
Counting Credibility based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm
Lianlian Song, Li Wang and Shibing Zhang
School of Electronics and Information, Nantong University, Seyuan Road, Nantong, China
Keywords: Cooperative Spectrum Sensing, Sensing Node, Channel Overhead, Lifecycle.
Abstract: In the cooperative spectrum sensing, if too many nodes take part in the cooperative data fusion, it would
weigh the channel overhead and energy loss lot but improve the spectrum sensing performance little. This
paper focuses on the channel overhead of cooperative spectrum sensing and the lifecycle of cognitive
networks, and proposes a novel cooperative spectrum sensing algorithm. In the algorithm, all of the nodes
are sorted by means of counting reliability. Only a part of nodes participate in the cooperative data fusion in
the fusion centre. It cut down the number of nodes participating in the data fusion and save the average
energy of the sensing nodes. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce
channel overhead and prolong the lifecycle of cognitive network in the premise of ensuring the spectrum
detection performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the growth of the wireless data traffic, the
spectrum resources become more and more scarce
(Akyildiz, 2008). Cognitive radio (CR) is an
intelligent spectrum sharing technology and taken as
a promising way to solve the problem (Wang et al.,
2011). The main idea of CR is to access spectrum
dynamically (Qu and Wang, 2009), (Yang et al.,
2009), (Li et al., 2011). In the CR network, cognitive
users (secondary users) opportunistically access the
empty spectrum bands which has been assigned to
the primary user (PU) but unused at present. The key
to reuse the empty spectrum and to improve the
spectrum efficiency is to ensure the CR senses
spectrum accurately. However, due to the channel
fading and multipath, a single cognitive node is
often difficult to guarantee the validity of the
spectrum sensing. Therefore, cooperative spectrum
sensing is put forward to improve the performance
of the spectrum sensing (Bai et al., 2013), (Mai et al.,
2011), (Liu et al., 2012), (Bao et al., 2012).
The cooperative spectrum detection based on soft
decision fusion makes full use of the information of
sensing nodes to make accurate spectrum decision,
but it increases the system overhead and the energy
loss of sensing nodes (Zhang and Yang, 2003). It
should be considered in cooperative spectrum
sensing that how to reduce the overhead of the data
transmission and the energy loss of the sensing
nodes as far as possible in the premise of ensuring
the spectrum sensing performance. Some algorithms
were proposed to overcome these problems (Chair
and Varshney, 1986), (Chen et al., 2008), (He et al.,
2008). But they solve the problems only from the
view of energy loss or lifecycle. A cooperative
spectrum sensing algorithm based on node
recognition (NRCS) was proposed to improve the
spectrum sensing performance in the case of
malicious nodes and reduce the system overhead
simultaneously (Zhang et al., 2014). But the
overhead of the data transmission and the energy
loss of the sensing nodes are not lowest because all
reliable nodes participate in the data fusion.
In this paper, we propose a counting credibility
based cooperative spectrum sensing algorithm
(CCCS) to reduce the channel overhead and prolong
the lifecycles of cognitive networks. In the
algorithm, all of the nodes are sorted according to
their counting reliability. Only a part of nodes with
largest or next larger reliability weighted factors take
part in the cooperative data fusion in the fusion
centre.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section II presents the system model. Section III
describes the cooperative spectrum sensing
algorithm. Some simulation results are discussed in
section IV. Conclusions are stated in section V.
71
Song L., Wang L. and Zhang S..
Counting Credibility based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0005574700710075
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems (WINSYS-2015), pages 71-75
ISBN: 978-989-758-119-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 SYSTEM MODEL
Assume that there are one primary user and N
cognitive users in the cognitive network, as shown in
Figure 1. Two hypotheses, H
1
and H
0
, represent the
spectrum detected in the network is busy (the
primary user uses the spectrum at present) and is
free (the primary user does not use the spectrum at
present), respectively. The spectrum sensing of the
i
th
cognitive user (sensing node), i=1······N, can be
modelled as a binary hypothesis testing problem as
follows
1
0
:
:
ii i
ii
H
xt ht st nt
Hxtnt
(1)
where x
i
(t) is the signal received in the i
th
sensing
node, s(t) is the signal transmitted by the primary
user, h
i
(t) is the channel gain of the i
th
sensing node,
n
i
(t) is the additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN)
in the signal received of the i
th
sensing node.
The cooperative spectrum sensing can be divided
into two steps, local detection and data fusion. In the
local detection, the i
th
sensing node makes
hypothesis testing after receiving the signal x
i
(t), and
obtains local detection result “1” or “0”. “1”
represents the hypothesis H
1
is supported, “0”
represents the hypothesis H
0
is supported. In the data
fusion, the fusion centre fuses the local detection
results from the sensing nodes, and makes final
decision according to the decision rule and decision
threshold.
Figure 1: System model.
3 COOPERATIVE SPECTRUM
SENSING ALGORITHM
It has been showed that the spectrum sensing
performance in the cooperative spectrum sensing is
dependant on the number sensing nodes which
participate in the data fusion, and their reliabilities
(Chair and Varshney, 1986). Note that the credibility
of the sensing node is a accumulative result of the
historical sensing information. That is to say, the
present credibility of the sensing node is related to
the sensing node’s historical sensing results.
Definition 1. The credibility of the i
th
sensing node
in the m
th
spectrum sensing is defined as
1
,1 ,1 ,1 ,1
,
1
,1 ,1 ,1 ,1
1
1
m
im i im FCm
im
m
im i im FCm
rrdd
r
rrdd
(2)
where r
i,m-1
is the credibility of i
th
sensing node in
(m-1)
th
spectrum sensing , ρ is a attenuation factor
which represents the strength of association with
historical information, 0<ρ<1; d
i,m-1
is the local
detection result of i
th
sensing node in (m-1)
th
spectrum sensing, d
FC,m-1
is the global decision result
in (m-1)
th
spectrum sensing.
According to the local detection result and the
global decision result in last time, the fusion center
updates the credibility of the sensing node i
cumulatively. When the local detection result of i
th
sensing node, d
i,m-1
, is the same as the global
decision result of the fusion centre, d
FC,m-1
, in (m-1)
th
spectrum sensing, “1” is added to the historical
weighted credibility. And then, the credibility of the
i
th
sensing node in the m
th
spectrum sensing is
updated. When the local detection result of i
th
sensing node, d
i,m-1
, is different with the global
decision result , d
FC,m-1
, in (m-1)
th
spectrum sensing,
“1” is subtract from the historical weighted
credibility. And then, the credibility of the i
th
sensing
node in the m
th
spectrum sensing is replaced. If the
credibility replaced is smaller than 0, it will be
replaced by 0. Moreover, the later credibility of the
sensing node has larger weighted factor by means of
the attenuation factor ρ. Therefore, the impact of
accidental errors on spectrum detection caused by
local detection can be eliminated as much as
possible.
Definition 2. The reliability weighted factor of the
i
th
sensing node in the m
th
spectrum sensing is
defined as
,1
,
,1
1
1, 2,
im
im
N
km
k
r
wiN
r
(3)
When the fusion centre obtains the reliability
weighted factors of all of the sensing nodes, it sorts
them according to their reliability weighted factors
and chooses the sensing node with largest reliability
weighted factor, for example sensing node l,
WINSYS2015-InternationalConferenceonWirelessInformationNetworksandSystems
72

l∈{1······N }, to participate the data fusion. Then,
d
i,m-1
is sent to the fusion centre and the global
detection statistics is formed as follows
,,
F
Clmlm
Twd
(4)
Next, the fusion center makes the global decision
according to the decision threshold as follows
1
0
:1,
:0,
FC FC
FC FC
Hd T
Hd T
(5)
where λ is the decision threshold (Zhang et al,
2014).
If the hypothesis H
1
is supported, the fusion
centre terminates the data fusion and achieves the
spectrum detection result H
1
in this time. Otherwise,
the fusion centre will select another with next larger
reliability weighted factor, for example sensing node
k, k
∈
{1······N }, to participate the fusion to form the
new global detection statistics based on the last
statistics as follows
,,
F
CFCkmkm
TTwd
(6)
The fusion center will make the global decision
again according to (5) until
H
1
is supported or all of
the sensing nodes have been selected to participate
in the data fusion.
The cooperative spectrum detection algorithm
based on the counting credibility above can be
summarized as in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: Counting Credibility Based Cooperative
Spectrum Sensing Algorithm.
1: Calculate the credibility of all sensing nodes
according to (2);
2: Calculate the reliability weighted factor of the all
sensing nodes according to (3);
3: Sort all of the sensing nodes according to their
reliability weighted factors;
4: Choose the sensing node with largest reliability
weighted factor and form the global detection
statistics according to (4);
5: Makes the global decision according to (5);
6: If the hypothesis
H
1
is supported, the fusion
centre ends the data fusion and achieves the
spectrum detection result in this time. Otherwise,
the fusion centre will select another with next
larger reliability weighted factor to participate
the fusion. Then it forms the new global
detection statistics according to (6).
7: Go back to Step 5 until
H
1
is supported or all of
the sensing nodes have been selected to
participate in the data fusion.
8: End.
4 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS
We simulate the CCCS algorithm proposed in this
paper in AWGN channel and compared it with
cooperative spectrum detection algorithm based on
node recognition (NRCS) (Zhang et al, 2014). In the
simulation, the primary signal is modelled as a phase
shift keying (PSK) signal with the 5000 Bauds and
10 MHz carrier frequency. The sampling frequency
is 100 MHz and the number of sampling is 512.
There are 8 sensing nodes in the CR network. The
attenuation factor
ρ of the node’s credibility is 0.5.
Figure 2 shows the percentages of the nodes
selected to participate in the cooperative data fusion.
We compare the percentages between the CCCS and
NRCS algorithms in two cases, there is one
malicious node (Num = 1) and two malicious nodes
(Num = 1), respectively. With the increase of SNR,
the number of the nodes selected to participate in the
cooperative data fusion in the CCCS algorithm
decreases, but the one in the NRCS algorithm is
relatively stable. In the case of one malicious node,
when SNR is equal to -13 dB, the percentage of the
CCCS algorithm is 0.5, while the one of the NRCS
algorithm is 0.87. In the case of two malicious
nodes, when SNR is equal to -13 dB, the percentage
of the CCCS algorithm is less than 0.4, while the
one of the NRCS algorithm is close to 0.75.
Compared with the NRCS algorithm, the CCCS
algorithm cuts down the number of the nodes to
participate in the cooperative data fusion and
reduces channel overhead effectively.
-16 -15 -14 -1
3
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
SNR
(
dB
)
Cooperative Percentage (
)
CCCS-
(Num=1)
NRCS-
(Num=1)
CCCS-
(Num=2)
NRCS-
(Num=2)
Figure 2: Percentages of cooperative nodes in the CCCS
and NRCS algorithms.
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the comparisons of the
detection probabilities and false alarm probabilities
of the CCCS and NRCS algorithms in the two cases
respectively. It is obvious that the spectrum sensing
CountingCredibilitybasedCooperativeSpectrumSensingAlgorithm
73
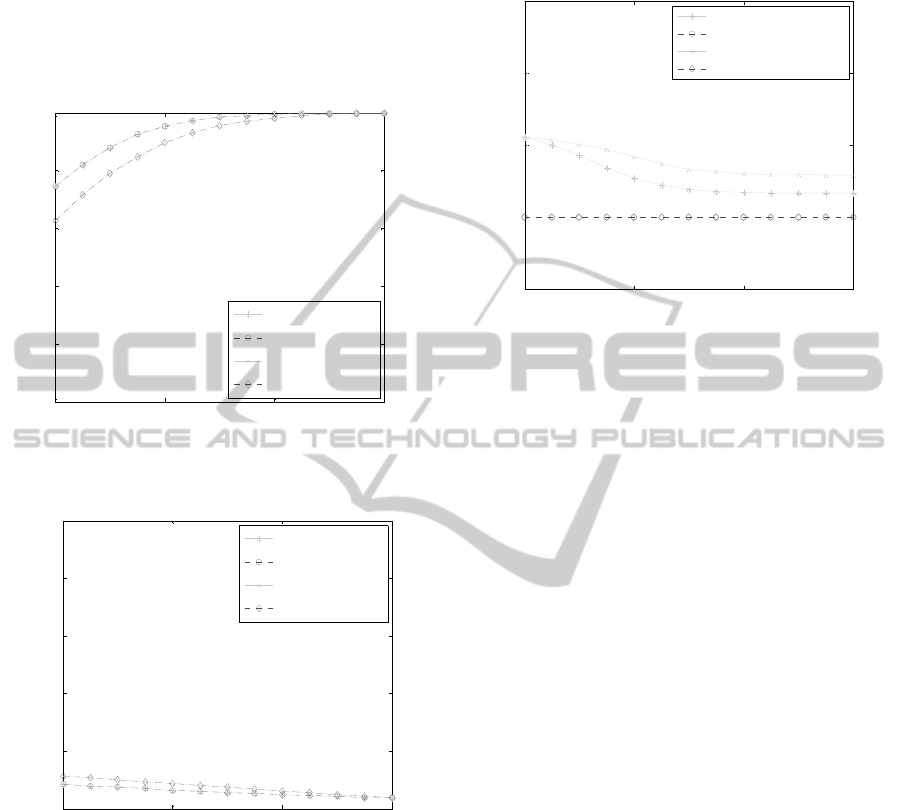
performance of the CCCS algorithm, no matter the
detection probability or the false alarm probability,
is almost the same as one of the NRCS algorithm.
That is to say the node selection algorithm based on
the counting reliability proposed does not decrease
the spectrum sensing performance of the cognitive
network.
-16 -15 -14 -1
3
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
SNR
(
dB
)
Detection Probability ( p
d
)
CCCS-P
d
(Num=1)
NRCS-P
d
(Num=1)
CCCS-P
d
(Num=2)
NRCS-P
d
(Num=2)
Figure 3: Detection probabilities of the CCCS and NRCS
algorithms.
-16 -15 -14 -13
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
SNR(dB)
False Alarm Probability ( p
f
)
CCCS-P
f
(Num=1)
NRCS-P
f
(Num=1)
CCCS-P
f
(Num=2)
NRCS-P
f
(Num=2)
Figure 4: False alarm probabilities of the CCCS and
NRCS algorithms.
Figure 5 shows the lifecycles of cognitive
networks which adopt the CCCS and NRCS
algorithms in the two cases. When the NRCS
algorithm is used, all of the reliable nodes participate
in the cooperative data fusion, every node consumes
it’s energy in each data fusion. Consequently, the
lifecycle is shorted. When the CCCS algorithm is
used, only nodes selected participate in the
cooperative data fusion, the average frequencies of
the sensing nodes participating in the data fusion is
reduced as far as possible, the energy loss of each
sensing node is minimized. Therefore, the lifecycle
is prolonged.
-16 -15 -14 -13
400
500
600
700
800
SNR(dB)
Lifecycle ( Round )
CCCS-Round(Num=1)
NRCS-Round(Num=1)
CCCS-Round(Num=2)
NRCS-Round(Num=2)
Figure 5: Lifecycles of cognitive networks with the CCCS
and NRCS algorithms.
From Figure 2 to Figure 5, we see that the CCCS
algorithm would cut down the number of node
participating in the cooperative data fusion, save the
average energy of the sensing nodes, reduce the
channel overhead of the system, and prolong the
lifecycle of the cognitive network. But it does not
debase the spectrum sensing performance of the
cognitive network.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In order to reduce the channel overhead and prolong
the lifecycle of the cognitive network, a novel
cooperative spectrum sensing algorithm based on
counting credibility is proposed. In the algorithm, all
of the nodes are sorted according to their counting
reliability. Only a part of nodes with best or Sub-
best reliability take part in the cooperative data
fusion in the fusion centre. It decreases the number
of node participating in the data fusion and save the
average energy of the sensing nodes. The simulation
results show that the proposed algorithm can
effectively reduce channel overhead and prolong the
lifecycle of cognitive networks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study is supported by the National Science
Foundation of China under 6137111 and 6137112,
and the applied basic research project of the
WINSYS2015-InternationalConferenceonWirelessInformationNetworksandSystems
74

Ministry of Transport of China under grant
2014319813220.
REFERENCES
Akyildiz I. F., Lee W. Y., Vuran M. C. and Mohanty S.,
2008, A survey on spectrum management in cognitive
radio networks, IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 46, no. 4,
pp. 40-48.
Wang B., Liu K. J. Ray, 2011. Advances in cognitive
radio networks: a survey, IEEE Journal on Selected
Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 5-23.
Qu D. M., Wang Z. Q., 2009. Signal spectrum forming
method of OFDM opportunistic spectrum access,
Journal of Electronics and Information Technology,
vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 1965-1968.
Yang X. Y., Yang Z. and Liu S. B., 2009. Prediction
mechanism-based opportunistic spectrum access in
cognitive radio networks, Journal of Chongqing
University of Posts and Telecommunications, vol. 21,
no. 1, pp. 14-19.
Li Z., Zhao L. J. and Liu Q., 2011. SDM-based
opportunistic spectrum access in cognitive radio
networks, Journal of Electronics and Information
Technology, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 1172-1177.
Bai Z. Q., Wang L. and Liang X. Y., 2013. Robust
cooperative spectrum sensing based on STBC scheme,
Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, vol.
33, no. 9, pp. 956-960.
Mai L. X., Qin X. W. and Dai X. C., 2011. Hidden
Markov model based spectrum sensing strategy with
cooperation, Journal of University of Science and
Technology of China, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 283-292.
Liu J., Chen W., Cao Z. G. and Zhang Y. J., 2012.
Cooperative beamforming for cognitive radio
networks: a cross-layer design, IEEE Trans.
Commun., vol. 60, no. 5, pp. 1420-1431.
Bao Z. H., Zhang S. B. and Zhang X. G., 2012. Research
on cognitive user pairing and cooperative sensing,
Journal of Communication, vol.33, no. 1, pp. 128-135.
Zhang X., Yang D. C., 2003. A study on the reduction of
overhead of resource management scheduling
algorithm, Journal of Beijing University of Posts and
Telecommunications, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 48-52.
Chair Z., Varshney P. K., 1986. Optimal data fusion in
multiple sensor detection systems, IEEE Transactions
on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 22, no. 1,
pp. 98-101.
Chen J. J., Fan X. P. and Qu Z. H., 2008. Subtractive
clustering based clustering routing algorithm for
wireless sensor networks, Information and Control,
vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 435-444.
He Z. Y., Long C. F. and Yin Q., 2008. A distributed
clustering algorithm for sensor networks based on
node density, Computer Applications and Software,
vol. 25, no. 12, pp. 19-20.
Zhang S. B., Song L. L. and Liu Y., 2014. Cooperative
spectrum detection algorithm based on node
recognition, Journal of Data Acquisition and
Processing, vol. 29, no. 9, pp. 688-693.
CountingCredibilitybasedCooperativeSpectrumSensingAlgorithm
75
