
Particle Swarm Optimization of Economic Dispatch Problem: A Brief
Review Transfer
2
Mahdi Zarif and
2
Reihane Kardehi Moghaddam ,
2
Sadegh Khaleghi ,
1
Elahe Faghihnia
1
Young Researchers and Elite Club, Mashhad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Mashhad, Iran
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, Mashhad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Mashhad, Iran
Keywords: Economic Dispatch, Optimization, Particle Swarm Optimization.
Abstract: Electrical energy production has changed various features of the energy manufacturing. According to this
map, lack of energy supplies, improving energy cost, environment matter, require optimal economic dispatch.
Economic load dispatch (ED) problem is essentially nonlinear. Since we know that the traditional methods
donot have the ability to solve problems like this for reasons such as caught up in the trap of local optimal
point or low convergence speed. Therefore, the use of algorithms that are more powerful is inevitable. An
efficient algorithm for solving ED problem is particle swarm optimization considering to its fast convergence
to global optima and computationally efficiency. PSO based algorithms has achieved a pluperfect
identification of the best solution for such kind of EDPs in last decade. In this paper, we try various techniques
associated with PSO, fully checked.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today's world, a world in which economic life is
importantو ED problem Plays a very important role in
the development and updated Modes of production
and consumption and optimize them for an efficient
and economical network in all areas of production,
distribution and transmission in a power systems. The
main purpose of ED is to be planed as a Coordinator
system which has efficient and responsive flawless
generating parts in order to meet the load demand
while Maintain the balance between supply and
demand .
In addition it should achieve the lowest cost and
satisfies all the constraints of the network. To achieve
this aim, we should have a detailed study on the
optimization methods to obtain an optimal algorithm
which has powerful network with high reliability
basically, ED problem was definite as economic cost
dispatch(ECD), though due to the transformation of
clean air act in 1990s, survival of emission dispatch
(EMD) leads to the formulation of mixed emission
economic dispatch (CEED) and emission controlled
economic dispatch (ECED) problem formulation, as
individual optimization of these two contradictory
objective will not serve the idea. Numerous traditional
methods like Bundle method (Mezger and de
Almeida, 2007), nonlinear programming (Mariano et
al., 2007), (Martinez Ramos et al.,2001), mixed
integer linear programming (Martinez Ramos et al.,
2001),(G. W. Chang et al., 2001),(Garcia-Gonzalez
and Castro, 2001), (García-González et al., 2007),
dynamic programming (S.-C. Chang et al.,1990),
quadratic programming (Finardi et al., 2005),
Lagrange relaxation method (Shiina and Watanabe,
2004), network flow method (Franco et al., 1994),
direct search method (Wood and Wollenberg, 2012)
reported in the literature are used to solve such
problems.
Practically, ED problem is nonlinear, nonconvex
type with multiple local optimal point due to the
liability of valve point loading effect, multiple fuel
options with diverse equality and inequality
constraints. Conventional methods have unsuccessful
to solve such problems as they are sensitive to major
approximations and converge into local optimal point
and computational convolution. Modern exploratory
optimization methods recommended by researchers
based on utilizable studies and artificial intelligence
theories such as evolutionary programming (Fogel and
Fogel, 1996), genetic algorithm (Whitley, 1994),
simulated annealing (Hwang, 1988), ant colony
optimization (Blum, 2005), Tabu search (Moscato,
1993), neural network (Dayhoff, 1990), particle
swarm optimization (Kennedy, 2010), Sure solution
introduced. Every method has its benefits and trouble.
Although PSO has attained reputation as the finest
72
Faghihnia E., Khaleghi S., Moghaddam R. and Zarif M..
Particle Swarm Optimization of Economic Dispatch Problem: A Brief Review Transfer.
DOI: 10.5220/0005507400720077
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2015), pages 72-77
ISBN: 978-989-758-122-9
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

solution algorithm for such problems. This article is a
response entry on previous activity of importance of
Population-based approaches such as PSO algorithm
to solve the numerous ED problems.
This paper is arranged as follows: Section 2
describes the cost function of ED problem with the
associated constraints of it. Section 3 provides a
comprehensive overview of the methods that have
been done so far. All methods are compared in the
table, in terms of mean time to achieve the best result
in the ED problem, in sections 4. In section 5 finally,
the results are concluded.
2 AN INTRODUCTION TO EDP
PROBLEM
The most important thing that should be noted in
EDPs for generating the electricity is to set of
generators such that the equilibrium is established
between supply and demand and finally the Minimum
Cost Reduction, considering all the constraints,
happened. Along with all these words, it should not be
forgotten that in order to achieve the desired, using a
procedure is necessary to achieve optimal point. In a
practical matter, Valve-Point loading effect also must
be considered which will complicate the issue, more
than before because virtually a linear section will be
added to the original problem and when it becomes a
big problem that it wants to be solved by the methods
listed in the previous. So there is no alternative unless
the use of new optimization techniques.
This methods achieve to a local or global
optimization point without considering the nature of
object function. Hence, to reach desirable results it is
important to use modern methods like evolutionary
optimization algorithms. As mentioned earlier, one of
the disadvantages of the traditional optimization
methods is being trapped in a local optimum solution.
Although these methods are useful in identification of
linear systems, but due to the properties of nonlinear
systems and the existence of multiple local optimal
point, these methods are usually not effective in
detecting nonlinear systems. The problem of
parameter estimation of nonlinear systems can be
easily changed to an optimization problem that can be
solved by intelligent methods.
3 FORMULARIES ED PROBLEM
The cost function of the economic dispatch problem is
proposed to minimize the fuel cost of thermal power
plants for a given load demand when involved to
various constraints.
The overall cost function of the EDP is defined as
follows:
Min
∑
F
P
Where n is the total number of generator units and
F
P
is a unit fuel cost in terms of
$
h
.
The objective function regardless of valve-point
loading effect is expressed as follows:
Min
∑
F
P
∑
a
b
P
c
P
(2)
Where P
is the power generated per MW by j
unit. The coefficients a
, b
and c
are the unit cost of
j
production. Considering the valve-point loading
effect, the objective function is defined as follows:
Min
∑
F
P
∑
a
b
P
c
P
e
sin
f
P
P
(3)
Where e
and f
are constant coefficients which are
related to the valve-point loading effects that these
coefficients are limited by the following constraints:
P
P
(4)
P
P
P
(5)
P
is the total power demand in MW. P
and P
,
respectively, are defined as the minimum and
maximum of j
units.
4 TRADITIONAL PSO
PSO is a social search algorithm that has been
modeled based on the social behavior of the flocks of
birds, fishes and warming theory in particular. In PSO
algorithm, at the first, particles distribute uniformly in
the search space and create the population, than in the
second stage particles change their states in the search
space according to their own experience and
knowledge and also the knowledge of their neighbors.
So particles learn from each other and searching
process of each particle is affected by the state of
other particles. Indeed PSO algorithm is based on the
principle that each particle sets its state in the search
space, with respect to the best state in its locality and
best state of other agents (particles).
Each particle in PSO includes three d-dimensional
vectors where d is the dimension of the search space
for i-th particle. These three factors include current
ParticleSwarmOptimizationofEconomicDispatchProblem:ABriefReviewTransfer
73

position of i-th partial (
), The velocity for i-th
particle(
), And the best position that ever has
experienced by i-th particle(
).
is a set of
coordinates that demonstrates current space of i-th
particle. In each iteration of algorithm,
calculates
as a solution of problem. If this position for
is
better than the previous answers, it would save in
.
is the objective function value, obtained
from
and (
) represents the objective function
value, obtained from
. Saving
is a
necessary process for doing the next comparison, but
saving f^i is not required. In each iteration new values
for
and
, Are achieved and velocity and position
of each particle will be updated.
In fact, for the swarm particles, solving the
problem is a social concept which is achieved from
behavior of each particle and from the interaction
between them. Best situation that is found with all
particles is represented as
, and is chosen by
comparison of all values of
for all particles and
between all
. Objective function value at
represented as
. n is the number of particles and
these concepts can be mathematically states as:
x
t
argmin
f
x
ζ
argmin
f
x
t
,
f
x
t1
(6)
,
1
(7)
,
1
(8)
,,…,
(9)
Relationships that change speed and position of
particles are as follows:
1
(10)
1
1
(11)
5 A BRIEF REVIEW
Traditional PSO algorithms because of the simplicity
and because in the first it was a relatively high
accuracy algorithm, It was considered as a powerful
algorithm. As previously noted, in this algorithm, the
particles are updated at every stage of their replication
in order to speed to the position of the particle that is
allocated the best results until this iteration and to the
best of his own experience. The algorithm is defined
as each particle alone is capable after passing the
problem constraints, considered as an answer and at
all stages of their repeated attempts to bring the
desired response and for the ED problem, particles has
all the characteristics of production and its constraints.
One of the fundamental problems in intelligent
algorithms is being trapped in a local optimum
solution that makes a drastic reduction in the rate of
convergence, and accuracy of the algorithm. To
resolve this problem different algorithm with a
change in the coefficient of inertia attempted to
improve system performance. Experimental studies
show that relatively large inertia weight has the
ability to search for more. While weight reduction
with a coefficient of inertia, leads to the speedy
convergence of the algorithm. Therefore, the weight
of inertia as a linear or nonlinear function should be
reduced.
Various methods have been tried with different
methods to improve the traditional algorithm. Some
changes were applied to the algorithm itself. This
means that it can be said as new methods and for other
algorithm only changes in weight matrices have
applied.
For example (Meng, Wang, Dong, & Wong,
2010) is examined various amounts of Weight matrix
(W) and best values for traditional PSO have been
proposed. In (Park, Jeong, Shin, & Lee, 2010) an
appropriate weight factor suggested for solving non-
convex ED problems in this article also
THE
simulation results from weight matrix of IPSO have
been compared with the traditional weight matrix.
The proposed IPSO algorithms have been
successfully applied to three different systems and it
was proven that it does not get stuck in the trap of
local optimality. In 2003 a useful article was
published (Victoire & Jeyakumar, 2004)and it was
introduced as a method of optimization and showed
that on the basis of the results of experiments and
simulations have been conducted it is better, in terms
of solving the optimization problem convergence
rate, solution time, minimum cost, and chance of
achieving better solutions until that time.
Until 2004, Sequential quadratic programming
(SQP), seemed to be the best method to solve the
problems for nonlinear constrained optimization. In
terms of efficiency, correctness, and percentage of
satisfied answer, after conducting several
experiments on benchmark functions. The method
follows nearly to Newton’s formula for constrained
optimization just as is resolved as other optimization
problems. At each iteration using the method an
initial estimate is made based on the Hessian of the
Lagrangian function using a BFGS quasi-Newton
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
74

updating method. After that, the main method used
for generate a quadratic programming (QP). The code
for this program can be summarized in the following
steps:
Step1: Getting information from the user or
system
Step2: Generate random points in the search space
and make the initial velocity for particles of PSO
Step3: Update the value of each particles in the
optimization problem and inertia weight and count t.
Step4: Determine the best particle among all the
particles of the moment called global best particle and
its cost.
Step5: Choose best particle as agent to start the
SQP method to solve the ED problem otherwise go to
the step7.
Step6: If the particles created in the SQP method
was more efficient than PSO method, replace the two
particles together.
Step7: Modify the particles in the search space
and its velocity.
Step8: Check out the exit condition.
(As an example for exit condition can be when
there is no betterment in the iteration.)
In 2010, a new method was introduced in the field
of intelligent optimization called QPSO (Meng et al.,
2010). The advantage in this method was presented as
it can have a higher convergence rate and enhance the
search space. The success of the method was tested
on 5 benchmark function and proved its efficiency
practically. In the QPSO, the state of each particle and
its velocity is introduced by quantum bit and an angel.
One of the fundamental problems in intelligent
algorithms is being trapped in a local optimum
solution that makes a drastic reduction in the rate of
convergence, and accuracy of the algorithm. To
resolve this problem different algorithm with a
change in the coefficient of inertia attempted to
improve system performance. Experimental studies
show that relatively large inertia weight has the
ability to search for more. While weight reduction
with a coefficient of inertia, leads to the speedy
convergence of the algorithm. Therefore, the weight
of inertia as a linear or nonlinear function should be
reduced.
As the process of searching for a PSO algorithm
is very complex and nonlinear, decreasing inertia
weight and acceleration coefficients without getting
feedback from the global optimal fitness does not
properly reflect the actual search process. In fact, if
general fitness is great, the particles are far from ideal
point. Hence, high speed is required to globally
search the solution space that means [w, c1, c2]
should have greater quantities. Against, when only
small movements are necessary the coefficients must
be adjusted in small quantities. According to this fact,
the proposed inertia weight and acceleration
coefficients are adjusted as a function of the overall
best fit. Hence, Inertia weight and acceleration
coefficients are proposed as follows:
1 1exp
⁄
(12)
c
1
1
1expαF
G
,1,2
(13)
Where
is the
iteration of the global
optimum fitness and parameters need to be pre-
defined. value can be set as follows:
α
1
F
G
(14)
In this case, coefficients vary according to the degree
of improvement in overall fitness. Through the study
of non-linear modulation parameter n, set a
reasonable choice for this parameter is derived in the
(1,2) range. Moreover, under this assumption and the
definitions above, one can conclude that:
0.5 w 1,1.5 c
2,1.5c
2
(15)
6 RESULTS OF THE FIRST
EXPERIMENT
For the first test IPSO algorithm is applied to three
generating units and the results obtained with twelve
other algorithms. For each system, the best results and
the best average results are compared and
improvement is clearly evident in the results. It
should be noted that the technical specifications of the
system used in the experiments are Pentium Duo-
Core computer with CPU 2.6 GHz and 4 GB RAM
memory And results obtained with MATLAB
r2013b. Also, all the data used were extracted from
(S.-C. Chang et al., 1990). To perform experiments
on three applications mentioned above, the initial
population of 40 is considered. Coefficients c1 and c2
are considered as mentioned in the past content.
6.1 The First System under Test
The system consists of three units that the total power
of 850 MW generation units of this test is considered.
The algorithm runs 50 times and the best result and
the average best individual results are listed in Table
1. The experiments were carried out for algorithms,
PSO and IPSO and the results were compared with
ParticleSwarmOptimizationofEconomicDispatchProblem:ABriefReviewTransfer
75
other algorithms in the same conditions.
Fig.1 shows the coefficients for simulation results
of 12 methods and Fig.2 shows the system consists of
3 generating units with a load demand of 850MW and
the comparison of the best and mean fuel costs of 50
trail runs achieved by using methods with those
reported in the paper.
Table 1: The coefficients used in the simulations
(G=Generator).
G
a b c e f
1
100 600 0.001562 7.92 561 300 0.0315
2
50 200 0.004820 7.97 78 150 0.063
3
100 400 0.001940 7.85 310 200 0.042
Table 2: Compare the values of all the methods at three
plants.
Algoritms Best results Mean results
CEP
8234.07 8235.97
FEP
8234.07 8234.24
MFEP
8234.08 8234.71
IFEP
8234.07 8234.16
EP
8234.07 8234.16
EP-SQP
8234.07 8234.09
PSO-SQP
8234.07 8234.72
Firefly
8234.07 8234.08
SPSO
8234.07 8234.18
QPSO
8234.07 8234.10
PSO
8234.07 8234.21
IPSO
8234.07 8234.38
Table 3: Comparison Of Best Results Between IPSO And
PSO.
THE 3-UNIT SYSTEM
Algorithm IPSO PSO
P1/MW 399.1973 300.2635
P2/MW 126.4041 400.0000
P3/MW 324.3986 149.7364
Total generation/MW 850 850
Cost/($.
–
)
8234.067 8234.073
Mean time/s 0.067 0.063
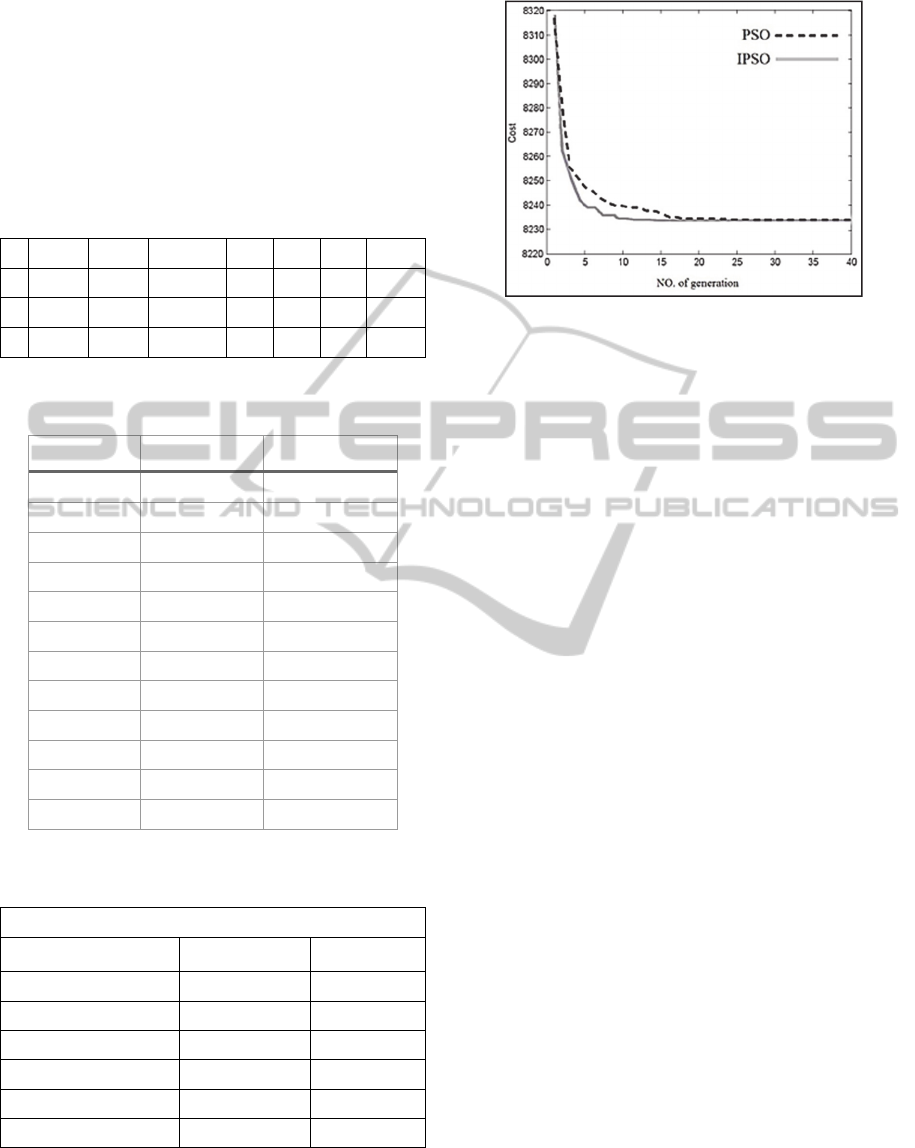
Figure 1: Convergence characteristics of IPSO and PSO for
the 3-unit test system.
7 INTERPRETATION OF TABLES
AND THE SIMULATION
In table1 the coefficients used for the simulation are
presented, and in table 2 traditional PSO method
compared with 11 other methods from the perspective
of the average number of runtime, the response from
the best value of cost function mean time from 50
times perform the program. The results obtained from
this comparison are showing the improved method is
superior to other methods of best value of cost
function vision and from the perspective of time, a
slight increase is observed.
Fig.1 depicted the convergence characteristics of
the IPSO and PSO for the 3-unit test system. From
Fig.1, it can be observed that the convergence rate of
IPSO is better than PSO algorithm.
8 RESULTS, ANALYSIS AND
CONCLUSIONS
This paper is an overview of the method of constrained
optimization and we try to introduce a new index for
solving the ED problems with valve point loading
effects and tried to introduce methods which were
much more effective. Finally method is implemented
to reach to a better global minimum and mean point.
After numerous tests it can be concluded that the
global optimum cost for mean cost function in 3-unit
mode decreases while the response time has a little
increment and also the global optimum cost for best
cost function in 3-unit mode has not any changes.
ICINCO2015-12thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
76

REFERENCES
Blum, C. (2005). Ant colony optimization: Introduction and
recent trends. Physics of Life Reviews, 2(4), 353-373.
Chang, G. W., Aganagic, M., Waight, J. G., Medina, J.,
Burton, T., Reeves, S., & Christoforidis, M. (2001).
Experiences with mixed integer linear programming
based approaches on short-term hydro scheduling.
Power Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 16(4), 743-749.
Chang, S.-C., Chen, C.-H., Fong, I.-K., & Luh, P. B. (1990).
Hydroelectric generation scheduling with an effective
differential dynamic programming algorithm. Power
Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 5(3), 737-743.
Dayhoff, J. E. (1990). Neural network architectures: an
introduction: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.
Finardi, E. C., Silva, E. L. d., & Sagastizábal, C. (2005).
Solving the unit commitment problem of hydropower
plants via Lagrangian relaxation and sequential
quadratic programming. Computational & applied
mathematics, 24(3), 317-342.
Fogel, D. B., & Fogel, L. J. (1996). An introduction to
evolutionary programming. Paper presented at the
Artificial Evolution.
Franco, P., Carvalho, M., & Soares, S. (1994). A network
flow model for short-term hydro-dominated
hydrothermal scheduling problems. Power Systems,
IEEE Transactions on, 9(2), 1016-1022.
Garcia-Gonzalez, J., & Castro, G. A. (2001). Short-term
hydro scheduling with cascaded and head-dependent
reservoirs based on mixed-integer linear programming.
Paper presented at the Power Tech Proceedings, 2001
IEEE Porto.
García-González, J., Parrilla, E., & Mateo, A. (2007). Risk-
averse profit-based optimal scheduling of a hydro-chain
in the day-ahead electricity market. European Journal
of Operational Research, 181(3), 1354-1369.
Hwang, C.-R. (1988). Simulated annealing: theory and
applications. Acta Applicandae Mathematicae, 12(1),
108-111.
Kennedy, J. (2010). Particle swarm optimization
Encyclopedia of Machine Learning (pp. 760-766):
Springer.
Mariano, S., Catalao, J., Mendes, V., & Ferreira, L. (2007).
Profit-based short-term hydro scheduling considering
head-dependent power generation. Paper presented at
the Power Tech, 2007 IEEE Lausanne.
Martinez Ramos, J., Lora, A. T., Santos, J. R., & Expósito,
A. G. (2001). Short-term hydro-thermal coordination
based on interior point nonlinear programming and
genetic algorithms. Paper presented at the Power Tech
Proceedings, 2001 IEEE Porto.
Meng, K., Wang, H. G., Dong, Z., & Wong, K. P. (2010).
Quantum-inspired particle swarm optimization for
valve-point economic load dispatch. Power Systems,
IEEE Transactions on, 25(1), 215-222.
Mezger, A. J., & de Almeida, K. C. (2007). Short term
hydrothermal scheduling with bilateral transactions via
bundle method. International Journal of Electrical
Power & Energy Systems, 29(5), 387-396.
Moscato, P. (1993). An introduction to population
approaches for optimization and hierarchical objective
functions: A discussion on the role of tabu search.
Annals of Operations Research, 41(2), 85-121.
Park, J.-B., Jeong, Y.-W., Shin, J.-R., & Lee, K. Y. (2010).
An improved particle swarm optimization for
nonconvex economic dispatch problems. Power
Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 25(1), 156-166.
Shiina, T., & Watanabe, I. (2004). Lagrangian relaxation
method for price-based unit commitment problem.
Engineering Optimization, 36(6), 705-719.
Victoire, T. A. A., & Jeyakumar, A. E. (2004). Hybrid
PSO–SQP for economic dispatch with valve-point
effect. Electric Power Systems Research, 71(1), 51-59.
Whitley, D. (1994). A genetic algorithm tutorial. Statistics
and Computing, 4(2), 65-85.
Wood, A. J., & Wollenberg, B. F. (2012). Power
generation, operation, and control: John Wiley & Sons.
ParticleSwarmOptimizationofEconomicDispatchProblem:ABriefReviewTransfer
77
