
Reality Vs Hype
Does Cloud Computing Meet the Expectations of SMEs?
Katie Wood
and Kevan Buckley
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Wolverhampton University, Woverhampton, U.K.
Keywords: Cloud Computing (CC), Security, Risk Management, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Cloud
Service Providers (CSP).
Abstract: Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) have become a primary target audience for Cloud Service Providers
(CSP), such as Amazon and Microsoft to promote their cloud offering. CSP strong marketing campaigns of
‘promised’ benefits from using their clouds is an attractive offer for SMEs especially where resources are
limited and they wish to become more agile and reduce IT costing to be competitive with larger rivals. This
paper argues that once SMEs remove the hype surrounding the concept of cloud computing (CC), the reality
of significant benefits do not materialize for SMEs. This paper demonstrates, through working with SMEs
considering the options of CC that the challenges and risks associated with cloud might actually hinder the
business, rather than providing any real long term value.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing (CC) has gained increased
attention and momentum within a short period of
time, even those the technology is still very much in
its infancy. The increase interest into this form of
distributed system has been fuelled by the strong
marketing campaigns form Cloud Service Providers
(CSP) that have promoted the promised of benefits.
It is frequently reported that
CC offers a variety of
benefits including cost-saving, agility, efficiency,
resource consolidation, business opportunities and
Green IT (Chang et al., 2010) Even so, cloud is still
a young and evolving paradigm that incorporates the
evolutionary development of many existing
computing technologies. This paper defines hyper
surrounding CC as being the extravagant or
intensive positive promotion of CC technologies by
CSP and through the media. Such extravagant
promotions, has lead to SMEs within this study to
consider using CC as significant benefits, especially
in term of cost saving and improved performance
were expected. However the observations and
findings of this study, suggest that in reality such
expectations have not be achieved.
This study identified there a lack of
understanding surrounding the terminology of CC
and the changing variable within CC makes it
challenging to alignment with SMEs needs.
Concerns surrounding security are noted as being a
majority issue for SMEs in terms of establishing
their role and the CSPs in protecting the systems.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows: Section 2 provides a brief outline of the
background and rational for undertaking a research
project. Section 3, presents an overview of unique
features of cloud where benefits are clamed. The
section continues through a detailed discussion of
the issues and how these limit the chance of any
business value of using cloud technology for SMEs,
if not understood or assessed during the decision
making process. Section 4 outlines the need for risk
assessment to be conducted and awareness of risks
associated of CC. Section 5 presents considerations
as part of a risk assessment that could be part of
assessing CC suitable. Section 6 concludes the
paper. Finally, section 7 outlines further work that
the authors have planned to continue on this project.
2 PRIMARY OBSERVATIONS
The findings outlined in this paper are from research
undertaken with SMEs in the West Midlands, UK.
SMEs from different industries where selected to
take part in a study to access SMEs understanding of
CC and what cloud technologies were currently
being used or considered. Initially a questionnaire
172
Wood K. and Buckley K..
Reality Vs Hype - Does Cloud Computing Meet the Expectations of SMEs?.
DOI: 10.5220/0005472401720177
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2015), pages 172-177
ISBN: 978-989-758-104-5
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

survey was used to collect data. 50 SMEs in the
West Midlands took part in this stage. Businesses
were selected based on the fact they heavily used
forms of technology in their operations, but were not
deemed as a business in the IT sector. The rationale
behind this selection was to access people who have
an average level of IT usage and experience of IT,
who would understand and interact successfully with
cloud technology without the need to be an IT
expert. The questionnaire survey allowed the
authors to gather valuable information and gauge
SMEs general understanding of the concept of
CC
and establish the level of interest and use from the
SME community. From the results of stage 1,
several SMEs were then invited to take part in a
deeper analysis. During this stage semi-structured, in
depth interviews were used and acted as the primary
data collection method for the project. The SMEs
selected were based on the responses from stage one.
SMEs selected for this stage were based on the
following criteria:
Table 1: Criteria for SME involved in stage 2 of study.
The business was involved in the initial
questionnaire stage of the project.
Staff had a fairly good level of IT skills
There was an interest in understanding more about
cloud and some evidence of some form of cloud
computing has been used.
The business wanted to consider using PaaS in the
future.
The business uses websites, email and database
applications, which would be suitable applications to
use and store within a form of cloud environment.
Each interview was individually conducted between
the author and participant and took around 45
minutes. A combination of closed and open
questions were selected relating to the business use
of IT, the business rationale for considering CC and
the participants understanding of use of CC. Results
and transcripts from the interviews have not been
shared or compromised at any point during the
project or discussed in this paper order to ensure
confidentiality and participant’s anonymity.
This paper outlines some of the responses from
the participants from both stage 1 and stage 2 to
highlight growing concerns of issues relating to
cloud computing and evidence of limited benefits
emerging. The findings overall conclude a growing
interest in the topic, however when it came to
practically using cloud, SMEs either had
experienced problems and disappointment through
using the technology, or the complexity led to the
decision to migrate to cloud being terminated. This
paper outlines several areas where SMEs stated
complexity and where potential benefits promoted
by the CSP have not materialized to produce overall
benefits.
3 CHALLENGES OF CLOUD
3.1 What Actually Is Cloud
Computing?
To establish the participants understanding of CC,
the first sets of questions asked to participants
during the interviews were to assess their
understanding of the concept of CC and user
experience. All participants involved in this study
had heard of the concept
CC, so you might wonder
why the question “Do you know what cloud
computing is?” was even asked? According to
results from a survey conducted in 2012 (Chang et
al., 2010). Participants in that study were asked to
explain the concept “the cloud” The majority
responded with the view it either referred to an
actual cloud (specifically a “fluffy white thing”) in
the sky or something related to the weather (29
percent). Only 16 percent of participants thought it
was related to computer networking to aid storage,
access and share data from Internet-connected
devices.
It this particular research project with SMEs
participants the results from this question concluded
that only 30% of the participants could actually
provide some clearly definition on what the term
means in the context of computing. Surprisingly
over half the participants believed they have actual
use a form of cloud technology, even those they
were not sure what was meant by the term CC. From
a security point of view, this statement is concerning
as participants are not aware of what technology,
services or systems they are actually using and the
risk associated.
Given the relatively immature nature of CC and
that it is still evolving. It is not surprising that end
users and businesses are finding it difficult to
understand what is exactly meant by the term cloud
computing. There has been work in recent years to
establish a benchmark and suitable definition for
cloud. Currently however there is still no precise
definition (Interworkscloud, 2013) for cloud, which
makes it a challenge for businesses to understand the
different elements that are required for a successful
uptake of CC. This has led to arguments by
researchers that the term “cloud computing” is far
too broad making it difficult to develop a single and
RealityVsHype-DoesCloudComputingMeettheExpectationsofSMEs?
173
clear definition. (Wood Katie, 2012) Currently, there
are over 20 different definitions. The most regularly
used definition is by the National Institute of
Standards and Technology (National Institute of
Standards and Technologies, 2009) Basically, `CC'
as an umbrella term being applied to different
situations and their solutions. It is the next stage in
the distributed and shared computing. This form of
computing provides a range of computation
facilities, storage and scalable functions and services
that are accessible anywhere via a connection to the
Internet.
3.2 SMEs Concerns
Graph 1: Results from stage 1 – Questionnaires Shows the
range of concerns SMEs have with cloud technologies.
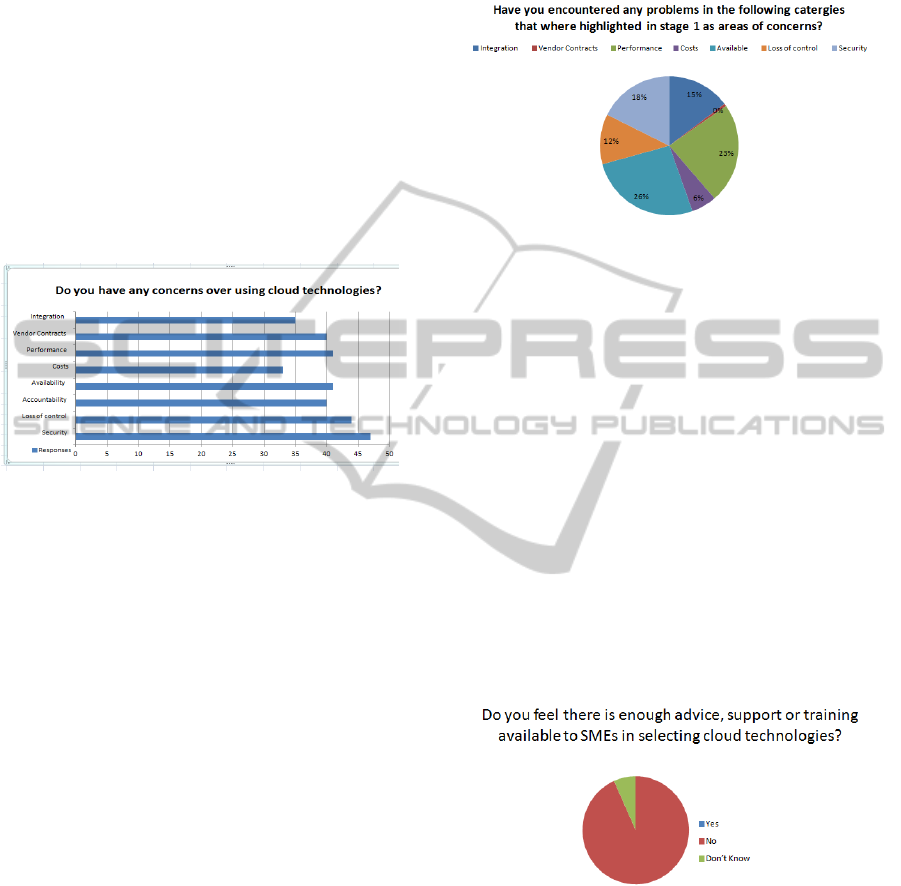
Graph 1 shows the different categories that
SMEs had concerns over using cloud technologies.
47/50 participants identified security has their major
concern. This was followed by a high proportion of
participants stating concerns over loss or control
43/50 and performance 41/50. Concerns highlighted
above led to a follow up question directly linked to
this during the interview stage in order to see if any
of the concerns raised by SMEs have also
materialize into real problems for SMEs that had
used cloud technologies. Unsurprisingly SMEs had
encountered problems in most of the categories
previously outline which showed that there is
evidence to back up the concerns from SMEs that
might still be weighting up the options of cloud.
26% of SME in stage 2 identified that they have
encountered security problems and 23% as having
experience performance problems. As semi
structured questions were used during this stage,
some SMEs further explained that the problems they
had occurred several times over a short period of
time. In once case led to a SME to reconsider using
cloud services to store data as the performance of the
system led to performance and available problems
which was seriously hindering the operational side
of the business. Cost of using cloud technologies did
not appear to be a concern by SME participants in
this study. There was a consensus from participants
that there is a wide option of price plans offered by
different CSPs which allowed for flexibly.
Graph 2: Results from stage 2 – Interviews Shows the
range of concerns SMEs have with cloud technologies.
3.3 Migration and Section
One of the first challenges for any potential cloud
user is dealing with selecting the correct cloud. CC
can be classified into three categories: Infrastructure
as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and
Software as a Service (SaaS). To further complex
the situation, CC can also be offered in different
deployment formation - public, private, community
and hybrid clouds. Each form of cloud and
deployment bring a whole set of different potential
benefits and associated risk. Therefore the first
challenge is assessing which form of cloud is
suitable for that business. In order to benefit from
cloud systems and services a business needs to have
an understanding of the difference between the
forms or clouds as well as looking at several CSPs.
Graph 3: Results from stage 1 – Questionnaires. Shows the
percentage of participants that feel there is not enough
advice, support or training available for SMEs.
As shown in graph 3. Participants for this study
felt strongly that training, education and support on
the subject of CC is currently lacking. Participants in
this study felt there is not enough advice, support or
training in dealing with the starting process over
selection and migration of systems and applications
and also the legal aspects to ensure their data and
rights are protected.
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
174

3.4 Compatibility
Linking to the migration to clouds, all businesses in
this study highlighted the need for cloud services
that are compatible with existing services and
application. Participants felt that there is not enough
guidelines or support in terms of how suitable clouds
are to meet their needs and also their compatibly
with exist systems and applications the business
might still require. As businesses has already invest
in systems prior to considering the option of cloud it
is important those systems and applications are not
ignored if these are still fit for purpose. There is
limited documentation and advice on the matter to
aid businesses in finding suitable and available tools
and techniques to support this objective. 80% of the
participants during stage 1 stated if cloud systems
where used, they would still feel current systems and
application would have to remain for certain tasks.
Therefore this would be increase outgoing costs of
maintaining both an existing systems and cloud
system, therefore not providing the businesses with
any cost saving.
3.5 Security
CSP often claiming that security in the cloud is
tighter than in most enterprises (David Binning,
2009) however the following questions need clear
and defined answers for CSPs. Will SMEs data be
safe in the cloud? What about data protection? What
will happen if security threats or breeches occur on
the cloud even those the technology has been around
for several years now, Gartner warned in 2013 that
there are still six major security issues that
businesses should tackle when considering cloud
adoption. (Warwick Ashford, 2013) Each cloud is
unique, offering different benefits and ways to
reduce costing. However there are also significant
drawbacks of cloud systems, particularly in security.
The variation of security threats and possible
breaches that the system could encounter, further
complicates cloud. [7 Distributed denial of service
attacks are on the raise on cloud systems, as clouds
host services for different customers on their severs,
so it’s no surprise these systems are a hot target for
cybercrimes. The fact that different businesses and
users sharing the cloud space also increases the risk
of access errors and leading to data been vulnerable
and at risk of being accessed by others. How data is
moved across and between CSP and the end user
also places greater risk and vulnerabilities.
One major downside of clouds is that the
provider has control of the user’s data. Users have to
relay and trust their provider will protect their data
and privacy. Privacy is an important issue for cloud
computing, both in terms of legal compliance and
user trust and this need to be considered at every
phase of design. (S. Srinivasamurthy and D. Q. Liu,
2010) Privacy has yet to be fully acknowledged as a
serious problem by policy makers and CSP. The
limited regulations and legislation being enforced on
privacy and user protection rights reflect this.
According to a recent Cloud Security Alliance
Report, insider attacks are the third biggest threat in
cloud computing. (Top Threats to Cloud Computing
v1.0, 2014) The reasons for this may vary, from
users not understanding the system and the
configuration processors, through to users who are
motivated to create damage and misuse.
Administrators and development need to deal with
this situation in a more consistent manner across
different cloud platforms. Therefore it is essential to
access the dynamics of a range of configuration
techniques and tools to evaluate and distinguish the
impact these issues have on a cloud.
The survey used in stage 1 showed that (75%) of
the SMEs stated concerns over employees IT
knowledge and felt that employees would have to
receive additional education and support in order to
use the technology effectively. (50%) of these
businesses further stated they are currently not in a
position to invest in providing such support for
employees at the moment. This further outlines
drawback to using cloud technologies that
businesses are assuming that high investment in
education and training would be required to use
these systems, when in fact the role of using clouds
could be to simplify certain IT tasks, for example
updates security countermeasures.
3.6 Costing
One of most hyped aspect of cloud computing is
surrounding cost savings. Yet has stated in early
sections of this paper, If SMEs have to continue
using existing systems and applications along a
cloud system there are no financial benefits.
Businesses and individuals considering using cloud,
expect appropriately reliable and timely service
delivery, easy-to-use interfaces, collaborative
support, information about their services, etc.(M. A.
Vouk, 2008) Such high exceptions are
understandable as the CSP have promoted their
cloud service as being able to achieve such goals.
All CSP will be affect at some point by downtime,
for example during upgrades. There was been recent
cases of security breaches in Amazon, Gmail and
RealityVsHype-DoesCloudComputingMeettheExpectationsofSMEs?
175

Hotmail. The user is often unaware of such problems
unless their CSP informs them or they are affected
by the security breach. There is currently no
legislation in place which states the CSP must
inform users of all security breaches on their
systems.
3.7 Performance
Clouds promote the benefits of scalability and
flexibility for customers as cloud computing shifts
everything from local, individual devices to
distributed, virtual, and scalable resources, thereby
enabling end-users to utilize the systems, storage,
and other application resources (which forms the
“cloud”) on-demand (Hayes, 2008). The term multi-
tenancy refers to the ability to run multiple
customers on a single software instance installed on
multiple servers. These systems have recently
become popular due to the multi-tenancy features
within which allows businesses to benefit from
reduced costs yet continue to gain access to data and
applications. (Wood and Anderson, 2011) Reliance
on cloud infrastructure provides issues for the end
user in terms of the reliability and availability of the
CSP and cloud services. It is crucial that CSPs
ensure they meet the privacy requirements of users
and legislative requirements. Reports on privacy
failure and loss of user data have had serious impact
on the creditability of Cloud technology and the
overall expansion of cloud services, as well as on the
end user. This clearly demonstrates the risk
associated with reducing control of own data
4 RISK ASSESSMENT
Given the nature of CC and its key characteristics
several risks can be determined. Some of these risks
are traditional risk and concerns that are common
with any form of networking technology. However,
there are also specific risks relating to cloud.
Businesses need to understand, analyse, and evaluate
important economics and elasticity capabilities of
different forms of cloud systems and technologies
and providers before making any commitment to
CC. Any selection should be based on the suitability
for meeting the business requirements and
alignment, rather than being motivated with
marketing and the desire for the least technologies.
For any business it is important to consider all the
options available. In the case of SMEs, it is more
critical given their limited budget to get outsider exit
advice – i.e. consultancy services to aid the decision
making process, due to financial constraints.
5 CONSIDERATIONS IN
TACKLING CLOUD
CHALLENGES
5.1 Testing and Evaluating
The development and integration of different system
hardware, storage, networks, interfaces,
administration and so on, should be careful planned
out. However businesses are not always sure what IT
they require in the short and long term. Before
committing to any cloud technologies, it is critical
that businesses assess and evaluate their business
needs as well as exploring the difference cloud
options available. This might appear time-
consuming and costly; however the right decision
must be made. There are too many different CSP
available and packages; therefore it is useful to
research against the business requirements a few
different CSP to see what is being offered. Several
CSP offer limited access to service as a free tail
approach in an attempt to entice users to commit to a
contract. These free trials can provide an opportunity
for businesses to compare and evaluate different
services and functionalities between providers.
5.2 Assurance Measures
Businesses that wish to explore cloud must seek
assurance from the CSP over how potential risks
will be prevented. It is important to check CSP
reliability reports to determine how often breaches
have occurred and the impacts to see if that CSP has
a good track record and provide the required level of
protection and support. Checking through blogs and
internet sites over any reports of major security
breaches or problems that other users have
experience can provide valuable insight into the
cloud culture.
5.3 Training, Education and Cloud
Awareness
Graph 3 shows that SMEs would consider using
clouds if more advice, support and training were
made available.
There need to inquire about what the
system/services are being offered and the privacy
policies that CSP has. This must be conducted
before users commit and hand over their data. A
CLOSER2015-5thInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
176

Graph 3: Shows the percentage of SMEs that would
consider using clouds if more advice, support and training
were made available.
contract which includes the Terms of Service (TOS)
and also s Privacy Policies and Service Level
Agreement (SLA) will insure a level of assurance
for users. This also provides grounds for legal action
against the CSP if the provider does not maintain
their side of the contract. For example, passing user
details on to a 3
rd
party. It is also essential that users
are aware of the data protection laws as their data
could be transferred across into regions which are
not as strict on data protection. This could result in
invasion of privacy. Like all forms of technology,
clouds are changing, aspects are being improved and
other forms of risks are emerging therefore users
need to be aware of changes to their cloud systems.
What applications are being updates or removed for
example, and how these might impact?
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has highlighted that CC often does not
meet the expectations of SMEs. Finding suggested
this is because SMEs have unrealistic expectations
from using CC and the fact that CSP promote a
range of benefits which can’t be achieved for all. CC
is not a one size fit all technology and as every
business differ in size, resources and IT experience it
is difficult to compare and contracts how CC
benefits can be achieved for the masses. Therefore
SMEs need to conduct an in depth risk assessment
and evaluation of existing systems and CC options
in order to access if CC is more suitable to that
particular business.
7 FUTURE WORK
Further work and support is required for SMEs to
actually deploy a cloud system that can be
integration with existing applications and systems.
Therefore the author’s further work will include
explores risks relating to the more technical aspects
of cloud and SMEs role in these, for example
configuration management and access rights in a
cloud system. Alongside this, a book will be
produced which will provide a framework to act as a
set of risk and support guidelines for SMEs during
the change cycle of migrating to a cloud.
REFERENCES
Chang, V., Bacigalupo, D., Wills, G. and De Roure, D.
(2010) A Categorisation of Cloud Computing
Business Models. In: CCGrid 2010, The 10th
IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster,
Cloud and Grid Computing, May 17-20, Melbourne,
Australia. pp. 509-512.
Interworkscloud. (2013) How much do people know about
the cloud really? [Online] Available from: http://
blog.interworkscloud.com/how-much-do-people-know
-about-the-cloud-really/ [Accessed: 19th June 2012]
Korri. T (2009) “Cloud computing: utility computing over
the Internet” Seminar on Internetworking 2009.
Wood Katie, "Exploring security issues in cloud
computing" (2012). UK Academy for Information
Systems Conference Proceedings 2012. Paper 30.
http://aisel.aisnet.org/ukais2012/30.
National Institute of Standards and Technologies; Draft
NIST Working Definition of Cloud Computing, May
14, 2009.
David Binning 24 April 2009 ‘Top five cloud computing
securityissues’ http://www.computerweekly.com/
news/2240089111/Top-five-cloud-computing-
security-issues#2.
Warwick Ashford [Friday 22 March 2013] ‘Six security
issues to tackle before encrypting cloud data’
http://www.computerweekly.com/news/2240180087/S
ix-security-issues-to-tackle-before-encrypting-cloud-
data.
Wood. K (2012) ‘Understanding Configuration
Management with Cloud Computing’ International
Conference on Computational Informatics and
Technology Enhanced Education (ICCITEE> 2012)
Amsterdam, Netherlands.
S. Srinivasamurthy and D. Q. Liu, "Survey on Cloud
Computing Security", Proc. Conf. on Cloud
Computing, CloudCom.'10.
Top Threats to Cloud Computing v1.0". Cloud Security
Alliance. Retrieved 24/10/2014.
M. A. Vouk Cloud computing — issues, research and
implementations Journal of Computing and
Information Technology - CIT 16, 2008, 4, 235–246
doi:10.2498/cit.1001391.
Hayes, B. “Cloud Computing,” Communications of the
ACM, 51(7):9–11 (2008).
Wood. K and Anderson. M (2011) ‘Understanding the
complexity surrounding multi-tenancy in cloud
computing’ 8th IEEE International Conference on e-
Business Engineering, Tsinghua University, (ICEBE
2011).
RealityVsHype-DoesCloudComputingMeettheExpectationsofSMEs?
177
