
Ubiquitous Classroom Enhanced by a Cloud-based Server
Rawia Bdiwi and Hichem Bargaoui
Higher School of Engineering and Technology, ESPRIT, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords: Smart Classroom, Ubiquitous Computing, Cloud Computing, Gateway, Collaborative Learning.
Abstract: The development of cloud computing technology, smart digital devices and ubiquitous computing systems,
bring many new opportunities for the area of education. Indeed, smart classrooms support the use of these
various technologies to enhance new ways of learning, teaching and assessment. This paper presents a novel
architecture of a ubiquitous classroom enhanced by a cloud-based server. The designed smart classroom
makes devices such as smart boards, projectors, printers, etc… connected through a gateway in order to
encourage active interactions between learners and teachers. By considering the benefits of cloud computing
in this field, we improved this model of classroom by implementing a cloud-based server that provides an
efficient remote control of the classroom devices through this gateway. This system facilitates the access to
learning data and educational applications for students using their smart devices. In this paper, we provided
an overview of the enhanced ubiquitous classroom based on cloud, its characteristics and finally we
reported some important scenarios offered by this model.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technologies have been used, to develop innovation
and changing in education, and to enhance the
quality of interaction between learners and teachers
through the implementation of smart classrooms
which are intelligent classrooms equipped with
many digital devices that can be reconfigured
automatically and can detect for example the arrival
of students; store the discussion of the lecture
through laptops, tablets, etc.
In fact, collaborative learning is based on groups
of students working together to search for
understanding, and to share experiences. The
achievement of this evolution in educational
environment requires the establishment of smart
spaces which are connected through different smart
devices. Thus, the advent of new technologies such
as cloud computing and pervasive computing…has
completely changed the concept of teaching that
provides an accomplished teacher-student
communication.
Classically, learning methods help students to
reach their goals by applying many approaches to
learning that encourage and motivate them to learn.
Therefore, an important number of concepts based
on using a wide variety of models in educational
technology such as e-learning or distance learning,
which is a teaching system implemented to be
remotely accessed via electronic communication.
The evolution of e-learning to other concepts for
instance m-learning and b-learning becomes very
interesting these recent years (Martin and Gil, 2008).
Mobile learning or m-learning (Klassen and
Elan, 2013) is the use of handheld devices to
facilitate access to training courses. Blended
learning or b-learning (Chao and JingDong, 2008) is
the combination of traditional classroom and e-
learning, this merge online with habitual face to face
activities. Hybrid education or b-learning uses online
technologies to develop the teaching process.
Eventually, the next evolution of learning and
development is called s-learning (Martin and Gil,
2008) that keeps the theory of using various
educational objects to make re-usable instructional
and advanced services to be readily incorporated in
Learning Management System (LMS).
However, in novel methods of learning systems,
students can interact within the smart classroom with
their own devices, such as tablets, mobile phones or
PCs. In addition, learners are already familiar with
the device that they are working with. So, the
advantages of using these personal resources are
many such as prepare practical labs or presentations,
working on assignments, writing their observations
or personal expression, etc. The last few years, many
546
Bdiwi R. and Bargaoui H..
Ubiquitous Classroom Enhanced by a Cloud-based Server.
DOI: 10.5220/0005484505460552
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2015), pages 546-552
ISBN: 978-989-758-108-3
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

students reported that using personal computer in
educational courses is better than writing with pencil
and notebooks for the reason that they might
perfectly review courses or labs at home, they could
modify their work in order to help them to take
advantage of the portability of learning content.
Moreover, this concept, offers the opportunity for
teachers to interact with their students, to further
improve courses taught and the quality of lecture
through the achievement of practical labs for
example which still available to learners during the
reviewing.
Hence, the potential benefit is the use of various
equipments in ubiquitous classroom environment
that enables real-time interactions and
communication to transmit digital educational
content. Therefore, teachers can receive instantly the
lecture feedback and the questions asked by students
via these smart devices. This new cooperative
approach to teaching in the field of education makes
reciprocally beneficial learning innovation for both
students and educators. On the other hand, the main
advantage that teachers can more perfectly remote
their classrooms through monitoring personal
devices of learners working in groups. Definitely,
the authors are aware of the benefits of combining
technologies and collaborative learning.
The main goal of this paper is to propose a new
architecture of ubiquitous classroom enhanced by a
cloud-based server. The designed smart classroom
makes all devices such as laptops, projectors, etc
connected through a gateway in order to allow
students to be more involved in collaborative
learning and to encourage active interactions among
learners and educators. Firstly, the cloud-based
server provides an efficient platform for the remote
control of the classroom devices through the
gateway. Secondly, students and teachers who are
connected to this improved server can access to
learning data and educational applications using
their various devices.
The rest of this paper is outlined as follows. In
section II and III, we briefly describe the
technology-enhanced classroom and then we present
some previous work. After that, we illustrate the
architecture and the design of our proposed system
(cloud-based classroom) in section IV. Finally, we
conclude in section V with summary and future
work.
2 TECHNOLOGY-ENHANCED
CLASSROOM
Technologies in the field of education are required
in today’s scalable learning environment. Smart
classrooms are a novel way that offers a high quality
of teaching to students by facilitating them the
improved training of concepts, enhancement in
communication skills and educational success.
Technology-enhanced classrooms are equipped
with audiovisual and electronic materials, smart
interactive whiteboards, data projectors, virtual labs
tools and computers, etc enabling educators to
benefit from a diversity of media while teaching.
Smart classroom is a current project at ESPRIT that
completely changes the method of “teachers” who
typically teach and “learners” who learn without
reflecting. These classrooms provide the use of
several technologies through the connection of
various devices in order to transform the learning
experience for students who have improved their
academic achievement at the university. Besides,
educators are able to use their own intelligent tests in
classroom through the system and employ them for
assessment. In addition, learners are using a variety
of devices such as tablets, mobile phones, personal
laptops to answer questions that replace actually the
pencil and the notebook. At home, the use of these
personal equipments as handheld remote or PCs
allows them to review their notes and assignments
anywhere.
Smart classrooms provide also the possibility to
share smart resources, connected to the classroom,
with several other locations. This concept is
supported by e-learning approach that brings new
opportunities for the way of education and provides
a high quality of the distributed information. This
method is offered to students, who have a prevention
to attend physically the lecture. The smart spaces are
implemented with embedded computers, information
devices, and multiple sensors that permit students to
follow the lecture and achieve assignments by
offering the possibility to remotely access the IT
system and computers. It provides operational
interfaces which allow the instructors to approve a
new teaching experience by implementing hardware
and software technologies to control students’
devices through displaying information at their
screens.
Over time, many educational researchers have
developed novel methodologies for the pedagogical
process; the most revolutionary method is known as
online learning or distance learning which offers an
efficient platform to achieve the same learning
UbiquitousClassroomEnhancedbyaCloud-basedServer
547

outcomes without the requirement of using the face
to face communication in the same place. Hopeful
students, have successfully spent towards a new
world of education which proves the concept saying
“each learner is able, at any place and any time
access to a classroom equipped with multimedia
materials”…instantly the student is liberated to a
world of information that responds to all constraints
of the pace of learning. Rather, based on this
approach there is a lot of researchers and learners
think about migration to the area of virtualization.
The system of virtual classrooms is accessible at
any moment unrestrictedly. This enables students to
approve a rich and new learning experience. The rate
of data transmission is relating to the user’s speed
connection because it is an instant communication
from the platform and the remote device used by
student. In addition, educators can dynamically
control the teaching process as they do in traditional
classroom; they interact with the real time feedback,
and provide a more sophisticated way of assessment
activities remotely.
However, there are multiple methods which can
be used in order to implement a performing system
of virtual classroom. This platform requires the
establishment of many particular equipment at both
sides the institution and learner. So, students must
have an extensive knowledge of operating systems,
networks and several tools used to provide remote
access. This type of classroom can be equipped with
a server that is configured with learners’ accounts
and other devices must be implemented to
accomplish this remote interaction such as video and
audio systems, interactive whiteboard, etc.
All technologies used currently in classrooms
leads us to ask the main question: Is there any way
to replace or to enhance smart classroom?
Obviously, ubiquitous learning is the most
appropriate answer because this kind of technologies
has an important impact on education. It is defined
as learning anytime, anywhere using several devices.
The use of pervasive or ubiquitous devices and
mobile technologies in educational environment
such as smart phones, PCs, iPods, and other
equipments as interactive whiteboards which use
numerous network connections include Wi-Fi or
Bluetooth, and NFC, provides an enhanced way of
learning to the students who receive the personalized
information.
The concept of u-learning (Joung-Souk, 2009)
illustrates the use of ubiquitous computing, that
offers an interesting mode of linking mobile devices.
These equipments and tiny sensors facilitate the
interaction with educational environment and allow
the exchange of data among students and teachers.
Let’s be deeper in the explanation of u-learning.
Typically, ubiquitous learning is a novel learning
environment which is available through a variety of
contexts. In fact, ubiquitous learning complies with
many characteristics such as the accessibility that
offer to students the remote access to their data or
videos from any place. The second criterion is the
interactivity that allows the two-way communication
between learners and educators in real time. Thus,
teachers have feedback instantly and the knowledge
becomes more accessible. In addition, the
permanency is very important in this context since
the students cannot lose their data, labs or work, all
the learning information or processes are saved daily
within the system.
U-learning is a particular category of distance
education which is based on the use of various
devices and technologies to encourage collaboration
through delivering comments, tips and instant
feedback even for students who attend distance
training. U-learning is known by its increased
capacity of moving physically the learning
environment anywhere. Hence, the main goal of any
type of learning is to overcome the constraints of
human everyday life and especially to improve the
quality of teaching, to achieve these objectives
already mentioned; so it is necessary to implement
new architectures using ubiquitous technologies and
specific tools.
It’s obvious that cloud computing represent a
significant change in the field of education as
ubiquitous computing. The cloud provides the
remote access data at any moment, and any place. It
changes the way of communication, learning, and
working in classroom. Thus, it’s necessary to use
several resources such as memory, data storage, and
the rate of bandwidth which will be shared among
distant learners.
3 RELATED WORK
This section presents some works which focuses on
presenting previous models of technologies used in
the context of smart classrooms. The main issue of
the existing work is smart classroom using
ubiquitous computing, web service technology,
cloud computing and management of online courses
classroom devices, in order to facilitate collaborative
learning.
There are many projects treating the progress of
traditional education with a wide variety of
technologies such as pervasive computing. These
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
548

researches cover several concepts of smart learning
activities. Thus, the problems of the ancient type of
education are numerous as the fact that students
cannot attend the course or the practical sessions and
write their observations, or results simultaneously.
So, through the use of cloud and pervasive
technology and the software solutions, teachers and
students can exchange comments and observations
through the screens of different devices connected to
the system.
The paper (Bargaoui and Bdiwi, 2014) presents a
designed gateway for ubiquitous classroom. It
enables teacher and students to have interactional
classroom where several devices are connecting
through this gateway. In (Shri and Subha, 2013) E-
learning application in private cloud (Cluster based
Environment) is developed using several
technologies. The paper demonstrates a cloud
computing architecture system that provides
persistent storage, scalability, and remote access, of
the E-learning system objects.
The researchers in this paper (Catherine and
Christos, 2012) explore the use of pervasive
computing devices in the higher educational
environment. A study on characteristics and
applications of the future ubiquitous computing
devices is illustrated.
The progress of ubiquitous learning environment
offers the combination of the benefits of an
intelligent learning environment, the advantages of
ubiquitous computing technology and finally the
usage of various mobile devices. The system of
learning between student and teacher is not restricted
to e-learning. There is an implementation of system
(Joung-Souk, 2009) that allows learners to be
supported with a way of authentication, an electronic
input, distribution, gathering, and support learning
multicast.
The main goal of this work (Di Lecce and
Taranto Giove, 2009) is to present the concept of the
implementation of a collaborative learning interface
based tool for virtual classroom; it is used in order to
analyze the users’ data to assess the rate of
participation of students in the e-learning system
proposed.
Other researchers have designed in (Kong and
Ogata, 2009) a type of smart classroom that provides
integration among a system of e-learning based on
web and simply classroom based e-learning that
offers the reporting system which connect numerous
modalities of communication.
The paper (Premchaiswadi and Tungkasthan,
2010) describes an overview of e-learning system
known as an interactive virtual classroom which use
a sophisticated protocol based on TCP real time
networking called RTMP (Real-Time Messaging
Protocol). It provides the synchronization of many
types of data and facilitates the interaction between
teachers and learners who can directly exchange
messages as in a real classroom through using a
web-based collaborative work.
A different system using cloud computing
technology (Wang and Hu, 2013) is implemented to
demonstrate how the future classroom can use
multiple services based on the technology of cloud
computing in order to ensure smart control, a very
high capacity of data storage level, the secure
management, which can be shared among many
devices. In (Dinita and Wilson, 2012) a cloud based
solution for learning in educational environment is
illustrated. This system use virtual infrastructures
based on various equipments such as switches,
routers and virtual PCs that explain many virtual
scenarios of communication among educators and
students.
4 CLOUD-BASED CLASSROOM
4.1 Ubiquitous Classroom
The ubiquitous classroom is a new classroom model
that contains multiple smart devices such as printers,
projectors, smart board. These devices which are
connected via a gateway acts automatically when
detecting learners.
This system provides a real-time communication
of information offered by the intelligent educational
environment, allowing the teacher and students to
have an interactive classroom. In addition, the
gateway manages the devices in the classroom and
serves as a platform for executing educative
applications that provides services to improve the
course. It allows for example the verification of
student’s attendance in a very simple way, when
they enter the classroom. The architecture of the
ubiquitous classroom is described by Figure 1.
This ubiquitous classroom has two major
components. The first component is the smart
devices and sensors. The students and the teacher
can interact with these several devices such as smart
board, computer, interactive response system, video
and audio devices.
The second component is the embedded
gateway, which enables the exchange of data with
smart devices. It contains a middleware that
provides the ability to run many educative
applications and add support for new devices.
UbiquitousClassroomEnhancedbyaCloud-basedServer
549
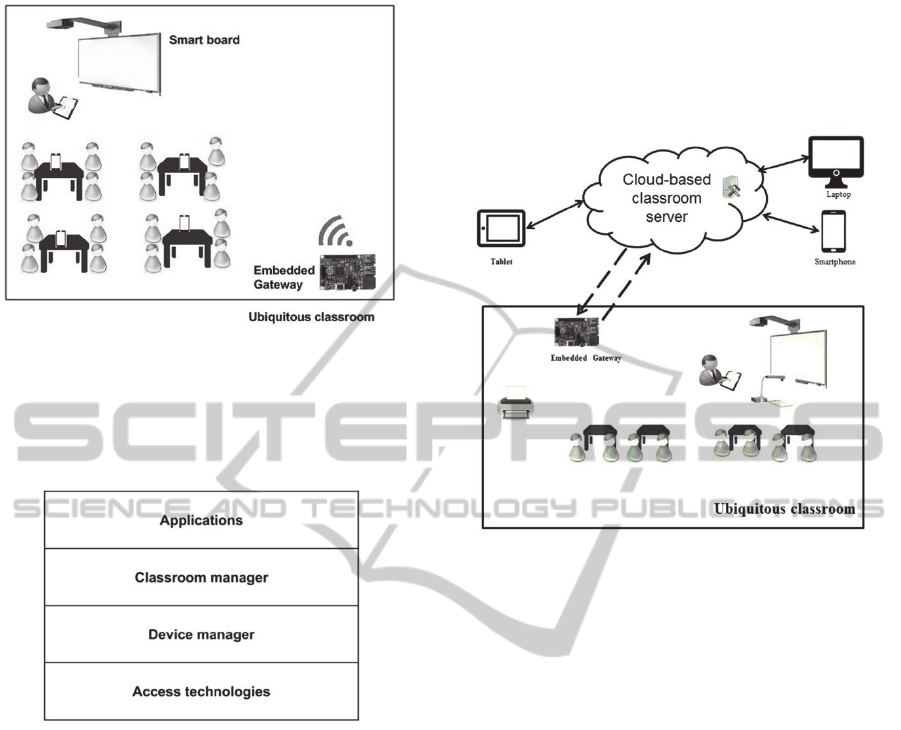
Figure 1: Architecture of ubiquitous classroom.
Figure 2 shows the software architecture of the
gateway. It consists of four layers: the layer of
access technologies, device manager, class manager
and the application layer.
Figure 2: Middleware architecture of the gateway.
The Application layer contains the services deployed
in the classroom. The second layer is the classroom
manager which provides an adaptive behaviour
based on the course profile. It permits also the
communication between devices. The device
manager layer role is to detect the currently
available devices, to provide a standard access to
devices through a common interface. Finally the
physical access layer is in charge of connectivity
over access technologies such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi,
USB, etc.
4.2 Cloud-based Server for Enhanced
Ubiquitous Classroom
The cloud-based classroom server contains a
platform of e-learning, administrative tools and
database server. Its main objectives are distance
learning, user management, and finally remote
management of multiple classrooms. The e-learning
platform is accessible from different client devices
through a thin client interface such as a web
browser. The designed ubiquitous classroom
enhanced by a cloud-based server is described by
Figure 3.
Figure 2: Architecture of ubiquitous classroom enhanced
by a cloud-based server.
Using the architecture presented above, learners and
teachers can connect to the server, which provides at
the same time distance learning and course loading
on smart board in the classroom. Further, it provides
a sophisticated assessment system and the remote
management of classroom’s embedded gateways.
Indeed, it can handle multiple classrooms because
each classroom has a profile on the server.
4.3 Implementation
For the implementation of our proposed solution, we
have chosen the Raspberry-Pi board and the OSGi
framework for the designed gateway. Thus, various
smart devices used throughout the system are
respectively RFID reader and smart video projector
controlled by an Arduino board. The main benefit of
Raspberry-Pi is that it combines the characteristics
of a single-board computer and has the size of a
credit card.
Let's explain why we used OSGi. It represents a
service platform and an efficient modular system for
the Java programming language which serves during
the implementation phase as a dynamic and
complete component mode. Therefore, the
educational applications can be remotely installed,
uninstalled, started or stopped, and finally updated
without restarting. The Arduino is also known as
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
550

single-board microcontroller dedicated to facilitate
the access to applications, interactive objects or
smart environments. Finally, RFID (Radio
Frequency Identification) is a set of technologies
used to identify persons and different objects
wirelessly.
In addition, an e-learning platform such as
Moodle will be deployed on the cloud server with
the integration of different modules in order to
manage the profiling system which control several
classrooms.
4.4 Applications Scenarios
In this part, we conducted two scenarios to validate
the ubiquitous classroom enhanced by a cloud-based
server.
The first scenario is about practical lab. This is
an example that can demonstrate the seamless
interaction among teachers and students with
classroom devices, and a cloud server. Students who
walk into the classroom have just their NFC tags
near the RFID reader to indicate their presence. This
information is transmitted instantly to the cloud
server via the gateway. Then, the application located
in the gateway will load from the cloud server the
teacher profile, the appropriate course and the list of
students. When the teacher enters into the classroom
an identification device based on RFID system will
detect his presence. Through the use of the cloud
server, the course will be loaded automatically into
the smart board depending on the already loaded
class profile. The document of the practical lab will
also be printed via the printer according to the
number of present students. The assessment of
student work will be achieved on the cloud server
through laptops or tablets.
The second scenario treats the assessment
process as for language exams. So, the subject of the
exam will be loaded from the cloud server and
projected to students on the smart board. Learners
using their tablets, laptops... are connected to the e-
learning platform on the cloud server. They can view
the problem situation on the board and interact with
the online assessment system by answering
questions simultaneously. In this way, teachers can
perform the online evaluation of the student
responses. Through this system, we described the
changing of the assessment method of student
learning that can improve the quality of teaching,
and it provides to the educators the possibility to
have an immediate feedback on the student learning
outcomes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we designed a ubiquitous classroom
enhanced by a Cloud-based server. It combines at
the same time the features provided by ubiquitous
classroom and virtual learning environment
deployed in a cloud server. Indeed, we explored the
benefits of cloud computing which can serve in
educational environment to overcome several
limitations of ubiquitous learning.
We are currently implementing the proposed
system which illustrates an ecosystem for both
virtual and ubiquitous classroom due to a very
thorough study which required a comparison among
the process of learning using our architecture and the
traditional educational environment.
The current presented design is still in progress
as a lot of open issues that have to be considered. As
part of our future work, the system needs the
evaluation phase that already complements the
implementation process in order to find out its
advantages and restrictions. Further, this phase will
demonstrate how our novel system can completely
enhance the performance of learners.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the ESPRIT
colleagues who reviewed this paper.
REFERENCES
Martin, S., Gil, R., Diaz, G., et al, 2008. From e-learning
to m-learning through b-learning and s-learning. In
Proceedings of ELMAR 2008, International
Symposium (Volume: 2), pp.341-344. Zadar, 50
th
edition.
Klassen, A., Elan, E.V., Eibrink-Lunzenauer, M.,
Gloggler, T., 2013. Requirements for Mobile Learning
Applications in Higher Education. IEEE International
Symposium on Multimedia (ISM). Anaheim,
1
st
edition.
Chao, Cao., JingDong, Zhu., Hui, Peng., 2008. Blended
Learning Based Educational Technology Training for
Teachers in Colleges and Universities. Education
Technology and Training 2008 and International
Workshop on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Joung-Souk, S., 2009. U-Learning Model Design Based
on Ubiquitous Environment. International Journal of
Advanced Science and Technology (Volume 13).
Bargaoui, H., Bdiwi, R., 2014. Smart classroom: Design
of a gateway for ubiquitous classroom. International
Conference on Web & Open Access to Learning.
UbiquitousClassroomEnhancedbyaCloud-basedServer
551

Dubai, 1
st
edition.
Shri, M.Lawanya., Subha, Dr.S., 2013. AN
IMPLEMENTATION OF ELEARNING SYSTEM IN
PRIVATE CLOUD. International Journal of
Engineering & Technology (0975-4024) Vol. 5 Issue
3, p3036.
Catherine, M., Christos, S., Petros, B., 2012. Employing
ubiquitous computing devices and technologies in the
higher education classroom of the future. International
Conference on Integrated Information Procedia-Social
and Behavioral Sciences (Volume 73), pp.487-494.
Budapest, 2
nd
edition.
Di Lecce, V., Taranto Giove, A., Quarto, A., 2009. A
virtual classroom interface for student participation
measurement. Virtual Environments, Human-
Computer Interfaces and Measurements Systems.
VECIMS '09.
Kong, S.C., Ogata, H., Arnseth, H.C., et al, 2009. Smart
Classroom 2.0: Context-aware Educational System. In
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Computers in Education Asia-Pacific Society for
Computers in Education. Hong Kong, 17
th
edition.
Premchaiswadi, W., Tungkasthan, A., Jongsawat, N.,
2010. Enhancing learning systems by using virtual
interactive classrooms and web-based collaborative
work. Education Engineering (EDUCON). Madrid, 1
st
edition.
Wang, Zhouxiu., Hu, Ting., Xu, Yafeng., Feng,
Nengshan., 2013. A Designing and Research of Future
Classroom Learning Support System Based on Cloud
Computing Technology. Intelligent System Design and
Engineering Applications (ISDEA). Hong kong, 3
th
edition.
Dinita, R.I., Wilson, G., Winckles, A., Cirstea, M., 2012.
A cloud-based virtual computing laboratory for
teaching computer networks. In Proceedings of
International Conference on Optimization of Electrical
and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM). Brasov, 13
th
edition.
CSEDU2015-7thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
552
