
Research on Construction of High-level Talents in Colleges and
Universities based on Three-dimensional Matrix Model
Xiao XiMing
1
and Bo Sun
2
1
Human Resources Division,Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, 2 North Baiyun Avenue, Guangzhou, China
2
Research Institute of International Services Outsourcing, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies,
2 North Baiyun Avenue, Guangzhou, China
{ shmf, sbgz168}@ gdufs.edu.cn
Keywords: High-level Talents, Three-dimensional Matrix, Construction, Employment, Cultivation.
Abstract: High-level Talents are the core competitiveness of universities and the key to the great-leap-forward
development of colleges and universities. Taking Guangdong University of Foreign Studies as an example,
this research organically combined talent development and subject category together via the management
theory of multidimensional matrix and established a dynamic model of three-dimensional matrix called
“Introduction, Employment, Cultivation” system (short for “IEC” system) of high-level talents, so as to
promote the movement effectively and cooperatively in terms of introduction, employment and cultivation
to high-level talents among colleges and universities and finally to realize the great-leap-forward
development of colleges and universities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The 21st century is the knowledge-era, which is in
the ascendant. The focus of competition is the
competition of talents. Under the new situation of
knowledge innovation, scientific and technological
innovation and industrial innovation, talent resource
has become an important strategic resource in the
world.
Colleges and universities are the fertile soil on
talent growth and development and the fountainhead
of knowledge innovation and technological
innovation. The sustainable development of talented
group demands a reasonable echelon, all ranks of
which are essential. Construction of high-level
talents has become a constant topic of human
resources work.
2 THREE-DIMENTION MATRIX
DYNAMIC MODEL OF HIGH-
LEVEL TALENTS
According to the national policy and the school
development strategy, GDUFS has experienced
three stages of talent introduction in the recent 10
years (details on chart one): Gathering Scale (2003-
2006), Adjustment and Transition (2007-2009),
Connotation Development (2010-2013). The talents
introduction in recent ten years is shown as table 1.
Table 1: Summary of talents introduction in recent ten
years.
Stage Year
No. of
Teacher
No. of
Returnee
No. of
Dr.
No. of
Prof.
Gath. Scale
2003-
2006
251
(50.8%)
33
(48.5%)
81
(34.5%)
72
(49.3%)
Adjustment
and
Transition.
2007-
2009
152
(30.8%)
18
(26.5%)
87
(37%)
46
(31.5%)
Connotation
and
Development
2010-
2013
91
(18.4%)
17
(25%)
67
(28.5%)
28
(19.2%)
Sum 494 68 235 146
2.1 Talent Structure
The elements of talent structure are quality, degree
and title. In the recent ten years, the total number of
full-time teachers has increased from 820 to 1150,
an increase of 40.2%; the number of teachers with
Master’s degree has increased from 552 to 1025, an
increase of 85.7%. The proportion of teachers with
doctoral degree has increased from 12.7% to 35.4%;
the proportion of teachers in senior positions has
increased from 39% (103 senior titles, 217 deputy
senior titles) to 53.7% (257 senior titles, 360 deputy
516
516
XiMing X. and Sun B.
Research on Construction of High-level Talents in Colleges and Universities based on Three-dimensional Matrix Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0006029705160519
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 516-519
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
senior titles). The changes of talents structure in
recent ten years is shown on table 2.
Table 2: Changes of talents structure in recent ten years.
Year
No.
(increasing
prop.)
Degree Title
M. (total
prop.,
increasing
prop.)
Doc. (total
prop.,
increasing
prop.)
Dep. Senior
(total prop.,
increasing
prop.)
Senior (total
prop.,
increasing
prop.)
2003 820
552
(67.3%)
104
(12.7%)
217
(26.5%)
103
(12.6%)
2013
1150
(40.2%)
1025
(89.1%,
85.7%)
407
(35.4%,
291%)
360
(31.3%,
65.9%)
257
(22.3%,
150%)
2.2 Talent Project Construction
As the main carrier of high-level talent introduction
and cultivation, talent projects are regarded as one of
the marks of teachers’ team building. The summary
on talent projects construction of GDUFS and the
same type of domestic universities are shown on
table 3. In the table 3, the 'Four key disciplinary
fields' includes English Language and Literature,
Germany Language and Literature, Linguistics and
Applied Linguistics, Japanese Language and
Literature; the 'Three key disciplinary fields'
includes English Language and Literature, Russian
Language and Literature, Arabic Language and
Literature; the 'Two key disciplinary fields' includes
International Trade, International Jurisprudence; and
the 'One key disciplinary field' includes Linguistics
and Applied Linguistics.
Table 3: Summary on talent projects construction of
GDUFS and other the same type of domestic universities.
No. 1 2 3 4
College Name A B C GDUFS
College
Category
Foreign
languages
category,
directly under
MOE, “Project
211”
universities
Foreign
languages
category,
directly under
MOE,
“Project 211”
universities
Economics
and trade
category,
directly under
MOE,
“Project 211”
universities
Provincial
university
Subject
Construction
Four key
disciplinary
fields
Three key
disciplinary
fields
Two key
disciplinary
fields
One key
disciplinary
field
Engineering
Talents from
Overseas
(Unit:
Thousand)
0 0 1 0
Yangtze River
Scholar
2 1 2 0
Candidates
b
y
the New
Century
Talents
3 0 3 3
Members
selected for
the New
Century
Excellent
Talents
24 14 36 13
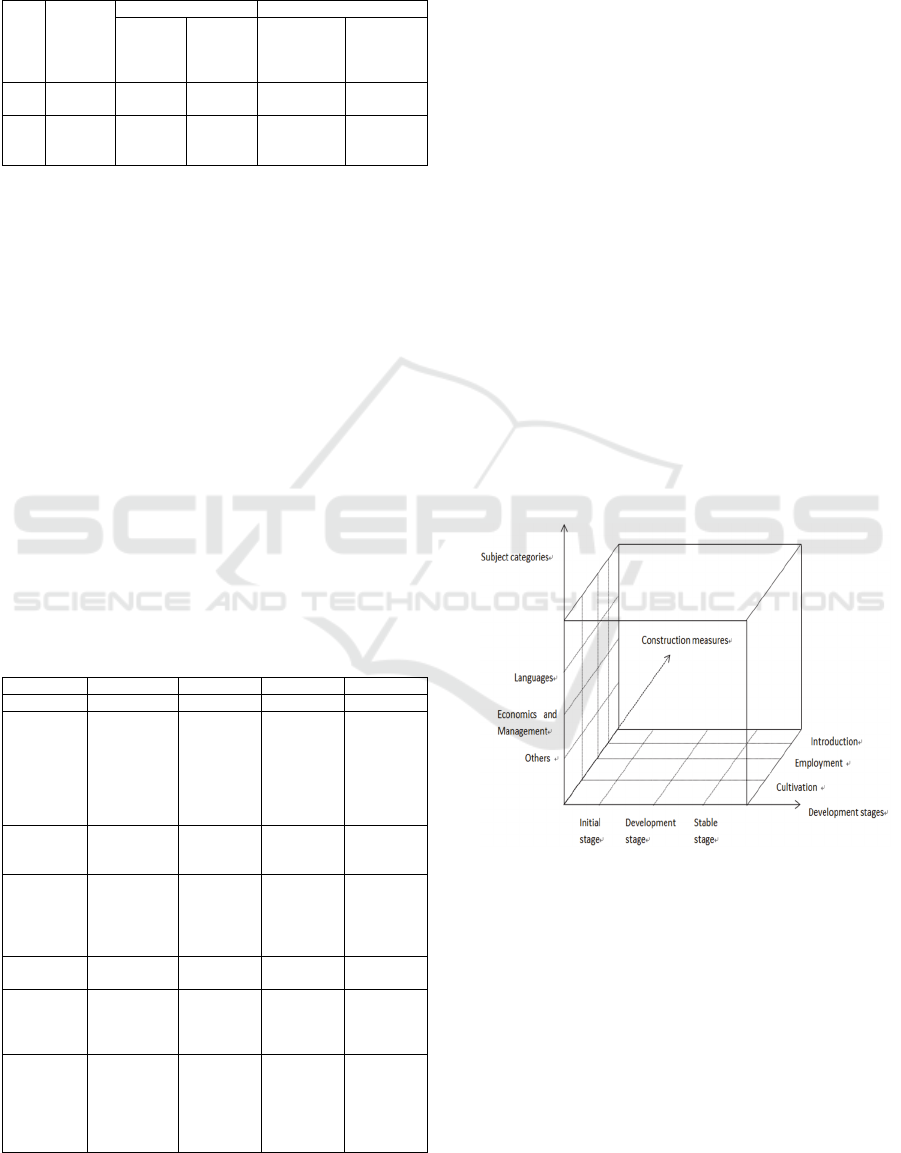
2.3 Construction of IEC System based
on Three-dimensional Matrix
Model of High-level Talents
High-level talents system in colleges is a dynamic
management matrix model, which takes the way of
fully analyzing the current situation towards the
existing talent teams as the starting point, the
construction plan of talent teams as the entry point
and the construction target of talent teams as the
foothold, mainly including three dimensions –
development stages, subject categories, construction
measures. According to the disciplinary planning
and the development strategy of GDUFS, the subject
categories, which is regarded as the first dimension
of high-level talents construction system in GDUFS,
are divided into three parts –languages, economics
and management, and other categories; the
construction process, as the second dimension, is
divided into three stages –initial stage, development
stage, and stable stage; based on the first two
dimensions, the third dimension divides high-level
talents team of GDUFS into three aspects –
introduction, Employment, and Cultivation. These
three dimensions construct the IEC system of high-
level talents, as shown in figure 1.
Figure 1: Structure of the IEC system of high-level talents.
2.4 Success of High-Level Talents
Construction
This part will introduce how to improve the
constructive system for high-level talents team based
on three-dimensional matrix dynamic model by
some cases.
a. The effect of multi-channel and overseas
approach to introduce high-level talents has
Research on Construction of High-Level Talents in Colleges and Universities Based on Three-Dimensional Matrix Model
517
Research on Construction of High-level Talents in Colleges and Universities based on Three-dimensional Matrix Model
517

gradually been enhanced; its attraction to high-
level talents has gradually improved.
As shown in table 1, among the talents introduced
by GDUFS from the year 2003 to 2013, except for
the liner increasing stage proportion of the number
of doctors, the stage proportion of the number of
returnees and above professional titles almost keeps
unchanged, especially that of returnees, which takes
a low ratio. At the gathering scale stage, the stage
proportion of the number of returnees only takes
13.1% although the total proportion of them in
recent ten years is 48.5%.
b. To cultivate talents in multi-mode ways; talent
structure tends to be reasonable; talents majoring
in each subject achieve balanced development.
From table 2 we can see that the total proportion
and the increasing proportion of degrees and titles
have improved from the year 2003 to 2013, and the
increasing proportion is higher than quantitative
increasing proportion, especially that of doctoral
degrees and senior titles, which has grown
substantially.
c. To employ talents in multi-form ways; the
talents project is in initial success; the talents
support system gradually becomes perfect.
GDUFS still does not make a break in national great
talent projects such as Thousands of Supporting
Engineering Talents from Overseas and Yangtze
River Scholar, as shown in table 3.
3 SUGGESTION TO
COMSTRUCT A BETTER
HIGH-LEVEL TALENTS
SYSTEM IN COLLEGES
The following will present a suggestion on how to
construct a better system of high-level talents in
colleges, which consists of three stages.
3.1 Initial Stage
At the beginning of the construction of high-level
talents system, GDUFS should take the resource
advantage of the school’s traditional subject, and
have a key introduction to the talents of languages
and economics and management, and give
consideration to the talents of other subjects.
3.2 Development Stage
At the stage of development, the platform of talents’
accumulation, the construction of talent system and
the introduction work of high-level talents have got
initial results; however, the system in terms of
“introduction, employment, cultivation” has not
been formed. In this stage, the working focus is to
carry out the work of high-level introduction and a
system of responsibility for work, so as to further
expand the channel of high-level talents introduction
work. To build the system of “Permanent Career
Teacher” so as to attract overseas high-level talents
to take the full-time job. To implement the way of
“Global Recruiting, Contract Management” and the
management mode of “Employment System plus
Annual Salary System”. To set up the working
platform that is helpful to the high-level talents
introduction and cultivation work. To normalize the
management of talent projects and to establish the
funded system for talent projects.
3.3 Stable Stage
After the first two stages of accumulation, GDUFS
has established IEC system covering languages,
economics and management and other subjects
such as the three disciplines. The project of
introduction has got remarkable results, the
structure of talents team has got obvious
improvement and the supporting measures have got
a gradual perfection. Specific measures are as
follows.
First, to set up a scientific evaluating
mechanism of talents and an incentive and
guarantee mechanism.
Second, to carry out the performance evaluation
of talent projects so that they can be dynamically
adjusted.
Third, to complete the distribution mechanism of
high-level talent performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by a grant from
Guangdong province science and technology
planning project. (2013B040404009).
REFERENCES
Yayang Tang, Zhonghua Yao, 2005. Developing talent
resources, constructing an overall teacher-building
system. In Chinese College Teachers’ Research.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
518
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
518

Wanmin Zheng, 2011.The position and mission of
University in strengthening the country through
talents, In Southwest University press. Chongqing.
Wenli Li, 2005. Innovating and constructing a teacher-
building system at the new era, in Chinese College
Teachers’ Research.
Zhang Ming, 2012. The application of Boston matrix in
the construction and management of teachers in
Chinese College. In the 3rd International Annual
Conference on Teaching Management Curriculum
Construction, SUNY-University press.
Yujin Zhang, 2014. Three-dimensional matrix model and
application of human resource for commercial aircraft
engine. In China Aviation News.
Research on Construction of High-Level Talents in Colleges and Universities Based on Three-Dimensional Matrix Model
519
Research on Construction of High-level Talents in Colleges and Universities based on Three-dimensional Matrix Model
519
