a
city IT department to work together to create projects
that enable the use of new, “smart” technologies. We
used this model as a theoretical basis to develop a
project that helped a city become smarter by mapping
the location of storm drains.
Figure 1: A Model of Co-Creation of IT Value.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Choice of the Community Service
Learning Project: Storm Drain
Data & Business Analytics Project
A service learning project was chosen so that it
incorporated the key success factors (knowledge
sharing and value creation potential, complementary
capabilities, shared assets, commitment, trust,
information exchange, and delivery performance)
identified in the research model (Figure 1). The Chief
Technology Officer (CTO) of the City had identified
GIS as a core strategic technology and wanted to use
GIS in all city processes and workflows. However,
the city did not have the in house expertise to make
this vision a reality nor did it have the financial
resources to commit to writing or paying consultants
to design and build custom applications. At the outset
of this partnership, in winter 2014, the university
centre (the centre) and city CTO spent several months
defining what the path to becoming a smart city is and
what projects could utilize a significant multi-year
investment in GIS technologies. Through these
meetings, the CTO understood what expertise was
available from the university and also understood
how the students’ learning would become part of the
design. By doing this, the CTO understood, that
students would be using experiential learning labs via
a specific class and therefore would be integrating
what work they did for the city and what they learned
into class (Chan, 2012). The centre had GIS mapping
equipment that was used in this project and the city
provided tools such as crowbars needed to lift the
storm drains. The City also shared its GIS database,
so the university and city both had access to the same
baseline of data. Thereby, both the centre and the
CTO understood the value-creation potential of the
project, had complementary capabilities, and agreed
to share assets.
To avoid many of the privacy concerns
promulgated by public administration and urban
planning researchers and to avoid entering in to a
project that could be seen as controversial, the city
and university chose a storm drain data collection
project to begin making the city smarter. By limiting
the project to one specific item, the storm drains, the
CTO and the Centre started a manageable project that
realized benefits for the city in a short period of time.
This project was also chosen because the city had
previously contracted with a private company to
collect information on all the storm drains’ GPS data.
The project with the private contract had been
running for three years, and the city had invested over
$375,000. The storm drain data was still incomplete
and while the city’s GIS application had the GPS
location of over 27,000 storm junctions stored, it was
estimated that 1000-3000 storm junctions still needed
to be located and added to the GIS database. The city
realized that the contractor had failed to collect drain
depth data for any drains. The city needed to go back
and measure the depth of every drain in the storm
drain system. This will allow the city to plan for flood
management based on rainfall forecasts, and to model
storm drain performance in different parts of the city
so as to meet EPA water drainage compliance rules
(U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2011).
Table 1: Case Study Design.
Yin’s Four Stages University Centre City
Planning
Written
requirements
documents
Needs analysis
and co-create the
requirements
document
Data Collection Collect depth data
Integrate into
ArcGIS maps
Analysis
Analyse results to
identify outliers
Analysis of
collected data
performed
Developing a Smart City by Operationalizing the Co-creation of Value Model
49
4 DESCRIPTION OF THE STORM
DRAIN PROJECT
4.1 Stages in Conducting the Storm
Drain Project
Yin (Yin, 2014) recommends that case study research
follow the stages of (a) plan and design, (b) prepare
and collect, (c) analyse, and (d) share. We used these
four stages in conducting the storm drain project and
describe the details in this section. (Table 1).
4.2 Project Plan and Design
This storm drain collection case study is a single
project with multiple phases that allowed students to
collect data on a city storm drain system and merge
this data with the existing data in a City’s GIS system.
The students then analysed this data and interpreted
their results.
4.3 Project Execution: Preparation,
Data Collection & Analysis
The city staff in cooperation with the centre built a
presentation so that students in each class understood
what the project was, what each type of storm
junction was, what data was going to be collected, and
safety requirements. This presentation was refined
each semester to take into account the class, the
objectives of the experiential learning, and the
technology being used by the students. The city also
took this opportunity to allow the students to fill out
the required city Human Resources’ paperwork for
work done within the City. The GPS devices were
programmed to collect the information. The GPS unit
could load the data directly into the ESRI GIS system,
once it was returned to the computer lab. This system
was tested by the graduate students and city staff to
ensure the data was collected, stored and loaded in to
the GIS system correctly. The centre divided the
students in to groups of three or four that would
conduct the learning activity for approximately 1 -2
hours.
4.4 Project Evaluation: Sharing and
Reporting
4.4.1 Phase 1: Importance of Correctly
Collecting Data
Upon return to class, the students reviewed the data
in class and reviewed the application and situation
within which GPS data and mapping data in general
could be used. Once the data was loaded in to the live
production ERSI GIS database for the city, the CTO
and GIS administrator returned to class to show the
students how their data was being used. This
presentation also included a lesson on how the city
uses GIS and a demonstration of how the student’s
collected data in particular would be used.
4.4.2 Phase 2: Business Analytics Influences
Decisions
During the data collection phase by the introduction
to MIS class, it was noted that there were issues with
the specialized GPS device. The CTO discussed with
the student why that was and explained why more
expensive and accurate GPS devices are needed. This
discussion had not taken place in the planning
sessions, but as the results from the tablet and the GPS
device were both useable, this allowed the students to
learn, how to choose the technology and accuracy
parameters required for a project to be considered a
success. The CTO also, attended the presentations
done by the students in the business analytics class.
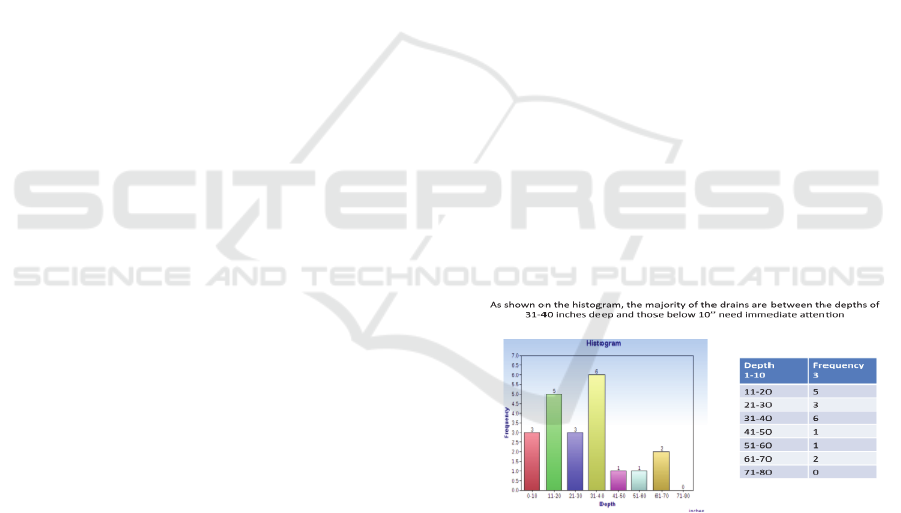
The students used graphs and bar charts to highlight
those storm drains where the depth was less than 10”
showing that these needed immediate attention
(Figure 2). They also produced charts that showed
damaged storm drains. The CTO used the outlier
analysis provided by the students to plan maintenance
activities on these drains by the street repair crews.
Figure 2: Outlier Analysis.
4.4.3 Phase 3: Feedback from City Helped
Improve the Learning Activities
Using Google maps to locate and add the depth data
made the data collection process very simple. The
down side of this application was that if a storm drain
was found that was not in the GPS table in Google
maps, it could not be added to the system. Students
recorded this data on paper, and the city went back
and used a specialized GPS device to record the new
storm drain GPS point and the data associated with
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
50
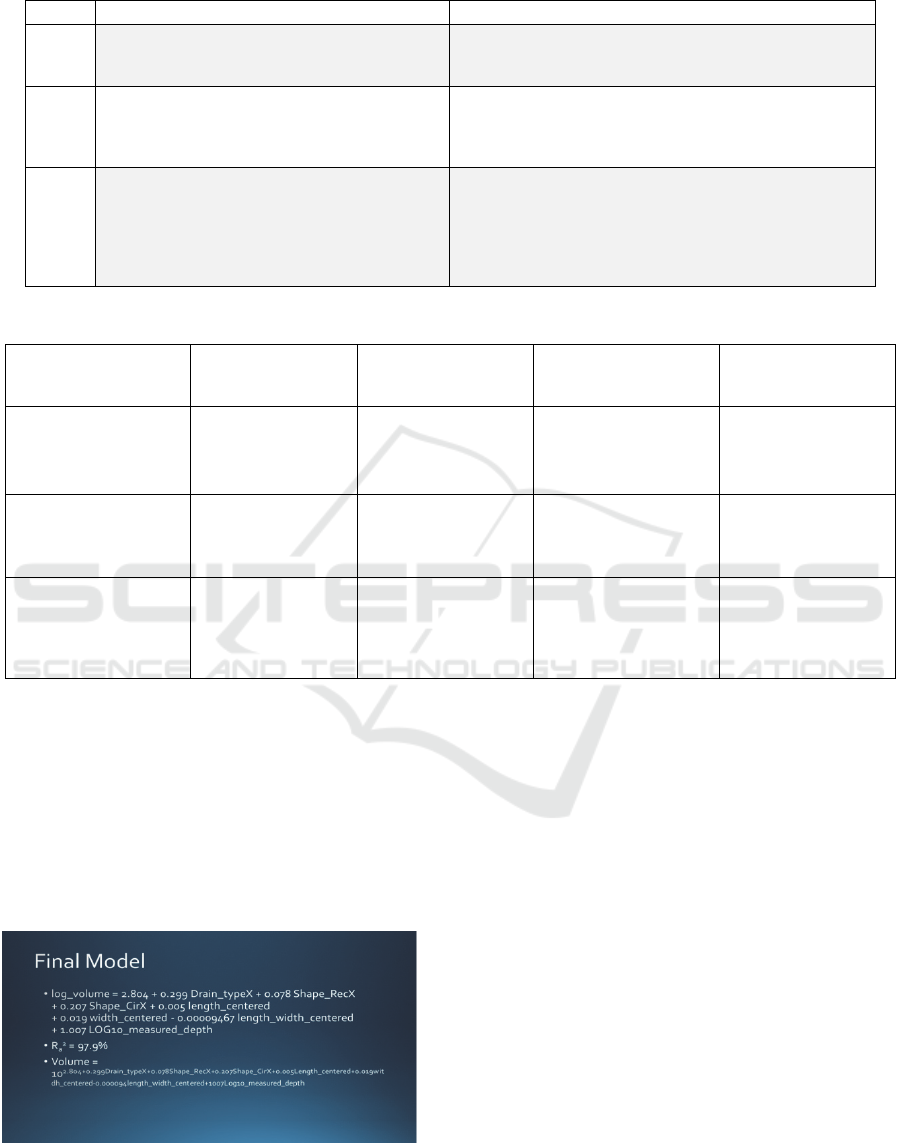
Table 2: Summary of Case Study.
Phase StudentExperientialLearningActivities CityUseofData
1
1. Storm Drain location using Specialized GPS
devices.
2. Uploading Data to ESRI GIS mapping system
1. Merged data collected to complete the storm drain mapping in
GIS
2
1. Storm Drain location using specialized and an
android tablet with specialized software.
2. Storm drain depth collection and Statistics analysis
1. Merged data collected to complete storm drain mapping in
GIS.
2. Used statistical analysis to generate maintenance work orders
for drains identified as outliers.
3
1. Storm drain depth collection using general use
GPS devices.
2. Statistical analysis and modeling
1. Merged drain depth data to GIS system to complete required
data set for each storm drain junction.
2. Added this semester’s data to previous semester to better
predict storm drain issues.
3. Used depth data in conjunction with existing LIDAR
*
data to
predict water flow with pipes under the ground.
Table 3: How the Storm Drain Project met the Conditions for a Smart City.
Requirements to be a
Smart City
Phase 1: Storm
Drain Location
Phase 2: Depth
collection and analysis
Phase 3: Depth
collection and advanced
analysis
Requirements to be a
Smart City
Integrate Science and
Technology through
Information Systems
Document current
GIS system maps and
collect new storm
drain data points
Collect depth data
using IT tools
Use data analytics tools
to perform outlier
analysis
Integrate Science and
Technology through
Information Systems
Integrate conditions of
critical infrastructure
Identification of all
storm drains on city
GIS map
Complete data about
each storm drain
available online
Analysis of data to
identify defective storm
drains
Integrate conditions of
critical infrastructure
Better optimize, plan,
and monitor resource
allocation
Collection of
information on all
storm drains
Analysis of storm drain
data
Regression analysis of
storm drain data leading
to identification of type
of storm drains that
cause issues
Better optimize, plan,
and monitor resource
allocation
this new point. After the statistical analysis portion of
the project was complete, city IT staff again attended
the student presentations of their data. The CTO also
presented to the class how the collected data was
being used and also showed how the data from the
previous classes had been used to build a maintenance
schedule for the storm drains that had depth
information collected on them (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Slide from CTO presentation to show how drain
volume can be calculate based on a multiple regression
model. This equation is based on two semesters of data.
5 HOW INCORPORATION OF
KEY SUCCESS FACTORS
LEADS TO VALUE
CO-CREATION
An analysis of the case study shows how this project
led to creation of value for the students and the city.
As described in Section 2, the project incorporated the
key success factors shown in Figure 1. For a
university-community partnership like this to work,
the city staff must want to be part of the educational
process. Without the city employees being an active
part of this project, the experiential learning would
not be complete and students would not get to see
their data in use. We have been unable to find any
research that includes such a close relationship
between an experiential learning project and
employer access to the classroom and students.
The city, by partnering with a university research
centre, found it had access to massive amounts of
Developing a Smart City by Operationalizing the Co-creation of Value Model
51

talent, data, and infrastructure which can be used for
meeting its vision of becoming a smart city. Without
these projects, the city would not have started the
process of becoming “Smart”.
5.1 Value to Students
In general, students conduct many assignments in
class, without any concept of how the data is collected
or in what way business or government goes about
collecting the data. The storm drain project shows
students that correctly collecting data, is as important
as the analysis itself. By getting out of the classroom
and collecting their own data, the students had
ownership of data, collected by their own efforts. By
allowing city staff to define the project, have the
students conduct their work, and then have the city
staff return to class to show how the data was used,
provided project closure for the students. These
creative processes
were only possible because the
students had physically interacted with the system
being analyzed.
While the statistical analysis of the data the
students conducted was correct, they had little
concept of how the results should be interpreted in
terms of the city’s goals. This was discussed during
the presentations and the analysis process was further
improved. They were delighted to learn that their
analysis influenced the city’s decision making
process.
5.2 Value to City
Hall et al., (2000) provides four conditions for a
project to be considered a contributor to a smart city.
We analyzed the value received by the city in each of
the three phases of the project according to these four
conditions and developed Table 3. The first condition
is to integrate science and technology through
information systems: this project collected GPS and
depth data to develop ArcGIS maps that were used by
the city to trouble-shoot their storm drains. The
second condition is to integrate information about
conditions of the infrastructure; this project produced
graphs and charts that showed the drains that were
outliers so that attention could be focused in repairing
them. The third condition is to optimize, plan, and
monitor resource allocation. The city generally
maintains the drains on a 5-year cycle irrespective of
which ones are most critical. The analysis identified
the drains that need to be maintained more often. The
fourth condition is to enhance the decision making
process. This project made it possible for the city to
apply advanced analytics tools to the data thereby
proactively identifying causes of overflow. This
analysis indicates that this project provided a good
opportunity for this city to become smarter by co-
creating value by working with the University center
.
6 LIMITATIONS, FUTURE
RESEARCH AND
CONCLUSIONS
This project has several limitations. First, it is an
exploratory study based on a single service learning
project, storm drains. Based on the positive results of
this project, the city and the centre have already
developed the next project –a cemetery management
system – so as to provide citizens access to
information on the people buried in the city emeteries.
Second, the metrics to evaluate the value obtained
by the students and city is subjective. In the future, it
is possible to create a set of metrics to evaluate the
city’s contribution to the class and student learning.
This would enable the centre to manage the city
staff’s interactions with the students and provide a
framework within which the project can function.
Third, this project provides experiential learning
activity to about 200 students every academic year.
But, about 800 students take the introductory data
analytics course in this university. Developing service
learning projects for large amounts of students are
hard to find. In the future, it is possible to develop a
process that integrates such experiences into the
curriculum.
The literature showed that there are many
definitions of a smart city, and the focus is on many
areas. Research needs to be done to unify the current
research and build a definition and model outlining
all the pieces that need to fit together to make a smart
city. For small cities, what is lacking, is a complete
set of definitions, and a corresponding set of
guidelines that focus on the ‘how to’ rather than ‘what
is?’ a Smart City. Future research is needed so that
practitioners can develop best practice guidelines for
developing a smart city project that can be followed
by any city. The ultimate goal of this storm drain data
collection project is the subsequent building of a
storm drain model within ESRI GIS system that will
help the city predict the storm drain system’s capacity
and performance under various weather conditions.
Another future research project is to deploy
sensors in each storm drain so that the information
from them can be integrated with the ArcGIS
database. But, this requires investigation and
deployment of newer technologies that can perform
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
52

such functions without need for electricity and can
work under water.
In conclusion, this case contributes as follows.
First, this case study was designed to show how, using
the co-creation of value model, a centre and a city can
make a small city “smarter” while also, creating value
for a university’s students, by providing a rich field
based, educational experience. Second, the case study
was conducted in semester size blocks to meet the
needs of individual class experiential learning. Third,
analysis of the case study and each of its parts showed
how the city used the data generated. Lastly, we
derive conclusions that answer the research question.
REFERENCES
Alavi, S., Ahuja, V. and Medury, Y. (2012), “Metcalfe’s
Law and Operational, Analytical and Collaborative
CRM-using Online Business Communities for Co-
creation”, Journal of Targeting, Measurement &
Analysis for Marketing, Vol. 20 No. 1, pp. 35-45.
Arnould, E.J. and Thompson, C.J. (2005), “Consumer
Culture
Theory
(CCT): Twenty Years of Research”,
Journal of Consumer Research, Vol. 31 No. 4, pp. 868-
882.
Burdon, S and Feeny, D. (2011). Mobilizing for Value
Added Partnerships. Journal of Information
Technology Case and Applications Research, 13(2):
22-41.
Calihoo, C., and Kowalski, E. (2003). Smarter Growth in a
Smaller City. Alternatives Journal, 29(3), 27.
Chan, C. K. (2012). Exploring an experiential learning
project through Kolb's Learning Theory using a
qualitative research method. European Journal of
Engineering Education, 37(4), 405-415.
Chapin, T. S. (2003, July). Revolutionizing the core: GIS in
the planning curriculum. Environment and planning. B,
Planning and design, 30(4), 565-573. doi:0265-8135.
Deakin, M. (Ed.). (2014). Smart Cities: Governing,
Modelling and Analzing the Transition. New York:
Routledge.
Doran, M.-A., and Daniel, S. (2014). Geomatics and Smart
City: A transversal contribution to the Smart City
development. Information Polity: The International
Journal of Government and Democracy in the
Information Age, 19(1/2), 57-72.
Esnard, A.-M. (1998). Cities, GIS, and Ethics. Journal of
Urban Technology, 5(3), 33-45.
ESRI. (2013). ESRI ArcGIS Desktop Help 9.2. Retrieved
March 8, 2015, from ESRI ArcGIS Help:
http://webhelp.esri.com/arcgisdesktop/9.2/index.cfm?
TopicName=What%20is%20a%20geometric%20netw
ork%3F.
Federal Geographic Data Committee. (2008, May 01).
Geographic Information Framework Data Standard.
(U. G. Survey, Ed.) Retrieved April 12, 2015, from
Federal Geographic Data Committee:
https://www.fgdc.gov/standards/projects/FGDC-stand
ards-projects/framework-data-standard/GI_Framework
DataStandard_Part6_Hydrography.pdf.
Gabriel, S. A., Faria, J. A., and Moglen, G. E. (2006). A
multiopbjective optimization sapproach a smart growth
in land development. Socio-Economic Planning
Sciences, 40(3), 212-248.
Galvagno, M., and Dalli, D. (2014). Theory of value co-
creation: a systematic literature review. Journal of
Service Theory and Practice, 24(6), 643-683.
doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/MSQ-09-2013-0187.
Grippa, F., De Maggio, M., Corallo, A., & Passiante, G.
(2010). Discovering the Hidden Dynamics of Learning
Communities. Journal of Information Technology Case
and Application Research, 12 (3), 34-55.
Grover, V., and Kohli, R. (2012). Cocreating IT Value:
New Capabilities and Metrics for Multifirm
Environments. MIS Quarterly, 36 (1), 225-232.
Hall, R. E., Bowerman, B., Taylor, J., Todosow, H., and von
Wimmersperg, U. (2000). The Vision of a Smart City.
2nd International Life Extension Technology Workshop
(pp. 1-6). Paris: Brookhaven National Labortory: U.S.
Department of Energy Contract No. DE-AC02-
98CH10886.
Harrison, C., Eckman, B., Hamilton, R., Hartswick, P.,
Kalagnanam, J., Paraszczak, J., and Williams, P.
(2010). Foundations for Smarter Cities. IBM Journal of
Research and Development, 54(4), 1-16. doi:1-
.1147/JRD.2010.2048257.
Hashim, R. (2010). Theory-Building from Multiple Case
Study Research on Information System Project
Implementation in Local Government. International
Journal of Interdisciplinary Social Sciences, 5(1), 297-
310.
Hollands, R. G. (2008, December). Will the real smart city
please stand up? City, 12(3), 303-320.
doi:10.1080/13604810802479126.
IBM. (2015, March 8). Smarter Cities. Retrieved March 8,
2015, from IBM: http://www.ibm.com/smarterplanet/
us/en/smarter_cities/overview.
Lloyd, C. D., Gregory, I. N., Shuttleworth, I. G., and Lilley,
K. D. (2012, March). Exploring change in urban areas
using GIS: data sources, linkages and problems. Annals
of GIS, 18(1), 71-80.
Lombardi, P., Giordano, S., Farouh, H., and Yousef, W.
(2012). Modelling the smart city performance.
Innovation - The European Journal of Science
Research, 25(2), 137-149.
MIT. (2015). Smart Cities: Vision. Retrieved February 28,
2015, from Smart Cities Group: http://smartcities.
media.mit.edu/frameset.html.
Mbarika, V. W., Sankar, C. S., Raju, P. K., & Raymond, J.
(2001). Importance of Learning-Driven Constructs on
Perceived Skill Development when Using Multimedia
Instructional Materials. Journal of Educational
Technology Systems, 29 (1), 67-87.
McNall, M., Reed, C. S., Brown, R., and Allen, A. (2009).
Brokering Community–University Engagement.
Innovative Higher Education, 33 (5), 317-331.
National League of Cities, (2015). Number of Municipal
Developing a Smart City by Operationalizing the Co-creation of Value Model
53

Governments & Population Distribution (2015).
Retrieved March 8, 2015, from National League of
Cities:http://www.nlc.org/build-skills-and-
networks/resources/cities-101/city-structures/number-
of-municipal-governments-and-population-
distribution.
Ostrom, A.L., Bitner, M.J., Brown, S.W., Burkhard, K.A.,
Goul, M., Smith-Daniels, V., Demirkan, H. and
Rabinovich, E. (2010), “Moving forward and making a
difference: research priorities for the science of
service”, Journal of Service Research, Vol. 13 No. 1,
pp. 4-36.
Sarkar, M. B., Echambadi, R., and Harrison, J.S. (2001).
Alliance Entrepreneurship and Firm Market
Performance, Strategic Management Journal, 22(6-7):
701-711.
Sankar, C. S., and Cumbie, B. A. (2014). Co-Creating
Value: Student Contributions to Smart Cities.
Knowledge Management & E-Learning, 6(4), 392-409.
Shelton, T., Zook, M., and Wiig, A. (2015). The 'actually
existing smart city'. Cambridge Journal of Regions,
Economy and Society, 8, 13-25.
doi:10.1093/cjres/rsu026.
Singh, R. R. (1999). Sketching the city: A GIS-based
approach. Environment & Planning B: Planning &
Design, 26(3), 455-464.
Thomas, C. (2015, Winter). ArcUser, pp. 42-43.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2011). Summary
of State Stormwater Standards (Draft). Washington
D.C: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved
April 5, 2015, from http://water.epa.gov/polwaste/
npdes/stormwater/upload/sw_state_summary_standard
s.pdf.
Vargo, S. L., and Lusch, R. F. (2011). It's all B2B...and
beyond: Toward a systems perspective of the market.
Industrial Marketing Management, 40(2), 181-187.
doi:10.1016:j.indmarman.2010.06.026.
Venigalla, M. M., and Baik, B. H. (2007). GIS-Based
Engineering Management Service Functions: Taking
GIS beyond Mapping for Municipal Governments.
Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 21(5), 331-
342.
Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case studies in IS
research: nature and method. European Journal of
Information Systems(4), 74-81. doi:10.1057/ejis.
1995.9.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case Study Research: Design and
Methods (5th ed.). Los Angeles: Sage.
Zwass, V. (2010). Co-Creation: Toward a Taxonomy and
an Integrated Research Perspective. International
Journal of Electronic Commerce, 15(1), 11-48.
doi:10.2753/JEC1086-4415150101.
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
54
